Stimulator of Interferon Genes Pathway Activation through the Controlled Release of STINGel Mediates Analgesia and Anti-Cancer Effects in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. STINGel Preparation
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Mouse Cancer Model
2.4. Nociceptive Behavioral Assays
2.4.1. Thermal Nociception Assay
2.4.2. Mechanical Nociception Assay
2.4.3. Facial Mechanical Nociception Assay
2.5. Single-Cell Suppression and Droplet-Based Single-Cell RNAseq
2.6. Single-Cell RNA Sequence Data Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
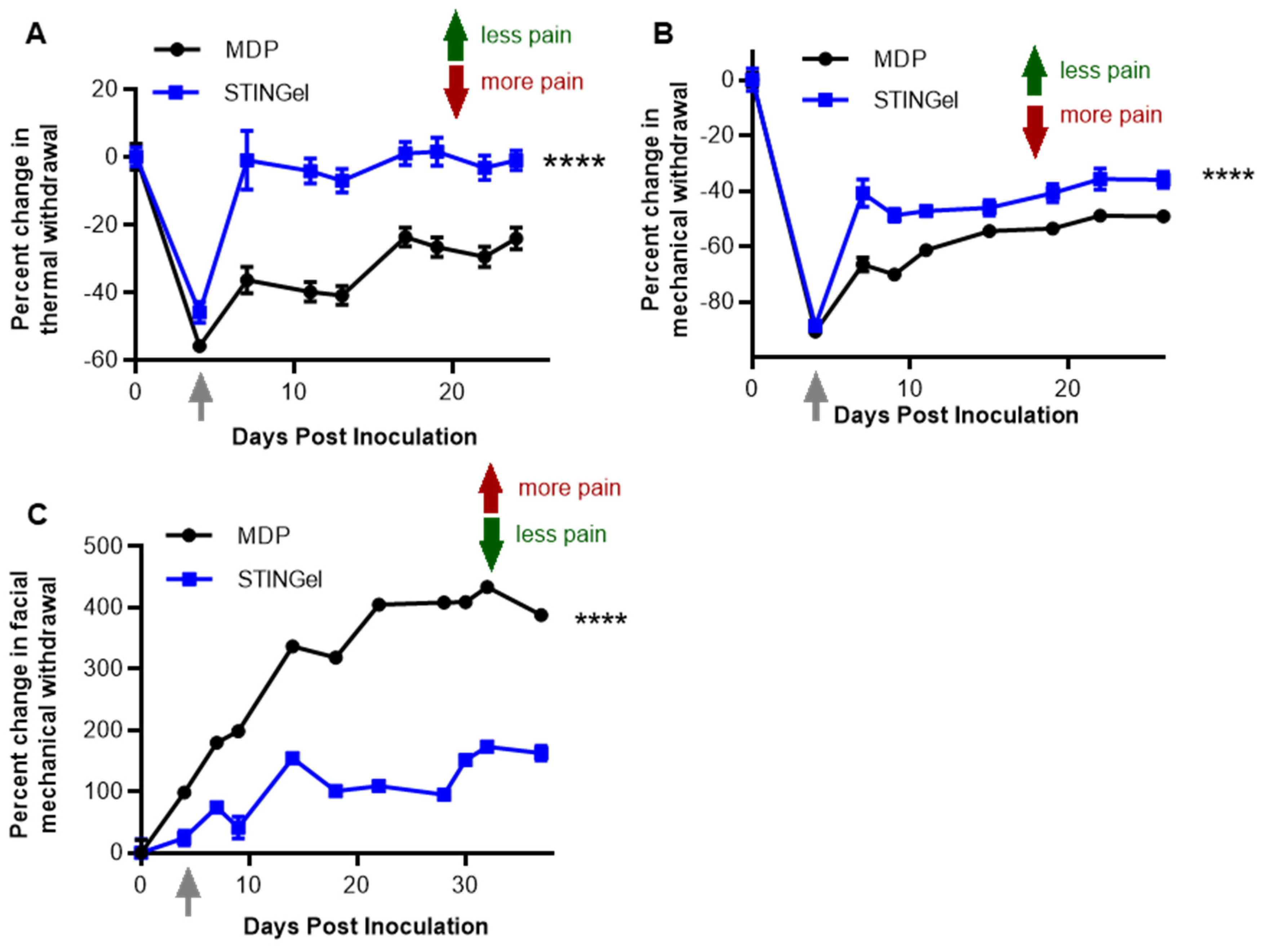
3.1. STINGel Treatment Reduced Facial Mechanical Allodynia in an Orofacial OSCC Mouse Model
3.2. STINGel Treatment Reduced Thermal Hyperalgesia and Mechanical Allodynia in an Orthotopic OSCC Mouse Model
3.3. STINGel Treatment Changed the Ratio of M1/M2 Macrophages and the Population of N1-like Neutrophils in the Mouse OSCC Model
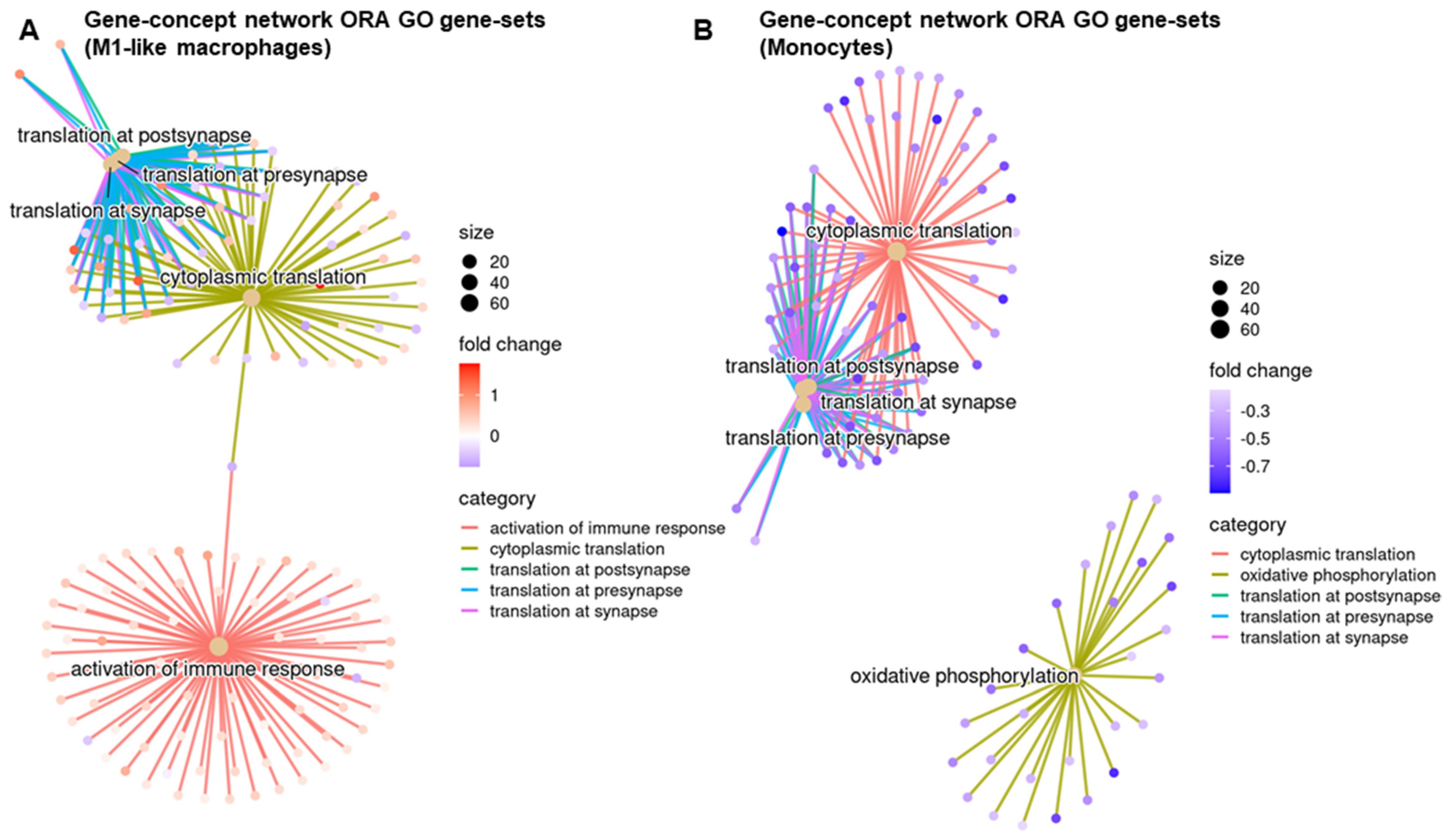
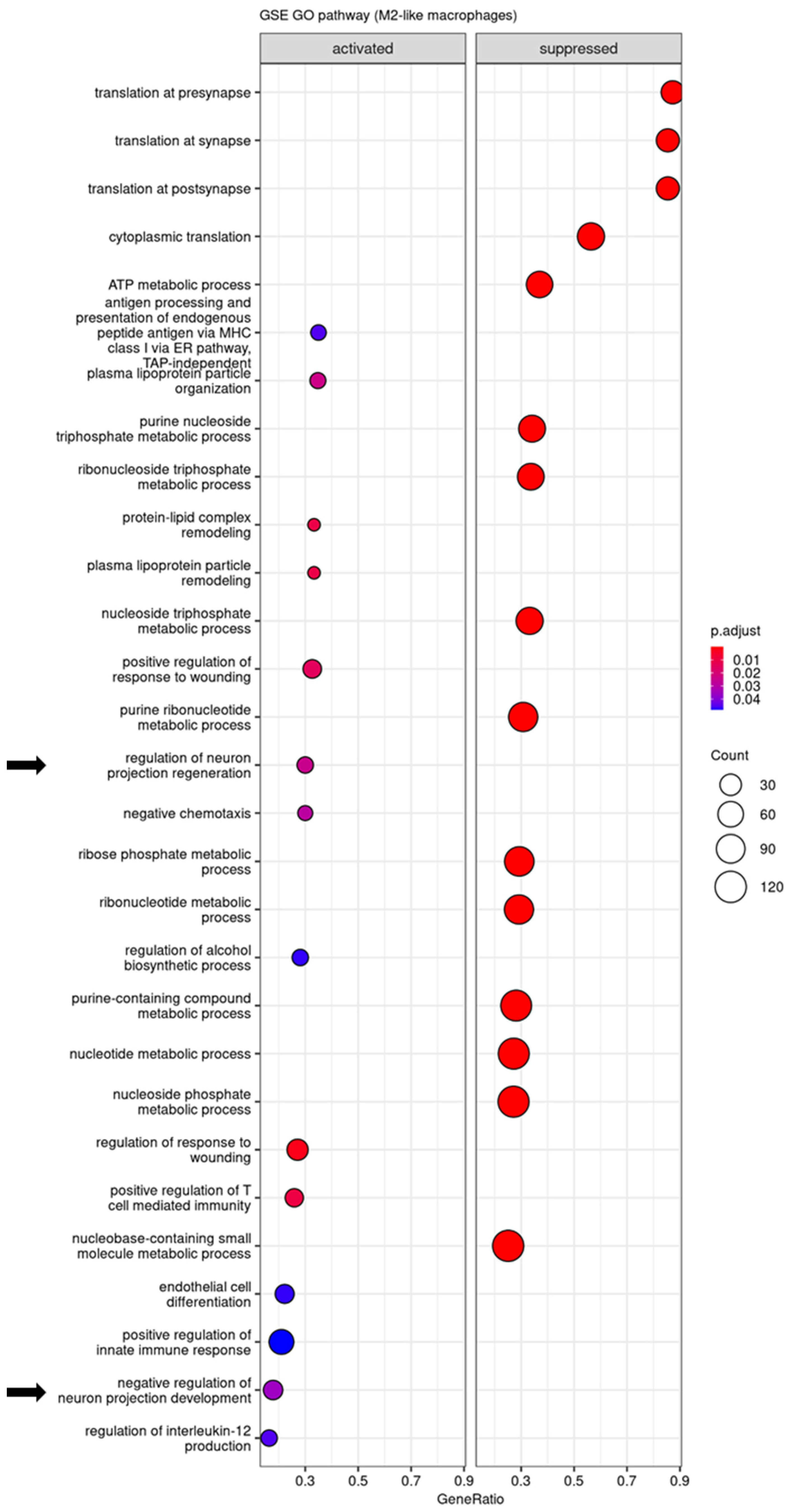
3.4. Regulatory Pathways Involved in STINGel Treatment
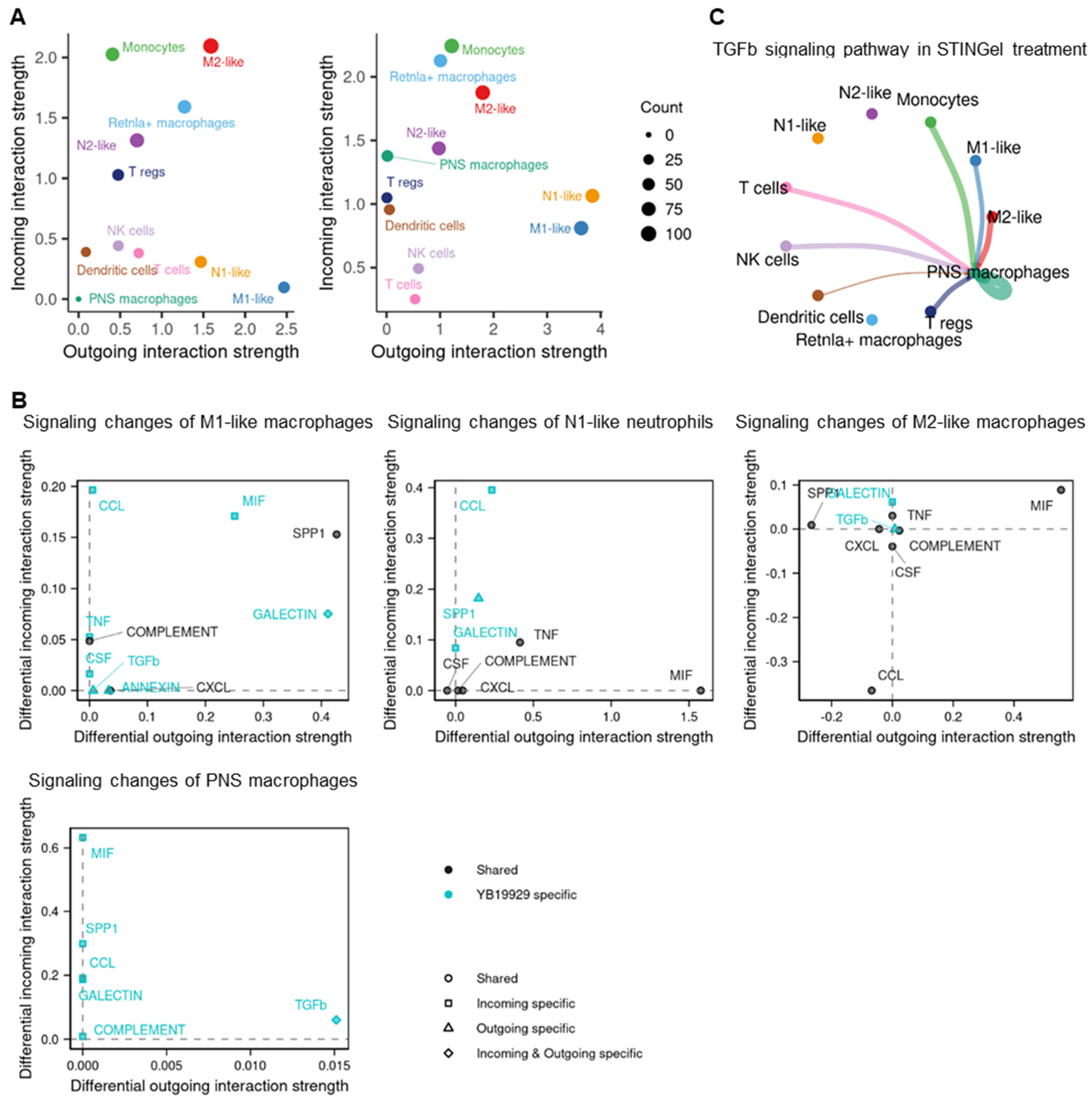
3.5. Cell–Cell Communication
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gulland, A. Oral cancer rates rise by two thirds. BMJ 2016, 355, i6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, J.H.; Iyer, N.G.; Tan, M.H.; Edgren, G. Changing epidemiology of oral squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue: A global study. Head Neck 2017, 39, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanuthai, K.; Rojanawatsirivej, S.; Thosaporn, W.; Kintarak, S.; Subarnbhesaj, A.; Darling, M.; Kryshtalskyj, E.; Chiang, C.P.; Shin, H.I.; Choi, S.Y.; et al. Oral cancer: A multicenter study. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2018, 23, e23–e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, A.J.; Wang, S.; Kutler, D.I.; Carvajal, R.D.; Philipone, E.; Wang, T.; Peters, S.M.; LaRoche, D.; Hernandez, B.Y.; McDowell, B.D.; et al. MicroRNA-based risk scoring system to identify early-stage oral squamous cell carcinoma patients at high-risk for cancer-specific mortality. Head Neck 2020, 42, 1699–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferris, R.L.; Blumenschein, G., Jr.; Fayette, J.; Guigay, J.; Colevas, A.D.; Licitra, L.; Harrington, K.; Kasper, S.; Vokes, E.E.; Even, C.; et