Journal Description
Optics
Optics
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on optics published bimonthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus, EBSCO, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 22.1 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 6.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Impact Factor:
1.6 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
1.5 (2024)
Latest Articles
Angle-Dependent Glare Behavior in LED Luminaires: A Unified cosm Model for Urban Observers
Optics 2026, 7(1), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/opt7010014 - 5 Feb 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Glare is a critical factor in the design of LED luminaires for street lighting, particularly in environments where pedestrians, cyclists and drivers coexist. Generally, glare assessments are performed for fixed geometries and a single observer, limiting their applicability to real urban environments. This
[...] Read more.
Glare is a critical factor in the design of LED luminaires for street lighting, particularly in environments where pedestrians, cyclists and drivers coexist. Generally, glare assessments are performed for fixed geometries and a single observer, limiting their applicability to real urban environments. This study examines the effect of angular redistribution of the beam on glare and illuminance by introducing the relative angular parameter α into the photometric model and the UGR calculation. A generic LED luminaire is modelled using a cosine-type luminous intensity distribution raised to a power, and the emitting surface is also discretized to evaluate the luminance, solid angle and Guth position index at the patch level. This approach is applied to three distinct observer geometries—pedestrian, cyclist and driver—allowing direct comparison using a unified mathematical formulation. The results show that beam redistribution affects each observer differently, reducing glare for pedestrians while simultaneously increasing it for drivers, whereas cyclists show limited sensitivity to angular changes. Although relative illuminance and UGR show similar monotonic trends, their physical and perceptual interpretation is different. This paper presents a novel tool for the preliminary analysis of trade-offs between visual comfort and luminous efficiency in urban lighting design.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Dynamic Optical Coherence Tomography Monitoring of Keloid Laser Treatment: A Single-Case Proof-of-Concept Study
by
Luca Guarino, Giovanni Cannarozzo, Luca Gargano, Elena Zappia, Alessandro Clementi, Mario Sannino, Giovanni Pellacani and Steven Paul Nisticò
Optics 2026, 7(1), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/opt7010013 - 4 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Keloids are fibroproliferative scars with a prominent vascular component, and pulsed dye laser (PDL) is an established treatment, but objective imaging biomarkers of response are lacking. Objective: To evaluate whether dynamic optical coherence tomography (D-OCT) can provide quantitative, depth-resolved monitoring of keloid
[...] Read more.
Background: Keloids are fibroproliferative scars with a prominent vascular component, and pulsed dye laser (PDL) is an established treatment, but objective imaging biomarkers of response are lacking. Objective: To evaluate whether dynamic optical coherence tomography (D-OCT) can provide quantitative, depth-resolved monitoring of keloid vascular remodeling under PDL and to explore candidate metrics for hypothesis-generating assessment in future studies. Methods: We conducted a prospective single-case pilot, hypothesis-generating study of a thoracic keloid treated with three sessions of 595 nm PDL, acquiring D-OCT scans at baseline and approximately 30, 60, and 90 days over a standardized 4 × 4 mm region of interest at 0.15, 0.30, and 0.50 mm depths. Primary D-OCT metrics included vascular en-face area, vessel length density, junction density, and mean vessel caliber. Results: The superficial layer (0.15 mm) showed an almost complete collapse of vascular signal (area −88% vs. baseline), the intermediate layer at 0.30 mm exhibited a sustained ~39% reduction in vascular area with parallel decreases in length and caliber at stable branching, and the deep layer at 0.50 mm showed modest area changes with longer but thinner vessels. These depth-resolved changes were consistent with clinical improvement in Vancouver Scar Scale and POSAS scores. Conclusions: D-OCT yielded quantitative, clinically interpretable vascular metrics that align with the expected effects of PDL in this single patient. In this patient, the percentage reduction in vascular area at 0.30 mm by week 8 emerged as a candidate quantitative metric for response monitoring; thresholds in the order of ≥25% could be tested prospectively as hypothesis-generating cut-offs in future controlled and reliability-tested studies, but are not proposed here as validated clinical criteria.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Composite Multi-Parameter Sensor Based on Misaligned Peanut-Shaped Structure for Measuring Strain and Temperature
by
Cheng Li, Bing Wu, Yu Zhang, Hang Zhu, Zhigang Gao, Jie Zhang, Linghao Kong, Xiaojun Cui, Guoyu Zhang and Feng Peng
Optics 2026, 7(1), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/opt7010012 - 4 Feb 2026
Abstract
A composite fiber optic sensor based on a misaligned peanut-shaped structure and the single-mode fiber–multimode fiber–single-mode fiber (SMS) structure is proposed for simultaneous strain and temperature measurements. The misaligned peanut-shaped structure is formed by introducing a certain core-offset during fusion splicing. Through a
[...] Read more.
