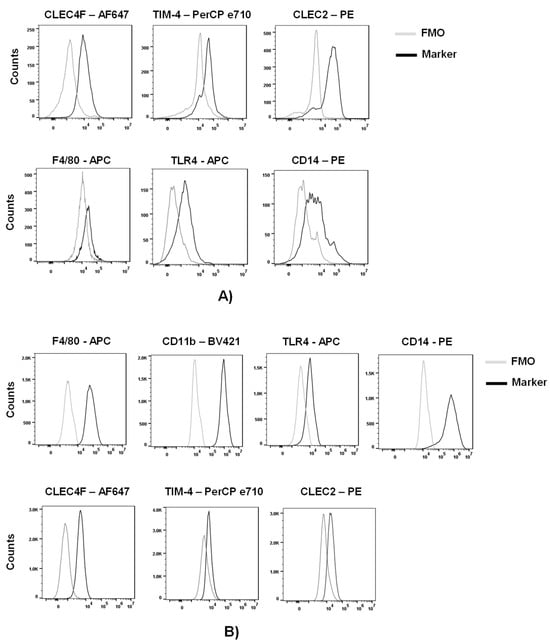
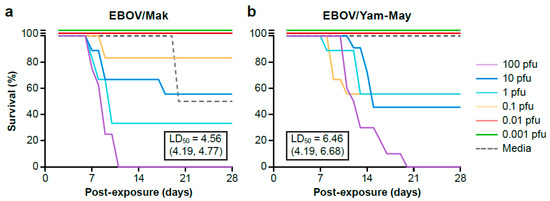
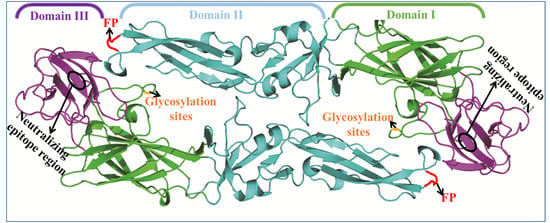
Advances in Ebolavirus, Marburgvirus, and Cuevavirus Research (Closed)
A topical collection in Viruses (ISSN 1999-4915). This collection belongs to the section "Animal Viruses".
Viewed by 656587Editor
Interests: arenaviruses; biodefense; bioengagement; BSL-4; filoviruses; henipaviruses; Kyasanur Forest disease virus; nairoviruses; phleboviruses; Omsk hemorrhagic fever virus; simian hemorrhagic fever virus
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
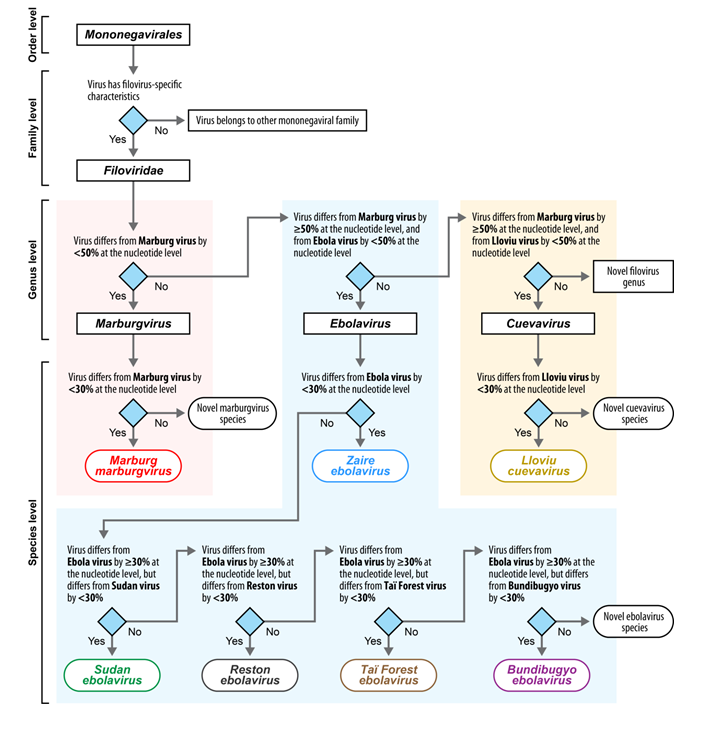
Filoviruses (cuevaviruses, ebolaviruses, and marburgviruses) are exotic high-consequence human and animal pathogens that must be handled in maximum (biosafety level 4) containment. This topic collection aims at providing an opportunity for filovirologists and other experts to publish not only general articles or reviews on any filovirus research topic, but also to distribute announcements of committee discussions or decisions, meeting reports, facility or method descriptions, and personal viewpoints or hypotheses. The goal of this open access topic collection is to further communication among interested scientists with particular emphasis on providing citable information on thoughts or ideas generally “known in the community” that are yet unpublished.
Sincerely,
Jens H. Kuhn
Keywords
- Ebola
- Ebola virus
- EBOV
- ebolavirus
- filovirid
- Filoviridae
- filovirus
- Marburg virus
- marburgvirus
- Bundibugyo virus
- BDBV
- Sudan virus
- SUDV
- Taï Forest virus
- TAFV
- Reston virus
- RESTV
- Bundibugyo ebolavirus
- Zaire ebolavirus
- Sudan ebolavirus
- Reston ebolavirus
- Taï Forest ebolavirus
- Marburg marburgvirus
- MARV
- Ravn virus
- mononegavirus
- mononegavirad
- Mononegavirales
- RAVV
- BSL-4
- BSL4
- biosafety level 4
- maximum containment
- bioterrorism
- biological terrorism
- biowarfare
- biological warfare
- bioweapon
- biological weapon
- medical countermeasure
- viral hemorrhagic fever
- viral haemorrhagic fever
- cuevavirus
- Lloviu virus
- LLOV
- Lloviu cuevavirus
Related Special Issue
- Advances in Filovirus Research 2012 in Viruses (25 articles)