Novel Strategies on Antiviral Drug Discovery Against Human Diseases
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Prof. Dr. Richard Y. Zhao
Prof. Dr. Richard Y. Zhao
 Prof. Dr. Richard Y. Zhao
Prof. Dr. Richard Y. Zhao
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Pathology, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, USA
Interests: virus-host interactions; viral pathogenicity; antiviral drug discovery and development; high throughput drug screening; viral drug resistance
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
 Prof. Dr. Lin Li
Prof. Dr. Lin Li
 Prof. Dr. Lin Li
Prof. Dr. Lin Li
E-Mail
Collection Editor
Department of AIDS Research, State Key Laboratory of Pathogen and Biosecurity, Beijing Institute of Microbiology and Epidemiology, Beijing 100071, China
Interests: retrovirus; transposable element; endogenous retrovirus; host-pathogen interactions; genetic diversity and evolution; genetic recombination; gene expression and regulation; diagnostic targets; therapeutic targets
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Viral infections can cause various diseases. The impact of viral infection on human health can range from mild diseases, such as the common cold or flu, to severe and life-threatening diseases, as seen with HIV/AIDS, Ebola or SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 infections. Besides natural human innate and acquired antiviral responses, vaccine and antiviral drugs are the two major arsenales that can be used to fight viral infection. Vaccines are developed through the activation of the human antiviral immune response against a specific viral infection. This is very effective in eliminating some viral infections, such as polio, measles, mumps, and rubella. It could also be effective in preventing viral infections such as HBV or flu infection. However, vaccine development is often challenged by the cross-reactivities of neutralizing antibodies, antibody-dependent enhancement of viral infection or antigenic diversity, such as those found in flaviviral infections. Antiviral drugs, on the other hand, have unique advantages in comparison with vaccination. It is typically designed to directly modulate a viral protein or a cellular pathway that the virus relies on for survival. Various classes of antiviral drugs have been used successfully to eradicate or curtail viral infection. One of the major breakthroughs in the last few decades was the cure of HCV infection. The successful use of combinational antiretroviral therapies (cART) against HIV-1 infection can now not only suppress HIV-1 viral load to under detectable levels, but also prolong patients’ lives to nearly normal lifespan. Interestingly, while cART is successful in curtailing HIV-infection, there is still no available anti-HIV vaccine, which provides a strong argument for the development of antivirals to battle viral infection. Unlike antibiotics used to fight bacterial infection, there are very limited or no specific antiviral drugs for most human viral diseases. Therefore, novel strategies or novel viral targets are needed for future antiviral drug discovery and development. The objective of this Collection is to accomplish just that, i.e., to collect novel ideas and/or novel viral targets and methods that could be used for the discovery and development of new antiviral drugs.
In this Collection, we welcome original research and review articles that are focused on these areas. The potential topics include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Novel strategies for antiviral drug discovery and development against human diseases;
- Novel viral targets for the discovery and development of new antivirals;
- Novel host-targeting antivirals;
- New strategies or methods for high-throughput drug screening and testing;
- Novel or effective structure-based antiviral designs;
- Artificial intelligence and virtual antiviral drug screening.
Dr. Jun Wang
Prof. Dr. Richard Y. Zhao
Prof. Dr. Lin Li
Collection Editors
Keywords
- drug discovery and development
- antiviral therapies
- novel viral target
- novel strategy
- human diseases
Published Papers (3 papers)
Open AccessBrief Report
Improving Drug Sensitivity of HIV-1 Protease Inhibitors by Restriction of Cellular Efflux System in a Fission Yeast Model
by
Jiantao Zhang, Qi Li, Shigehiro A. Kawashima, Mohamed Nasr, Fengtian Xue and Richard Y. Zhao
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2336
Abstract
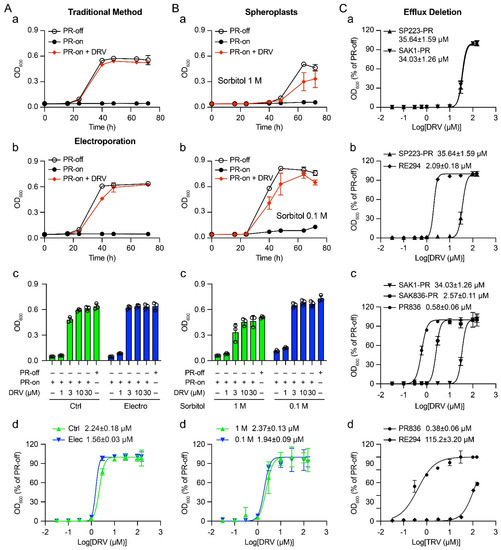
Fission yeast can be used as a cell-based system for high-throughput drug screening. However, higher drug concentrations are often needed to achieve the same effect as in mammalian cells. Our goal here was to improve drug sensitivity so reduced drugs could be used.
[...] Read more.
