The Inflammasome Adaptor Protein ASC in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
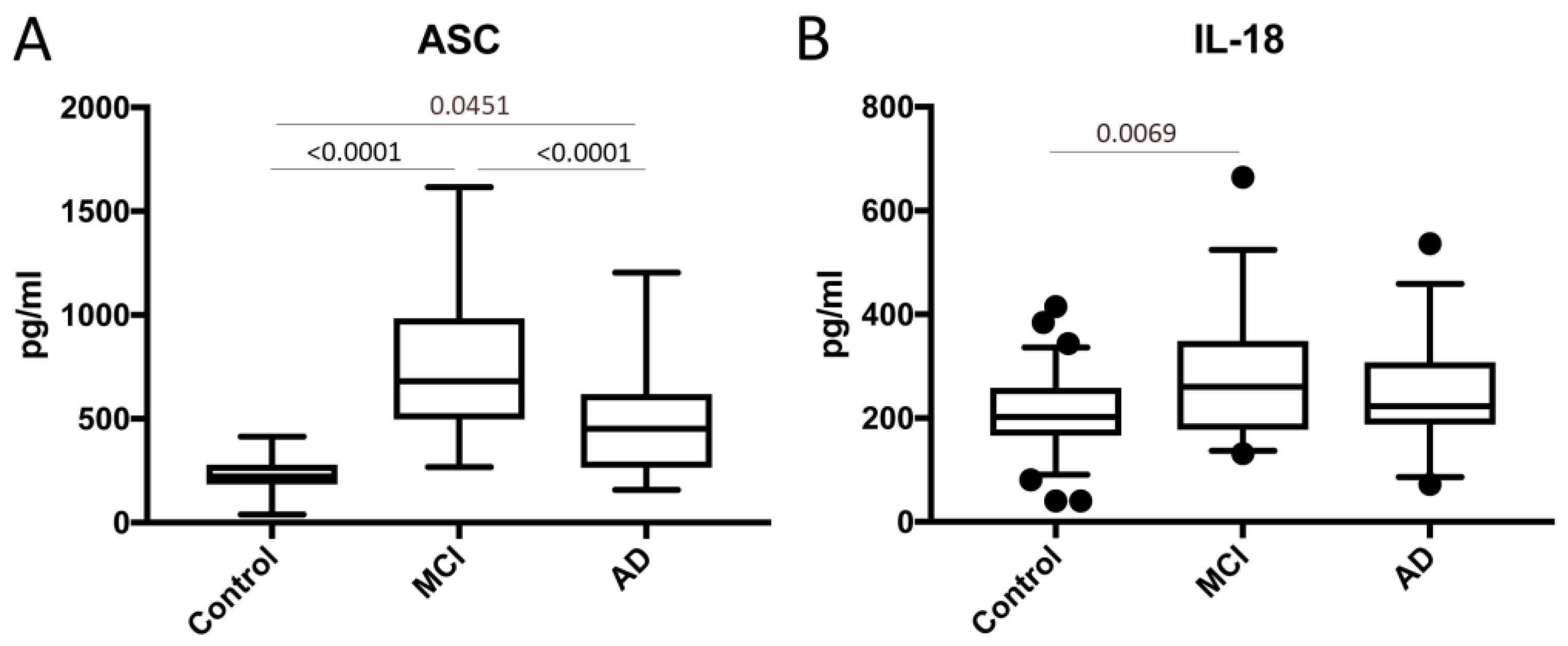
2.1. ASC and IL-18 Are Elevated in the Serum of Patients with MCI and AD
2.2. ASC Is a Promising Serum Biomarker of MCI and AD
2.3. MCI, AD and sAPPα/sAPPβ
2.4. MCI, AD and NfL
2.5. Cluster Analysis Using ASC Protein Levels in Control, MCI and AD Patients
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Participants
4.2. Simple Plex Assay
4.3. MSD Multi-SPOT sAPPα/sAPPβ Assay
4.4. Biomarker Analyses
4.5. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Padovani, A.; Borroni, B.; Colciaghi, F.; Pettenati, C.; Cottini, E.; Agosti, C.; Lenzi, G.L.; Caltagirone, C.; Trabucchi, M.; Cattabeni, F.; et al. Abnormalities in the pattern of platelet amyloid precursor protein forms in patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease. Arch. Neurol. 2002, 59, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petersen, R.C. Aging, mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol. Clin. 2000, 18, 789–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, R.C.; Smith, G.E.; Waring, S.C.; Ivnik, R.J.; Tangalos, E.G.; Kokmen, E. Mild cognitive impairment: Clinical characterization and outcome. Arch. Neurol. 1999, 56, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozoki, A.; Giordani, B.; Heidebrink, J.L.; Berent, S.; Foster, N.L. Mild cognitive impairments predict dementia in nondemented elderly patients with memory loss. Arch. Neurol. 2001, 58, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morris, J.C.; Storandt, M.; Miller, J.P.; McKeel, D.W.; Price, J.L.; Rubin, E.H.; Berg, L. Mild cognitive impairment represents early-stage Alzheimer disease. Arch. Neurol. 2001, 58, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blennow, K.; Hampel, H. CSF markers for incipient Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2003, 2, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanemaru, K.; Kameda, N.; Yamanouchi, H. Decreased CSF amyloid beta42 and normal tau levels in dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurology 2000, 54, 1875–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjogren, M.; Minthon, L.; Davidsson, P.; Granerus, A.K.; Clarberg, A.; Vanderstichele, H.; Vanmechelen, E.; Wallin, A.; Blennow, K. CSF levels of tau, beta-amyloid(1-42) and GAP-43 in frontotemporal dementia, other types of dementia and normal aging. J. Neural Transm. (Vienna) 2000, 107, 563–579. [Google Scholar]
- Andreasen, N.; Sjogren, M.; Blennow, K. CSF markers for Alzheimer’s disease: Total tau, phospho-tau and Abeta42. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 4, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terajima, M.; Arai, H.; Itabashi, S.; Higuchi, M.; Zhu, C.; Kosaka, Y.; Nakagawa, T.; Sasaki, H. Elevated cerebrospinal fluid tau levels: Implications for the early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1996, 44, 1012–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, W.; Hattori, K.; Kanemaru, K.; Yokoi, Y.; Omachi, Y.; Takano, H.; Sakata, M.; Yoshida, S.; Tsukamoto, T.; Murata, M.; et al. Re-evaluation of soluble APP-alpha and APP-beta in cerebrospinal fluid as potential biomarkers for early diagnosis of dementia disorders. Biomark Res. 2017, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zetterberg, H. Neurofilament Light: A Dynamic Cross-Disease Fluid Biomarker for Neurodegeneration. Neuron 2016, 91, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parbo, P.; Madsen, L.S.; Ismail, R.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Eskildsen, S.F.; Vorup-Jensen, T.; Brooks, D.J. Low plasma neurofilament light levels associated with raised cortical microglial activation suggest inflammation acts to protect prodromal Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2020, 12, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayeli, M.; Mirshahvalad, S.M.; Aghamollaii, V.; Tafakhori, A.; Abdolalizadeh, A.; Rahmani, F. Plasma Neurofilament Light Chain Levels Are Associated With Cortical Hypometabolism in Alzheimer Disease Signature Regions. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2019, 78, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawelec, G.; Goldeck, D.; Derhovanessian, E. Inflammation, ageing and chronic disease. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2014, 29, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aden, K.; Rosenstiel, P. The Dark Age(ing) of the Inflammasome. Immunity 2017, 46, 173–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latz, E.; Duewell, P. NLRP3 inflammasome activation in inflammaging. Semin. Immunol. 2018, 40, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawhinney, L.J.; de Rivero Vaccari, J.P.; Dale, G.A.; Keane, R.W.; Bramlett, H.M. Heightened inflammasome activation is linked to age-related cognitive impairment in Fischer 344 rats. BMC Neurosci. 