miRNA and mRNA Expression Profiles Associated with Lymph Node Metastasis and Prognosis in Penile Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Description of the Sample
2.2. miRNA and mRNA Expression as Prognostic Markers for Lymph Node Metastasis and Association with Clinicopathological Variables
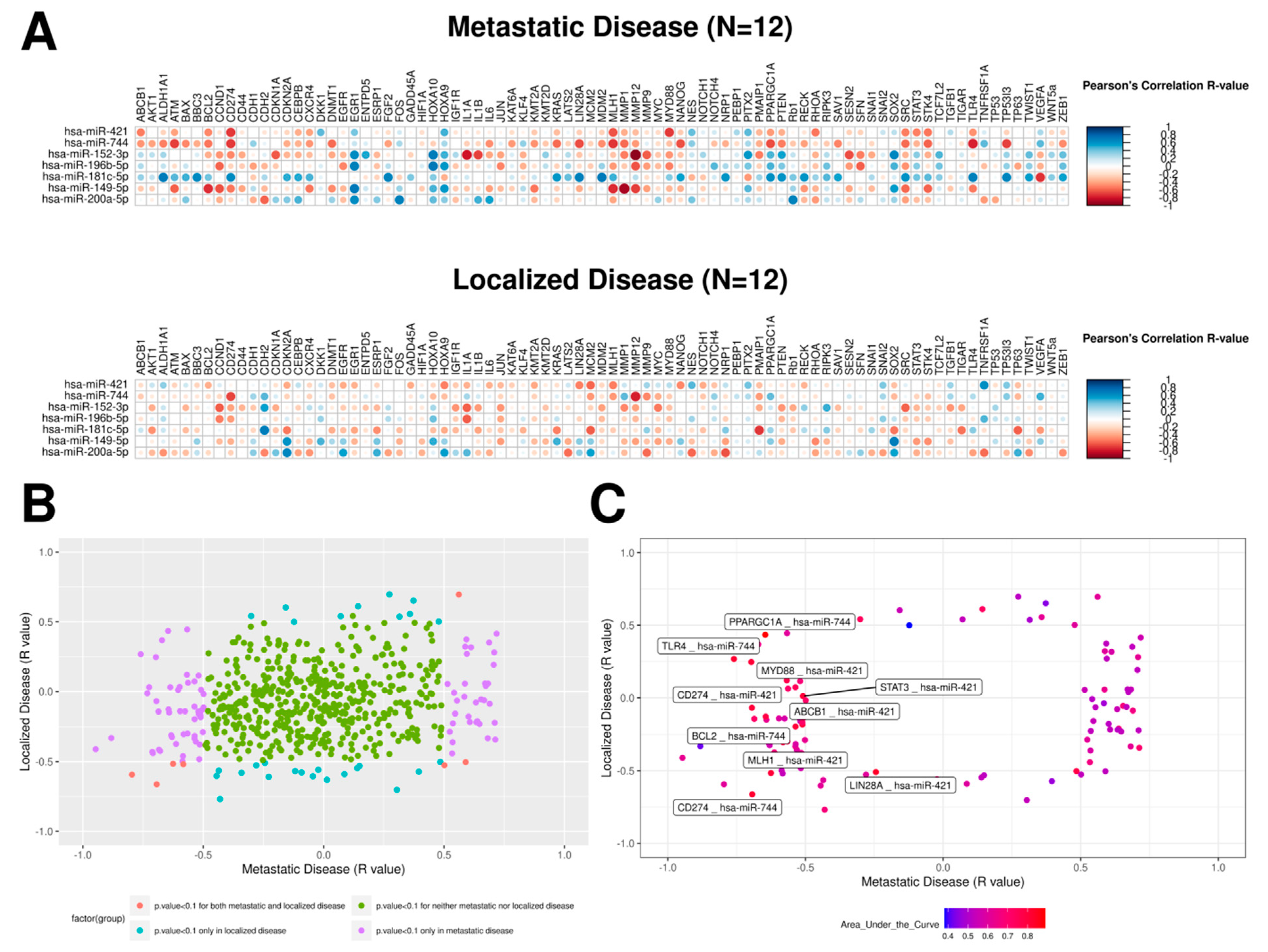
2.3. mRNA–miRNA Ratios Proposed as Prognosis Biomarkers for PeC
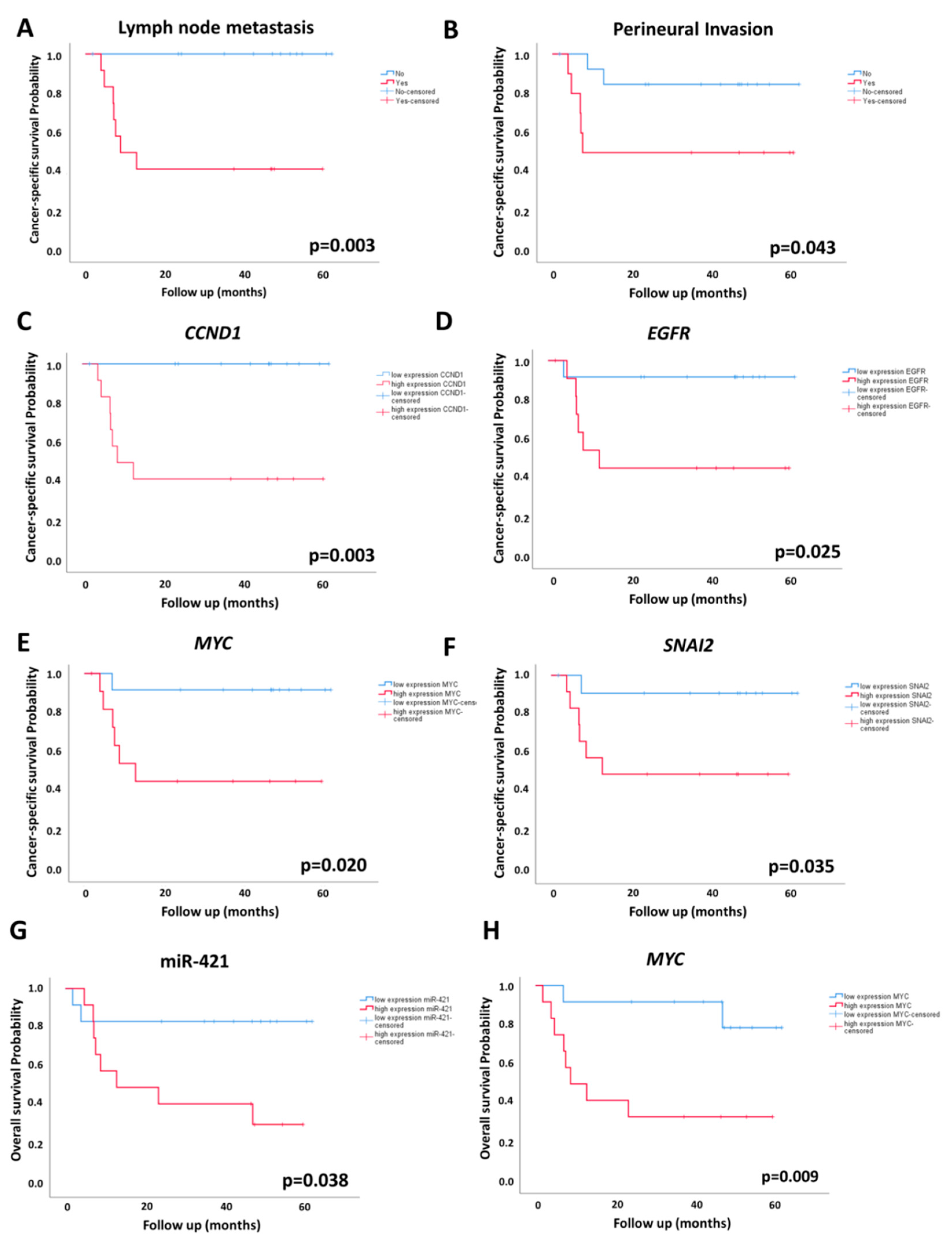
2.4. Association of miRNA and mRNA Levels with OS and CSS
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Total RNA Extraction
4.3. miRNA Expression Profiling
4.4. Validation of DEmiRs by Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
4.5. mRNA Expression Profiling
4.6. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Detection
4.7. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakenberg, O.W.; Compérat, E.; Minhas, S.; Necchi, A.; Protzel, C.; Watkin, N.; Compérat, E. The European Association of Urology (EAU) Guidelines on Penile Cancer. Available online: http://uroweb.org/guideline/penile-cancer/#10 (accessed on 5 June 2018).