A composite fiber optic sensor based on a misaligned peanut-shaped structure and the single-mode fiber–multimode fiber–single-mode fiber (SMS) structure is proposed for simultaneous strain and temperature measurements. The misaligned peanut-shaped structure is formed by introducing a certain core-offset during fusion splicing. Through a simulation analysis of the sensor, the optical field distribution of the sensor structure under different offset amounts is obtained. The experimental results demonstrate that the sensor achieves a maximum strain sensitivity of −48.21 pm/µε with an offset of 35.61 µm under a strain range of 0–600 µε and a maximum temperature sensitivity of 124.29 pm/°C at a 24.35 µm offset with a temperature range of 35–95 °C. Meanwhile, the sensor with a 35.61 µm offset has two resonance peaks that are selected for simultaneous measurements, with strain sensitivities of −48.21 pm/µε and −47.04 pm/µε and temperature sensitivities of 75.71 pm/°C and 84.29 pm/°C, respectively. Therefore, the simultaneous measurement of the strain and temperature can be achieved through a matrix method, demonstrating that the sensor possesses a dual-parameter sensing capability for the strain and temperature.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Optical Sensing and Optical Communication: Technologies, Systems, and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Design of Double-Lattice Photonic Crystal of DUV Laser by ANN-RBF Neural Network
by
Bochao Zhang, Minyan Zhang, Lei Li, Jianglang Bie, Shuoyi Jiao, Zhuanzhuan Guo, Xinjie Cai and Bowen Hou
Optics 2026, 7(1), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/opt7010011 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
In this study, a double-lattice photonic crystal structure was designed to achieve deep ultraviolet lasing without the use of any Distributed Bragg Reflector (DBR), which is called a photonic-crystal surface-emitting laser (PCSEL). The plane wave expansion (PWE) method was used to study the
[...] Read more.
In this study, a double-lattice photonic crystal structure was designed to achieve deep ultraviolet lasing without the use of any Distributed Bragg Reflector (DBR), which is called a photonic-crystal surface-emitting laser (PCSEL). The plane wave expansion (PWE) method was used to study the influence of various structural parameters on the resonant wavelength. Utilizing the random forest algorithm, we determined that the importance of the lattice constant to the resonant wavelength is 95.24%. Furthermore, we realized the reverse design of double-lattice photonic crystals from the target wavelength to optimal structural parameters through a radial basis function (RBF) network algorithm. Comparative analysis of the extreme learning machine (ELM) and back propagation (BP) algorithms demonstrated that RBF-based performance was notably superior to the training outcomes of other algorithms. The mean absolute error (MAE) of the lattice constant of the test set in the training results was 0.7610 nm, root mean square error (RMSE) was
(This article belongs to the Topic Nanomaterials for Photonics and Optoelectronics: Practical Applications and Advances)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Extra-Virgin Olive Oil as a Natural Photosensitizer in Photodynamic Therapy Against MDR Candida spp.: In Vitro Study
by
Cinzia Casu, Antonia Sinesi, Andrea Butera, Sara Fais, Alessandro Chiesa, Andrea Scribante and Germano Orrù
Optics 2026, 7(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/opt7010010 - 26 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The growing prevalence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) Candida spp. necessitates the development of new antifungal strategies. Photodynamic therapy (PDT), already widely used in the treatment of various oral infections, is based on the synergistic interaction of three key elements: a photosensitizer capable of selectively
[...] Read more.
The growing prevalence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) Candida spp. necessitates the development of new antifungal strategies. Photodynamic therapy (PDT), already widely used in the treatment of various oral infections, is based on the synergistic interaction of three key elements: a photosensitizer capable of selectively binding to microbial cells, a light source with the appropriate wavelength, and the presence of molecular oxygen. This interaction results in the production of singlet oxygen and reactive oxygen species, responsible for the selective destruction of microorganisms. In recent years, numerous natural compounds have been explored as potential photosensitizers. Olive oil, a cornerstone of the Mediterranean diet, was recently recognized by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as a medicinal substance thanks to its soothing, immunomodulatory, and antimicrobial properties, which have also been documented in regard to oral administration. Materials and Methods: The aim of this in vitro study was to evaluate the efficacy of activated olive oil as a novel photosensitizer in PDT against Candida species. Oral MDR clinical isolates of C. albicans, C. krusei, and C. glabrata were analyzed using the Kirby–Bauer method according to EUCAST protocols. Six different experimental conditions were considered for each strain: (i) 100 μL of extra-virgin olive oil (EVOO); (ii) 100 μL of EVOO pre-activated with 3% H2O2 (EVOO-H); (iii) 100 μL of EVOO irradiated for 5 min with polarized light (480–3400 nm, 25 W); (iv) 100 μL of EVOO-H subjected to the same polarized light; (v) 100 μL of EVOO irradiated for 5 min with a 660 nm diode laser (100 mW); and (vi) 100 μL of EVOO-H irradiated with the same laser. All plates were incubated at 37 °C for 48 h. Results: The results showed a variable response among the different Candida species. C. glabrata showed sensitivity to all experimental conditions, with a 50% increase in the diameter of the inhibition zone in the presence of polarized light. C. krusei showed no sensitivity under any of the conditions tested. C. albicans showed antifungal activity exclusively when EVOO-H was activated by light. In particular, activation of EVOO and EVOO-H with polarized light resulted in the largest inhibition zones. Conclusions: In conclusion, olive oil, both alone and pre-activated with hydrogen peroxide, can be considered an effective photosensitizer against drug-resistant Candida spp., especially when combined with polarized light.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Propagation of Correlation Singularities of a Partially Coherent Field
by
Jinhyung Lee, Geunwoong Jeon, Byeongjun Yoon, Donghyun Kim, Hyeunwoo Kim and Sun-Myong Kim
Optics 2026, 7(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/opt7010009 - 22 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
We investigate the structure of correlation singularities for the Laguerre–Gauss beam of order
We investigate the structure of correlation singularities for the Laguerre–Gauss beam of order

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Advanced Performance of Photoluminescent Organic Light-Emitting Diodes Enabled by Natural Dye Emitters Considering a Circular Economy Strategy
by
Vasyl G. Kravets, Vasyl Petruk, Serhii Kvaterniuk and Roman Petruk
Optics 2026, 7(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/opt7010008 - 15 Jan 2026
Abstract
Organic optoelectronic devices receive appreciable attention due to their low cost, ecology, mechanical flexibility, band-gap engineering, brightness, and solution process ability over a broad area. In this study, we designed and studied organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) consisting of an assembly of natural dyes,
[...] Read more.
Organic optoelectronic devices receive appreciable attention due to their low cost, ecology, mechanical flexibility, band-gap engineering, brightness, and solution process ability over a broad area. In this study, we designed and studied organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) consisting of an assembly of natural dyes, extracted from noble fir leaves (evergreen) and blue hydrangea flowers mixed with poly-methyl methacrylate (PMMA) as light emitters. We experimentally demonstrate the effective conversion of blue light emitted by an inorganic laser/photodiode into longer-wavelength red and green tunable photoluminescence due to the excitation of natural dye–PMMA nanostructures. UV-visible absorption and photoluminescence spectroscopy, ellipsometry, and Fourier transform infrared methods, together with optical microscopy, were performed for confirming and characterizing the properties of light-emitting diodes based on natural dyes. We highlighted the optical and physical properties of two different natural dyes and demonstrated how such characteristics can be exploited to make efficient LED devices. A strong pure red emission with a narrow full-width at half maximum (FWHM) of 23 nm in the noble fir dye–PMMA layer and a green emission with a FWHM of 45 nm in blue hydrangea dye–PMMA layer were observed. It was revealed that adding monolayer MoS2 to the nanostructures can significantly enhance the photoluminescence of the natural dye due to a strong correlation between the emission bands of the inorganic–organic emitters and back mirror reflection of the excitation blue light from the monolayer. Based on the investigation of two natural dyes, we demonstrated viable pathways for scalable manufacturing of efficient hybrid OLEDs consisting of assembly of natural-dye polymers through low-cost, purely ecological, and convenient processes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Engineering Optics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Room-Temperature Phosphorescence of Quinine Sulfate in PVA Films: The Effect of Humidity
by
Agnieszka Jablonska, Bong Lee, R. Max Petty, Danh Pham, Rajveer Sagoo, Trang Thien Pham, Zygmunt Gryczynski and Ignacy Gryczynski
Optics 2026, 7(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/opt7010007 - 14 Jan 2026
Abstract
We report the first observation of room-temperature phosphorescence (RTP) of quinine sulfate (QS) in poly (vinyl alcohol) (PVA) films. Steady-state and time-gated measurements were performed to characterize the phosphorescence spectra, anisotropies, and lifetimes to estimate the phosphorescence properties. The RTP response of organic
[...] Read more.