2011, 12, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mejias, N.H.; Martinez, C.C.; Stephens, M.E.; de Rivero Vaccari, J.P. Contribution of the inflammasome to inflammaging. J. Inflamm. (Lond) 2018, 15, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Platnich, J.M.; Muruve, D.A. NOD-like receptors and inflammasomes: A review of their canonical and non-canonical signaling pathways. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 670, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, B.S.; Bossaller, L.; De Nardo, D.; Ratter, J.M.; Stutz, A.; Engels, G.; Brenker, C.; Nordhoff, M.; Mirandola, S.R.; Al-Amoudi, A.; et al. The adaptor ASC has extracellular and ‘prionoid’ activities that propagate inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerr, N.; Lee, S.W.; Perez-Barcena, J.; Crespi, C.; Ibanez, J.; Bullock, M.R.; Dietrich, W.D.; Keane, R.W.; de Rivero Vaccari, J.P. Inflammasome proteins as biomarkers of traumatic brain injury. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0210128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, N.; Garcia-Contreras, M.; Abbassi, S.; Mejias, N.H.; Desousa, B.R.; Ricordi, C.; Dietrich, W.D.; Keane, R.W.; de Rivero Vaccari, J.P. Inflammasome Proteins in Serum and Serum-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Biomarkers of Stroke. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keane, R.W.; Dietrich, W.D.; de Rivero Vaccari, J.P. Inflammasome Proteins As Biomarkers of Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed, S.A.; Beurel, E.; Loewenstein, D.A.; Lowell, J.A.; Craighead, W.E.; Dunlop, B.W.; Mayberg, H.S.; Dhabhar, F.; Dietrich, W.D.; Keane, R.W.; et al. Defective Inflammatory Pathways in Never-Treated Depressed Patients Are Associated with Poor Treatment Response. Neuron 2018, 99, 914–924.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Friker, L.L.; Scheiblich, H.; Hochheiser, I.V.; Brinkschulte, R.; Riedel, D.; Latz, E.; Geyer, M.; Heneka, M.T. beta-Amyloid Clustering around ASC Fibrils Boosts Its Toxicity in Microglia. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 3743–3754.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venegas, C.; Kumar, S.; Franklin, B.S.; Dierkes, T.; Brinkschulte, R.; Tejera, D.; Vieira-Saecker, A.; Schwartz, S.; Santarelli, F.; Kummer, M.P.; et al. Microglia-derived ASC specks cross-seed amyloid-beta in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2017, 552, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rivero Vaccari, J.P.; Brand, F.J., III; Sedaghat, C.; Mash, D.C.; Dietrich, W.D.; Keane, R.W. RIG-1 receptor expression in the pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflamm 2014, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brubaker, A.L.; Palmer, J.L.; Kovacs, E.J. Age-related Dysregulation of Inflammation and Innate Immunity: Lessons Learned from Rodent Models. Aging Dis. 2011, 2, 346–360. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Cao, B.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, H.; McIntyre, R.S.; Rosenblat, J.D.; Zhou, H. Soluble TREM2 changes during the clinical course of Alzheimer’s disease: A meta-analysis. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 686, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M.A. Age-related neuroinflammatory changes negatively impact on neuronal function. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2010, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calabrese, V.; Giordano, J.; Signorile, A.; Laura Ontario, M.; Castorina, S.; De Pasquale, C.; Eckert, G.; Calabrese, E.J. Major pathogenic mechanisms in vascular dementia: Roles of cellular stress response and hormesis in neuroprotection. J. Neurosci. Res. 2016, 94, 1588–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, G.; Jaehne, E.J.; Corrigan, F.; Toben, C.; Baune, B.T. Inflammasomes in neuroinflammation and changes in brain function: A focused review. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weinstein, G.; Lutski, M.; Goldbourt, U.; Tanne, D. C-reactive protein is related to future cognitive impairment and decline in elderly individuals with cardiovascular disease. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2017, 69, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloane, J.A.; Hollander, W.; Moss, M.B.; Rosene, D.L.; Abraham, C.R. Increased microglial activation and protein nitration in white matter of the aging monkey. Neurobiol. Aging 1999, 20, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prolla, T.A. DNA microarray analysis of the aging brain. Chem. Senses 2002, 27, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adamczak, S.; Dale, G.; de Rivero Vaccari, J.P.; Bullock, M.R.; Dietrich, W.D.; Keane, R.W. Inflammasome proteins in cerebrospinal fluid of brain-injured patients as biomarkers of functional outcome: Clinical article. J. Neurosurg. 