- Article
Angle-Dependent Glare Behavior in LED Luminaires: A Unified cosm Model for Urban Observers
- Juan de Dios Unión-Sánchez,
- Manuel Jesus Hermoso-Orzaez and
- Julio Terrados-Cepeda
- + 1 author
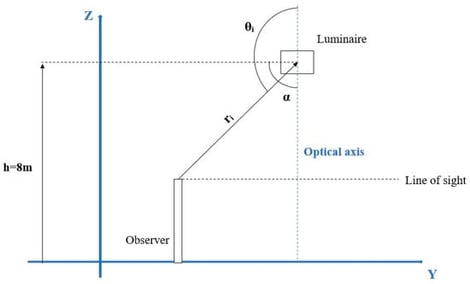
Glare is a critical factor in the design of LED luminaires for street lighting, particularly in environments where pedestrians, cyclists and drivers coexist. Generally, glare assessments are performed for fixed geometries and a single observer, limiting their applicability to real urban environments. This study examines the effect of angular redistribution of the beam on glare and illuminance by introducing the relative angular parameter α into the photometric model and the UGR calculation. A generic LED luminaire is modelled using a cosine-type luminous intensity distribution raised to a power, and the emitting surface is also discretized to evaluate the luminance, solid angle and Guth position index at the patch level. This approach is applied to three distinct observer geometries—pedestrian, cyclist and driver—allowing direct comparison using a unified mathematical formulation. The results show that beam redistribution affects each observer differently, reducing glare for pedestrians while simultaneously increasing it for drivers, whereas cyclists show limited sensitivity to angular changes. Although relative illuminance and UGR show similar monotonic trends, their physical and perceptual interpretation is different. This paper presents a novel tool for the preliminary analysis of trade-offs between visual comfort and luminous efficiency in urban lighting design.
5 February 2026