Enhancement of Binding Affinity of Folate to Its Receptor by Peptide Conjugation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Folate-Phe Conjugation by Click Reactions
2.2. Preparation of Folate-Peptide Conjugates by the SPAAC Click Reaction
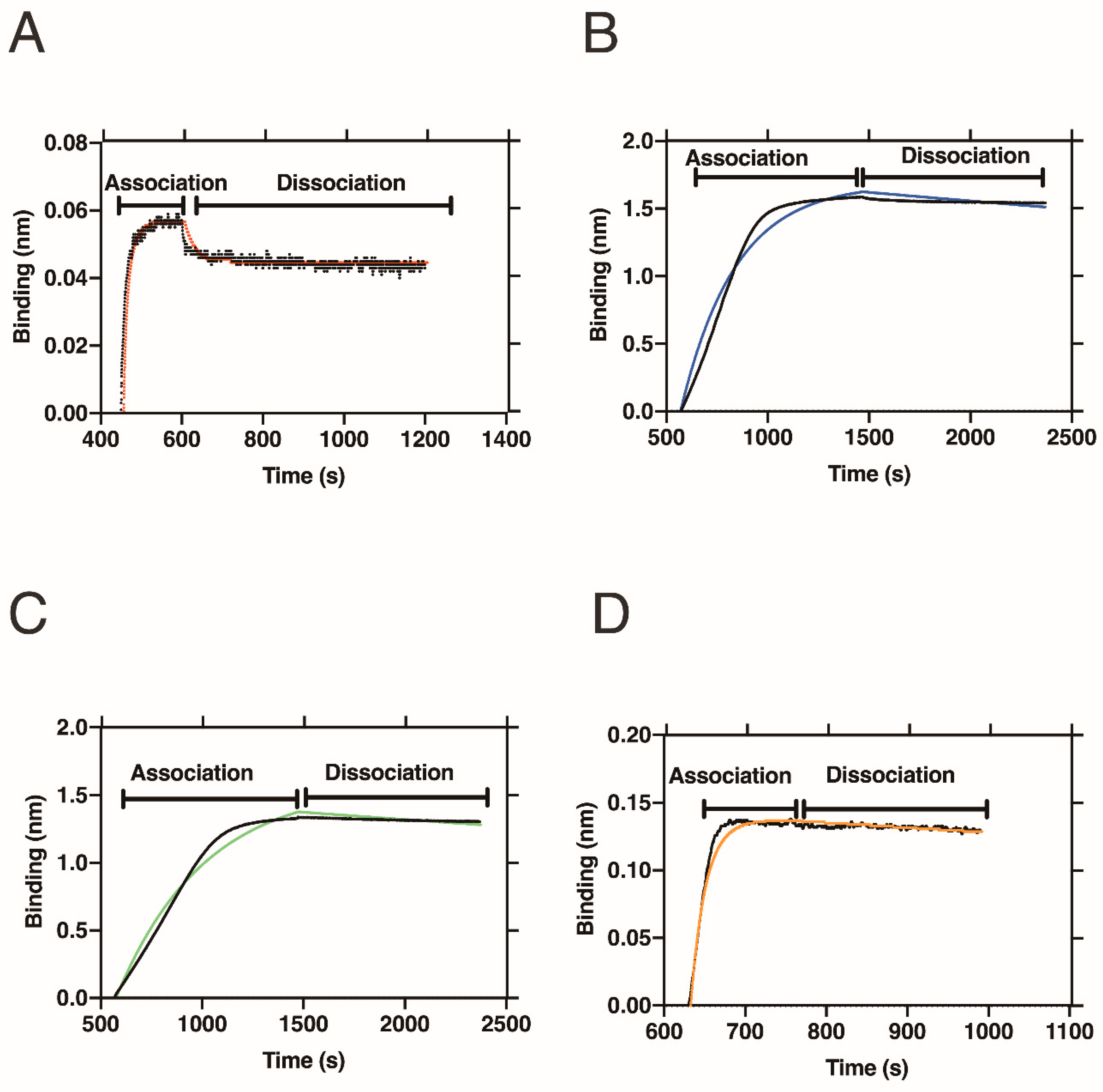
2.3. BLI Measurement
2.4. Interaction of Folate-Peptide Conjugates with FRα
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Folate-Propargyl and Folate-DBCO
3.2.1. Compound 2
3.2.2. Compound 3
3.2.3. Compound 4
3.2.4. Compound 6
3.2.5. Compound 7
3.2.6. Compound 8
3.2.7. Compound 9 (Folate-Propargyl)
3.2.8. Compound 11
3.2.9. Compound 12
3.2.10. Compound 13
3.2.11. Compound 14
3.2.12. Compound 15
3.2.13. Compound 16 (Folate-DBCO)
3.3. Click Reaction of Folate-Propargyl or Folate-DBCO with AzPhe-Fmoc
3.4. Synthesis and Purification of Peptides with N-terminal Biotin-PEG24
3.5. SPAAC Click Chemistry to Conjugate Folate into Peptides
3.6. Purification and Refolding of FRα
3.7. BLI Measurements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AcOH | Acetic acid |
| ADC | Antibody-drug conjugate |
| AzPhe | 4-Azido phenylalanine |
| BimH3 | Tris-(2-benzimidazolylmethyl) amine |
| BLI | Biolayer interferometry |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| brs | Broad singlet |
| CDI | 1,1′-carbonyldiimidazole |
| CuAAC | Cu(I)-catalyzed alkyne-azide cycloaddition |
| d | Duplet |
| DBCO | Dibenzylcyclooctyne |
| DMF | N,N-Dimethylformamide |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| EDC | 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride |
| eq | Equivalent |
| EtOH | Ethanol |
| Et2O | Diethyl ether |
| Et3N | Triethylamine |
| Fmoc | 9-Fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl group |
| FR | Folate receptor |
| FRα | Folate receptor alpha |
| ka | Association rate constant |
| KD | Equilibrium dissociation constant |
| kd | Dissociation rate constant |
| m | Multiplet |
| MALDI-TOF MS | Matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry |
| MeOH | Methanol |
| MTBD | 7-Methyl-1,5,7-triazabicyclo [4.4.0] dec-5-ene |
| NHS | N-hydroxysuccinimide |
| NMP | N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone |
| PBS | Phosphate buffered saline |
| PEG | Polyethylene glycol |
| q | Quartet |
| RT | Room temperature |
| s | Singlet |
| SA | Streptavidin |
| SPAAC | Strain-promoted alkyne-azide cycloaddition |
| TBAF | Tetrabutylammonium fluoride |
| TFA | Trifluoroacetic acid |
| THF | Tetrahydrofuran |
| TMS | Tetramethylsilane |
References
- Bahrami, B.; Mohammadnia-Afrouzi, M.; Bakhshaei, P.; Yazdani, Y.; Ghalamfarsa, G.; Yousefi, M.; Sadreddini, S.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F.; Hojjat-Farsangi, M. Folate-conjugated nanoparticles as a potent therapeutic approach in targeted cancer therapy. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 5727–5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrettos, E.I.; Mezo, G.; Tzakos, A.G. On the design principles of peptide-drug conjugates for targeted drug delivery to the malignant tumor site. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 930–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Jin, C.S.; Ujiie, H.; Lee, D.; Fujino, K.; Wada, H.; Hu, H.P.; Weersink, R.A.; Chen, J.; Kaji, M.; et al. Nanoparticle targeted folate receptor 1-enhanced photodynamic therapy for lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2017, 113, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, M.; Javaid, F.; Chudasama, V. Advances in targeting the folate receptor in the treatment/imaging of cancers. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 790–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ak, G.; Yilmaz, H.; Gunes, A.; Hamarat Sanlier, S. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of folate receptor-targeted a novel magnetic drug delivery system for ovarian cancer therapy. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 926–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, A.; Bax, H.J.; Josephs, D.H.; Ilieva, K.M.; Pellizzari, G.; Opzoomer, J.; Bloomfield, J.; Fittall, M.; Grigoriadis, A.; Figini, M.; et al. Targeting folate receptor alpha for cancer treatment. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 52553–52574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.; Watari, H.; AbuAlmaaty, A.; Ohba, Y.; Sakuragi, N. Apoptosis and molecular targeting therapy in cancer. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 150845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, S.; Zou, Y.; Togao, O.; Pastor, J.V.; John, G.B.; Wang, L.; Shiizaki, K.; Gotschall, R.; Schiavi, S.; Yorioka, N.; et al. Klotho inhibits transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) signaling and suppresses renal fibrosis and cancer metastasis in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 8655–8665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Pyo, S.; Kang, C.H.; Lee, C.O.; Lee, H.K.; Choi, S.U.; Park, C.H. Folate receptor 1 (FOLR1) targeted chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells for the treatment of gastric cancer. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, A.; Renukuntla, J.; Shah, S.; Boddu, S.H.S.; Vadlapudi, A.D.; Vadlapatla, R.K.; Pal, D. Functional characterization and expression of folate receptor-α in T47D human breast cancer cells. Drug Dev. Ther. 2015, 6, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasassi, T.; Giusti, A.M.; Raimondi, M.; Ravagnan, G.; Sapora, O.; Gratton, E. Cholesterol protects the phospholipid bilayer from oxidative damage. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1995, 19, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, J.M. Antibody-based therapeutics to watch in 2011. mAbs 2014, 3, 76–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnakat, H.; Ratnam, M. Distribution, functionality and gene regulation of folate receptor isoforms: Implications in targeted therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 1067–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Ke, J.; Zhou, X.E.; Yi, W.; Brunzelle, J.S.; Li, J.; Yong, E.L.; Xu, H.E.; Melcher, K. Structural basis for molecular recognition of folic acid by folate receptors. Nature 2013, 500, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlahov, I.R.; Leamon, C.P. Engineering folate-drug conjugates to target cancer: From chemistry to clinic. Bioconjug. Chem. 2012, 23, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam, N.W.; O’Connell, M.; Wisdom, J.A.; Dai, H. Carbon nanotubes as multifunctional biological transporters and near-infrared agents for selective cancer cell destruction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11600–11605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Dong, D.; Yu, Z.-L.; Zhao, Y.-F.; Pang, D.-W.; Zhang, Z.-L. Folate-Engineered Microvesicles for Enhanced Target and Synergistic Therapy toward Breast Cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 5100–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Du, R.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, X.; Qian, J.; Tian, X.; Zhou, J.; He, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. A pH-Responsive Yolk-Like Nanoplatform for Tumor Targeted Dual-Mode Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Chemotherapy. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 7049–7059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Yao, X.; Chen, L.; Gao, Z.; Xie, B. Improved drug targeting to liver tumor by sorafenib-loaded folate-decorated bovine serum albumin nanoparticles. Drug Deliv. 