2012, 117, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, J.K.Y.; Pickard, B.S.; Chan, E.W.L.; Gan, S.Y. The Role of Neuronal NLRP1 Inflammasome in Alzheimer’s Disease: Bringing Neurons into the Neuroinflammation Game. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 7741–7753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhao, F.; Chojnacki, J.E.; Fulp, J.; Klein, W.L.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, X. NLRP3 Inflammasome Inhibitor Ameliorates Amyloid Pathology in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 1977–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saco, T.; Parthasarathy, P.T.; Cho, Y.; Lockey, R.F.; Kolliputi, N. Inflammasome: A new trigger of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, M.S.; Yu, J.T.; Jiang, T.; Zhu, X.C.; Tan, L. The NLRP3 inflammasome in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2013, 48, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rivero Vaccari, J.P.; Dietrich, W.D.; Keane, R.W. Therapeutics targeting the inflammasome after central nervous system injury. Transl. Res. 2016, 167, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Rivero Vaccari, J.P.; Lotocki, G.; Alonso, O.F.; Bramlett, H.M.; Dietrich, W.D.; Keane, R.W. Therapeutic neutralization of the NLRP1 inflammasome reduces the innate immune response and improves histopathology after traumatic brain injury. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2009, 29, 1251–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Rivero Vaccari, J.P.; Lotocki, G.; Marcillo, A.E.; Dietrich, W.D.; Keane, R.W. A molecular platform in neurons regulates inflammation after spinal cord injury. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 3404–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desu, H.L.; Plastini, M.; Illiano, P.; Bramlett, H.M.; Dietrich, W.D.; de Rivero Vaccari, J.P.; Brambilla, R.; Keane, R.W. IC100: A novel anti-ASC monoclonal antibody improves functional outcomes in an animal model of multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, N.A.; de Rivero Vaccari, J.P.; Abbassi, S.; Kaur, H.; Zambrano, R.; Wu, S.; Dietrich, W.D.; Keane, R.W. Traumatic Brain Injury-Induced Acute Lung Injury: Evidence for Activation and Inhibition of a Neural-Respiratory-Inflammasome Axis. J. Neurotrauma 2018, 35, 2067–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; de Rivero Vaccari, J.P.; Truettner, J.S.; Dietrich, W.D.; Keane, R.W. The role of microglial inflammasome activation in pyroptotic cell death following penetrating traumatic brain injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopman, D.S.; Penman, A.D.; Catellier, D.J.; Coker, L.H.; Shibata, D.K.; Sharrett, A.R.; Mosley, T.H., Jr. Vascular risk factors and longitudinal changes on brain MRI: The ARIC study. Neurology 2011, 76, 1879–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerhan, J.R.; Folsom, A.R.; Mortimer, J.A.; Shahar, E.; Knopman, D.S.; McGovern, P.G.; Hays, M.A.; Crum, L.D.; Heiss, G. Correlates of cognitive function in middle-aged adults. Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study Investigators. Gerontology 1998, 44, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, F.J., 3rd; Forouzandeh, M.; Kaur, H.; Travascio, F.; de Rivero Vaccari, J.P. Acidification changes affect the inflammasome in human nucleus pulposus cells. J. Inflamm. (Lond) 2016, 13, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Biomarker | Area | Std. Error | 95% C.I. | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control vs. MCI | ||||
| ASC | 0.974 | 0.01301 | 0.9485 to 0.9995 | <0.0001 |
| IL-18 | 0.6896 | 0.06086 | 0.5703 to 0.8089 | 0.0025 |
| sAPPα | 0.9687 | 0.0216 | 0.9263 to 1.011 | <0.0001 |
| sAPPβ | 0.9068 | 0.03784 | 0.8327 to 0.981 | <0.0001 |
| NfL | 0.7734 | 0.05821 | 0.6594 to 0.8875 | 0.0002 |
| Control vs. AD | ||||
| ASC | 0.8328 | 0.05053 | 0.7338 to 0.9319 | <0.0001 |
| IL-18 | 0.6105 | 0.06124 | 0.4905 to 0.7305 | 0.0749 |
| sAPPα | 0.9563 | 0.02490 | 0.9074 to 1.005 | <0.0001 |
| sAPPβ | 0.9185 | 0.03592 | 0.8481 to 0.9889 | <0.0001 |
| NfL | 0.7165 | 0.06817 | 0.5829 to 0.8501 | 0.0040 |
| MCI vs. AD | ||||
| ASC | 0.7157 | 0.06472 | 0.5889 to 0.8426 | 0.0033 |
| IL-18 | 0.5847 | 0.07332 | 0.441 to 0.7284 | 0.2482 |
| sAPPα | 0.6351 | 0.07146 | 0.4950 to 0.7752 | 0.0654 |
| sAPPβ | 0.5247 | 0.07514 | 0.3774 to 0.6720 | 0.7401 |
| NfL | 0.5569 | 0.07502 | 0.4099 to 0.7040 | 0.4498 |
| Biomarker | Cut-Off Point (pg/mL) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | PPV (%) | NPV (%) | Likelihood Ratio | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control vs. MCI | |||||||
| ASC | >264.9 | 100 | 74 | 65 | 100 | 3.882 | 83 |
| IL-18 | >213.9 | 74 | 58 | 44 | 83 | 1.765 | 63 |
