Serum Angiopoietin-like Protein 3 Level Is Associated with Peripheral Arterial Stiffness in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Anthropometric Analysis
2.3. Biochemical Investigations
2.4. Measurements of Blood Pressure and Brachial-Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity
2.5. Statistical Analysis
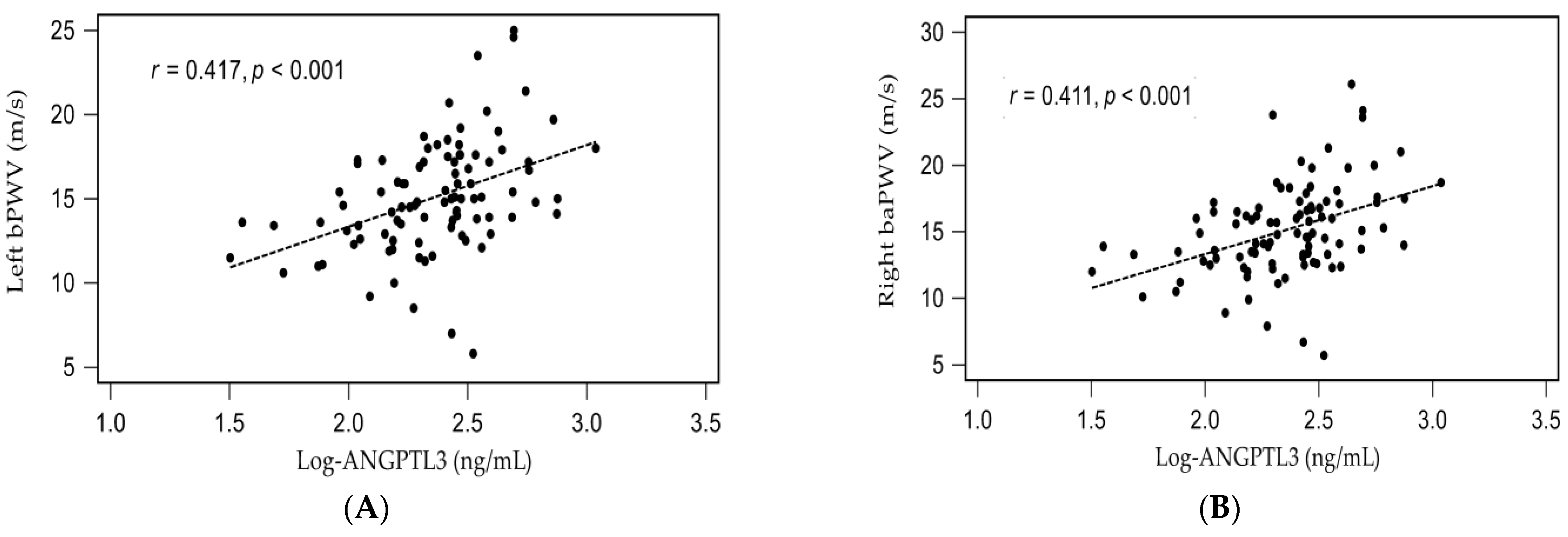
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, M.A.; Hashim, M.J.; Mustafa, H.; Baniyas, M.Y.; Al Suwaidi, S.K.B.M.; AlKatheeri, R.; Alblooshi, F.M.K.; Almatrooshi, M.E.A.H.; Alzaabi, M.E.H.; Al Darmaki, R.S.; et al. Global epidemiology of ischemic heart disease: Results from the global burden of disease study. Cureus 2020, 12, e9349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willum-Hansen, T.; Staessen, J.A.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Rasmussen, S.; Thijs, L.; Ibsen, H.; Jeppesen, J. Prognostic value of aortic pulse wave velocity as index of arterial stiffness in the general population. Circulation 2006, 113, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, G.F.; Hwang, S.J.; Vasan, R.S.; Larson, M.G.; Pencina, M.J.; Hamburg, N.M.; Vita, J.A.; Levy, D.; Benjamin, E.J. Arterial stiffness and cardiovascular events: The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 2010, 121, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alarhabi, A.Y.; Mohamed, M.S.; Ibrahim, S.; Hun, T.M.; Musa, K.I.; Yusof, Z. Pulse wave velocity as a marker of severity of coronary artery disease. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2009, 11, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.L.; Jin, K.N.; Seo, J.B.; Choi, Y.H.; Chung, W.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, M.A.; Zo, J.H. The association of brachial- ankle pulse wave velocity with coronary artery disease evaluated by coronary computed tomography angiography. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, Z.; Zhu, C.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, M.; Wu, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y. Relationship between arterial stiffness assessed by brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity and coronary artery disease severity assessed by the SYNTAX score. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2012, 19, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vlachopoulos, C.; Aznaouridis, K.; Stefanadis, C. Prediction of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality with arterial stiffness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 1318–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kato, A.; Takita, T.; Furuhashi, M.; Maruyama, Y.; Miyajima, H.; Kumagai, H. Brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity and the cardio-ankle vascular index as a predictor of cardiovascular outcomes in patients on regular hemodialysis. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2012, 16, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachopoulos, C.; Aznaouridis, K.; Terentes-Printzios, D.; Ioakeimidis, N.; Stefanadis, C. Prediction of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality with brachial-ankle elasticity index: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hypertension 2012, 60, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kersten, S. Angiopoietin-like 3 in lipoprotein metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musunuru, K.; Pirruccello, J.P.; Do, R.; Peloso, G.M.; Guiducci, C.; Sougnez, C.; Garimella, K.V.; Fisher, S.; Abreu, J.; Barry, A.J.; et al. Exome sequencing, ANGPTL3 mutations, and familial combined hypolipidemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2220–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lupo, M.G.; Ferri, N. Angiopoietin-like 3 (ANGPTL3) and atherosclerosis: Lipid and non-lipid related effects. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2018, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.; Choi, Y.; Mizushima, R.; Yoshikawa, T.; Myoenzono, K.; Tagawa, K.; Matsui, M.; Tanaka, K.; Maeda, S.J. Dietary modification reduces serum angiopoietin-like protein 2 levels and arterial stiffness in overweight and obese men. Exerc. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 23, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.C.; Chiang, W.C.; Tsai, M.H.; Chou, Y.H.; Pan, S.Y.; Chang, Y.T.; Yeh, P.Y.; Chen, Y.T.; Chiang, C.K.; Chen, Y.M.; et al. Angiopoietin-2-induced arterial stiffness in CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 1198–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukami, H.; Morinaga, J.; Okadome, Y.; Nishiguchi, Y.; Iwata, Y.; Kanki, T.; Nakagawa, T.; Izumi, Y.; Kakizoe, Y.; Kuwabara, T.; et al. Circulating angiopoietin-like protein 2 levels and arterial stiffness in patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis: A cross-sectional study. Atherosclerosis 2020, 315, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desjardins, M.P.; Thorin-Trescases, N.; Sidibé, A.; Fortier, C.; De Serres, S.A.; Larivière, R.; Thorin, E.; Agharazii, M. Levels of angiopoietin-like-2 are positively associated with aortic stiffness and mortality after kidney transplantation. Am. J. Hypertens. 2017, 30, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.S.; Wang, J.H.; Lee, C.J.; Hsu, B.G. Positive correlation of the serum angiopoietin-like protein 3 levels with the aortic augmentation index in patients with coronary artery disease. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2018, 14, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.C.; Hsu, B.G.; Lee, C.J.; Wang, J.H. High serum angiopoietin-like protein 3 levels associated with cardiovascular outcome in patients with coronary artery disease. Int. J. Hypertens. 2020, 2020, 2980954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ho, G.J.; Lee, M.C.; Lee, C.J.; Chen, Y.C.; Hsu, B.G. Hypoadiponectinemia correlates with arterial stiffness in kidney transplantation patients. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2015, 19, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, B.G.; Liou, H.H.; Lee, C.J.; Chen, Y.C.; Ho, G.J.; Lee, M.C. Serum sclerostin as an independent marker of peripheral arterial stiffness in renal transplantation recipients-a cross-sectional study. Medicine 2016, 95, e3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munakata, M.; Ito, H.; Ueda, S.; Vlachopoulos, C.; Higashi, Y.; Inoue, T.; Node, K. Physiological diagnostic criteria for vascular failure. Hypertension 2018, 72, 1060–1071. [Google Scholar]
- Tomiyama, H.; Shiina, K. State of the art review: Brachial-ankle PWV. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2020, 27, 621–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munakata, M. Brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity: Background, method, and clinical evidence. Pulse 2016, 3, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.M.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, I.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, B.H.; Kim, M.K.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, C.W.; Kim, M.C.; Ahn, J.H.; et al. Arterial stiffness is an independent predictor for risk of mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: The REBOUND study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.L.; Luo, Q.; Zhu, B.X.; Zhou, F.F. Brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity could be a predictor of mortality in patients on peritoneal dialysis. Perit. Dial. Int. 2018, 38, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, Y.; Kitamura, A.; Shinozaki, T.; Seino, S.; Yokoyama, Y.; Narita, M.; Amano, H.; Matsuyama, Y.; Fujiwara, Y.; Shinkai, S. Trajectories of arterial stiffness and all-cause mortality among community-dwelling older Japanese. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2018, 18, 1108–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.C.; Jin, K.N.; Kim, H.L.; Kim, Y.N.; Im, M.S.; Lim, W.H.; Seo, J.B.; Kim, S.H.; Zo, J.H.; Kim, M.A. Additional prognostic value of brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity to coronary computed tomography angiography in patients with suspected coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 2018, 268, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prenner, S.B.; Chirinos, J.A. Arterial stiffness in diabetes mellitus. Atherosclerosis 2015, 238, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeva-Andany, M.M.; Funcasta-Calderón, R.; Fernández-Fernández, C.; Ameneiros-Rodríguez, E.; Domínguez-Montero, A. Subclinical vascular disease in patients with diabetes is associated with insulin resistance. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2019, 13, 2198–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; Wu, W.; Cai, Z.; Chen, Z.; Yan, X.; Wu, S. Total cholesterol, arterial stiffness, and systolic blood pressure: A mediation analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, M.; Yoo, H.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.H. Age-specific determinants of pulse wave velocity among metabolic syndrome components, inflammatory markers, and oxidative stress. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2018, 25, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ojima, S.; Kubozono, T.; Kawasoe, S.; Kawabata, T.; Miyata, M.; Miyahara, H.; Maenohara, S.; Ohishi, M. Association of risk factors for atherosclerosis, including high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, with carotid intima-media thickness, plaque score, and pulse wave velocity in a male population. Hypertens. Res. 2020, 43, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.H.; Lee, M.C.; Ho, G.J.; Liu, C.H.; Hsu, B.G. Association of low serum l-carnitine levels with peripheral arterial stiffness in patients who undergo kidney transplantation. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geladari, E.; Tsamadia, P.; Vallianou, N.G. ANGPTL3 inhibitors–Their role in cardiovascular disease through regulation of lipid metabolism. Circ. J. 2019, 83, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stitziel, N.O.; Khera, A.V.; Wang, X.; Bierhals, A.J.; Vourakis, A.C.; Sperry, A.E.; Natarajan, P.; Klarin, D.; Emdin, C.A.; Zekavat, S.M.; et al. ANGPTL3 deficiency and protection against coronary artery disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 2054–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewey, F.E.; Gusarova, V.; Dunbar, R.L.; O’Dushlaine, C.; Schurmann, C.; Gottesman, O.; McCarthy, S.; Van Hout, C.V.; Bruse, S.; Dansky, H.M.; et al. Genetic and pharmacologic inactivation of ANGPTL3 and cardiovascular disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aminuddin, A.; Lazim, M.R.M.; Hamid, A.A.; Hui, C.K.; Mohd Yunus, M.H.; Kumar, J.; Ugusman, A. The association between inflammation and pulse wave velocity in dyslipidemia: An evidence-based review. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 4732987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, R.R.; Wilkinson, I.B.; Schiffrin, E.L.; Avolio, A.P.; Chirinos, J.A.; Cockcroft, J.R.; Heffernan, K.S.; Lakatta, E.G.; McEniery, C.M.; Mitchell, G.F.; et al. Recommendations for improving and standardizing vascular research on arterial stiffness: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Hypertension 2015, 66, 698–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Characteristics | All Participants (n = 95) | Control Group (n = 78) | PAS Group (n = 17) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 65.20 ± 8.87 | 64.28 ± 8.86 | 69.41 ± 7.80 | 0.030 * |
| Height (cm) | 161.61 ± 8.08 | 162.09 ± 7.78 | 159.41 ± 9.27 | 0.217 |
| Body weight (kg) | 69.05 ± 12.08 | 69.19 ± 12.49 | 68.41 ± 10.33 | 0.812 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 26.35 ± 3.55 | 26.22 ± 3.60 | 26.93 ± 3.34 | 0.459 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 131.46 ± 16.74 | 129.54 ± 15.32 | 140.29 ± 20.42 | 0.016 * |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 72.94 ± 10.29 | 72.82 ± 10.15 | 73.47 ± 11.21 | 0.815 |