al. Nivolumab for Recurrent Squamous-Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leach, D.G.; Dharmaraj, N.; Piotrowski, S.L.; Lopez-Silva, T.L.; Lei, Y.L.; Sikora, A.G.; Young, S.; Hartgerink, J.D. STINGel: Controlled release of a cyclic dinucleotide for enhanced cancer immunotherapy. Biomaterials 2018, 163, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammerlid, E.; Bjordal, K.; Ahlner-Elmqvist, M.; Boysen, M.; Evensen, J.F.; Biorklund, A.; Jannert, M.; Kaasa, S.; Sullivan, M.; Westin, T. A prospective study of quality of life in head and neck cancer patients. Part I: At diagnosis. Laryngoscope 2001, 111, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Beuken-van Everdingen, M.H.; de Rijke, J.M.; Kessels, A.G.; Schouten, H.C.; van Kleef, M.; Patijn, J. Prevalence of pain in patients with cancer: A systematic review of the past 40 years. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol./ESMO 2007, 18, 1437–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Beuken-van Everdingen, M.H.; de Rijke, J.M.; Kessels, A.G.; Schouten, H.C.; van Kleef, M.; Patijn, J. High prevalence of pain in patients with cancer in a large population-based study in The Netherlands. Pain 2007, 132, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffum, D.; Koetters, T.; Cho, M.; Macera, L.; Paul, S.M.; West, C.; Aouizerat, B.; Dunn, L.; Dodd, M.; Lee, K.; et al. The effects of pain, gender, and age on sleep/wake and circadian rhythm parameters in oncology patients at the initiation of radiation therapy. J. Pain Off. J. Am. Pain Soc. 2011, 12, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, M.J.; Cho, M.H.; Miaskowski, C.; Painter, P.L.; Paul, S.M.; Cooper, B.A.; Duda, J.; Krasnoff, J.; Bank, K.A. A randomized controlled trial of home-based exercise for cancer-related fatigue in women during and after chemotherapy with or without radiation therapy. Cancer Nurs. 2010, 33, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glover, J.; Dibble, S.L.; Dodd, M.J.; Miaskowski, C. Mood states of oncology outpatients: Does pain make a difference? J. Pain Symptom Manag. 