The Genetic and Epigenetic Footprint in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis: A State-of-the-Art Review
Abstract
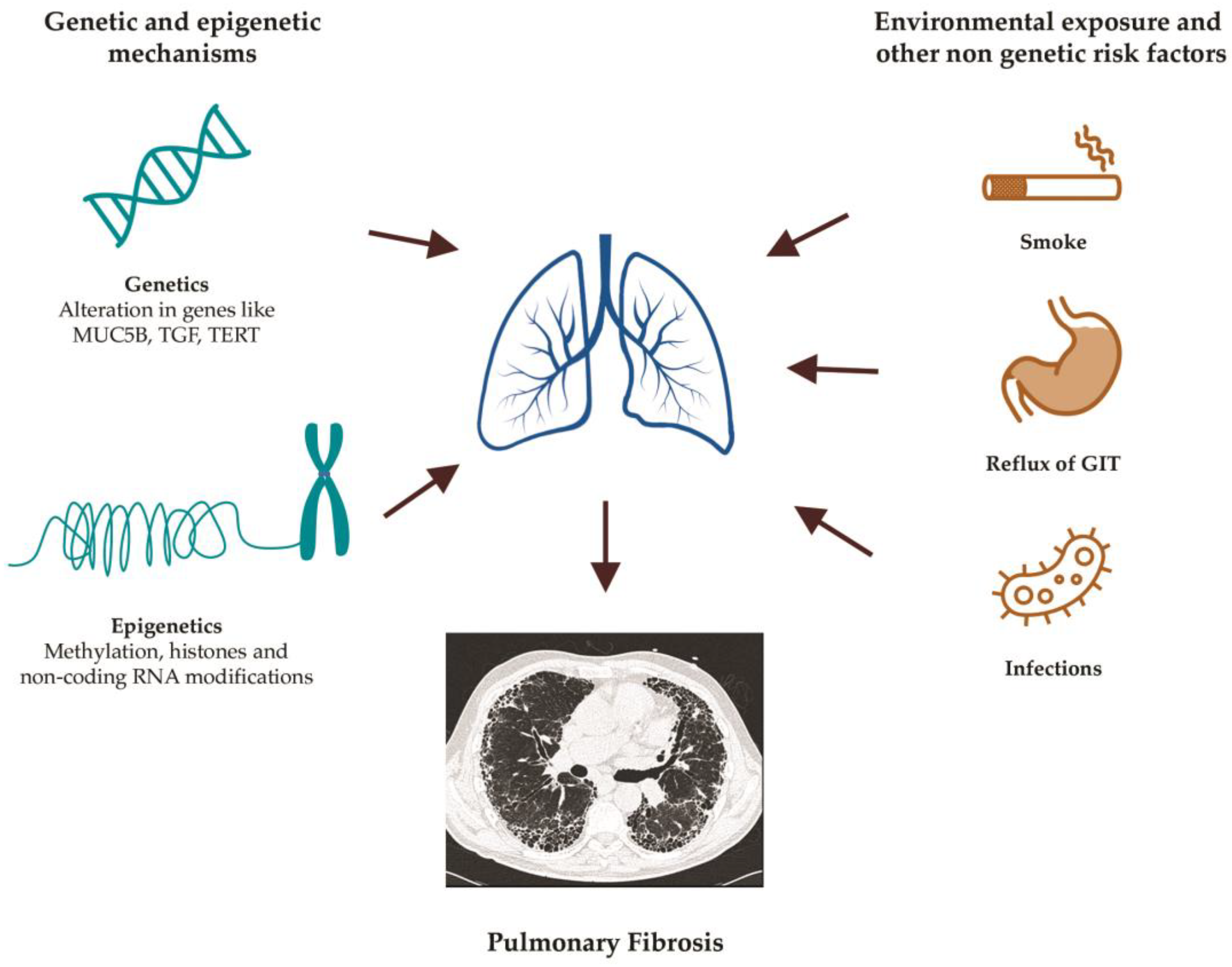
:1. Introduction
2. The Genetic Basis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis
2.1. Telomere Dysfunction
2.2. MUC5B
2.3. TOLLIP
2.4. SFTP and ABCA3
3. The Epigenetic Influence in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis
3.1. DNA Methylation
3.2. Histone Modification
3.3. Non-Coding RNA Gene Silencing
4. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer: A Common Genetic Background?