| sAPPα | >1.39 (ng/mL) | 97 | 74 | 81 | 95 | 3.763 | 86 |
| sAPPβ | >0.2639 (ng/mL) | 90 | 78 | 78 | 90 | 4.065 | 84 |
| NfL | >24.15 | 72 | 75 | 71 | 75 | 2.875 | 74 |
| Control vs. AD | |||||||
| ASC | >258.7 | 81 | 71 | 57 | 89 | 2.801 | 74 |
| IL-18 | >196.5 | 72 | 42 | 37 | 76 | 1.24 | 51 |
| sAPPα | >2.573 (ng/mL) | 91 | 91 | 92 | 90 | 10.57 | 91 |
| sAPPβ | >0.2906 (ng/mL) | 83 | 81 | 80 | 85 | 4.5 | 82 |
| NfL | >21.48 | 64 | 56 | 56 | 64 | 1.469 | 60 |
| MCI vs. AD | |||||||
| ASC | <560.0 | 71 | 63 | 65 | 69 | 1.892 | 67 |
| IL-18 | >290.3 | 72 | 48 | 59 | 63 | 1.393 | 60 |
| sAPPα | <8.846 (ng/mL) | 72 | 55 | 64 | 63 | 1.592 | 64 |
| sAPPβ | >0.6364 (ng/mL) | 60 | 45 | 49 | 56 | 1.094 | 52 |
| NfL | <33.92 | 71 | 44 | 53 | 64 | 1.27 | 57 |
| Age | Gender | Race | Diagnosis | Medications | Historical Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 83 | Male | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Prostate Cancer, Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Infection, Hyperlipidemia (HLD), Hypertension (HTN), Diverticulitis, Amnesia | Omega 3 1000 mg, Plavix 75 mg, Toprol 50 mg, Vitamin B12-Folic Acid 0.5–1 mg, Vitamin D 400 IU, Zetia 10 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 18 (20 February 2018) |
| 81 | Female | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Type 2 Diabetes, Hypercholesterolemia | Aspirin 81 mg, Gabapentin 100 m, Eliquis 2.5 mg, Ranitidine 150 mg, Aricept 10 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 18 (22 May 2018) |
| 62 | Male | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Type 2 Diabetes, Hypertension (HTN), Hyperlipidemia (HLD), Asthma | Omeprazole 20 mg, Benicar 40–12.5 mg, Metformin HCLl 500 mg, Glucotrol XL 5 mg, Singulair 10 mg, Clobetasol Propionate 0.05%, Glipizide 5 mg, Advair Diskus 250/50 μg, Crestor 10 mg, Ipratropium-Albuterol 0.5–2.5 mg/3 mL, Ventolin HFA 108 μg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 30 (15 May 2018) |
| 69 | Female | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Asthma, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), Hypertension (HTN) | Alendronate 70 mg, Meclizine 12.5 mg, Prozac 40 mg, Seroquel 50 mg, Trilipix 54 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 21 (30 May 2018) |
| 75 | Male | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Colon Cancer | Vitamin B12 2500 IU, Avastin, Adrucil, Amoxicillin 500 mg, Lisinopril 20 mg, Metformin HCLl 500 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 12 (27 March 2018) |
| 72 | Male | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), Lumbar Spondylosis, Barrett’s Esophagus, Atrial Ectopy, Hypertension (HTN) | Tamsulosin HCLl 0.4 mg, Finasteride 5 mg, Multivitamin, Fish Oil 1000 mg, Viagra 100 mg, Tramadol HCLl 50 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 15 (10 May 2018) |
| 64 | Male | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Type 2 Diabetes, Hypertension (HTN), Hypercholesterolemia, Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) | Zolpidem 10 mg, Cialis 5 mg, Aspirin 81 mg, Tamsulosin 0.4 mg, Rosuvastatin 20 mg, Metformin 500 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 34 (4 April 2018) |
| 84 | Female | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Hypertension (HTN), Psychoses, Cellulitis, Mitral Valve Prolapse (MVP), Hyperlipidemia (HLD) | Simvastatin 20 mg, Potassium Chloride 10 mEq, Amlodipine Besylate 2.5 mg, Dutasteride 0.5 mg, Losartan Potassium 100 mg, Aspirin 81 mg, Furosemide 20 mg, Potassium Chloride 10 mEq, Avodart 0.4 mg, Amlodipine Besylate 2.5 mg, Ramipril 10 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 8 (10 May 2018) |
| 68 | Female | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Multiple Sclerosis | Tysabri, Lexapro, Gabapentin | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 15 (6 April 2018) |
| 69 | Female | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Hypercholesterolemia, Hypertension (HTN), Type 2 Diabetes, Premature Ventricular Contraction | Crestor 5 mg, Omega 3, Zolpidem Tartrate 5 mg, Glucosamine 1500 mg, Fiber, Calcium, Multivitamin, Zyrtec, Chlordiazepoxide-Clidinium 2.5–5 mg, Valacyclovir 500 mg, Lisinopril 10 mg, Janumet 50–500 mg, Metoprolol Succinate 25 mg, Levothyroxine Sodium 100 μg, Rosuvastatin Calcium 5 mg, Omega 3-Acid Ethyl Esters 1 g, Trazodone 50 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 33 (1 May 2018) |
| 50 | Female | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Hypercholesterolemia | None | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 30 (24 April 2018) |
| 78 | Male | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) | Zaleplon 10 mg, Lorazepam 1 mg, Plavix 75 mg, Aspirin, Allopurinol 300 mg, Levothyroxine Sodium 125mcg, Atorvastatin Calcium 20 mg, Metformin HCLl 1000 mg, Pantoprazole Sodium 40 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 24 (27 April 2018) |