1995, 10, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portenoy, R.K.; Payne, D.; Jacobsen, P. Breakthrough pain: Characteristics and impact in patients with cancer pain. Pain 1999, 81, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breivik, H.; Cherny, N.; Collett, B.; de Conno, F.; Filbet, M.; Foubert, A.J.; Cohen, R.; Dow, L. Cancer-related pain: A pan-European survey of prevalence, treatment, and patient attitudes. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 1420–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temel, J.S.; Greer, J.A.; Muzikansky, A.; Gallagher, E.R.; Admane, S.; Jackson, V.A.; Dahlin, C.M.; Blinderman, C.D.; Jacobsen, J.; Pirl, W.F.; et al. Early palliative care for patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portenoy, R.K.; Sibirceva, U.; Smout, R.; Horn, S.; Connor, S.; Blum, R.H.; Spence, C.; Fine, P.G. Opioid use and survival at the end of life: A survey of a hospice population. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2006, 32, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florence, C.S.; Zhou, C.; Luo, F.; Xu, L. The Economic Burden of Prescription Opioid Overdose, Abuse, and Dependence in the United States, 2013. Med. Care 2016, 54, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, D.K.; Schmidt, B.L. Orofacial pain onset predicts transition to head and neck cancer. Pain 2011, 152, 1206–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjordal, K.; Ahlner-Elmqvist, M.; Hammerlid, E.; Boysen, M.; Evensen, J.F.; Biorklund, A.; Jannert, M.; Westin, T.; Kaasa, S. A prospective study of quality of life in head and neck cancer patients. Part II: Longitudinal data. Laryngoscope 2001, 111, 1440–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viet, C.T.; Schmidt, B.L. Biologic mechanisms of oral cancer pain and implications for clinical therapy. J. Dent. Res. 2012, 91, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viet, C.T.; Ye, Y.; Dang, D.; Lam, D.K.; Achdjian, S.; Zhang, J.; Schmidt, B.L. Re-expression of the methylated EDNRB gene in oral squamous cell carcinoma attenuates cancer-induced pain. Pain 2011, 152, 2323–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Kim, Y.H.; Li, H.; Luo, H.; Liu, D.L.; Zhang, Z.J.; Lay, M.; Chang, W.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Ji, R.R. PD-L1 inhibits acute and chronic pain by suppressing nociceptive neuron activity via PD-1. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, C.; He, Q.; Matsuda, M.; Han, Q.; Wang, K.; Bang, S.; Ding, H.; Ko, M.C.; Ji, R.R. Anti-PD-1 treatment impairs opioid antinociception in rodents and nonhuman primates. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaaw6471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.H.; Li, H.T.; Lin, W.Q.; Tan, H.Y.; Xie, L.; Zhong, Z.J.; Zhou, J.H. Morphine, a potential antagonist of cisplatin cytotoxicity, inhibits cisplatin-induced apoptosis and suppression of tumor growth in nasopharyngeal carcinoma xenografts. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Chen, P.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Chen, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, S.; Ye, L.; He, Y.; et al. cGAS-STING, an important pathway in cancer immunotherapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrales, L.; Glickman, L.H.; McWhirter, S.M.; Kanne, D.B.; Sivick, K.E.; Katibah, G.E.; Woo, S.R.; Lemmens, E.; Banda, T.; Leong, J.J.; et al. Direct Activation of STING in the Tumor Microenvironment Leads to Potent and Systemic Tumor Regression and Immunity. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 1018–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Donnelly, C.R.; Jiang, C.; Liao, Y.; Luo, X.; Tao, X.; Bang, S.; McGinnis, A.; Lee, M.; Hilton, M.J.; et al. STING suppresses bone cancer pain via immune and neuronal modulation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, X.; Dou, R.; Wang, P.; Zhou, M.; Cao, C.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, G.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; et al. Ropivacaine-loaded hydrogels for prolonged relief of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathic pain and potentiated chemotherapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Qiu, Y.; Qu, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Q. Hydrogels for Treatment of Different Degrees of Osteoarthritis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 858656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.N.; Hartgerink, J.D. Self-Assembling Multidomain Peptide Nanofibers for Delivery of Bioactive Molecules and Tissue Regeneration. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, D.G.; Young, S.; Hartgerink, J.D. Advances in immunotherapy delivery from implantable and injectable biomaterials. Acta Biomater. 