- Mulherkar, R.; Hasan, S.; Wegner, R.E.; Verma, V.; Glaser, S.M.; Kalash, R.; Beriwal, S.; Horne, Z.D. National patterns of care for early-stage penile cancers in the United States: How is radiation and brachytherapy utilized? Brachytherapy 2019, 18, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopman, J.M.; Djajadiningrat, R.S.; Baumgarten, A.S.; Espiritu, P.N.; Horenblas, S.; Zhu, Y.; Protzel, C.; Pow-Sang, J.M.; Kim, T.; Sexton, W.J.; et al. Predicting postoperative complications of inguinal lymph node dissection for penile cancer in an international multicentre cohort. BJU Int. 2015, 116, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornellas, A.A.; Kinchin, E.W.; Nobrega, B.L.; Wisnescky, A.; Koifman, N.; Quirino, R. Surgical treatment of invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the penis: Brazilian National Cancer Institute long-term experience. J. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 97, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornellas, A.A.; Nobrega, B.L.; Wei Kin Chin, E.; Wisnescky, A.; da Silva, P.C.; de Santos Schwindt, A.B. Prognostic factors in invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the penis: Analysis of 196 patients treated at the Brazilian National Cancer Institute. J. Urol. 2008, 180, 1354–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benard, V.B.; Johnson, C.J.; Thompson, T.D.; Roland, K.B.; Lai, S.M.; Cokkinides, V.; Tangka, F.; Hawkins, N.A.; Lawson, H.; Weir, H.K. Examining the association between socioeconomic status and potential human papillomavirus-associated cancers. Cancer 2008, 113, 2910–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzon, L.; Cappellesso, R.; Peta, E.; Militello, V.; Sinigaglia, A.; Fassan, M.; Simonato, F.; Guzzardo, V.; Ventura, L.; Blandamura, S.; et al. Profiling of expression of human papillomavirus-related cancer miRNAs in penile squamous cell carcinomas. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 3376–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wei, P.; Shen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhou, J.; Fan, S.; Hao, Z.; Shi, H.; Zhang, X.; et al. MicroRNA Expression Profile in Penile Cancer Revealed by Next-Generation Small RNA Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartz, J.M.; Engelmann, D.; Furst, K.; Marquardt, S.; Spitschak, A.; Goody, D.; Protzel, C.; Hakenberg, O.W.; Putzer, B.M. Integrated Loss of miR-1/miR-101/miR-204 Discriminates Metastatic from Nonmetastatic Penile Carcinomas and Can Predict Patient Outcome. J. Urol. 2016, 196, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuasne, H.; Barros-Filho, M.C.; Busso-Lopes, A.; Marchi, F.A.; Pinheiro, M.; Munoz, J.J.; Scapulatempo-Neto, C.; Faria, E.F.; Guimaraes, G.C.; Lopes, A.; et al. Integrative miRNA and mRNA analysis in penile carcinomas reveals markers and pathways with potential clinical impact. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 15294–15306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinho, J.D.; Silva, G.E.B.; Teixeira Junior, A.A.L.; Belfort, M.R.C.; Mendes, J.M.; Cunha, I.W.D.; Quintana, L.G.; Calixto, J.R.R.; Nogueira, L.R.; Coelho, R.W.P.; et al. MIR-107, MIR-223-3P and MIR-21-5P Reveals Potential Biomarkers in Penile Cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 21, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoubian, H.; Heinzelmann, J.; Holters, S.; Khalmurzaev, O.; Pryalukhin, A.; Loertzer, P.; Heinzelbecker, J.; Lohse, S.; Geppert, C.; Loertzer, H.; et al. miRNA Expression Characterizes Histological Subtypes and Metastasis in Penile Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuya, T.K.; Murta, C.B.; Murillo Carrasco, A.G.; Uno, M.; Sichero, L.; Villa, L.L.; Cardilli, L.; Coelho, R.F.; Guglielmetti, G.B.; Cordeiro, M.D.; et al. Disruption of miRNA-mRNA Networks Defines Novel Molecular Signatures for Penile Carcinogenesis. Cancers 2021, 13, 4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Cui, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; Li, S. Upregulated expression of miR-421 is associated with poor prognosis in non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 2627–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, P.