| 77 | Male | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Hypertension (HTN), Hyperlipidemia (HLD), Vitamin D Deficiency | Aciphex 20 mg, Citric Acid-d-Gluconic Acid, Avodart 0.5 mg, Cozaar 100 mg, Ranitidine Acid Reducer 75 mg, Polyethylene Glycol, MiraLAX, Symbicort 4.5–80 μg, Proair 108 μg, Ipratropium Bromide 0.03%, Prevacid 15 mg, Losartan Potassium 100 mg, Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride 5 mg, Cialis 5 mg, Albuterol, Rabeprazole Sodium 20 mg, Atorvastatin Calcium 20 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 24 (9 May 2018) |
| 73 | Female | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Hypercholesterolemia, Hypothyroidism, Hypothyroidism, Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), Vitamin D Deficiency, Hypertension (HTN) | Rabeprazole Sodium 20 mg, Synthroid 75 μg, Crestor 5 mg, Zyrtec Allergy 10 mg, Aspirin, Calcium 150 mg, CoQ10 400 mg, Aciphex 20 mg, Zenpep 3000 IU-10,000 IU, Ipratropium Bromide 0.03%, Rosuvastatin Calcium 5 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 37 (9 May 2018) |
| 71 | Male | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Dyslipidemia, Valvular Heart Disease, Hypertension (HTN), Hyperlipidemia (HLD), Aortic Aneurysm, Ulcerative Colitis (UC) | Epipen, Metoprolol Succinate ER 50 mg, Zyrtec, Montelukast, Pepcid, Tramadol 50 mg, Diazepam 5 mg, Metamucil 48.57%, Aspirin 81 mg, Plavix 75 mg, Nexium 40 mg, Lipitor 10 mg, Asacol 800 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 24 (10 May 2018) |
| 74 | Female | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Asthma, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), Type 2 Diabetes, Hypercholesterolemia, Congestive Heart Failure (CHF), Hypothyroidism | Levothyroxine 75 mg, Metformin 500 mg, Losartan 100 mg, Symbicort, Proventil, Calcium, Vitamin D3, Zyrtec 10 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 30 (11 May 2018) |
| 75 | Male | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Neuropathy, Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), Hypertension (HTN), Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), Sjogren’s Syndrome, Glaucoma, Allergic Rhinitis, Nasal Obstruction, Type 2 Diabetes | Patanase 0.6%, Timolol Hemihydrate, Latanoprost 0.005%, Methotrexate, Prednisone, Folic Acid, Vitamin D, Finasteride 5 mg, Tamsulosin HCLl 0.4 mg, Gabapentin 100 mg, Vicodin 5–300 mg, Losartan Potassium 50 mg, Pilocarpine HCLl 5 mg, Calcium 600 mg, Vitamin B12 100 μg, Docusate Sodium 100 mg, MiraLAX, Polyethylene Glycol, Ventolin HFA 90 μg, Azithromycin 250 mg, Lasix 20 mg, Levaquin 500 mg, Evoxac 30 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = Refused (18 May 2018) |
| 75 | Male | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Hypercholesterolemia, Thyroid Disease | Levothyroxine Sodium 25 μg, Crestor 40 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 35 (24 May 2018) |
| 75 | Male | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Hypercholesterolemia, Age Related Macular Degeneration (AMD), Erectile Dysfunction (ED) | Pravachol 40 mg, Ocuvite, Viagra 50 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 31 (19 February 2018) |
| 75 | Female | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Type 2 Diabetes, Hypertension (HTN), Dyslipidemia, Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD), Pulmonary Nodule, Hyperlipidemia (HLD) | Metformin 500 mg, Atorvastatin Calcium 20 mg, Cozaar 100 mg, Aspirin 81 mg, Hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg, Lipitor 20 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 42 (1 May 2018) |
| 76 | Female | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Hyperlipidemia (HLD), Hypertension (HTN), Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), Anxiety, Hypothyroidism | Donepezil HCL 10 mg, Levothyroxine Sodium 50 μg, Tramadol HCLl 50 mg, Atorvastatin Calcium 20 mg, Omeprazole 20 mg, Losartan Potassium 50 mg, Aricept 10 mg, Paxil 20 mg, Namenda 10 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 7 (4 May 2018) |
| 76 | Male | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Hypertension (HTN), Type 2 Diabetes, Peripheral Polyneuropathy, Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) | Novolog, Lantus 100 U/mL, Metoprolol Succinate 25 mg, Tacrolimus, Terazosin HCLL 10 mg, CellCept 250 mg, Aspirin 81 mg, Allopurinol 150 mg, Atorvastatin Calcium 10 mg, Losartan Potassium 100 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 28 (15 May 2018) |
| 67 | Female | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Asthma, Hypercholesterolemia | Crestor 40 mg, Omeprazole 20 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 40 (7 May 2018) |