2019, 26, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudimack, J.; Lee, R.J. Targeted drug delivery via the folate receptor. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2000, 41, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Low, P.S. Folate-mediated delivery of macromolecular anticancer therapeutic agents. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 675–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, Y.; Jang, W.-D.; Nishiyama, N.; Fukushima, S.; Kataoka, K. Multifunctional polymeric micelles with folate-mediated cancer cell targeting and pH-triggered drug releasing properties for active intracellular drug delivery. Mol. Biosyst. 2005, 1, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, Y.; Nishiyama, N.; Kataoka, K. In Vivo Antitumor Activity of the Folate-Conjugated pH-Sensitive Polymeric Micelle Selectively Releasing Adriamycin in the Intracellular Acidic Compartments. Bioconjug. Chem. 2007, 18, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Xu, Y.; Sun, K.; Wang, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Caliskan, B.; Qiu, Z.; et al. Identification of a peptide for folate receptor alpha by phage display and its tumor targeting activity in ovary cancer xenograft. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Roberts, R.W. A Novel Strategy for In Vitro Selection of Peptide-Drug Conjugates. Chem. Biol. 2003, 10, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hirano, Y.; Uzawa, T.; Liu, M.Z.; Taiji, M.; Ito, Y. In vitro selection of a peptide aptamer that potentiates inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 by purvalanol. Medchemcomm 2014, 5, 1400–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hirano, Y.; Uzawa, T.; Taiji, M.; Ito, Y. Peptide-Assisted Enhancement of Inhibitory Effects of Small Molecular Inhibitors for Kinases. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2016, 89, 444–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazewicz, C.G.; Liskov, M.T.; Hines, K.J.; Brewer, S.H. Sensitive, site-specific, and stable vibrational probe of local protein environments: 4-azidomethyl-L-phenylalanine. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 8987–8993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Link, A.J.; Mock, M.L.; Tirrell, D.A. Non-canonical amino acids in protein engineering. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 2003, 14, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhao, J.; Han, G. Ultralow-Power Near Infrared Lamp Light Operable Targeted Organic Nanoparticle Photodynamic Therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 14586–14591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consoli, G.M.L.; Granata, G.; Fragassi, G.; Grossi, M.; Sallese, M.; Geraci, C. Design and synthesis of a multivalent fluorescent folate–calix[4]arene conjugate: Cancer cell penetration and intracellular localization. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 3298–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, P.; Gondi, S.R.; Sumerlin, B.S. Folate-Conjugated Thermoresponsive Block Copolymers: Highly Efficient Conjugation and Solution Self-Assembly. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, B.M.; Zhao, Y.; Kawashima, T.E.; Branchaud, B.P.; Pluth, M.D.; Jasti, R. Expanding the Chemical Space of Biocompatible Fluorophores: Nanohoops in Cells. ACS Cent. Sci. 2018, 4, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, R.; Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Hunziker, P. Efficient Receptor Mediated siRNA Delivery in Vitro by Folic Acid Targeted Pentablock Copolymer-Based Micelleplexes. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 2654–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golas, P.L.; Tsarevsky, N.V.; Matyjaszewski, K. Structure-re activity correlation in “Click” chemistry: Substituent effect on azide reactivity. Macromol. Rapid Comm. 2008, 29, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, N.; Wong, W.T. The Chemistry of Molecular Imaging; Wiley: London, UK, 2014; pp. 25–54. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Aneja, R.; Chaiken, I. Click chemistry in peptide-based drug design. Molecules 2013, 18, 9797–9817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, C.S.; Finn, M.G. Click chemistry in complex mixtures: Bioorthogonal bioconjugation. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 1075–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wibowo, A.S.; Singh, M.; Reeder, K.M.; Carter, J.J.; Kovach, A.R.; Meng, W.; Ratnam, M.; Zhang, F.; Dann, C.E., 3rd. Structures of human folate receptors reveal biological trafficking states and diversity in folate and antifolate recognition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 15180–15188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dommerholt, J.; Rutjes, F.; van Delft, F.L. Strain-Promoted 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition of Cycloalkynes and Organic Azides. Top. Curr. Chem. (Cham) 2016, 374, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmatti, R.; Miyatake, H.; Zhang, C.; Ren, X.; Yumoto, A.; Kiga, D.; Yamamura, M.; Ito, Y. Escherichia coli expression, purification, and refolding of human folate receptor alpha (hFRalpha) and beta (hFRbeta). Protein Expr. Purif. 2018, 149, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Folate-alkyne a | Molar Ratio of Folate-alkyne: Azide | Reaction Conditions | Yield (%) b |
| 9 | 1:1 | CuCl (0.1 mM), BimH3 (0.1 mM), Na ascorbate (0.1 mM), 11% (v/v) DMSO + 89% (v/v) H2O, room temperature (RT), 12 h | N.D. |
| 9 | 1:1 | CuCl (0.2 mM), BimH3 (0.1 mM), Na ascorbate (0.2 mM), 11% (v/v) DMSO + 89% (v/v) H2O, 50 °C, 10 h | N.D. |
| 9 | 1:1 | CuSO4 (0.1mM), BimH3 (0.1 mM), Na ascorbate (0.6 mM), 11% (v/v) DMSO + 89% (v/v) H2O, MW c, 1h | N.D. |
| 16 | 1:1 | 10% (v/v) DMF + 10% (v/v) H2O + 80% (v/v) MeOH, RT, 16 h | 60 |
| 16 | 1:1 | 10% (v/v) DMF + 10% (v/v) H2O + 80% (v/v) MeOH, 50 °C, 16 h | 56 |
| 16 | 2:1 | 20% (v/v) DMF + 10% (v/v) H2O + 70% (v/v) MeOH, RT, 16 h | 88 |
| Ligands | KD (nM) | ka (M−1 s−1) | kd (s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Folate | 1.14 | 6.74 × 106 | 7.69 × 10−3 |
| GFZIQ | 0.18 | 4.11 × 105 | 7.53 × 10−5 |
| SEZKA | 0.90 | 8.91 × 104 | 8.01 × 10−5 |
| DSEZKAY | 0.24 | 1.10 × 106 | 2.65 × 10−4 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dharmatti, R.; Miyatake, H.; Nandakumar, A.; Ueda, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Kiga, D.; Yamamura, M.; Ito, Y. Enhancement of Binding Affinity of Folate to Its Receptor by Peptide Conjugation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092152
Dharmatti R, Miyatake H, Nandakumar A, Ueda M, Kobayashi K, Kiga D, Yamamura M, Ito Y. Enhancement of Binding Affinity of Folate to Its Receptor by Peptide Conjugation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(9):2152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092152
Chicago/Turabian StyleDharmatti, Roopa, Hideyuki Miyatake, Avanashiappan Nandakumar, Motoki Ueda, Kenya Kobayashi, Daisuke Kiga, Masayuki Yamamura, and Yoshihiro Ito. 2019. "Enhancement of Binding Affinity of Folate to Its Receptor by Peptide Conjugation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 9: 2152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092152
APA StyleDharmatti, R., Miyatake, H., Nandakumar, A., Ueda, M., Kobayashi, K., Kiga, D., Yamamura, M., & Ito, Y. (2019). Enhancement of Binding Affinity of Folate to Its Receptor by Peptide Conjugation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(9), 2152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092152