Fission yeast can be used as a cell-based system for high-throughput drug screening. However, higher drug concentrations are often needed to achieve the same effect as in mammalian cells. Our goal here was to improve drug sensitivity so reduced drugs could be used. Three different methods affecting drug uptakes were tested using an FDA-approved HIV-1 protease inhibitor (PI) drug Darunavir (DRV). First, we tested whether spheroplasts without cell walls increase the drug sensitivity. Second, we examined whether electroporation could be used. Although small improvements were observed, neither of these two methods showed significant increase in the EC
50 values of DRV compared with the traditional method. In contrast, when DRV was tested in a mutant strain PR836 that lacks key proteins regulating cellular efflux, a significant increase in the EC
50 was observed. A comparison of nine FDA-approved HIV-1 PI drugs between the wild-type RE294 strain and the mutant PR836 strain showed marked enhancement of the drug sensitivities ranging from an increase of 0.56 log to 2.48 logs. Therefore, restricting cellular efflux through the adaption of the described fission yeast mutant strain enhances the drug sensitivity, reduces the amount of drug used, and increases the chance of success in future drug discovery.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Understanding COVID-19 Pathogenesis: A Drug-Repurposing Effort to Disrupt Nsp-1 Binding to Export Machinery Receptor Complex
by
Sona Vasudevan and James N. Baraniuk
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 4161
Abstract
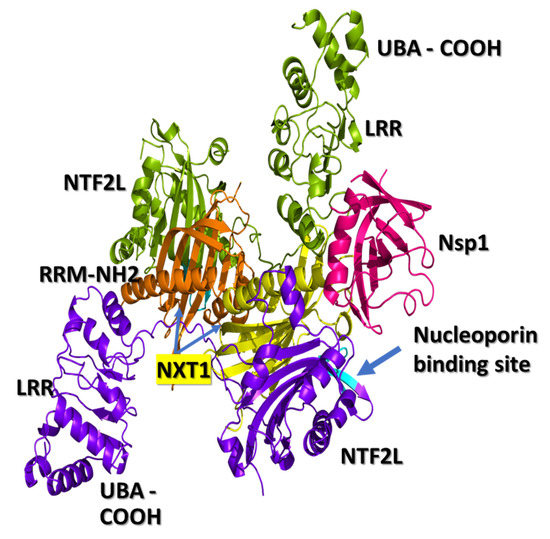
Non-structural protein 1 (Nsp1) is a virulence factor found in all beta coronaviruses (b-CoVs). Recent studies have shown that Nsp1 of SARS-CoV-2 virus interacts with the nuclear export receptor complex, which includes nuclear RNA export factor 1 (NXF1) and nuclear transport factor 2-like
[...] Read more.
Non-structural protein 1 (Nsp1) is a virulence factor found in all beta coronaviruses (b-CoVs). Recent studies have shown that Nsp1 of SARS-CoV-2 virus interacts with the nuclear export receptor complex, which includes nuclear RNA export factor 1 (NXF1) and nuclear transport factor 2-like export factor 1 (NXT1). The NXF1–NXT1 complex plays a crucial role in the transport of host messenger RNA (mRNA). Nsp1 interferes with the proper binding of NXF1 to mRNA export adaptors and its docking to the nuclear pore complex. We propose that drugs targeting the binding surface between Nsp1 and NXF1–NXT1 may be a useful strategy to restore host antiviral gene expression. Exploring this strategy forms the main goals of this paper. Crystal structures of Nsp1 and the heterodimer of NXF1–NXT1 have been determined. We modeled the docking of Nsp1 to the NXF1–NXT1 complex, and discovered repurposed drugs that may interfere with this binding. To our knowledge, this is the first attempt at drug-repurposing of this complex. We used structural analysis to screen 1993 FDA-approved drugs for docking to the NXF1–NXT1 complex. The top hit was ganirelix, with a docking score of −14.49. Ganirelix competitively antagonizes the gonadotropin releasing hormone receptor (GNRHR) on pituitary gonadotrophs, and induces rapid, reversible suppression of gonadotropin secretion. The conformations of Nsp1 and GNRHR make it unlikely that they interact with each other. Additional drug leads were inferred from the structural analysis of this complex, which are discussed in the paper. These drugs offer several options for therapeutically blocking Nsp1 binding to NFX1–NXT1, which may normalize nuclear export in COVID-19 infection.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Single-Agent and Fixed-Dose Combination HIV-1 Protease Inhibitor Drugs in Fission Yeast (Schizosaccharomyces pombe)
by
Jiantao Zhang, Kasey Vernon, Qi Li, Zsigmond Benko, Anthony Amoroso, Mohamed Nasr and Richard Y. Zhao
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 4266
Abstract
Successful combination antiretroviral therapies (cART) eliminate active replicating HIV-1, slow down disease progression, and prolong lives. However, cART effectiveness could be compromised by the emergence of viral multidrug resistance, suggesting the need for new drug discoveries. The objective of this study was to
[...] Read more.
Successful combination antiretroviral therapies (cART) eliminate active replicating HIV-1, slow down disease progression, and prolong lives. However, cART effectiveness could be compromised by the emergence of viral multidrug resistance, suggesting the need for new drug discoveries. The objective of this study was to further demonstrate the utility of the fission yeast cell-based systems that we developed previously for the discovery and testing of HIV protease (PR) inhibitors (PIs) against wild-type or multi-PI drug resistant
M11PR that we isolated from an infected individual. All thirteen FDA-approved single-agent and fixed-dose combination HIV PI drugs were tested. The effect of these drugs on HIV PR activities was tested in pure compounds or formulation drugs. All FDA-approved PI drugs, except for a prodrug FPV, were able to suppress the wild-type PR-induced cellular and enzymatic activities. Relative drug potencies measured by EC
50 in fission yeast were discussed in comparison with those measured in human cells. In contrast, none of the FDA-approved drugs suppressed the multi-PI drug resistant
M11PR activities. Results of this study show that fission yeast is a reliable cell-based system for the discovery and testing of HIV PIs and further demonstrate the need for new PI drugs against viral multi-PI resistance.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures