Prevalence, Knowledge and Attitudes Concerning Dietary Supplements among a Student Population in Croatia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Measurement
2.3. Statistical Analysis
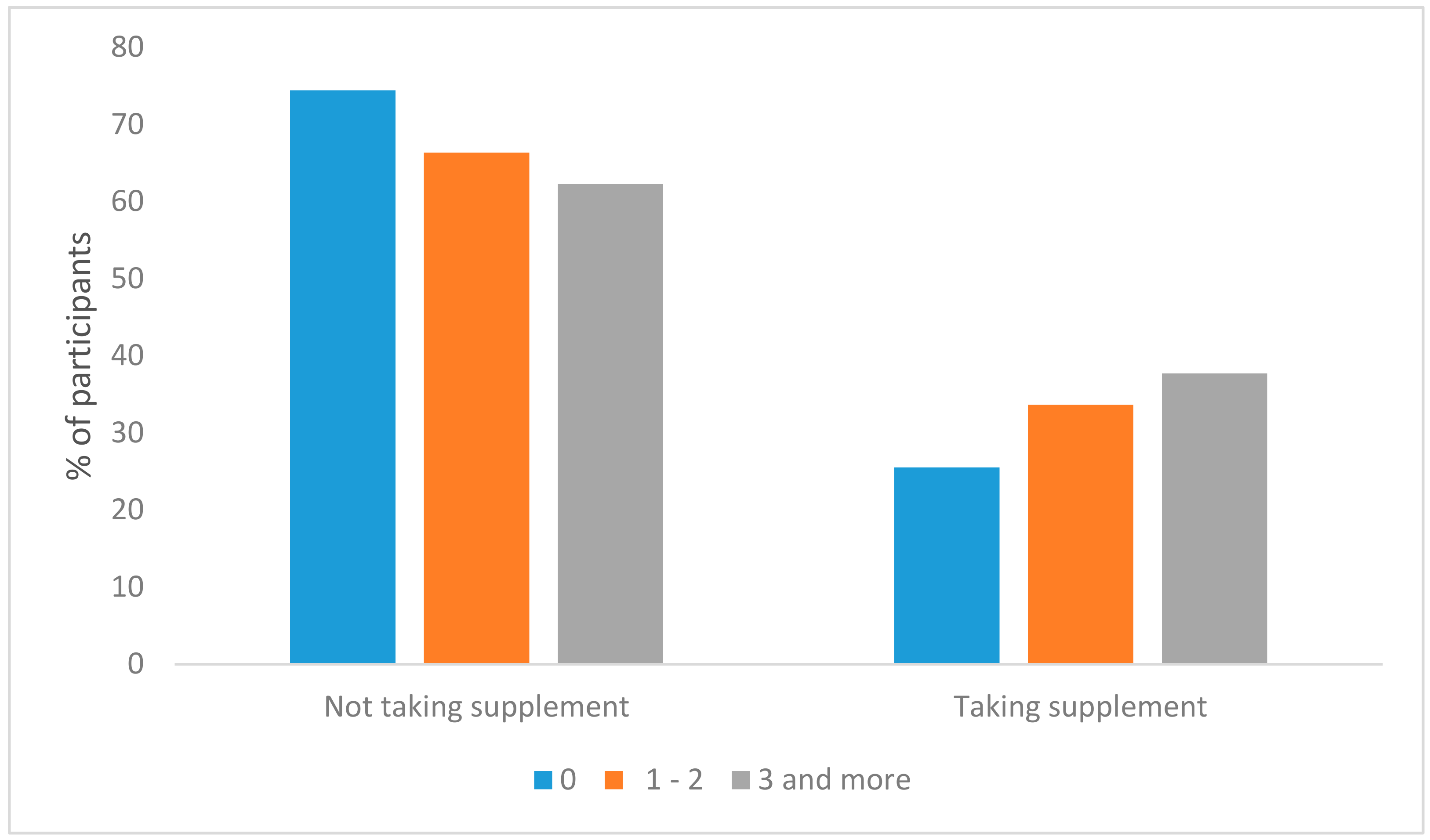
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Block, G.; Jensen, C.D.; Norkus, E.P.; Dalvi, T.B.; Wong, L.G.; McManus, J.F.; Hudes, M.L. Usage patterns, health, and nutritional status of long-term multiple dietary supplement users: A cross-sectional study. Nutr. J. 2007, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hovan-Somborac, J. Risk factors for chronic non-communicable diseases: A follow-up model. Med. Pregl. 2002, 55, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archer, S.L.; Stamler, J.; Moag-Stahlberg, A.; Van Horn, L.; Garside, D.; Chan, Q.; Buffington, J.J.; Dyer, A.R. Association of dietary supplement use with specific micronutrient intakes among middle-aged American men and women: The INTERMAP study. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2005, 105, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institues of Health. Office of Dietary Supplements. Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994. Public Low 103-417. 108 Stat 4325. Available online: https://ods.od.nih.gov/About/DSHEA_Wording.aspx (accessed on 18 January 2018).
- Directive 2002/46/EC of the European Communities 2002. L183/51. Available online: https://www.fsai.ie./legsilation/food_legislation/food_supplement.html#eu_legislation (accessed on 24 January 2018).
- Narodne Novine. Pravilnik O Dodacima Prehrani. Broj 126. (NN 126/2013). Available online: https://narodne-novine.nn.hr/clanci/sluzbeni/2013_10_126_2740.html (accessed on 27 January 2018).
- Federal Research Center for Nutrition and Food. Nationale Verzehrs Studie II. Ergebnisbericht, Teil 2. Available online: https://www.mri.bund.de/fileadmin/MRI/Institute/EV/NVSII_Abschlussbericht_Teil_2.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2018).
- Murphy, S.P.; White, K.K.; Park, S.Y.; Sharma, S. Multivitamin-multimineral supplements’ effect on total nutrient intake. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 280s–284s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanojevic-Ristic, Z.; Stevic, S.; Rasic, J.; Valjarevic, D.; Dejanovic, M.; Valjarevic, A. Influence of pharmacological education on perceptions, attitudes and use of dietary supplements by medical students. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Naggar, R.A.; Chen, R. Prevalence of vitamin-mineral supplements use and associated factors among young Malaysians. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2011, 12, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bailey, R.L.; Fulgoni, V.L., 3rd; Keast, D.R.; Lentino, C.V.; Dwyer, J.T. Do dietary supplements improve micronutrient sufficiency in children and adolescents? J. Pediatr. 2012, 161, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Department of Education. Profile of 2007-08 First-Time Bachelor’s Degree Recipients in 2009. Available online: https://nces.ed.gov/pubs2013/2013150.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2018).
- Paffenbarger, R.S., Jr.; Kampert, J.B.; Lee, I.M. Physical activity and health of college men: Longitudinal observations. Int. J. Sports Med. 1997, 18, S200–S203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borsari, B.; Carey, K.B. Peer influences on college drinking: A review of the research. J. Subst. Abus. 2001, 13, 391–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, A.; Sood, R.; Brinker, F.J.; Mann, R.; Loehrer, L.L.; Wahner-Roedler, D.L. Potential for interactions between dietary supplements and prescription medications. Am. J. Med. 2008, 121, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, H.H.; Lin, H.W.; Pickard, A.S.; Tsai, H.Y.; Mahady, G.B. Evaluation of documented drug interactions and contraindications associated with herbs and dietary supplements: A systematic literature review. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2012, 66, 1056–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardiner, P.; Woods, C.; Kemper, K.J. Dietary supplement use among health care professionals enrolled in an online curriculum on herbs and dietary supplements. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2006, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotoudeh, G.; Kabiri, S.; Yeganeh, H.S.; Koohdani, F.; Khajehnasiri, F.; Khosravi, S. Predictors of dietary supplement usage among medical interns of Tehran university of medical sciences. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2015, 33, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alhomoud, F.K.; Basil, M.; Bondarev, A. Knowledge, attitudes and practices (KAP) relating to dietary supplements among health sciences and non-health sciences students in one of the universities of United Arab Emirates (UAE). J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, JC05–JC09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Han, J.H.; Keen, C.L. Vitamin and mineral supplement use by healthy teenagers in Korea: Motivating factors and dietary consequences. Nutrition 2001, 17, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axon, D.R.; Vanova, J.; Edel, C.; Slack, M. Dietary supplement use, knowledge, and perceptions among student pharmacists. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2017, 81, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miljkovic, M.; Stojiljkovic, M.; Radulovic, O. Knowledge, attitudes and use of dietary supplement among students of the University of Nis (Serbia). Med. Pregl. 2013, 66, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiltgren, A.R.; Booth, A.O.; Kaur, G.; Cicerale, S.; Lacy, K.E.; Thorpe, M.G.; Keast, R.S.; Riddell, L.J. Micronutrient supplement use and diet quality in university students. Nutrients 2015, 7, 1094–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suleiman, A.A.; Alboqai, O.K.; Yasein, N.; Al-Essa, M.K.; El Masri, K. Prevalence of vitamin-mineral supplement use among Jordan University students. Saudi Med. J. 2008, 29, 1326–1331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marques-Vidal, P. Vitamin supplement usage and nutritional knowledge in a sample of Portuguese health science students. Nutr. Res. 2004, 24, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojiljković, M.; Radulović, O.; Jović, S. Differences in the use of dietary supplements between medical and non-medical students from University of Niš (Serbia). Biomed. Istraž. 2012, 3, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Saeedi, P.; Nasir, M.T.; Hazizi, A.S.; Vafa, M.R.; Foroushani, A.R. Nutritional supplement use among fitness club participants in Tehran, Iran. Appetite 2013, 60, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darvishi, L.; Askari, G.; Hariri, M.; Bahreynian, M.; Ghiasvand, R.; Ehsani, S.; Mashhadi, N.S.; Rezai, P.; Khorvash, F. The use of nutritional supplements among male collegiate athletes. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 4, S68–S72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Azizi, M.; Aghaee, N.; Ebrahimi, M.; Ranjabar, K. Nutrition knowledge, the attitude and practices of college students. Facta Univ. 2011, 9, 349–357. [Google Scholar]
- Dundas, M.L.; Keller, J.R. Herbal, vitamin, and mineral supplement use and beliefs of university students. Top. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 18, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variables | N | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Men | 238 | 26.2 |
| Women | 672 | 73.8 | |
| Faculty | Medical sciences students (MSS) | 362 | 39.8 |
| Nonmedical sciences students (NMSS) | 548 | 60.2 | |
| University status | Freshmen | 326 | 35.8 |
| Juniors | 422 | 46.4 | |
| Seniors | 162 | 17.8 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | Underweight | 60 | 6.6 |
| Normal | 718 | 78.9 | |
| Overweight | 106 | 11.6 | |
| Obese | 26 | 2.9 | |
| Smoking | Yes | 358 | 39.3 |
| No | 552 | 60.7 | |
| Physical activity (times/week) | 0 | 490 | 53.8 |
| 1–2 | 198 | 21.8 | |
| 3 and more | 222 | 24.4 | |
| Take dietary supplements | Yes | 278 | 30.5 |
| No | 632 | 69.5 |
| Questions | Total (N = 910) | MSS (N = 362) | NMSS (N = 548) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Do you know what dietary supplements are? | ||||
| Yes | 834 (91.6) | 338 (93.4) | 325 (59.3) | <0.001 ** |
| No | 46 (5.1) | 20 (5.5) | 197 (36.0) | <0.001 ** |
| Do not know | 30 (3.3) | 4 (1.1) | 26 (4.7) | <0.001 ** |
| Have you attended any health campaigns/workshops on dietary supplements? | ||||
| Yes | 102 (11.2) | 30 (8.3) | 72 (13.1) | 0.108 |
| No | 790 (86.8) | 322 (88.9) | 468 (85.4) | 0.274 |
| Do not know | 18 (2.0) | 10 (2.8) | 8 (1.5) | 0.329 |
| Do you use any dietary supplements? | ||||
| Yes | 278 (30.5) | 120 (33.1) | 158 (28.8) | 0.132 |
| No | 632 (69.5) | 242 (66.9) | 390 (71.2) | 0.328 |
| I always look for professional medical help when taking a dietary supplement. | ||||
| Yes | 134 (14.7) | 54 (14.9) | 80 (14.6) | 0.924 |
| No | 724 (79.6) | 290 (80.1) | 434 (79.2) | 0.813 |
| Do not know | 52 (5.7) | 18 (5.0) | 34 (6.2) | 0.580 |
| Do you think the use of dietary supplements is always safe? | ||||
| Yes | 68 (7.5) | 32 (8.8) | 85 (15.5) | 0.009 * |
| No | 548 (60.2) | 178 (49.2) | 321 (58.6) | <0.001 ** |
| Do not know | 294 (32.3) | 152 (42.0) | 142 (25.9) | <0.001 ** |
| Do you think that drug, food or drinks taken with dietary supplements might interact? | ||||
| Yes | 219 (24.1) | 76 (21.0) | 143 (26.1) | 0.166 |
| No | 333 (36.6) | 146 (40.3.) | 187 (34.1) | 0.197 |
| Do not know | 358 (39.3) | 140 (38.7) | 218 (39.8) | 0.825 |
| Source | Total (N = 910) | MSS (N = 362) | NMSS (N = 548) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare professionals | 302 (33.2) | 122 (33.7) | 180 (32.8) | 0.849 |
| Internet | 602 (66.1) | 224 (61.9) | 378 (69.0) | 0.017 |
| Product information leaflets | 166 (18.2) | 108 (29.8) | 58 (10.6) | <0.001 ** |
| Professional literature | 172 (19.0) | 64 (17.7) | 108 (19.7) | 0.588 |
| Friends and relatives | 202 (22.2) | 48 (13.3) | 154 (28.1) | <0.001 ** |
| TV or journal advertisements | 250 (27.5) | 132 (36.5) | 118 (21.5) | <0.001 ** |
| Reasons | ||||
| Maintain good health | 240 (26.4) | 84 (23.2) | 156 (28.5) | 0.212 |
| Ensure adequate nutrition | 224 (24.6) | 64 (17.7) | 160 (29.2) | 0.007 * |
| Treat minor illnesses | 46 (5.1) | 8 (2.2) | 38 (6.9) | 0.024 * |
| Satisfy energy needs | 216 (23.7) | 76 (21.0) | 140 (25.5) | 0.263 |
| Prevent diseases | 44 (4.8) | 10 (2.8) | 34 (6.2) | 0.090 |
| Weight loss | 58 (6.4) | 10 (2.8) | 48 (8.6) | 0.010 * |
| No specific reason | 12 (1.3) | 4 (1.1) | 8 (1.5) | 0.745 |
| Attitudes that study participants agreed with | ||||
| Dietary supplements are necessary for all ages | 118 (13.0) | 38 (32.2) | 80 (67.8) | 0.001 * |
| Dietary supplements are generally harmless | 194 (21.3) | 78 (40.2) | 116 (59.8) | 0.026 * |
| Regular use of supplements prevents chronic diseases | 110 (12.1) | 32 (29.1) | 78 (70.9) | <0.001 ** |
| Dietary supplements can prevent cancers | 74 (8.1) | 16 (21.6) | 58 (78.4) | <0.001 ** |
| Health personnel should promote supplement use | 146 (16.0) | 50 (34.2) | 96 (65.8) | 0.002 * |
| Variables | Cramér’s V |
|---|---|
| Sex | 0.0473 |
| Knowledge | −0.0067 |
| Physical activity | 0.1147 |
| BMI | 0.1350 |
| University status | 0.1028 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Žeželj, S.P.; Tomljanović, A.; Jovanović, G.K.; Krešić, G.; Peloza, O.C.; Dragaš-Zubalj, N.; Prokurica, I.P. Prevalence, Knowledge and Attitudes Concerning Dietary Supplements among a Student Population in Croatia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15061058
Žeželj SP, Tomljanović A, Jovanović GK, Krešić G, Peloza OC, Dragaš-Zubalj N, Prokurica IP. Prevalence, Knowledge and Attitudes Concerning Dietary Supplements among a Student Population in Croatia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(6):1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15061058
Chicago/Turabian StyleŽeželj, Sandra Pavičić, Ana Tomljanović, Gordana Kenđel Jovanović, Greta Krešić, Olga Cvijanović Peloza, Nataša Dragaš-Zubalj, and Iva Pavlinić Prokurica. 2018. "Prevalence, Knowledge and Attitudes Concerning Dietary Supplements among a Student Population in Croatia" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 6: 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15061058
APA StyleŽeželj, S. P., Tomljanović, A., Jovanović, G. K., Krešić, G., Peloza, O. C., Dragaš-Zubalj, N., & Prokurica, I. P. (2018). Prevalence, Knowledge and Attitudes Concerning Dietary Supplements among a Student Population in Croatia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(6), 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15061058






