Waterborne Pathogens and Their Surrogates: Detection, Inactivation and Challenges
A special issue of Pathogens (ISSN 2076-0817).
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (30 April 2023) | Viewed by 3495
Special Issue Editors
Interests: water quality; environmental microbiology; microbial fate and transport
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: identifying the microbial composition of water resources using next generation sequencing; tracking the sources of faecal pollution in environmental waters using rapid molecular based methods; development and evaluation of microbial methods for the detection and quantification of pathogens in water; quantitative microbial risk assessment; roof-harvested rainwater and recreational water quality; novel techniques for pathogen detection/quantification
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: method development; viral pathogens; wastewater microbiology
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
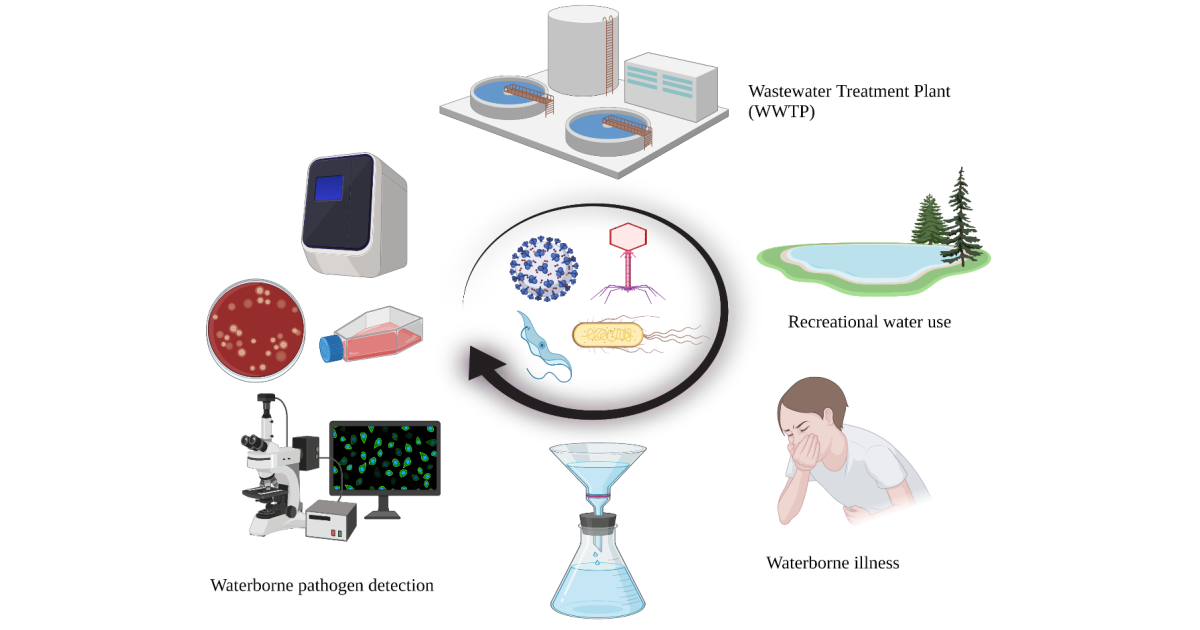
The majority of waterborne disease outbreaks associated with recreational use of untreated waters are caused by pathogenic microorganisms including bacteria, parasites, and viruses, yet direct monitoring strategies for waterborne pathogens remain technically challenging, and in some cases not feasible. While fecal indicator bacteria (e.g., Escherichia coli, enterococci) and other alternative indicator organisms (i.e., bacteriophages, microbial source tracking markers, Clostridium spp.) are suitable indicators of fecal pollution, their relationship with waterborne pathogens, especially viruses, is tenuous at best, and influenced by many different factors. We are excited to announce the launch of a new Special Issue titled “Waterborne Pathogens and their Surrogates: Detection, Inactivation and Challenges”. The focus of the Special Issue includes but is not limited to (1) occurrence of waterborne pathogens in ambient waters and wastewater, (2) methodological advances in waterborne pathogen detection and quantification, and (3) explorations of the waterborne pathogen relationship with various indicator organisms, including their inactivation properties. We welcome original research articles, literature reviews and a limited number of other communications, including perspectives and opinions.
Dr. Asja Korajkic
Dr. Warish Ahmed
Brian McMinn
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Pathogens is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2200 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- waterborne pathogens
- fecal indicator organisms
- occurrence patterns
- detection strategies
- inactivation/decay properties
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- e-Book format: Special Issues with more than 10 articles can be published as dedicated e-books, ensuring wide and rapid dissemination.
Further information on MDPI's Special Issue polices can be found here.