5. The Interplay between Genetics and Antifibrotic Therapy
6. Outlook and Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Myers, J.L.; Richeldi, L.; Ryerson, C.J.; Lederer, D.J.; Behr, J.; Cottin, V.; Danoff, S.K.; Morell, F.; et al. Diagnosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, e44–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Richeldi, L.; Thomson, C.C.; Inoue, Y.; Johkoh, T.; Kreuter, M.; Lynch, D.A.; Maher, T.M.; Martinez, F.J.; et al. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (an Update) and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Adults: An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, e18–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirelli, C.; Morandi, V.; Valentini, A.; La Carrubba, C.; Dore, R.; Zanframundo, G.; Morbini, P.; Grignaschi, S.; Franconeri, A.; Oggionni, T.; et al. Multidisciplinary Approach in the Early Detection of Undiagnosed Connective Tissue Diseases in Patients With Interstitial Lung Disease: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richeldi, L.; du Bois, R.M.; Raghu, G.; Azuma, A.; Brown, K.K.; Costabel, U.; Cottin, V.; Flaherty, K.R.; Hansell, D.M.; Inoue, Y.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Nintedanib in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2071–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- King, T.E., Jr.; Bradford, W.Z.; Castro-Bernardini, S.; Fagan, E.A.; Glaspole, I.; Glassberg, M.K.; Gorina, E.; Hopkins, P.M.; Kardatzke, D.; Lancaster, L.; et al. A Phase 3 Trial of Pirfenidone in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2083–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Molyneaux, P.L.; Maher, T.M. The role of infection in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2013, 22, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Newton, C.A. Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis: Genetic Features and Clinical Implications. Chest 2021, 160, 1764–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borie, R.; Tabèze, L.; Thabut, G.; Nunes, H.; Cottin, V.; Marchand-Adam, S.; Prevot, G.; Tazi, A.; Cadranel, J.; Mal, H.; et al. Prevalence and characteristics of TERT and TERC mutations in suspected genetic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 1721–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garcia, C.K. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, Update on Genetic Discoveries. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2011, 8, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, D.H.; Segal, M.; Boyraz, B.; Guinan, E.; Hofmann, I.; Cahan, P.; Tai, A.K.; Agarwal, S. Poly(A)-specific ribonuclease (PARN) mediates 3′-end maturation of the telomerase RNA component. Nat Genet. 2015, 47, 1482–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirelli, C.; Zanframundo, G.; Valentini, A.; Bortolotto, C.; Dore, R.; Oggionni, T.; Milani, P.; Bravi, E.; Kadija, Z.; Mariani, F.; et al. CT-guided biopsy in the differential diagnosis of Sjogren syndrome associated cystic lung disease: A case of lung nodular AL-k amyloidosis. Radiol. Case Rep. 2020, 15, 2331–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noth, I.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, S.-F.; Flores, C.; Barber, M.; Huang, Y.; Broderick, S.M.; Wade, M.S.; Hysi, P.; Scuirba, J.; et al. Genetic variants associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis susceptibility and mortality: A genome-wide association study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2013, 1, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Velagacherla, V.; Mehta, C.H.; Nayak, Y.; Nayak, U.Y. Molecular pathways and role of epigenetics in the idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Life Sci. 2022, 291, 120283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richeldi, L.; Collard, H.R.; Jones, M.G. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet 2017, 389, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armanios, M.Y.; Chen, J.J.-L.; Cogan, J.D.; Alder, J.K.; Ingersoll, R.G.; Markin, C.; Lawson, W.E.; Xie, M.; Vulto, I.; Phillips, J.A.; et al. Telomerase Mutations in Families with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selman, M.; Pardo, A. Revealing the Pathogenic and Aging-related Mechanisms of the Enigmatic Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An Integral Model. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helling, B.A.; Yang, I.V. Epigenetics in lung fibrosis: From pathobiology to treatment perspective. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2015, 21, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newton, C.A.; Batra, K.; Torrealba, J.; Kozlitina, J.; Glazer, C.S.; Aravena, C.; Meyer, K.; Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Garcia, C.K. Telomere-related lung fibrosis is diagnostically heterogeneous but uniformly progressive. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 1710–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stanley, S.E.; Gable, D.L.; Wagner, C.L.; Carlile, T.M.; Hanumanthu, V.S.; Podlevsky, J.D.; Khalil, S.E.; DeZern, A.E.; Rojas-Duran, M.F.; Applegate, C.D.; et al. Loss-of-function mutations in the RNA biogenesis factor NAF1 predispose to pulmonary fibrosis–emphysema. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 351ra107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kannengiesser, C.; Manali, E.D.; Revy, P.; Callebaut, I.; Ba, I.; Borgel, A.; Oudin, C.; Haritou, A.; Kolilekas, L.; Malagari, K.; et al. First heterozygous NOP10 mutation in familial pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1902465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiri, K.D.; Cronkhite, J.T.; Kuan, P.J.; Xing, C.; Raghu, G.; Weissler, J.C.; Rosenblatt, R.L.; Shay, J.W.; Garcia, C.K. Adult-onset pulmonary fibrosis caused by mutations in telomerase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7552–7557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diaz de Leon, A.; Cronkhite, J.T.; Katzenstein, A.L.; Godwin, J.D.; Raghu, G.; Glazer, C.S.; Rosenblatt, R.L.; Girod, C.E.; Garrity, E.R.; Xing, C.; et al. Telomere lengths, pulmonary fibrosis and telomerase (TERT) mutations. PLoS ONE 2010, 19, e10680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cronkhite, J.T.; Xing, C.; Raghu, G.; Chin, K.M.; Torres, F.; Rosenblatt, R.L.; Garcia, C.K. Telomere Shortening in Familial and Sporadic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 178, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kropski, J.A.; Mitchell, D.B.; Markin, C.; Polosukhin, V.V.; Choi, L.; Johnson, J.E.; Lawson, W.E.; Phillips, J.A.; Cogan, J.D.; Blackwell, T.S.; et al. A Novel Dyskerin (DKC1) Mutation Is Associated with Familial Interstitial Pneumonia. Chest 2014, 146, e1–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gaysinskaya, V.; Stanley, S.E.; Adam, S.; Armanios, M. Synonymous Mutation in DKC1 Causes Telomerase RNA Insufficiency Manifesting as Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis. Chest 2020, 158, 2449–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alder, J.; Stanley, S.E.; Wagner, C.L.; Hamilton, M.; Hanumanthu, V.S.; Armanios, M. Exome Sequencing Identifies Mutant TINF2 in a Family with Pulmonary Fibrosis. Chest 2015, 147, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoffman, T.W.; van der Vis, J.J.; van Oosterhout, M.F.M.; van Es, H.W.; van Kessel, D.A.; Grutters, J.C.; van Moorsel, C.H.M. TINF2 Gene Mutation in a Patient with Pulmonary Fibrosis. Case Rep. Pulmonol. 2016, 2016, 1310862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kannengiesser, C.; Borie, R.; Ménard, C.; Réocreux, M.; Nitschké, P.; Gazal, S.; Mal, H.; Taillé, C.; Cadranel, J.; Nunes, H.; et al. HeterozygousRTEL1mutations are associated with familial pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alder, J.K.; Chen, J.J.-L.; Lancaster, L.; Danoff, S.; Su, S.-C.; Cogan, J.D.; Vulto, I.; Xie, M.; Qi, X.; Tuder, R.M.; et al. Short telomeres are a risk factor for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13051–13056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gansner, J.M.; Rosas, I.O.; Ebert, B.L. Pulmonary Fibrosis, Bone Marrow Failure, and Telomerase Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1551–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Rodrigues, F.; Donaires, F.S.; Pinto, A.; Vicente, A.; Dillon, L.W.; Clé, D.V.; Santana, B.A.; Pirooznia, M.; Msc, M.D.P.F.I.; Townsley, D.M.; et al. Pathogenic TERT promoter variants in telomere diseases. Genet. Med. 2019, 21, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrovski, S.; Todd, J.L.; Durheim, M.T.; Wang, Q.; Chien, J.W.; Kelly, F.L.; Frankel, C.; Mebane, C.M.; Ren, Z.; Bridgers, J.; et al. An Exome Sequencing Study to Assess the Role of Rare Genetic Variation in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dressen, A.; Abbas, A.R.; Cabanski, C.; Reeder, J.; Ramalingam, T.R.; Neighbors, M.; Bhangale, T.R.; Brauer, M.J.; Hunkapiller, J.; Reeder, J.; et al. Analysis of protein-altering variants in telomerase genes and their association with MUC5B common variant status in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A candidate gene sequencing study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, B.D.; Choi, J.; Zaidi, S.; Xing, C.; Holohan, B.; Chen, R.; Choi, M.; Dharwadkar, P.; Torres, F.; Girod, C.E.; et al. Exome sequencing links mutations in PARN and RTEL1 with familial pulmonary fibrosis and telomere shortening. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benyelles, M.; O’Donohue, M.-F.; Kermasson, L.; Lainey, E.; Borie, R.; Peyrou, C.L.; Nunes, H.; Cazelles, C.; Fourrage, C.; Ollivier, E.; et al. NHP2 deficiency impairs rRNA biogenesis and causes pulmonary fibrosis and Høyeraal–Hreidarsson syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2020, 29, 907–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, T.W.; van der Vis, J.J.; van der Smagt, J.J.; Massink, M.P.G.; Grutters, J.C.; van Moorsel, C.H.M. Pulmonary fibrosis linked to variants in the ACD gene, encoding the telomere protein TPP1. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1900809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gable, D.L.; Gaysinskaya, V.; Atik, C.C.; Talbot, C.C., Jr.; Kang, B.; Stanley, S.E.; Pugh, E.W.; Amat-Codina, N.; Schenk, K.M.; Arcasoy, M.O.; et al. ZCCHC8, the nuclear exosome targeting component, is mutated in familial pulmonary fibrosis and is required for telomerase RNA maturation. Genes Dev. 2019, 33, 1381–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Zhou, Z.; Abu-Hijleh, M.; Batra, K.; Xing, C.; Garcia, C.K. Homozygous Rare PARN Missense Mutation in Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 797–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kropski, J.A.; Reiss, S.; Markin, C.; Brown, K.K.; Schwartz, D.A.; Schwarz, M.I.; Loyd, J.E.; Phillips, J.A.; Blackwell, T.S.; Cogan, J.D. Rare Genetic Variants in PARN Are Associated with Pulmonary Fibrosis in Families. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 1481–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, P.; Blasco, M.A. Replicating through telomeres: A means to an end. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015, 40, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.M.; Pendlebury, D.F.; Nandakumar, J. Structural biology of telomeres and telomerase. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armanios, M.; Blackburn, E.H. The telomere syndromes. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperka, T.; Song, Z.; Morita, Y.; Nalapareddy, K.; Guachalla, L.M.; Lechel, A.; Begus-Nahrmann, Y.; Burkhalter, M.; Mach, M.; Schlaudraff, F.; et al. Puma and p21 represent cooperating checkpoints limiting self-renewal and chromosomal instability of somatic stem cells in response to telomere dysfunction. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 14, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grill, S.; Nandakumar, J. Molecular mechanisms of telomere biology disorders. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 296, 100064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Xu, L.; Cong, Y.-S. Telomere Dysfunction in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 739810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.R.; Lee, J.; Reddy, R.; Williams, G.N.; Kikuchi, A.; Freiberg, Y.; Warburton, D.; Driscoll, B. Partial pneumonectomy of telomerase null mice carrying shortened telomeres initiates cell growth arrest resulting in a limited compensatory growth response. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2011, 300, 898–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povedano, J.M.; Martinez, P.; Flores, J.M.; Mulero, F.; Blasco, M.A. Mice with Pulmonary Fibrosis Driven by Telomere Dysfunction. Cell Rep. 2015, 12, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Yu, Y.; Huang, H.; Hu, Y.; Fu, S.; Wang, Z.; Shi, M.; Zhao, X.; Yuan, J.; Li, J.; et al. Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis Is Caused by Elevated Mechanical Tension on Alveolar Stem Cells. Cell 2020, 180, 107–121.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsellem, V.; Gary-Bobo, G.; Marcos, E.; Maitre, B.; Chaar, V.; Validire, P.; Stern, J.-B.; Noureddine, H.; Sapin, E.; Rideau, D.; et al. Telomere Dysfunction Causes Sustained Inflammation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alder, J.K.; Barkauskas, C.E.; Limjunyawong, N.; Stanley, S.E.; Kembou, F.; Tuder, R.M.; Hogan, B.L.M.; Mitzner, W.; Armanios, M. Telomere dysfunction causes alveolar stem cell failure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5099–5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, P.; Li, S.; Chen, H. Macrophages in Lung Injury, Repair, and Fibrosis. Cells 2021, 10, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, M.G.; Livraghi-Butrico, A.; Fletcher, A.A.; McElwee, M.M.; Evans, S.E.; Boerner, R.M.; Alexander, S.N.; Bellinghausen, L.K.; Song, A.S.; Petrova, Y.M.; et al. Muc5b is required for airway defence. Nature 2013, 505, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seibold, M.A.; Wise, A.L.; Speer, M.C.; Steele, M.P.; Brown, K.K.; Loyd, J.E.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Zhang, W.; Gudmundsson, G.; Groshong, S.D.; et al. A common MUC5B promoter polymorphism and pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 364, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maitra, M.; Wang, Y.; Gerard, R.D.; Mendelson, C.R.; Garcia, C.K. Surfactant protein A2 mutations associated with pulmonary fibrosis lead to protein instability and endoplasmic reticulum stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 22103–22113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Evans, C.M.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Schwarz, M.I.; Lynch, D.; Kurche, J.; Warg, L.; Yang, I.V.; Schwartz, D.A. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Genetic Disease That Involves Mucociliary Dysfunction of the Peripheral Airways. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1567–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakano, Y.; Yang, I.V.; Walts, A.D.; Watson, A.M.; Helling, B.A.; Fletcher, A.A.; Lara, A.R.; Schwarz, M.I.; Evans, C.M.; Schwartz, D.A. MUC5B promoter variant rs35705950 affects MUC5B expression in the distal airways in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 464–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borie, R.; Crestani, B.; Dieude, P.; Nunes, H.; Allanore, Y.; Kannengiesser, C.; Airo, P.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Wallaert, B.; Israel-Biet, D.; et al. The MUC5B Variant Is Associated with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis but Not with Systemic Sclerosis Interstitial Lung Disease in the European Caucasian Population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Guo, W.; Cao, L.; Zhang, H.; Xu, L.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y. Mucin 5B Promoter Polymorphism Is Associated with Susceptibility to Interstitial Lung Diseases in Chinese Males. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Li, W.; Luo, Z.; Chen, Y. The minor T allele of the MUC5B promoter rs35705950 associated with susceptibility to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peljto, A.L.; Zhang, Y.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Ma, S.-F.; Garcia, J.G.N.; Richards, T.J.; Silveira, L.J.; Lindell, K.O.; Steele, M.P.; Loyd, J.; et al. Association Between the MUC5B Promoter Polymorphism and Survival in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. JAMA 2013, 309, 2232–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondini, D.; Cocconcelli, E.; Bernardinello, N.; Lorenzoni, G.; Rigobello, C.; Lococo, S.; Castelli, G.; Baraldo, S.; Cosio, M.G.; Gregori, D.; et al. Prognostic role of MUC5B rs35705950 genotype in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) on antifibrotic treatment. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molyneaux, P.L.; Cox, M.J.; Willis-Owen, S.A.G.; Mallia, P.; Russell, K.E.; Russell, A.