- Article
Random Walks and Spin Projections
- Jean-Christophe Pain
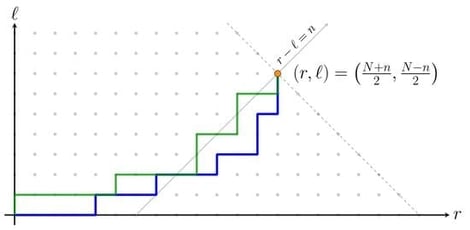
The purpose of this article is to highlight the connections between two seemingly distinct domains: random walks and the distribution of angular-momentum projections in quantum physics (the magnetic quantum numbers m). It is well known that there is indeed a deep mathematical link between the two, via the vector composition of angular momenta and rotational symmetry. Random walks are considered in the framework of an interpretation of the probability of microstates in statistical physics. The ideas presented in this work aim to illustrate the relevance of this perspective for modeling angular momentum in atomic physics.
2 February 2026