State-of-the-Art Polymer Science and Technology in Poland
A topical collection in Polymers (ISSN 2073-4360). This collection belongs to the section "Innovation of Polymer Science and Technology".
Viewed by 73777Editors
Interests: biocompatible and biodegradable polymer systems; polymer mass spectrometry; bioactive oligomers; controlled drug delivery systems; ring-opening polymerization; forensic engineering of advanced polymeric materials
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: polyesters; tissue engineering; impants; electrospinning; photocurable systems; biopolymers; renewable resources; composites and nanocomposites
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: biopolymers; lignin chemistry; synthesis, characterization and applications of advanced functional materials; hybrid materials, biomaterials; polymer composites, biocomposites; chemical modification of synthetic and natural polymers; application of ligno-cellulosic materials in polymer chemistry; (bio)additives and eco-friendly fillers
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: amphiphilic polymers; graft copolymers; molecular brushes; micellization; drug delivery systems
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: materiel characterization; nanomaterials sunthesis; molecularly imprinted polymers
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
The history of polymers manufacturing in Poland dates back before the World War II, when regenerated cellulose films (1931) and polybutadiene (erythrene rubber, 1938) were introduced to the market. Currently, the scientific potential of Polish institutions conducting research in the field of chemistry, technology and polymer engineering is significant and recognized not only at national but also international level. Among the most active institutions, the Polish Academy of Sciences institutions have to be listed: Center for Polymer and Carbon Materials in Zabrze, Center of Molecular and Macromolecular Studies in Łódź and the Institute of Fundamental Technological Research in Warsaw. A strong research potential is also located at Polish Technical Universities in: Warsaw, Wrocław, Szczecin, Gliwice, Kraków, Poznań, Gdańsk, Częstochowa, Rzeszów and the Adam Mickiewicz University in Poznań, the Jagiellonian University in Kraków, Univerity of Warsaw, Maria Curie-Skłodowska University in Lublin, the Silesian University in Katowice and the Nicolaus Copernicus University in Toruń. The research on applied polymer materials is carried out mainly by the industrial institutes. These are mainly the Industrial Chemistry Research Institute in Warsaw and the Institute for Engineering of Polymer Materials and Dyes in Toruń.
In this Special Issue, we aim to present a broad overview on recent developments in the field of polymer science and technology in Poland. Reviews, original articles, and state-of-the-art research papers, covering all the aspects of current trends in polymeric materials research performed in Poland or by Polish researchers working abroad are welcome.
The topics of this collection will include, but are not limited to:
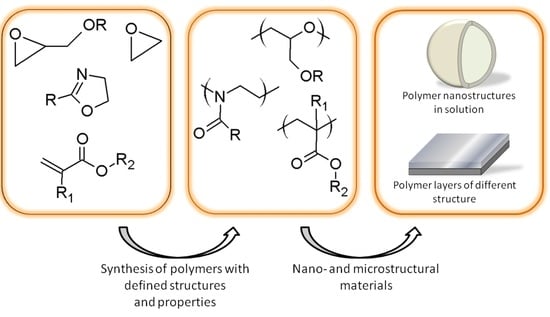
- Macromolecular synthesis and characterization
- Polymer physics and structure
- Polymer composites and nanocomposites
- Polymers processing
- Biodegradable and functional polymers
- Biopolymers
Prof. Dr. Marek Kowalczuk
Prof. Dr. Miroslawa El Fray
Dr. Łukasz Klapiszewski
Prof. Dr. Dorota Neugebauer
Dr. Michał Cegłowski
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Polymers is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- polymers
- polymeric materials
- polymer chemistry
- polymer physics
- polymer engineering
- forensic engineering of polymeric materials