-M.; Murphy, E.; Johnston, S.L.; Schwartz, D.A.; Wells, A.U.; et al. The role of bacteria in the pathogenesis and progression of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kolosova, I.A.; Verin, A.D. Toll Like Receptors Signaling Pathways as a Target for Therapeutic Interventions. Curr. Signal Transduct. Ther. 2011, 6, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldham, J.M.; Ma, S.F.; Martinez, F.J.; Anstrom, K.J.; Raghu, G.; Schwartz, D.A.; Valenzi, E.; Witt, L.; Lee, C.; Vij, R.; et al. TOLLIP, MUC5B, and the response to N-acetylcysteine among individuals with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brissoni, B.; Agostini, L.; Kropf, M.; Martinon, F.; Swoboda, V.; Lippens, S.; Everett, H.; Aebi, N.; Janssens, S.; Meylan, E.; et al. Intracellular Trafficking of Interleukin-1 Receptor I Requires Tollip. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 2265–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kim, S.E.; Chen, T.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Tabib, T.; Tan, J.; Guo, B.; Fung, S.; Zhao, J.; et al. Toll interacting protein protects bronchial epithelial cells from bleomycin-induced apoptosis. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 9884–9898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonella, F.; Campo, I.; Zorzetto, M.; Boerner, E.; Ohshimo, S.; Theegarten, D.; Taube, C.; Costabel, U. Potential clinical utility of MUC5B und TOLLIP single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the management of patients with IPF. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulugeta, S.; Nguyen, V.; Russo, S.J.; Muniswamy, M.; Beers, M.F. A Surfactant Protein C Precursor Protein BRICHOS Domain Mutation Causes Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Proteasome Dysfunction, and Caspase 3 Activation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2005, 32, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitsett, J.A.; Wert, S.E.; Weaver, T.E. Alveolar Surfactant Homeostasis and the Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Disease. Annu. Rev. Med. 2010, 61, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nogee, L.M.; Dunbar, A.E.; Wert, S.E.; Askin, F.; Hamvas, A.; Whitsett, J.A. A Mutation in the Surfactant Protein C Gene Associated with Familial Interstitial Lung Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kuan, P.J.; Xing, C.; Cronkhite, J.T.; Torres, F.; Rosenblatt, R.L.; DiMaio, J.M.; Kinch, L.N.; Grishin, N.V.; Garcia, C.K. Genetic Defects in Surfactant Protein A2 Are Associated with Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 84, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nathan, N.; Giraud, V.; Picard, C.; Nunes, H.; Moal, F.D.-L.; Copin, B.; Galeron, L.; De Ligniville, A.; Kuziner, N.; Reynaud-Gaubert, M.; et al. GermlineSFTPA1mutation in familial idiopathic interstitial pneumonia and lung cancer. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 1457–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takezaki, A.; Tsukumo, S.-I.; Setoguchi, Y.; Ledford, J.; Goto, H.; Hosomichi, K.; Uehara, H.; Nishioka, Y.; Yasutomo, K. A homozygous SFTPA1 mutation drives necroptosis of type II alveolar epithelial cells in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 2724–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klay, D.; Platenburg, M.; van Rijswijk, R.H.; Grutters, J.C.; van Moorsel, C.H. ABCA3 mutations in adult pulmonary fibrosis patients: A case series and review of literature. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2020, 26, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanjore, H.; Blackwell, T.S.; Lawson, W.E. Emerging evidence for endoplasmic reticulum stress in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2012, 302, L721–L729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamano, G.; Funahashi, H.; Kawanami, O.; Zhao, L.-X.; Ban, N.; Uchida, Y.; Morohoshi, T.; Ogawa, J.; Shioda, S.; Inagaki, N. ABCA3 is a lamellar body membrane protein in human lung alveolar type II cells1. FEBS Lett. 2001, 508, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, W. Candidate genes of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Current evidence and research. Appl. Clin. Genet. 2016, 9, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weichert, N.; Kaltenborn, E.; Hector, A.; Woischnik, M.; Schams, A.; Holzinger, A.; Kern, S.; Griese, M. Some ABCA3 mutations elevate ER stress and initiate apoptosis of lung epithelial cells. Respir. Res. 2011, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campo, I.; Zorzetto, M.; Mariani, F.; Kadija, Z.; Morbini, P.; Dore, R.; Kaltenborn, E.; Frixel, S.; Zarbock, R.; Liebisch, G.; et al. A large kindred of pulmonary fibrosis associated with a novel ABCA3 gene variant. Respir. Res. 2014, 15, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.K.; Kugler, M.C.; Wolters, P.J.; Robillard, L.; Galvez, M.G.; Brumwell, A.N.; Sheppard, D.; Chapman, H.A. Alveolar epithelial cell mesenchymal transition develops in vivo during pulmonary fibrosis and is regulated by the extracellular matrix. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13180–13185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanjore, H.; Xu, X.C.; Polosukhin, V.V.; Degryse, A.L.; Li, B.; Han, W.; Sherrill, T.P.; Plieth, D.; Neilson, E.G.; Blackwell, T.S.; et al. Contribution of Epithelial-derived Fibroblasts to Bleomycin-induced Lung Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 180, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marmai, C.; Sutherland, R.E.; Kim, K.K.; Dolganov, G.M.; Fang, X.; Kim, S.S.; Jiang, S.; Golden, J.A.; Hoopes, C.W.; Matthay, M.A.; et al. Alveolar epithelial cells express mesenchymal proteins in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2011, 301, L71–L78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, I.V.; Burch, L.H.; Steele, M.P.; Savov, J.D.; Hollingsworth, J.W.; McElvania-Tekippe, E.; Berman, K.G.; Speer, M.C.; Sporn, T.A.; Brown, K.K.; et al. Gene expression profiling of familial and sporadic interstitial pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 175, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Selman, M.; Pardo, A.; Barrera, L.; Estrada, A.; Watson, S.R.; Wilson, K.; Aziz, N.; Kaminski, N.; Zlotnik, A. Gene Expression Profiles Distinguish Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis from Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaminski, N. Microarray analysis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2003, 29 (Suppl. 