2019, 88, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, N.P.; Winkler, A.E.; Murillo-Sauca, O.; Brotman, J.J.; Law, J.H.; Lewis, J.S.; Dunn, G.P.; Bui, J.D.; Sunwoo, J.B.; Uppaluri, R. ERK1/2 regulation of CD44 modulates oral cancer aggressiveness. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leach, D.G.; Dharmaraj, N.; Lopez-Silva, T.L.; Venzor, J.R.; Pogostin, B.H.; Sikora, A.G.; Hartgerink, J.D.; Young, S. Biomaterial-Facilitated Immunotherapy for Established Oral Cancers. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, N.H.; Jensen, D.D.; Anderson, B.M.; Chen, E.; Jimenez-Vargas, N.N.; Scheff, N.N.; Inoue, K.; Tran, H.D.; Dolan, J.C.; Meek, T.A.; et al. Legumain Induces Oral Cancer Pain by Biased Agonism of Protease-Activated Receptor-2. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickering, V.; Jay Gupta, R.; Quang, P.; Jordan, R.C.; Schmidt, B.L. Effect of peripheral endothelin-1 concentration on carcinoma-induced pain in mice. Eur. J. Pain 2008, 12, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deseure, K.; Koek, W.; Adriaensen, H.; Colpaert, F.C. Continuous administration of the 5-hydroxytryptamine1A agonist (3-Chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)-[4-fluoro-4-[[(5-methyl-pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-amino]-methyl]piperidin-1-yl]-methadone (F 13640) attenuates allodynia-like behavior in a rat model of trigeminal neuropathic pain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 306, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Hao, S.; Andersen-Nissen, E.; Mauck, W.M.; Zheng, S.; Butler, A.; Lee, M.J.; Wilk, A.J.; Darby, C.; Zager, M.; et al. Integrated analysis of multimodal single-cell data. Cell 2021, 184, 3573–3587.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGinnis, C.S.; Murrow, L.M.; Gartner, Z.J. DoubletFinder: Doublet Detection in Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Data Using Artificial Nearest Neighbors. Cell Syst. 2019, 8, 329–337.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aran, D.; Looney, A.P.; Liu, L.; Wu, E.; Fong, V.; Hsu, A.; Chak, S.; Naikawadi, R.P.; Wolters, P.J.; Abate, A.R.; et al. Reference-based analysis of lung single-cell sequencing reveals a transitional profibrotic macrophage. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Guerrero-Juarez, C.F.; Zhang, L.; Chang, I.; Ramos, R.; Kuan, C.H.; Myung, P.; Plikus, M.V.; Nie, Q. Inference and analysis of cell-cell communication using CellChat. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selders, G.S.; Fetz, A.E.; Radic, M.Z.; Bowlin, G.L. An overview of the role of neutrophils in innate immunity, inflammation and host-biomaterial integration. Regen. Biomater. 2017, 4, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccard, H.; Muschel, R.J.; Opdenakker, G. On the dual roles and polarized phenotypes of neutrophils in tumor development and progression. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2012, 82, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.A.; Yu, J.; Cheung, C.W. Immune Actions on the Peripheral Nervous System in Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, G.N. STING: Infection, inflammation and cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leach, D.G.; Newton, J.M.; Florez, M.A.; Lopez-Silva, T.L.; Jones, A.A.; Young, S.; Sikora, A.G.; Hartgerink, J.D. Drug-Mimicking Nanofibrous Peptide Hydrogel for Inhibition of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 6755–6765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, J.M.; Guérin, M.V.; Regnier, F.; Renault, G.; Galy-Fauroux, I.; Vimeux, L.; Feuillet, V.; Peranzoni, E.; Thoreau, M.; Trautmann, A.; et al. The STING agonist DMXAA triggers a cooperation between T lymphocytes and myeloid cells that leads to tumor regression. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1346765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkuri, T.; Kosaka, A.; Ishibashi, K.; Kumai, T.; Hirata, Y.; Ohara, K.; Nagato, T.; Oikawa, K.; Aoki, N.; Harabuchi, Y.; et al. Intratumoral administration of cGAMP transiently accumulates potent macrophages for anti-tumor immunity at a mouse tumor site. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 66, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, E.; Clavijo, P.E.; Davis, R.; Cash, H.; Van Waes, C.; Kim, Y.; Allen, C. Established T Cell-Inflamed Tumors Rejected after Adaptive Resistance Was Reversed by Combination STING Activation and PD-1 Pathway Blockade. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2016, 4, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, H.; Hagerling, C.; Werb, Z. Roles of the immune system in cancer: From tumor initiation to metastatic progression. Genes Dev. 2018, 32, 1267–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, C.R.; Jiang, C.; Andriessen, A.S.; Wang, K.; Wang, Z.; Ding, H.; Zhao, J.; Luo, X.; Lee, M.S.; Lei, Y.L.; et al. STING controls nociception via type I interferon signalling in sensory neurons. Nature 2021, 591, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuol, N.; Stojanovska, L.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Nurgali, K. Crosstalk between cancer and the neuro-immune system. J. Neuroimmunol. 2018, 315, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Mei, C.; Chen, P.; Chen, X. The contribution of neuro-immune crosstalk to pain in the peripheral nervous system and the spinal cord. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 107, 108700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, S.W.; Nagaraja, A.S.; Lutgendorf, S.K.; Green, P.A.; Sood, A.K. Sympathetic nervous system regulation of the tumour microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, K.; Bastian, P. Neurotransmitter effects on tumor cells and leukocytes. Prog. Exp. Tumor Res. 2007, 39, 99–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shurin, M.R.; Shurin, G.V.; Zlotnikov, S.B.; Bunimovich, Y.L. The Neuroimmune Axis in the Tumor Microenvironment. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Gu, X.; Yi, S. The Regulatory Effects of Transforming Growth Factor-β on Nerve Regeneration. Cell Transpl. 2017, 26, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lantero, A.; Tramullas, M.; Díaz, A.; Hurlé, M.A. Transforming growth factor-β in normal nociceptive processing and pathological pain models. Mol. Neurobiol. 2012, 45, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, F.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Zheng, Z. TGF-β1 suppresses CCL3/4 expression through the ERK signaling pathway and inhibits intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation-related pain in a rat model. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeboudj, L.; Sideris-Lampretsas, G.; Silva, R.; Al-Mudaris, S.; Picco, F.; Fox, S.; Chambers, D.; Malcangio, M. Silencing miR-21-5p in sensory neurons reverses neuropathic allodynia via activation of TGF-β-related pathway in macrophages. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e164472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Park, C.K.; Xie, R.G.; Ji, R.R. Intrathecal bone marrow stromal cells inhibit neuropathic pain via TGF-β secretion. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 3226–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Logu, F.; Marini, M.; Landini, L.; Souza Monteiro de Araujo, D.; Bartalucci, N.; Trevisan, G.; Bruno, G.; Marangoni, M.; Schmidt, B.L.; Bunnett, N.W.; et al. Peripheral Nerve Resident Macrophages and Schwann Cells Mediate Cancer-Induced Pain. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 3387–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, M.P.; Dharmaraj, N.; Kaminagakura, E.; Xue, J.; Leach, D.G.; Hartgerink, J.D.; Zhang, M.; Hanks, H.-J.; Ye, Y.; Aouizerat, B.E.; et al. Stimulator of Interferon Genes Pathway Activation through the Controlled Release of STINGel Mediates Analgesia and Anti-Cancer Effects in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 920. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12040920
Dong MP, Dharmaraj N, Kaminagakura E, Xue J, Leach DG, Hartgerink JD, Zhang M, Hanks H-J, Ye Y, Aouizerat BE, et al. Stimulator of Interferon Genes Pathway Activation through the Controlled Release of STINGel Mediates Analgesia and Anti-Cancer Effects in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(4):920. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12040920
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Minh Phuong, Neeraja Dharmaraj, Estela Kaminagakura, Jianfei Xue, David G. Leach, Jeffrey D. Hartgerink, Michael Zhang, Hana-Joy Hanks, Yi Ye, Bradley E. Aouizerat, and et al. 2024. "Stimulator of Interferon Genes Pathway Activation through the Controlled Release of STINGel Mediates Analgesia and Anti-Cancer Effects in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma" Biomedicines 12, no. 4: 920. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12040920
APA StyleDong, M. P., Dharmaraj, N., Kaminagakura, E., Xue, J., Leach, D. G., Hartgerink, J. D., Zhang, M., Hanks, H.-J., Ye, Y., Aouizerat, B. E., Vining, K., Thomas, C. M., Dovat, S., Young, S., & Viet, C. T. (2024). Stimulator of Interferon Genes Pathway Activation through the Controlled Release of STINGel Mediates Analgesia and Anti-Cancer Effects in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biomedicines, 12(4), 920. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12040920