| Left baPWV (m/s) | 15.06 ± 3.30 | 14.02 ± 2.42 | 19.86 ± 2.43 | <0.001 * |
| Right baPWV (m/s) | 15.13 ± 3.53 | 13.98 ± 2.50 | 20.45 ± 2.54 | <0.001 * |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 168.65 ± 35.69 | 167.95 ± 36.38 | 171.88 ± 33.14 | 0.683 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 113.00 (89.00–164.00) | 116.00 (92.75–172.00) | 97.00 (69.00–153.00) | 0.310 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 45.19 ± 12.54 | 44.60 ± 11.57 | 47.88 ± 16.44 | 0.331 |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 97.78 ± 27.06 | 97.10 ± 26.62 | 100.88 ± 29.67 | 0.604 |
| Fasting glucose (mg/dL) | 111.00 (97.00–137.00) | 105.50 (96.75–131.25) | 137.00 (113.50–200.00) | 0.008 * |
| Blood urea nitrogen (mg/dL) | 16.00 (13.00–19.00) | 16.00 (13.00–18.25) | 17.00 (13.50–23.50) | 0.225 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.00 (0.90–1.30) | 1.00 (0.90–1.20) | 1.30 (0.90–1.50) | 0.122 |
| eGFR (mL/min) | 68.84 ± 18.64 | 72.21 ± 17.24 | 58.93 ± 21.41 | 0.070 |
| Total calcium (mg/dL) | 9.11 ± 0.36 | 9.10 ± 0.34 | 9.15 ± 0.48 | 0.665 |
| Phosphorus (mg/dL) | 3.51 ± 0.54 | 3.52 ± 0.56 | 3.45 ± 0.46 | 0.624 |
| iPTH (pg/mL) | 46.70 (34.30–66.10) | 46.30 (34.30–70.20) | 47.50 (33.35–56.15) | 0.738 |
| ANGPTL3 (ng/mL) | 260.38 (155.31–336.19) | 208.41 (146.51–301.83) | 347.86 (247.89–493.74) | 0.001 * |
| C-reactive protein (mg/dL) | 0.19 (0.14–0.26) | 0.18 (0.14–0.23) | 0.27 (0.18–0.50) | 0.002 * |
| Female, n (%) | 24 (25.3) | 19 (24.4) | 5 (29.4) | 0.664 |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 41 (43.2) | 28 (35.9) | 13 (76.5) | 0.002 * |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 77 (81.1) | 61 (78.2) | 16 (94.1) | 0.129 |
| ACE inhibitor use, n (%) | 28 (29.5) | 23 (29.5) | 5 (29.4) | 0.995 |
| ARB use, n (%) | 37 (38.9) | 28 (35.9) | 9 (52.9) | 0.192 |
| β-blocker use, n (%) | 55 (57.9) | 45 (57.7) | 10 (58.8) | 0.932 |
| CCB use, n (%) | 32 (33.7) | 24 (30.8) | 8 (47.1) | 0.198 |
| Statin use, n (%) | 69 (72.6) | 59 (75.6) | 10 (58.8) | 0.159 |
| Fibrate use, n (%) | 21 (22.1) | 16 (20.5) | 5 (29.4) | 0.423 |
| Aspirin, n (%) | 72 (75.8) | 61 (78.2) | 11 (64.7) | 0.239 |
| Clopidogrel, n (%) | 25 (26.3) | 20 (25.6) | 5 (29.4) | 0.749 |
| Variables | Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Angiopoietin-like protein 3, 1 ng/mL | 1.004 | 1.000–1.007 | 0.041 * |
| Age, 1 year | 1.138 | 1.028–1.259 | 0.012 * |
| Diabetes, present | 3.699 | 0.737–18.574 | 0.112 |
| C-reactive protein, 0.1 mg/dL | 1.196 | 0.956–1.497 | 0.118 |
| Fasting glucose, 1 mg/dL | 1.011 | 0.997–1.025 | 0.119 |
| Systolic blood pressure, 1 mmHg | 1.028 | 0.986–1.072 | 0.189 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsiao, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Wang, J.-H.; Hsu, B.-G. Serum Angiopoietin-like Protein 3 Level Is Associated with Peripheral Arterial Stiffness in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. Medicina 2021, 57, 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57101011
Hsiao C-H, Chen Y-C, Wang J-H, Hsu B-G. Serum Angiopoietin-like Protein 3 Level Is Associated with Peripheral Arterial Stiffness in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. Medicina. 2021; 57(10):1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57101011
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsiao, Chien-Hao, Yu-Chih Chen, Ji-Hung Wang, and Bang-Gee Hsu. 2021. "Serum Angiopoietin-like Protein 3 Level Is Associated with Peripheral Arterial Stiffness in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease" Medicina 57, no. 10: 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57101011
APA StyleHsiao, C.-H., Chen, Y.-C., Wang, J.-H., & Hsu, B.-G. (2021). Serum Angiopoietin-like Protein 3 Level Is Associated with Peripheral Arterial Stiffness in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. Medicina, 57(10), 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57101011