We report the first observation of room-temperature phosphorescence (RTP) of quinine sulfate (QS) in poly (vinyl alcohol) (PVA) films. Steady-state and time-gated measurements were performed to characterize the phosphorescence spectra, anisotropies, and lifetimes to estimate the phosphorescence properties. The RTP response of organic emitters in polymer matrices is particularly sensitive to ambient humidity and oxygen levels. Hence, to assess the environmental stability of the system, QS-doped PVA films were cast from a single batch and divided into paired specimens, one of which was encapsulated with a pressure-sensitive laminate, while the other one was left non-laminated. Over 14 days under ambient laboratory conditions, the absorbance and fluorescence of both films remained unchanged, whereas the exhibited phosphorescence diverged significantly. The unlaminated film exhibited a progressive loss of afterglow intensity, a noticeable red shift in the phosphorescence spectrum, and a pronounced shortening of the phosphorescence lifetime, while the laminated film retained its initial RTP intensity, spectral profile, and lifetime throughout the entire experiment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Optoelectronic Thin Films)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Compact Digital Holography-Based Refractometer for Non-Invasive Characterization of Transparent Media
by
Brandon R. Sulvarán-Salmoreno, Diego Torres-Armenta, Dulce Gonzalez-Utrera and David Moreno-Hernández
Optics 2026, 7(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/opt7010006 - 9 Jan 2026
Abstract
This work presents a compact refractometric system based on In-Line Digital Holography (ILDH) for the non-invasive characterization of transparent media, encompassing both liquids and high-refractive-index optical glasses. The core of the system is a cost-effective, lensless setup in which a 532 nm laser
[...] Read more.
This work presents a compact refractometric system based on In-Line Digital Holography (ILDH) for the non-invasive characterization of transparent media, encompassing both liquids and high-refractive-index optical glasses. The core of the system is a cost-effective, lensless setup in which a 532 nm laser source and a microscope objective generate a divergent spherical wavefront that illuminates a 10 μm aluminum particle. The resulting diffraction pattern, modulated by samples in the optical path, is recorded by a CMOS sensor. The refractive index of the sample is determined by numerically locating the axial position of the particle-reconstructed image, which directly corresponds to the optical path difference introduced by the test medium. The optimal reconstruction plane is objectively located using an autofocus algorithm based on the Kurtosis metric, which identifies the sharpest image. The system successfully characterizes media across a broad refractive index range from 1.33 to 1.78, yielding linear calibration curves for both liquid and solid samples. The instrument achieves an axial reconstruction resolution of 30 μm and a refractive index precision of ±0.01 RIU. This ILDH approach offers a highly portable, cost-effective, and non-contact solution for refractive index measurement, demonstrating significant potential for industrial quality control and high-throughput point-of-care applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Biophotonics Using Optical Microscopy Techniques)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Terahertz Modulation of Silicon-Based Lead-Free Small-Bandgap Cs2CuSbCl6 Double Perovskite Nanocrystals
by
Xintian Song, Zhongxin Zhang, Reyihanguli Tudi, Abulimiti Yasen, Mei Xiang and Bumaliya Abulimiti
Optics 2026, 7(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/opt7010005 - 4 Jan 2026
Abstract
In this work, we synthesized a lead-free halide double perovskite, Cs2CuSbCl6, with high carrier mobility via a one-pot hot-injection method. When combined with a high-resistivity silicon wafer, it forms a Type-II heterojunction structure, and its modulation depth reaches 84%
[...] Read more.
In this work, we synthesized a lead-free halide double perovskite, Cs2CuSbCl6, with high carrier mobility via a one-pot hot-injection method. When combined with a high-resistivity silicon wafer, it forms a Type-II heterojunction structure, and its modulation depth reaches 84% by adjusting the annealing temperature. It demonstrates promising modulation performance at 532 nm. Owing to its strong absorption in the ultraviolet region, Cs2CuSbCl6 shows potential for application in ultraviolet-controlled terahertz modulation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Terahertz Optics: Sciences, Technologies and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Design of a Monocentric Multiscale Optical System for Near-Diffraction-Limited Imaging with High Resolution and Large Field of View
by
Xiongxiong Wu, Yanning Yang and Zhihui He
Optics 2026, 7(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/opt7010004 - 4 Jan 2026
Abstract
Multiscale optical imaging is expected to address the trade-off between field of view (FOV) and resolution in optical systems. To achieve high resolution imaging with a large FOV, this study employs a double-layer monocentric lens to design the front-stage objective lens and utilizes
[...] Read more.