3), S32–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartczak, K.; Białas, A.J.; Kotecki, M.J.; Górski, P.; Piotrowski, W.J. More than a Genetic Code: Epigenetics of Lung Fibrosis. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2020, 24, 665–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taskar, V.S.; Coultas, D.B. Is idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis an environmental disease? Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2006, 3, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Luckhardt, T.; Hecker, L.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, G.; Antony, V.B.; De Andrade, J.; Thannickal, V.J. New Insights into the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Drugs 2011, 71, 981–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, M.P.; Speer, M.C.; Loyd, J.E.; Brown, K.K.; Herron, A.; Slifer, S.H.; Burch, L.H.; Wahidi, M.M.; Sporn, T.A.; McAdams, H.P.; et al. The Clinical and Pathologic Features of Familial Interstitial Pneumonia (FIP) Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 172, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Maurano, M.T.; Qu, H.; Varley, K.E.; Gertz, J.; Pauli, F.; Lee, K.; Canfield, T.; Weaver, M.; Sandstrom, R.; et al. Widespread plasticity in CTCF occupancy linked to DNA methylation. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1680–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinovich, E.I.; Selman, M.; Kaminski, N. Epigenomics of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 473–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Helling, B.A.; Gerber, A.N.; Kadiyala, V.; Sasse, S.K.; Pedersen, B.S.; Sparks, L.; Nakano, Y.; Okamoto, T.; Evans, C.M.; Yang, I.V.; et al. Regulation of MUC5B Expression in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 57, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.K.; Fisher, A.S.; Scruggs, A.M.; White, E.S.; Hogaboam, C.M.; Richardson, B.C.; Peters-Golden, M. Hypermethylation of PTGER2 Confers Prostaglandin E2 Resistance in Fibrotic Fibroblasts from Humans and Mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 2245–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagood, J.S.; Prabhakaran, P.; Kumbla, P.; Salazar, L.; MacEwen, M.W.; Barker, T.H.; Ortiz, L.A.; Schoeb, T.; Siegal, G.P.; Alexander, C.B.; et al. Loss of Fibroblast Thy-1 Expression Correlates with Lung Fibrogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 167, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanders, Y.Y.; Kumbla, P.; Hagood, J.S. Enhanced Myofibroblastic Differentiation and Survival in Thy-1(−) Lung Fibroblasts. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2007, 36, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.M.; Zhang, Y.; Kim, H.P.; Zhou, Z.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.A.; Liu, F.; Ifedigbo, E.; Xu, X.; Oury, T.D.; Kaminski, N.; et al. Caveolin-1: A critical regulator of lung fibrosis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2895–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, E.S.; Atrasz, R.G.; Hu, B.; Phan, S.H.; Stambolic, V.; Mak, T.W.; Hogaboam, C.M.; Flaherty, K.R.; Martinez, F.J.; Kontos, C.D.; et al. Negative Regulation of Myofibroblast Differentiation by PTEN (Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog Deleted on Chromosome 10). Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, Y.Y.; Pardo, A.; Selman, M.; Nuovo, G.J.; Tollefsbol, T.O.; Siegal, G.P.; Hagood, J.S. Thy-1 promoter hypermethylation: A novel epigenetic pathogenic mechanism in pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2008, 39, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, C.M.; Neary, R.; Levendale, A.; Watson, C.J.; Baugh, A.J. Hypoxia-induced DNA hypermethylation in human pulmonary fibroblasts is associated with Thy-1 promoter methylation and the development of a pro-fibrotic phenotype. Respir. Res. 2012, 13, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanders, Y.Y.; Cisneros, J.; Nuovo, G.; Selman, M.; Hagood, J.S. Epigenetic regulation mediates Thy-1 gene silencing and induction of the myofibroblast phenotype. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2008, 5, 363–364. [Google Scholar]
- Neveu, W.A.; Mills, S.T.; Staitieh, B.S.; Sueblinvong, V. TGF-β1 epigenetically modifies Thy-1 expression in primary lung fibroblasts. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2015, 309, C616–C626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, K.; Singh, I.; Dobersch, S.; Sarvari, P.; Günther, S.; Cordero, J.; Mehta, A.; Wujak, L.; Cabrera-Fuentes, H.; Chao, C.-M.; et al. Inactivation of nuclear histone deacetylases by EP300 disrupts the MiCEE complex in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanders, Y.Y.; Tollefsbol, T.O.; Varisco, B.M.; Hagood, J.S. Epigenetic Regulation of Thy-1 by Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor in Rat Lung Fibroblasts. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 45, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glenisson, W.; Castronovo, V.; Waltregny, D. Histone deacetylase 4 is required for TGFβ1-induced myofibroblastic differentiation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2007, 1773, 1572–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Selman, M.; López-Otín, C.; Pardo, A. Age-driven developmental drift in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 538–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cushing, L.; Kuang, P.P.; Qian, J.; Shao, F.; Wu, J.; Little, F.; Thannickal, V.J.; Cardoso, W.V.; Lü, J. miR-29 Is a Major Regulator of Genes Associated with Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 45, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oak, S.R.; Murray, L.; Herath, A.; Sleeman, M.; Anderson, I.; Joshi, A.D.; Coelho, A.L.; Flaherty, K.R.; Teows, G.B.; Knight, D.; et al. A micro RNA processing defect in rapidly progressing idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pottier, N.; Maurin, T.; Chevalier, B.; Puissegur, M.-P.; Lebrigand, K.; Robbe-Sermesant, K.; Bertero, T.; Cardenas, C.L.; Courcot, E.; Rios, G.; et al. Identification of Keratinocyte Growth Factor as a Target of microRNA-155 in Lung Fibroblasts: Implication in Epithelial-Mesenchymal Interactions. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, K.V.; Corcoran, D.; Yousef, H.; Yarlagadda, M.; Tzouvelekis, A.; Gibson, K.F.; Konishi, K.; Yousem, S.A.; Singh, M.; Handley, D.; et al. Inhibition and Role of let-7d in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.; Friggeri, A.; Yang, Y.; Milosevic, J.; Ding, Q.; Thannickal, V.J.; Kaminski, N.; Abraham, E. miR-21 mediates fibrogenic activation of pulmonary fibroblasts and lung fibrosis. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Liang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Yang, X.; Xu, D.; Gou, X.; Sathiaseelan, R.; Senavirathna, L.K.; Wang, P.; Liu, L. Long Noncoding RNA FENDRR Exhibits Antifibrotic Activity in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 62, 440–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savary, G.; Dewaeles, E.; Diazzi, S.; Buscot, M.; Nottet, N.; Fassy, J.; Courcot, E.; Henaoui, I.-S.; Lemaire, J.; Van der Hauwaert, C.; et al. The long noncoding RNA DNM3OS is a reservoir of fibromiRs with major functions in lung fibroblast response to TGF-b and pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schembri, F.; Sridhar, S.; Perdomo, C.; Gustafson, A.M.; Zhang, X.; Ergun, A.; Lu, J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, X.; Bowers, J.; et al. MicroRNAs as modulators of smoking-induced gene expression changes in human airway epithelium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2319–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stella, G.M.; D’Agnano, V.; Piloni, D.; Saracino, L.; Lettieri, S.; Mariani, F.; Lancia, A.; Bortolotto, C.; Rinaldi, P.; Falanga, F.; et al. The oncogenic landscape of the idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A narrative review. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2022, 11, 472–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, G.M.; Balestro, E.; Lacedonia, D.; Baraldo, S. Telomeropathies: An emerging spectrum of disorders with important implications for patients with interstitial lung disease. Minerva Med. 2016, 107, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Boggaram, V. Thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF-1/Nkx2.1/TITF1) gene regulation in the lung. Clin. Sci. 2009, 116, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wan, S.; Han, Y.; Huang, L.; Zheng, J.; Li, Q. The Relationship between TTF-1 Expression and EGFR Mutations in Lung Adenocarcinomas. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blackwell, T.S. Lung injury and fibrosis induced by a mutant form of surfactant protein C. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 3745–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nobili, S.; Lapucci, A.; Landini, I.; Coronnello, M.; Roviello, G.; Mini, E. Role of ATP-binding cassette transporters in cancer initiation and progression. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 60, 72–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, J.; Moller, D.E. The Mechanisms of Action of PPARs. Annu. Rev. Med. 2002, 53, 409–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sauter, W.; Rosenberger, A.; Beckmann, L.; Kropp, S.; Mittelstrass, K.; Timofeeva, M.; Wölke, G.; Steinwachs, A.; Scheiner, D.; Meese, E.; et al. Matrix Metalloproteinase 1 (MMP1) Is Associated with Early-Onset Lung Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2008, 17, 1127–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rabinovich, E.I.; Kapetanaki, M.G.; Steinfeld, I.; Gibson, K.F.; Pandit, K.; Yu, G.; Yakhini, Z.; Kaminski, N. Global Methylation Patterns in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreus, M.; Lehtonen, S.; Skarp, S.; Kaarteenaho, R. Extracellular matrix proteins produced by stromal cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and lung adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheu, C.-C.; Chang, W.-A.; Tsai, M.-J.; Liao, S.-H.; Chong, I.-W.; Kuo, P.-L. Gene Expression Changes Associated with Nintedanib Treatment in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Fibroblasts: A Next-Generation Sequencing and Bioinformatics Study. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Oksvold, P.; Kampf, C.; Djureinovic, D.; Odeberg, J.; Habuka, M.; Tahmasebpoor, S.; Danielsson, A.; Edlund, K.; et al. Analysis of the Human Tissue-specific Expression by Genome-wide Integration of Transcriptomics and Antibody-based Proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014, 13, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raghu, G.; van den Blink, B.; Hamblin, M.J.; Brown, A.W.; Golden, J.A.; Ho, L.A.; Wijsenbeek, M.S.; Vasakova, M.; Pesci, A.; Antin-Ozerkis, D.E.; et al. Effect of Recombinant Human Pentraxin 2 vs. Placebo on Change in Forced Vital Capacity in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2018, 319, 2299–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Justet, A.; Klay, D.; Porcher, R.; Cottin, V.; Ahmad, K.; Molina, M.M.; Nunes, H.; Reynaud-Gaubert, M.; Naccache, J.M.; Manali, E.; et al. Safety and efficacy of pirfenidone and nintedanib in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and carrying a telomere-related gene mutation. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2003198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwapiszewska, G.; Gungl, A.; Wilhelm, J.; Marsh, L.M.; Puthenparampil, H.T.; Sinn, K.; Didiasova, M.; Klepetko, W.; Kosanovic, D.; Schermuly, R.T.; et al. Transcriptome profiling reveals the complexity of pirfenidone effects in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1800564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Povedano, J.M.; Martinez, P.; Serrano, R.; Tejera, Á.; Gómez-López, G.; Bobadilla, M.; Flores, J.M.; Bosch, F.; Blasco, M.A. Therapeutic effects of telomerase in mice with pulmonary fibrosis induced by damage to the lungs and short telomeres. eLife 2018, 7, e31299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, M.; Ebina, M.; Orson, F.M.; Nakamura, A.; Kubota, K.; Koinuma, D.; Akiyama, K.-I.; Maemondo, M.; Okouchi, S.; Tahara, M.; et al. Hepatocyte Growth Factor Gene Transfer to Alveolar Septa for Effective Suppression of Lung Fibrosis. Mol. Ther. 2005, 12, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, A.; Fujii, M.; Matsumura, R.; Kumano, K.; Saito, Y.; Miyazono, K.; Iwamoto, I. Transient gene transfer and expression of Smad7 prevents bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakamoto, S.; Yazawa, T.; Baba, Y.; Sato, H.; Kanegae, Y.; Hirai, T.; Saito, I.; Goto, T.; Kurahashi, K. Keratinocyte Growth Factor Gene Transduction Ameliorates Pulmonary Fibrosis Induced by Bleomycin in Mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 45, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbuzenko, O.B.; Ivanova, V.; Kholodovych, V.; Reimer, D.C.; Reuhl, K.R.; Yurkow, E.; Adler, D.; Minko, T. Combinatorial treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis using nanoparticles with prostaglandin E and siRNA(s). Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2017, 13, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Li, P.; Pan, H.; Li, Y.; Xu, Q.; Xu, T.; Ji, X.; Liu, Y.; Yao, W.; Han, L.; et al. miR-542-5p Attenuates Fibroblast Activation by Targeting Integrin α6 in Silica-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Liu, W.; Cao, G.; Xv, P.; Zhang, J.; Lv, C.; et al. miR-30a as Potential Therapeutics by Targeting TET1 through Regulation of Drp-1 Promoter Hydroxymethylation in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Protein | Disease (OMIM) | Phenotype | Inheritance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TERT | Telomerase reverse transcriptase | PFBMFT1 (614742) | Pulmonary fibrosis and/or bone marrow failure, telomere-related | AD |
| TERC | Telomerase RNA component | PFBMFT2 (614743) | Pulmonary fibrosis and/or bone marrow failure, telomere-related | AD |
| RTEL1 | Regulator Of Telomere Elongation Helicase 1 | PFBMFT3 (616373) | Pulmonary fibrosis, adult onset | AD |
| PARN | Poly(A)-Specific Ribonuclease | PFBMFT4 (616371) | Pulmonary fibrosis, adult onset | AD |
| ZCCHC8 | Zinc Finger CCHC-Type Containing 8 | PFBMFT5 (618674) | Pulmonary fibrosis and/or bone marrow failure, adult onset | AD |
| RPA1 | Replication Protein A1 | PFBMFT6 (619767) | Pulmonary fibrosis and/or bone marrow failure and skin abnormalities | AD |
| SFTPA2 | Surfactant Protein A2 | ILD2 (178500) | Pulmonary fibrosis, interstitial pneumonia, lung cancer | AD |
| FAM111B | FAM111 Trypsin Like Peptidase B | POIKTMP (615704) | Poikiloderma, hereditary fibrosing, with tendon contractures, myopathy, and pulmonary fibrosis | AD |
| Gene 1 | Main Function | Profibrotic Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| TERT | Telomerase | Decreased activity of telomerase |
| TERC | Reverse Transcription in Telomerase | Decreased activity of telomerase |
| PARN | Stability of mRNA in Telomerase | Shortening of telomeres |
| RTEL1 | DNA helicase in Telomerase | Shortening of telomeres |
| SFTPA1 | Modulate surface tension in the alveoli | Increased ER stress |
| SFTPA2 | Modulate innate and adaptive immunity | Increased ER stress |
| SFTPC | Stabilize the surfactant fluid | Increased ER stress |
| ABCA3 | Lipid transport across membranes | Increased ER stress and apoptosis |
| MUC5B | Mucin 5B production | Muco-ciliary disfunction |
| TOLLIP | Inhibitory adaptor protein within TLR | Decreased protection against ROS |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tirelli, C.; Pesenti, C.; Miozzo, M.; Mondoni, M.; Fontana, L.; Centanni, S. The Genetic and Epigenetic Footprint in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis: A State-of-the-Art Review. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3107. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123107
Tirelli C, Pesenti C, Miozzo M, Mondoni M, Fontana L, Centanni S. The Genetic and Epigenetic Footprint in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis: A State-of-the-Art Review. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(12):3107. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123107
Chicago/Turabian StyleTirelli, Claudio, Chiara Pesenti, Monica Miozzo, Michele Mondoni, Laura Fontana, and Stefano Centanni. 2022. "The Genetic and Epigenetic Footprint in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis: A State-of-the-Art Review" Diagnostics 12, no. 12: 3107. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123107
APA StyleTirelli, C., Pesenti, C., Miozzo, M., Mondoni, M., Fontana, L., & Centanni, S. (2022). The Genetic and Epigenetic Footprint in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis: A State-of-the-Art Review. Diagnostics, 12(12), 3107. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123107