| 56 | Female | Caucasian/Japanese | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) | Daily Vitamins, Aspirin 81 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 41 (8 May 2018) |
| 58 | Female | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Hyperlipidemia (HLD) | Simvastatin 20 mg, Caltrate 600 mg-Vitamin D 800 IU, Vitamin D 2000 IU, Ibuprofen 800 mg, Prolia 60 mg/mL | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 42 (8 May 2018) |
| 75 | Female | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), AF, Dyslipidemia, Hypertension (HTN), Hypothyroidism | Crestor 10 mg, Armour Thyroid 60 mg, Ramipril 5 mg, Hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg, Promethium 200 mg, Augmentin 125–875 mg, Rosuvastatin Calcium 10 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 31 (11 May 2018) |
| 84 | Female | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Venous Insufficiency, Hyperlipidemia (HLD), Hypothyroidism, Parkinson’s Disease (PD), Mitral Valve Prolapse (MVP), Anxiety | Cipro 500 mg, Ibuprofen 800 mg, Xanax 0.5 mg, Fluconazole 150 mg, Carbidopa-Levodopa 25–100 mg, Potassium Chloride 20 mEq, Simvastatin 20 mg, Furosemide 40 mg, Levothyroxine Sodium 75 μg, Atenolol 25 mg, Lasix, Aspirin 81 mg, Acetaminophen 500 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 19 (11 May 2018) |
| 88 | N/A | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Hyperlipidemia (HLD), Peripheral Vascular Disease, Hypertension (HTN), Hyperlipidemia, Mild Intermittent Asthma, Hypercholesterolemia, Type 2 Diabetes | Cozaar 100 mg, Crestor 10 mg, Aspirin, Prilosec 20 mg, Amlodipine Besylate 5 mg, D3 1000 IU, Vitamin C 100 mg, Multi for Him, Omeprazole 20 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 8 (22 May 2018) |
| 71 | Male | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Hypertension (HTN), Hypercholesterolemia, Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD), Palsy of Conjugate Gaze, Short Term Memory, Hyperlipidemia, Cervical Spondylosis, Basal Cell Cancer (BCC), Complex Partial Epileptic Seizure, Chronic Tremor, Lumbosacral Radiculitis, Allergic Rhinitis, Lumbar Arthritis, Arthritis, Bilateral Hearing Loss | Aspirin 81 mg, Brimonidine 0.15%, Cialis 20 mg, Dexamethasone 4 mg/mL, Donepezil 5 mg, Fexofenadine 180 mg, Lamotrigine 200 mg, Lisinopril 5 mg, Meloxicam 15 mg, Pramipexole 0.25 mg, Simvastatin 40 mg, Virtussin 10–100 mg/5 mL | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 44 (24 May 2018) |
| 86 | Male | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Hypertensive Heart and Renal Disease with Congestive Heart Failure, Cyst and Pseudocyst of Pancreas, Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), Type 2 Diabetes, Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD), Hypokalemia, Chronic Systolic Heart Disease, Mitral Valve Prolapse (MVP), Atrial Fibrillation (AF), Hyperlipidemia, Sensorineural Hearing Loss, Left Bundle Branch Block, Pulmonary Hypertension (HTN), Hyperparathyroidism | Amlodipine 5 mg, Glimepiride 1 mg, Nitroglycerin 0.2 mg, Potassium Chloride 20 mEq, Warfarin 2 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 48 (17 May 2018) |
| 91 | Female | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Type 2 Diabetes, Hypertension (HTN), Hypercholesterolemia, Benign Prostate Hyperplasia (BPH), Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Atrial Fibrillation (AF) | Amlodipine Besylate 5 mg, Atorvastatin Calcium 40 mg, Coumadin, Plavix 75 mg, Toprol 50 mg | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 31 (13 March 2018) |
| 88 | Male | Caucasian | Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), Hypercholesterolemia, Melanoma, Depression, Squamous Cell Carcinoma, GERD, Hemorrhoids, TIA | Trintellix 10 mg, Aripiprazole 2.5 mg, Rosuvastatin 20 mg, Modafinil 200 mg, Amphetamine 20 mg, Namenda 28 mg, Esomeprazole 20 mg, Lutein 5 mg, Vitamin D3 1000 IU, Aspirin 81 mg, Vitamin B12 | ARIC MRI Cognitive Function Score = 16 (21 February 2018) |
| Gender | Age | Race | Diagnosis | Medications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 82 | Caucasian | Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), Sleep Apnea, Malignant Basal Cell Neoplasm of Skin, Depression, Dermatitis, Osteoarthritis (OA), Thrombocytopenia | Aricept 10 mg, B Complex 100 0.4 mg, Doxazosin 8 mg, Finasteride 5 mg, Melatonin 10 mg, Multivitamin 9 mg, Omeprazole 20 mg, Sertraline, Simvastatin 80 mg, Vitamin D3 2000 IU, Voltaren 1% |
| Male | 87 | Caucasian | Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Hypertension (HTN), Hyperlipidemia, Dementia | Cartia XT 120 mg, Prilosec 20 mg, Namenda 28XL, Exelon Patch 9.5 mg, Paxil 20 mg |
| Female | 84 | Caucasian | Hypertension (HTN), Vitamin D Deficiency, Hyperlipidemia (HLD), Skin Cancer, Anemia, Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) | Cerefolin NAC 6–200 mg, Clopidogrel Bisulfate 75 mg, Multivitamin, Galantamine Hydrobromide ER 16 mg, Memantine HCLHCL 10 mg, Vitamin D3, Zolpidem Tartrate 5 mg, Iron 325 mg, Remeron 15 mg, Plavix 75 mg |