Multiscale optical imaging is expected to address the trade-off between field of view (FOV) and resolution in optical systems. To achieve high resolution imaging with a large FOV, this study employs a double-layer monocentric lens to design the front-stage objective lens and utilizes multiple relay lenses for the secondary system. The design results demonstrate that the RMS value of the image spot size across the full FOV is controlled within 2 μm, and the system’s optical modulation transfer function (MTF) across the full FOV approaches the diffraction limit. Specifically, the MTF values across the full FOV exceed 0.35 at the cutoff frequency of 250 lp/mm. The designed optical system features a simple structure and high imaging quality. When a larger number of secondary relay imaging systems are employed, it is capable of achieving a large FOV with high resolution imaging performance, as required by the optical system. Moreover, it holds significant application potential in wide-area, large-range imaging and related fields.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Engineering Optics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Accurate Automatic Object Identification Under Complex Lighting Conditions via AI Vision on Enhanced Infrared Polarization Images
by
Ruixin Jia, Hongming Fei, Han Lin, Yibiao Yang, Xin Liu, Mingda Zhang and Liantuan Xiao
Optics 2026, 7(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/opt7010003 - 3 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Object identification (OI) is widely used in fields like autonomous driving, security, robotics, environmental monitoring, and medical diagnostics. OI using infrared (IR) images provides high visibility in low light for all-day operation compared to visible light. However, the low contrast often causes OI
[...] Read more.
Object identification (OI) is widely used in fields like autonomous driving, security, robotics, environmental monitoring, and medical diagnostics. OI using infrared (IR) images provides high visibility in low light for all-day operation compared to visible light. However, the low contrast often causes OI failure in complex scenes with similar target and background temperatures. Therefore, there is a stringent requirement to enhance IR image contrast for accurate OI, and it is ideal to develop a fully automatic process for identifying objects in IR images under any lighting condition, especially in photon-deficient conditions. Here, we demonstrate for the first time a highly accurate automatic IR OI process based on the combination of polarization IR imaging and artificial intelligence (AI) vision (Yolov7), which can quickly identify objects with a high discrimination confidence level (DCL, up to 0.96). In addition, we demonstrate that it is possible to achieve accurate IR OI in complex environments, such as photon-deficient, foggy conditions, and opaque-covered objects with a high DCL. Finally, through training the model, we can identify any object. In this paper, we use a UAV as an example to conduct experiments, further expanding the capabilities of this method. Therefore, our method enables broad OI applications with high all-day performance.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Position Estimation Method for a Fluorescently Labeled Tumor Based on Beer’s Law: An Analysis Using Monte Carlo Simulations
by
Hiroki Suto, Yugo Minegishi and Yasutomo Nomura
Optics 2026, 7(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/opt7010002 - 25 Dec 2025
Abstract
Estimating the depth of a fluorescently labeled tumor is beneficial in tumor resection. In this study, we proposed a method for the three-dimensional position estimation of fluorescent tumors using Monte Carlo simulations. A limited proof-of-concept experiment was conducted, and the two-dimensional position of
[...] Read more.
Estimating the depth of a fluorescently labeled tumor is beneficial in tumor resection. In this study, we proposed a method for the three-dimensional position estimation of fluorescent tumors using Monte Carlo simulations. A limited proof-of-concept experiment was conducted, and the two-dimensional position of a tumor was estimated by calculating the centroid of the fluorescence distribution, which was obtained by using excitation light to scan the surface of the model. The depth of the tumor was estimated by fitting the analytical equation based on Beer’s law to the diffuse fluorescence profile on the surface of the model. In the estimation of the two-dimensional position, the distance between the embedded and estimated tumor coordinates was 0.71 mm. The estimated tumor depths of 2–6 mm closely matched the embedded depths, with an error rate of approximately 20%. In previous studies, depth estimation was limited to 1–5 mm using visible light, whereas for the simulation used in the present study, the use of longer wavelengths enabled estimation at slightly greater depths.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Biomedical Optics)
►▼
Show Figures
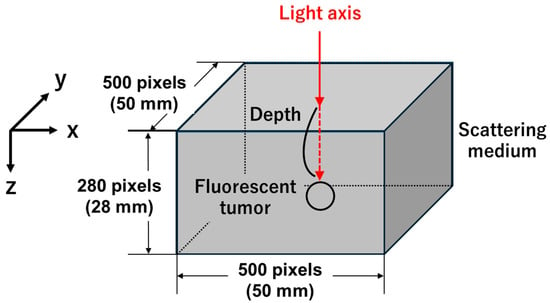
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
HF-Free Synthesis of Narrow-Band Cs2GeF6: Mn4+ Red Phosphors via a Molten Salt Method
by
Chenxing Liao, Huihuang Cai, Jiabao Wu, Wei Xie and Liaolin Zhang
Optics 2026, 7(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/opt7010001 - 22 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Mn4+-activated fluoride phosphors possess outstanding luminescent properties, making them highly suitable for applications in lighting and display technologies. However, the synthesis of such phosphors generally requires the use of large amounts of highly toxic aqueous HF, leading to serious environmental pollution.
[...] Read more.
Mn4+-activated fluoride phosphors possess outstanding luminescent properties, making them highly suitable for applications in lighting and display technologies. However, the synthesis of such phosphors generally requires the use of large amounts of highly toxic aqueous HF, leading to serious environmental pollution. To eliminate the use of hazardous HF solution, a low-temperature molten salt method employing NH4HF2 was developed to synthesize the narrow-band red emitter Cs2GeF6: Mn4+ phosphor. Following the reaction, the product was washed with a dilute H2O2 solution to remove residual NH4HF2 and other impurities. The phase purity and morphology were analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), respectively, and the luminescence properties were examined via photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy. The obtained phosphors exhibit bright red emission characteristics of Mn4+ under blue-violet excitation. Among them, Cs2GeF6: 0.08 Mn4+ shows the highest emission intensity, with an internal quantum efficiency (IQE) of 78%. A white light-emitting diode (WLED) fabricated by combining this phosphor with a blue chip and commercial Y3Al5O12: Ce3+ (YAG) phosphor achieved a high luminous efficacy (LE) of ~146 lm/W, a correlated color temperature (CCT) of ~4396 K, and a color rendering index (Ra) of ~83, alongside excellent operational color stability.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Microwave Dynamic Modulation Metasurface Absorber Based on Origami Structure
by
Zhaoxu Pan, Qiaobai He, Ruicong Zhang, Tianyu Wang, Jiaqi Zhu and Zicheng Song
Optics 2025, 6(4), 67; https://doi.org/10.3390/opt6040067 - 15 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
With the rapid advancement of detection technologies, traditional static electromagnetic absorbers increasingly struggle to meet controllable stealth requirements across diverse dynamic environments. To achieve active and controllable modulation of electromagnetic reflection characteristics, this paper proposes a transparent reconfigurable metamaterial absorber based on an
[...] Read more.
With the rapid advancement of detection technologies, traditional static electromagnetic absorbers increasingly struggle to meet controllable stealth requirements across diverse dynamic environments. To achieve active and controllable modulation of electromagnetic reflection characteristics, this paper proposes a transparent reconfigurable metamaterial absorber based on an origami structure. By adjusting the folding angles of the indium tin oxide (ITO)-polyethylene terephthalate (PET) film, the structure achieves reversible deformation from the vertical state to the horizontal state. This enables continuous modulation of the reflectance from below −10 dB (absorbing state) to nearly 0 dB (reflecting state) within the 4–18.9 GHz frequency range, with a relative bandwidth exceeding 130% and excellent angular stability. The energy loss and current distribution under different states are analyzed, revealing the mechanisms behind broadband absorption and deep modulation. Experimental measurements of the fabricated metamaterial align well with simulation results. Leveraging its flexible structure, reversible modulation capability, and angular stability, this origami-inspired reconfigurable metamaterial demonstrates promising application potential in the fields of adaptive electromagnetic camouflage and stealth protection.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
High-Resolution Caustic Beam Shaping via Polarization Transformation Through Highly Anisotropic Scattering Media
by
Yu-Han Zhou, Guang-Ze Li, Lu-Hong Zhang, Ning-Chen Cao, Li-Ming Zhu, Xiao-Bo Hu, Yan Wu, Khian-Hooi Chew and Rui-Pin Chen
Optics 2025, 6(4), 66; https://doi.org/10.3390/opt6040066 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Manipulating complex light fields through highly anisotropic scattering medium (HASM) remains a fundamental challenge due to the intricate underlying physics and broad application potential. We introduce a unified theoretical and experimental framework for generating and controlling arbitrarily polarized curved caustic beams using an
[...] Read more.
Manipulating complex light fields through highly anisotropic scattering medium (HASM) remains a fundamental challenge due to the intricate underlying physics and broad application potential. We introduce a unified theoretical and experimental framework for generating and controlling arbitrarily polarized curved caustic beams using an extended polarization transfer matrix (EPTM) for the first time, enabling intuitive polarization transformation through HASM. The EPTM is experimentally measured via a four-step phase-shifting technique, and its submatrices are independently modulated with tailored caustic phase profiles. This strategy facilitates the creation of diverse high-resolution caustic beams, including Gaussian and vortex types with tunable energy distribution, polarization states, and vorticity. The achievement of polarization transformation through HASM by our approach offers versatile manipulation over optical field properties such as multiple high-resolution caustic beams, angular momentum flux, and polarization, paving the way for enhanced functionality in advanced optical systems.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Improving Channel Uniformity of Multiplexer with High-Degree-of-Freedom Auxiliary Waveguides
by
Qingran Liu, Chenyan Zhang, Pengju Hu, Huanjie Chen, Xiyan Xu and Chongfu Zhang
Optics 2025, 6(4), 65; https://doi.org/10.3390/opt6040065 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In order to further mitigate the channel non-uniformity at the junction between the input slab and the arrayed waveguide grating in traditional AWG structures, we design a highly flexible, structurally adaptive linear auxiliary waveguide. Through systematic parameter scanning utilizing the Particle Swarm Optimization
[...] Read more.
In order to further mitigate the channel non-uniformity at the junction between the input slab and the arrayed waveguide grating in traditional AWG structures, we design a highly flexible, structurally adaptive linear auxiliary waveguide. Through systematic parameter scanning utilizing the Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) algorithm, an optimal set of geometric parameters for the auxiliary waveguide is identified. This optimization strategy achieves a significant reduction in loss non-uniformity by 0.5 dB relative to the conventional AWG configuration, culminating in a final non-uniformity of merely 0.253 dB. This improvement underscores the critical role of advanced structural tuning and algorithmic optimization in enhancing the performance of photonic integrated circuits, particularly in dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) applications for next-generation communication systems such as radio-over-fiber (RoF) architecture-based 6G. The method can provide a scalable and efficient pathway toward high-uniformity, AWG designs without introducing additional fabrication complexity or incurring substantial costs.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Development of a High-Accuracy Spectral Irradiance Modeling for Evaluating Properties of Output Light from White Light-Emitting Diodes
by
Quang-Khoi Nguyen and Quoc-Cuong Nguyen
Optics 2025, 6(4), 64; https://doi.org/10.3390/opt6040064 - 10 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
An efficient method for evaluating the spectral irradiance properties of the white light of white LEDs is conducted. The method includes two main steps. The first step is to build up spectral irradiance modeling for the blue and yellow emission bands. The photometric
[...] Read more.
An efficient method for evaluating the spectral irradiance properties of the white light of white LEDs is conducted. The method includes two main steps. The first step is to build up spectral irradiance modeling for the blue and yellow emission bands. The photometric parameter of the spectral irradiance of white light which is generated by yellow and blue light mixing is determined based on the photometry and colorimetry theories. The correlated color temperature value strongly depends on the power ratios of blue and yellow light. In addition, the result indicates that the emission bandwidth of yellow phosphor is also an important factor for increasing the color performance of output light. The selection of material with a broader bandwidth of yellow light can control a slower variation in color property compared to the case of using a material with a narrower bandwidth. In addition, the blue light hazard ratio of the spectral irradiance of white light can be extracted, which is helpful for designing the white light with moderate blue and yellow power ratios before fabricating the white LEDs product.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Optimizing SAW Device Performance Using Titanium-Doped Lithium Niobate Substrates
by
Mohamed Beriniz, Kamal Maaider, Noureddine El Barbri, Ali Amkor and Abdelghani Khalil
Optics 2025, 6(4), 63; https://doi.org/10.3390/opt6040063 - 4 Dec 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
This study introduces a new theoretical framework for the ferroelectric phase transition in lithium niobate (LiNbO3), which explicitly incorporates electrostatic interactions between both first and second nearest-neighbor ions. This extended model is applied to estimate the inverse quality factor (Q
[...] Read more.