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Pu, H. MicroRNA-421 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer cells by targeting claudin-11. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 2625–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Qiao, S.; Li, N.; Zhu, X. MiR-744 Functions as an Oncogene Through Direct Binding to c-Fos Promoter and Facilitates Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Progression. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 29, 1465–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamae, M.; Komatsu, S.; Ichikawa, D.; Kawaguchi, T.; Hirajima, S.; Okajima, W.; Ohashi, T.; Imamura, T.; Konishi, H.; Shiozaki, A.; et al. Plasma microRNA profiles: Identification of miR-744 as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaniel, A.S.; Hovelson, D.H.; Cani, A.K.; Liu, C.-J.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Weizer, A.Z.; Mehra, R.; Feng, F.Y.; Alva, A.S.; et al. Genomic Profiling of Penile Squamous Cell Carcinoma Reveals New Opportunities for Targeted Therapy. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 5219–5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, S.M.; Pal, S.K.; Wang, K.; Palma, N.A.; Sanford, E.; Bailey, M.; He, J.; Elvin, J.A.; Chmielecki, J.; Squillace, R.; et al. Comprehensive Genomic Profiling of Advanced Penile Carcinoma Suggests a High Frequency of Clinically Relevant Genomic Alterations. Oncologist 2016, 21, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carthon, B.C.; Ng, C.S.; Pettaway, C.A.; Pagliaro, L.C. Epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted therapy in locally advanced or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the penis. BJU Int. 2014, 113, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loh, C.-Y.; Chai, J.; Tang, T.; Wong, W.; Sethi, G.; Shanmugam, M.; Chong, P.; Looi, C. The E-Cadherin and N-Cadherin Switch in Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition: Signaling, Therapeutic Implications, and Challenges. Cells 2019, 8, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Huang, H.; Ma, H.; Cai, W.; Hou, J.; Huang, L.; Dai, Y.; Yu, T.; Zhou, X. Deregulation of Snai2 is associated with metastasis and poor prognosis in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 2249–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cai, J.; Wang, D.; Zhang, G.; Guo, X. The Role Of PD-1/PD-L1 Axis In Treg Development And Function: Implications For Cancer Immunotherapy. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 8437–8445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davidsson, S.; Carlsson, J.; Giunchi, F.; Harlow, A.; Kirrander, P.; Rider, J.; Fiorentino, M.; Andren, O. PD-L1 Expression in Men with Penile Cancer and its Association with Clinical Outcomes. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 2, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deguine, J.; Barton, G.M. MyD88: A central player in innate immune signaling. F1000Prime Rep. 2014, 6, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damasdi, M.; Kovacs, K.; Farkas, N.; Jakab, F.; Kovacs, G. Down-regulation of Toll-like Receptor TLR4 Is Associated with HPV DNA Integration in Penile Carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 5515–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gao, Y.; Song, D.; Liu, T.; Feng, Y. Correlation between microRNA-421 expression level and prognosis of gastric cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 15128–15132. [Google Scholar]
- Hollander, M.C.; Sheikh, M.S.; Bulavin, D.V.; Lundgren, K.; Augeri-Henmueller, L.; Shehee, R.; Molinaro, T.A.; Kim, K.E.; Tolosa, E.; Ashwell, J.D.; et al. Genomic instability in Gadd45a-deficient mice. Nat. Genet. 1999, 23, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tront, J.S.; Huang, Y.; Fornace, A.A.; Hoffman, B.; Liebermann, D.A. Gadd45a Functions as a Promoter or Suppressor of Breast Cancer Dependent on the Oncogenic Stress. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 9671–9681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, C.L.; Jensen, J.L.; Orntoft, T.F. Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: A model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 5245–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saiki, R.K.; Gelfand, D.H.; Stoffel, S.; Scharf, S.J.; Higuchi, R.; Horn, G.T.; Mullis, K.B.; Erlich, H.A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science 1988, 239, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kleter, B.; van Doorn, L.J.; Schrauwen, L.; Molijn, A.; Sastrowijoto, S.; ter Schegget, J.; Lindeman, J.; ter Harmsel, B.; Burger, M.; Quint, W. Development and clinical evaluation of a highly sensitive PCR-reverse hybridization line probe assay for detection and identification of anogenital human papillomavirus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 2508–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Patients | Total Sample n (%) | Microarray Sample n (%) | Validation Sample n (%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 24 | 11 | 13 | |
| Age at surgery–Mean (SD) years old | 61.8 (16.1) | 61.6 (14.2) | 61.9 (18.2) | 0.931 |
| Follow up–Median (range) months | 39.8 (2–68) | 47.5 (8–62) | 34.9 (2–61) | |
| cT | 0.378 | |||
| cT1 | 3 (12.5) | 2 (18.2) | 1 (7.7) | |
| cT2 | 13 (5.2) | 4 (36.4) | 9 (69.2) | |
| cT3 | 8 (33.3) | 5 (45.4) | 3 (23.1) | |
| cN | 0.327 | |||
| cN0 | 9 (37.5) | 5 (45.4) | 4 (30.8) | |
| cN1 | 8 (33.3) | 3 (27.3) | 5 (38.4) | |
| cN2 | 4 (16.7) | 3 (27.3) | 1 (7.7) | |
| cN3 | 3 (12.5) | 0 (0) | 3 (23.1) | |
| Penectomy | 0.476 | |||
| Partial | 17 (70.8) | 7 (63.6) | 10 (76.9) | |
| Total | 7 (29.2) | 4 (36.4) | 3 (23.1) | |
| Grade | 0.854 | |||
| I | 3 (12.5) | 2 (18.2) | 1 (7.7) | |
| II | 13 (54.2) | 6 (54.5) | 7 (53.9) | |
| III | 8 (33.3) | 3 (27.3) | 5 (38.4) | |
| T Stage | 0.246 | |||
| pT1 | 4 (16.6) | 3 (27.2) | 1 (7.7) | |
| pT2 | 13 (54.2) | 4 (36.4) | 9 (69.2) | |
| pT3 | 7 (29.2) | 4 (36.4) | 3 (23.1) | |
| Inguinal Lymphadenectomy | 16 (66.7) | 7 (63.6) | 9 (69.2) | 0.772 |
| Pelvic Lymphadenectomy | 4 (16.7) | 2 (18.1) | 2 (15.4) | 1.000 |
| Lymph node metastasis | 12 (50.0) | 6 (54.5) | 6 (46.2) | 0.682 |
| HPV DNA detection | 8 (33.3) | 3 (27.3) | 5 (38.4) | 0.562 |
| Tumor Size (>5 cm) | 8 (33.3) | 5 (45.5) | 3 (23.1) | 0.247 |
| Lymphovascular invasion | 6 (25.0) | 3 (27.3) | 3 (23.1) | 0.813 |
| Perineural invasion | 10 (41.7) | 4 (36.4) | 6 (46.2) | 0.628 |
| Group Risk (EAU) | 0.381 | |||
| Low | 1 (4.2) | 1 (9.1) | 0 (0) | |
| Intermediate | 3 (12.5) | 2 (18.2) | 1 (7.7) | |
| High | 20 (83.3) | 8 (72.7) | 12 (92.3) |
| Regulation | DEmiR | Microarray | qRT-PCR Independent Cohort | qRT-PCR Total Cohort | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FC | p | FC | p | FC | p | ||
| Up | miR-421 | 2.89 | <0.001 * | 2.12 | 0.051 | 2.21 | 0.005 * |
| miR-149-5p | 6.30 | 0.002 * | 0.77 | 0.367 | 1.92 | 0.375 | |
| miR-744-5p | 1.65 | 0.001 * | 1.36 | 0.190 | 1.61 | 0.003 * | |
| miR-200a-5p | 2.10 | 0.047 * | 0.90 | 0.600 | 1.00 | 0.686 | |
| miR-152-3p | 2.60 | 0.033 * | 1.15 | 0.928 | 1.48 | 0.243 | |
| miR-196b-5p | 1.66 | 0.025 * | 1.00 | 0.504 | 1.33 | 0.550 | |
| Down | miR-181c-5p | 0.63 | 0.031 * | 1.68 | 0.126 | 1.17 | 0.851 |
| Clinicopathological Variables | mRNA | FC | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lymph node metastasis (yes vs. no) | IGF1R | 1.44 | 0.020 |
| MYC | 1.55 | 0.028 | |
| CCND1 | 1.63 | 0.034 | |
| SNAI2 | 1.82 | 0.010 | |
| ENTPD5 | 2.04 | 0.011 | |
| HOXA10 | 2.24 | 0.014 | |
| EGFR | 3.69 | 0.006 | |
| Perineural Invasion (yes vs. no) | MMP9 | 0.28 | 0.044 |
| KLF4 | 0.47 | 0.040 | |
| TP53I3 | 1.68 | 0.034 | |
| MMP1 | 5.43 | 0.007 | |
| Lymphovascular Invasion (yes vs. no) | IL1A | 3.29 | 0.027 |
| pT stage (T2 + T3 vs. T1) | ABCB1 | 0.39 | 0.020 |
| MMP1 | 7.44 | 0.018 | |
| Histological Grade (III vs. I + II) | RIPK3 | 0.60 | 0.037 |
| SRC | 1.68 | 0.005 | |
| CCND1 | 1.92 | 0.006 | |
| MMP1 | 3.91 | 0.045 | |
| EGFR | 5.27 | 0.001 | |
| HPV infection (presence vs. absence) | SNAI2 | 0.54 | 0.014 |
| BAX | 0.72 | 0.030 | |
| Tumor Size (> 5 cm vs. ≤ 5 cm) | LIN28A | 0.36 | 0.047 |
| NANOG | 0.40 | 0.042 | |
| TP53 | 0.50 | 0.014 | |
| MMP1 | 3.98 | 0.042 |
| Survival | miRNA or mRNA | p Log-Rank | HR (95% CI) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cancer-specific survival # | CCND1 | 0.003 * | 115.14 (0.71–18810) | 0.068 |
| CDH1 | 0.014 * | 0.254 (0.03–2.25) | 0.219 | |
| CDKN1A | 0.039 * | 0.615 (0.07–5.74) | 0.669 | |
| EGFR | 0.025 * | 2.40 (0.28–20.65) | 0.425 | |
| GADD45A | 0.018 * | 20.89 (1.47–297.0) | 0.025 * | |
| KLF4 | 0.031 * | 0.36 (0.04–3.08) | 0.352 | |
| MYC | 0.020 * | 2.92 (0.34–24.9) | 0.327 | |
| SNAI2 | 0.035 * | 3.98 (0.46–34.63) | 0.212 | |
| SRC | 0.027 * | 13.92 (0.95–204.1) | 0.055 | |
| TP63 | 0.046 * | 0.20 (0.02–1.80) | 0.153 | |
| Overall survival | miR-421 | 0.038 * | 4.50 (0.95–21.33) | 0.058 |
| CDH1 | 0.001 * | 0.07 (0.01–0.56) | 0.012 * | |
| FGF2 | 0.009 * | 6.23 (1.30–29.84) | 0.022 * | |
| GADD45A | 0.008 * | 6.43 (1.34–30.84) | 0.020 * | |
| IL6 | 0.045 * | 3.68 (0.94–14.36) | 0.061 | |
| MYC | 0.009 * | 6.31 (1.31–30.29) | 0.021 * | |
| NES | 0.015 * | 5.56 (1.17–26.37) | 0.031 * | |
| NRP1 | 0.013 * | 5.78 (1.22–27.36) | 0.027 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Murta, C.B.; Furuya, T.K.; Carrasco, A.G.M.; Uno, M.; Sichero, L.; Villa, L.L.; Faraj, S.F.; Coelho, R.F.; Guglielmetti, G.B.; Cordeiro, M.D.; et al. miRNA and mRNA Expression Profiles Associated with Lymph Node Metastasis and Prognosis in Penile Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23137103
Murta CB, Furuya TK, Carrasco AGM, Uno M, Sichero L, Villa LL, Faraj SF, Coelho RF, Guglielmetti GB, Cordeiro MD, et al. miRNA and mRNA Expression Profiles Associated with Lymph Node Metastasis and Prognosis in Penile Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(13):7103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23137103
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurta, Claudio B., Tatiane K. Furuya, Alexis G. M. Carrasco, Miyuki Uno, Laura Sichero, Luisa L. Villa, Sheila F. Faraj, Rafael F. Coelho, Giuliano B. Guglielmetti, Mauricio D. Cordeiro, and et al. 2022. "miRNA and mRNA Expression Profiles Associated with Lymph Node Metastasis and Prognosis in Penile Carcinoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 13: 7103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23137103