| Female | 76 | Caucasian | Hyperlipidemia (HLD), Hypertension (HTN), Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), Anxiety, Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Hypothyroidism | Donepezil HCLHCL 10 mg, Levothyroxine Sodium 50 μg, Tramadol HCLHCL50 mg, Atorvastatin Calcium 20 mg, Omeprazole 20 mg, Losartan Potassium 50 mg, Aricept 10 mg, Paxil 20 mg, Namenda 10 mg |
| Male | 47 | Caucasian | Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) | Donepezil 10 mg |
| Male | 67 | African | Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) | Rivastigmine 3 mg, Multivitamin |
| Male | 61 | Caucasian | Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Type 2 Diabetes, Hypertension (HTN), Hypercholesterolemia | Atorvastatin 40 mg, Gabapentin 300 mg, Aspirin 81 mg, Razadyne 16 mg, Metformin 500 mg |
| Female | 60 | African | Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Hypertension (HTN) | Clonidine 0.3 mg, Ambien, Quetiapine 300 mg |
| Male | 47 | N/A | Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Asthma, Anxiety | Gabapentin 300 mg |
| Male | 60 | African | Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Type 2 Diabetes | Donepezil, Metformin, Humalog |
| Male | 74 | Caucasian | Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Hypertension (HTN), Hypercholesterolemia | Aspirin 80 mg, Plavix 75 mg, Lisinopril 25 mg, Simvastatin 10 mg, Digoxin 30 mg, Metoprolol 50 mg, Razadyne 24 mg |
| Male | 50 | African | Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Seizures | Keppra 500-750 mg, Exelon Patch |
| Male | 67 | African | Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Hypertension (HTN) | Aspirin 81 mg, Lisinopril 5 mg, Metoprolol Succinate 500 mg |
| Male | 59 | Mixed Race | Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Type 2 Diabetes, Hypertension (HTN), Anxiety | Metoprolol 50 mg, Amlodipine/Benazepril 10–40 mg, Seroquel 50 mg, Aricept 23 mg, Creon 36000 IU, Gabapentin 600 mg, Prandin 2 mg, Metformin 1000 mg |
| Male | 54 | African | Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), HTN | Donepezil 10 mg, Multivitamin, Atenolol 50 mg |
| Female | 58 | N/A | Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Asthma, Hypertension (HTN), Hypercholesterolemia, Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), Type 2 Diabetes | Combivent 103 μg, Symbicort 160 μg, Budesonide 0.5 mg, Singulair 10 mg, Prandin 2 mg, Metoprolol 50 mg, Lotrel 20 mg, Janumet 1000 mg, Donepezil 10 mg, Maxzide 37.5 mg |
| Male | 75 | Caucasian | Osteomyelitis, Type 2 Diabetes, Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD), Dyslipidemia, Hypertension (HTN), Erectile Dysfunction (ED), Atherosclerosis, Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) | Hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg, Humalog 100 U/mL, Lantus 100 U/mL, Metformin HCLHCL 1000 mg, Testosterone Cypionate 200 mg/mL, Amlodipine Besylate 10 mg, Ventolin HFA 108 μg, Carvedilol 25 mg, Lipitor 20 mg, Benazepril HCLHCL 40 mg, Azithromycin 250 mg, Proair 108 μg |
| Female | 75 | Caucasian | Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Allergy (Seasonal) | Aricept 10 mg, Namenda 10 mg, Calcitrate 200 mg, Centrum Silver, Cetirizine 10 mg, Folic Acid 400 μg, Magnesium 250 mg |
| Female | 73 | Caucasian | Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Type 2 Diabetes, Hypercholesterolemia, Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) | Vitamin D6, Folic Acid, Warfarin 5 mg, Losartan/Hydrochlorothiazide 50 mg/12.5 mg, Metformin 500 mg, Aricept 10 mg |
| Male | 55 | N/A | Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Hypertension (HTN), Bilateral Carpal Tunnel | Losartan/Hydrochlorothiazide 50 mg/12.5 mg, Meloxicam 15 mg, Norvasc 10 mg |
| Male | 84 | Caucasian | Hypertension (HTN), Hypercholesterolemia, Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) | Metoprolol 25 mg, Atorvastatin 40 mg, Aspirin 81 mg, Theragran |
| Male | 51 | African | Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Hypertension (HTN), Hypercholesterolemia | Hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg, Razadyne 16 mg |
| Male | 64 | N/A | Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Hypertension (HTN), Hypercholesterolemia, Type 2 Diabetes | Exelon 6 mg, Metformin 500 mg, Atorvastatin 40 μg, Ramipril 10 mg, Lantus 100 U/mL |
| Female | 84 | Caucasian | Hypertension (HTN), Hallucinations, Psychoses, Cellulitis, Dementia, Mitral Valve Prolapse (MVP), Hyperlipidemia (HLD), Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) | Simvastatin 20 mg, Potassium Chloride 10 mEq, Amlodipine Besylate 2.5 mg, Dutasteride 0.5 mg, Losartan Potassium 100 mg, Aspirin 81 mg, Furosemide 20 mg, Potassium Chloride 10 mEq, Avodart 0.4 mg, Amlodipine Besylate 2.5 mg, Ramipril 10 mg |
| Female | 62 | Caucasian | Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Asthma | Topamax 150 mg, Vesicare 5 mg, Prozac 60 mg, Levoxyl 75 mg, Xarelto 20 mg, Hydrocodone-Acetaminophen 5–325 mg, Butran Patch 15 mg, Gabapentin 600 mg, Celebrex 200 mg, Breo 100 mg, ProAir, Bentyl 20 mg, Pantoprazole 40 mg |
| Male | 68 | Caucasian | Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Type 2 Diabetes, Hypertension (HTN), Hypercholesterolemia, Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA), Parkinsonism, Peripheral Neuropathy, Hypothyroidism, Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), Depression, Anxiety, Glaucoma, Hernia | NamEnda 5 mg, Tamsulosin HCLHCL 0.4 mg, Atorvastatin 40 mg, Valsartan 320 mg, Zetia 10 mg, Carvedilol 25 mg, Aspirin 325 mg, Bupropion HCLl ER 200 mg, Venlafaxine ER 150 mg, Finasteride 5 mg, Synthroid 50 μg, Zolpidem 10 mg, Novolog 100 units/mL, Lantus 100 units/mL, Latanoprost 0.005%, Azelastine 0.15%, Glucagon 1 mg |
| Male | 72 | Caucasian | Hypertension (HTN), Hypercholesterolemia, Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) | Omega-3 Fatty acids/Docosahexanoic acid/EPA/Fish oil 350 mg/235 mg/90 mg/597 mg, CoQ10 100 mg, Vitamin B Complex, Aspirin 81 mg, Pravastatin 20 mg, Losartan 50 mg, Namenda XR 28 mg, Donepezil 10 mg, Crenizumab |
| Male | 79 | Caucasian | Asthma, Hypertension (HTN), Hypercholesterolemia, Basal Cell Cancer (BCC), Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) | Aspirin 81 mg, Amlodipine/Benazepril 10 mg/20 mg, Terazosin 2 mg, Hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg, Atenolol 50 mg, Multivitamin, Calcium, Vitamin D, Atorvastatin 40 mg |
| Female | 77 | Caucasian | Hypertension (HTN), Allergic Rhinitis, Hematuria, Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD), Hypertensive Nephropathy, Hypercholesterolemia, Menopausal, Osteopenia, Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), Large Hiatal Hernia, Gastritis, Esophagitis, Basal Cell Cancer (BCC), Degenerative Joint Disease, Rosacea, Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Obesity, Dyspepsia | Vitamin D 2000 IU, Omeprazole 20 mg, Tylenol |
| Male | 71 | Caucasian | Atrial Fibrillation, End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD), Congestive Heart Failure (CHF), Coronary Artery Disease (CAD), Hyperlipidemia, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), Hyperparathyroidism, Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) | Lanthanum Carbonate 1000 mg, Midodrine 10 mg, Sensipar 30 mg, Pantoprazole 40 mg, Pravastatin 40 mg, Ventolin 90 μg, Warfarin 3 mg |
| Female | 82 | Caucasian | Type 2 Diabetes, Hypothyroidism, Coronary Artery Disease (CAD), Atrial Fibrillation (AF), Hypertension (HTN), Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Hyperlipidemia (HLD), Depression, Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA), Coronary Artery Disease (CAD), Vertigo, Anemia | Digoxin 125 μg, Potassium Chloride 20 mEq, Metoprolol Succinate 200 mg, Furosemide 20 mg, Levothyroxine Sodium 88 μg, Lipitor 20 mg, Memantine HCL 5 mg, Lisinopril 10 mg, Xarelto 15 mg, Amlodipine Besylate 2.5 mg, Zoloft 50 mg, Aricept 10 mg, Metformin HCL 500 mg |
| Male | 78 | Caucasian | Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD), Diabetic Nephropathy, Diabetic Neuropathy, Coronary Artery Disease (CAD), History Of Myocardial Infarction, Hyperlipidemia (HLD), Type 1 Diabetes, Depression, Age Related Macular Degeneration (AMD), Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Dementia, Acute Renal Failure (ARF) | Humalog Mix 100 IU, Aspirin 81 mg, Centrum Silver, l-Glutamine, Metoprolol Succinate 50 mg, Lipitor 20 mg, Novolog, Humulin N, Gabapentin 100 mg, Alprazolam 0.5 mg, Fluticasone Propionate Cream, Citalopram Hydrobromide 20 mg, Cartia XT 120 mg, Aricept 5 mg, Citalopram Hydrobromide 20 mg |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scott, X.O.; Stephens, M.E.; Desir, M.C.; Dietrich, W.D.; Keane, R.W.; de Rivero Vaccari, J.P. The Inflammasome Adaptor Protein ASC in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4674. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21134674
Scott XO, Stephens ME, Desir MC, Dietrich WD, Keane RW, de Rivero Vaccari JP. The Inflammasome Adaptor Protein ASC in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(13):4674. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21134674
Chicago/Turabian StyleScott, Xavier O., Marisa E. Stephens, Marie C. Desir, W. Dalton Dietrich, Robert W. Keane, and Juan Pablo de Rivero Vaccari. 2020. "The Inflammasome Adaptor Protein ASC in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 13: 4674. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21134674