This study introduces a new theoretical framework for the ferroelectric phase transition in lithium niobate (LiNbO3), which explicitly incorporates electrostatic interactions between both first and second nearest-neighbor ions. This extended model is applied to estimate the inverse quality factor (Q−1), the equivalent mechanical resistance (Rm), and the Curie temperature (Tc) of pure and titanium-doped lithium niobate (LiNbO3:Ti). The proposed analytical expression for Tc is given by:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Strain Engineering of Two-Dimensional Materials for Electronic/Optoelectronic Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
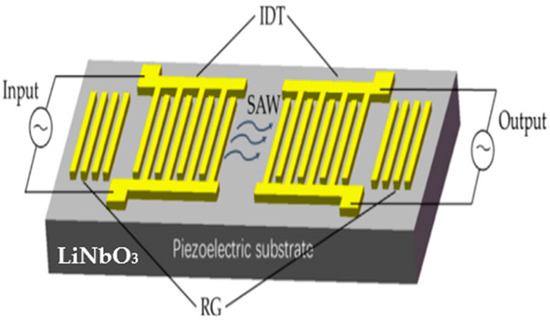
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Harmonic Suppression Method for Optical Encoder Based on Photosensitive Unit Parameter Optimization
by
Bowei Lv, Shitao Li and Jie Liu
Optics 2025, 6(4), 62; https://doi.org/10.3390/opt6040062 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
Optical encoders are high-precision positioning sensors based on the principle of grating diffraction. However, harmonic distortion remains a critical factor limiting the further improvement of measurement accuracy. In response to this challenge, this paper proposes a strategy to suppress harmonic components in the
[...] Read more.
Optical encoders are high-precision positioning sensors based on the principle of grating diffraction. However, harmonic distortion remains a critical factor limiting the further improvement of measurement accuracy. In response to this challenge, this paper proposes a strategy to suppress harmonic components in the output signals of optical encoders. In this work, a general expression for the light intensity distribution of the grating image is derived. Then, orthogonal sine-cosine signals are generated using a grid photoelectric sensor array, which replaces the conventional slit grating. Furthermore, a method for the co-optimization of the photosensitive unit width and offset is proposed, which effectively suppresses the third and fifth harmonic components. Theoretical and simulation results collectively demonstrate that the proposed method achieves near-complete suppression of the third and fifth harmonics, leading to a significant improvement in output signal quality. This work provides an effective approach for developing high-precision optical encoder systems with low harmonic distortion.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Optical Sensing and Optical Communication: Technologies, Systems, and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Energies, Entropy, Photonics, Technologies, Optics, Solar
Advances in Solar Technologies, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Jayanta Deb Mondol, Annamaria Buonomano, Biplab DasDeadline: 31 March 2026
Topic in
Electronics, Photonics, Sensors, Energies, Optics
Quantum Wireless Sensing
Topic Editors: Deepak Mishra, Chao Cai, Jie ZhangDeadline: 30 April 2026
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Optics, Sensors, Materials, Fibers, Photonics, Micromachines
Distributed Optical Fiber Sensors
Topic Editors: Jian Li, Hao Wu, Giancarlo C. Righini, Zhe Ma, Yahui WangDeadline: 30 June 2026
Topic in
Nanomaterials, Polymers, Photonics, Nanomanufacturing, Crystals, Applied Sciences, Optics
Nanomaterials for Photonics and Optoelectronics: Practical Applications and Advances
Topic Editors: Luciana R. P. Kassab, Raul Rangel-Rojo, Rafael Salas-MontielDeadline: 5 June 2027

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Optics
Optoelectronic Thin Films
Guest Editors: Jigang Wang, Junming Li, Zhenjun Li, Tao Jiang, Meng LiDeadline: 28 February 2026
Special Issue in
Optics
Strain Engineering of Two-Dimensional Materials for Electronic/Optoelectronic Applications
Guest Editors: Cong Wang, Jianling MengDeadline: 31 March 2026
Special Issue in
Optics
Advances in Fiber Lasers: Design and Applications
Guest Editors: Hanbin Wang, Xinyang Su, Yanxiang ZhangDeadline: 20 May 2026
Special Issue in
Optics
Optical Sensing and Optical Communication: Technologies, Systems, and Applications
Guest Editors: Xizheng Ke, Feng PengDeadline: 30 June 2026














