- Communication
Valorization of Hop (Humulus lupulus L.) Brewing Residue as a Natural Photoprotective Adjuvant
- Ana Gabriela Urbanin Batista de Lima,
- Claudinéia Aparecida Sales de Oliveira Pinto and
- André Rolim Baby
- + 4 authors
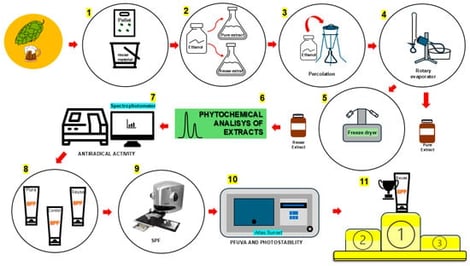
The transition to more sustainable models of production and consumption has encouraged the scientific community to seek innovative solutions that promote environmental responsibility and reduce waste. The cosmetic industry, in particular, has increasingly invested in natural and eco-friendly ingredients as alternatives to synthetic and environmentally harmful components. In this context, plant-derived bioactive compounds with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential have gained attention for their ability to enhance photoprotection and reduce the concentration of conventional ultraviolet (UV) filters in sunscreens. Humulus lupulus L. (hop), a plant traditionally used in the brewing industry, generates large amounts of organic waste after the beer production process, especially through the dry-hopping technique. Despite often being discarded, this residual biomass retains important secondary metabolites with high biological value. Our investigation researched the sustainable valorization of hop brewing residues as a source of bioactive compounds for the development of more natural photoprotective products. We performed HLPC-MS/MS analysis and confirmed the presence of α-acids in both pure and reused hop material extracts, while a xanthohumol-like prenylated flavonoid was tentatively detected exclusively in the extract obtained from reused hop extract. In vitro tests demonstrated that sunscreens containing extract obtained from reused material significantly increased the sun protection factor (SPF) without negatively altering the critical wavelength when water was used as the solvent. None of the samples developed higher UVAPF values compared to the control. Our investigation, to the best of our knowledge, constitutes the first successful proof of concept demonstrating the use of both pure (non-reused) and reused hop material extracts as functional photoprotective adjuvants in sunscreen formulations evaluated by a robust, standardized in vitro methodology. This work highlights the dual benefit of reducing industrial waste and developing more sustainable, consumer-friendly cosmetic products.
2 February 2026