Effects of Oral Bicarbonate Supplementation on the Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Serum Nutritional Markers in Non-Dialysed Chronic Kidney Disease Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations of the Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raphael, K.L. Metabolic Acidosis in CKD: Core Curriculum 2019. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 74, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yaqoob, M.M. Acidosis and progression of chronic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2010, 19, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesson, D.E.; Jo, C.H.; Simoni, J. Angiotensin II receptors mediate increased distal nephron acidification caused by acid retention. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 1184–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moranne, O.; Froissart, M.; Rossert, J.; Gauci, C.; Boffa, J.J.; Haymann, J.P.; M’rad, M.B.; Jacquot, C.; Houillier, P.; Stengel, B.; et al. Timing of onset of CKD-related metabolic complications. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eustace, J.A.; Astor, B.; Muntner, P.M.; Ikizler, A.; Coresh, J. Prevalence of acidosis and inflammation and their association with low serum albumin in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, S.N.; Abramowitz, M.; Hostetter, T.H.; Melamed, M.L. Serum bicarbonate levels and the progression of kidney disease: A cohort study. Am. J. Kid. Dis. 2009, 54, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Widmer, B.; Gerhardt, R.E.; Harrington, J.T.; Cohen, J.J. Serum electrolyte and acid base composition. The influence of graded degrees of chronic renal failure. Arch. Intern. Med. 1979, 139, 1099–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraut, J.A.; Madias, N.E. Metabolic acidosis: Pathophysiology, diagnosis and management. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2010, 6, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Mehrotra, R.; Fouque, D.; Kopple, J.D. Metabolic acidosis and malnutrition-inflammation complex syndrome in chronic renal failure. Semin. Dial. 2004, 17, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phisitkul, S.; Hacker, C.; Simoni, J. Dietary protein causes a decline in the glomerular filtration rate of the remnant kidney mediated by metabolic acidosis and endothelin receptors. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ng, H.Y.; Chen, H.C.; Tsai, Y.C.; Yang, Y.K.; Lee, C.T. Activation of intrarenal renin-angiotensin system during metabolic acidosis. Am. J. Nephrol. 2011, 34, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, E.; Ai, M.; Yoshida, M.; Kuriyama, R.; Shiigai, T. High serum bicarbonate level within the normal range prevents the progression of chronic kidney disease in elderly chronic kidney disease patients. BMC Nephrol. 2013, 14, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobre, M.; Yang, W.; Chen, J.; Drawz, P.; Hamm, L.L.; Horwitz, E.; Hostetter, T.; Jaar, B.; Lora, C.M.; Nessel, L.; et al. Association of serum bicarbonate with risk of renal and cardiovascular outcomes in CKD: A report from the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) study. Am. J. Kidney 2013, 62, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goraya, N.; Wesson, D.E. Does correction of metabolic acidosis slow chronic kidney disease progression? Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2013, 22, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtaszek, E.; Oldakowska-Jedynak, U.; Kwiatkowska, M.; Głogowski, T.; Małyszko, J. Uremic Toxins, Oxidative Stress, Atherosclerosis in Chronic Kidney Disease, and Kidney Transplantation. Oxidat. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 6651367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovesdy, C.; Anderson, J.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Association of serum bicarbonate levels with mortality in patients with non-dialysis-dependent CKD. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2009, 24, 1232–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navaneethan, S.; Schold, J.; Arrigain, S.; Jolly, S.E.; Wehbe, E.; Raina, R. Serum bicarbonate and mortality in stage 3 and stage 4 chronic kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 2395–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.; Stevens, P.E.; Bilous, R.W.; Coresh, J.; de Francisco, A.L.M.; de Jong, P.E.; Griffith, K.E.; Hemmelgarn, B.R.; Iseki, K.; Lamb, E.J. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2013, 3, 1–150. [Google Scholar]
- Adamczak, M.; Masajtis-Zagajewska, A.; Mazanowska, O.; Katarzyna Madziarska, K.; Stompór, T.; Więcek, A. Diagnosis and Treatment of Metabolic Acidosis in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease—Position Statement of the Working Group of the Polish Society of Nephrology. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2018, 43, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bushinsky, D.A. Tolerance to Sodium in Patients With CKD-Induced Metabolic Acidosis: Does the Accompanying Anion Matter? Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 73, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Brito-Ashurst, I.; Varanugam, M.; Raftery, M.J.; Muhammad, M.Y. Bicarbonate supplementation slows progression CKD and improves nutritional status. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahajan, A.; Simoni, J.; Sheather, S.J.; Broglio, K.R.; Rajab, M.H.; Wesson, D.E. Daily oral sodium bicarbonate preserves glomerular filtration rate by slowing its decline in early hypertensive nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2010, 78, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubey, A.K.; Sahoo, J.; Vairappan, B.; Haridasan, S.; Parameswan, S.; Priyamwada, P.S. Correction of metabolic acidosis improves muscle mass and renal function in chronic kidney disease stages 3 and 4: A randomized controlled trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2020, 35, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phisitkul, S.; Khanna, A.; Simoni, J.; Broglio, K.; Sheather, S.; Rajab, M.H.; Wesson, D.E. Amelioration of metabolic acidosis in patients with low GFR reduced kidney endothelin production and kidney injury, and better preserved GFR. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melamed, M.; Horwitz, E.; Dobre, M.; Abramowitz, M.K.; Zhang, L.; Lo, Y.; Mitch, W.E.; Hostetter, T.H. Effects of Sodium Bicarbonate in CKD Stages 3 and 4: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Multicenter Clinical Trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 75, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hostetter, T.H.; Meyer, T.W.; Rennke, H.G.; Brenner, B.M. Chronic effects of dietary protein in the rat with intact and reduced renal mass. Kidney Int. 1986, 30, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuchs, F.; Whelton, P. High Blood Pressure and Cardiovascular Disease. Hypertension 2020, 75, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkubo, T.; Imai, Y.; Tsuji, I.; Nagai, K.; Watanabe, N.; Minami, N.; Itoh, O.; Bando, T.; Sakuma, M.; Fukao, A.; et al. Prediction of mortality by ambulatory blood pressure monitoring versus screening blood pressure measurements: A pilot study in Ohasama. J. Hypertens. 1997, 15, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikizler, T.A.; Burrowes, J.D.; Byham-Gray, L.D.; Campbell, K.L.; Carrero, J.-J.; Chan, W.; Fouque, D.; Friedman, A.N.; Ghaddar, S.; Goldstein-Fuchs, D.J.; et al. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline for Nutrition in CKD: 2020 Update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76, S1–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The BiCARB Study Group; Witham, M.D.; Band, M. Clinical and cost-effectiveness of oral sodium bicarbonate therapy for older patients with chronic kidney disease and low-grade acidosis (BiCARB): A pragmatic randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 91. [Google Scholar]
- Lambers Heerspink, H.J.; Navis, G.; Ritz, E. Salt intake in kidney disease—A missed therapeutic opportunity? Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2012, 27, 3435–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Humalda, J.K.; Navis, G. Dietary sodium restriction: A neglected therapeutic opportunity in chronic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2014, 23, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luft, F.C.; Zemel, M.B.; Sowers, J.A.; Fineberg, N.S.; Weinberger, M.H. Sodium bicarbonate and sodium chloride: Effects on blood pressure and electrolyte homeostasis in normal and hypertensive man. J. Hypertens. 1990, 8, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotchen, T.A.; Kotchen, J.M. Dietary sodium and blood pressure: Interactions with other nutrients. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 65, 708S–711S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Husted, F.C.; Nolph, K.D.; Maher, J.F. NaHCO3 and NaCl tolerance in chronic renal failure. J. Clin. Investig. 1975, 56, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husted, F.C.; Nolph, K.D. NaHCO3 and NaCl tolerance in chronic renal failure II. Clin. Nephrol. 1977, 7, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz, T.W.; Al-Bander, H.A.; Morris, R.C. “Salt-sensitive” essential hypertension in men. Is the sodium ion alone important? N. Engl. J. Med. 1987, 317, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shore, A.C.; Markandu, N.D.; MacGregor, G.A. A randomized crossover study to compare the blood pressure response to sodium loading with and without chloride in patients with essential hypertension. J. Hypertens. 1988, 6, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Soon Kil, K.; Hye-Young, K. Effect of Bicarbonate Supplementation on Renal Function and Nutritional Indices in Predialysis Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease Electrolyte. Electrolytes Blood Press. 2014, 12, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, R.P.; Dash, S.C.; Gupta, N.; Prakash, S.; Saxena, S.; Bhowmik, D. Effects of correction of metabolic acidosis on blood urea and bone metabolism in patients with mild to moderate chronic kidney disease: A prospective randomized single blind controlled trial. Ren. Fail. 2006, 28, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopple, J.D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Mehrotra, R. Risks of chronic metabolic acidosis in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2005, 95, S21–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kendrick, J.B.; Zelnick, L.; Chonchol, M.B.; Siscovick, D.; Hoofnagle, A.N.; Ix, J.H. Serum Bicarbonate is Associated with Heart Failure in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). Am. J. Nephrol. 2017, 45, 118–126. [Google Scholar]
- Riesenhuber, S.; Repitz, A.; Aigner, C.; Cejka, D.; Sunder-Plassmann, G.; Gaggl, M. Effect of sodium bicarbonate load on 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure measurements in patients with chronic metabolic acidosis and chronic kidney disease: Preliminary results of the SOBIC study. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2019, 34, gfz103.SP046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, M.K.; Soiza, R.L.; Witham, M.D. Oral bicarbonate therapy in chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trial. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navaneethan, S.D.; Shao, J.; Buysse, J.; Bushinsky, D.A. Effects of treatment of metabolic acidosis in CKD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, L.; Li, Z.; Leffler, N.R.; Asch, A.S.; Chi, J.T.; Yang, L.V. Acidosis activation of the proton-sensing GPR4 receptor stimulates vascular endothelial cell inflammatory responses revealed by transcriptome analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wesson, D.E.; Simoni, J.; Broglio, K.; Sheather, S. Acid retention accompanies reduced GFR in humans and increases plasma levels of endothelin and aldosterone. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2011, 300, F830–F837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehta, P.K.; Griendling, K.K. Angiotensin II cell signaling: Physiological and pathological effects in the cardiovascular system. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 292, C82–C97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoungas, S.; Cameron, J.D.; Kerr, P.G.; Wolfe, R.; Muske, C.; McNeil, J.J.; McGrath, B.P. Association of carotid intima-medial thickness and indices of arterial stiffness with cardiovascular disease outcomes in CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2007, 50, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, A.; Haymann, J.P.; Bozec, E.; Metzger, M.; Jacquot, C.; Maruani, G.; Houillier, P.; Froissart, M.; Stengel, B.; Guardiola, P.; et al. Large artery stiffening and remodeling are independently associated with all-cause mortality and cardiovascular events in chronic kidney disease. Hypertension 2012, 60, 1451–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chirinos, J.A.; Khan, A.; Bansal, N.; Dries, D.L.; Feldman, H.I.; Ford, V.; Anderson, A.H.; Kallem, R.; Lash, J.P.; Ojo, A.; et al. Arterial stiffness, central pressures, and incident hospitalized heart failure in the chronic renal insufficiency cohort study. Circ. Heart Fail. 2014, 7, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Solis, A.J.; Gonzalez-Pacheco, F.R.; Deudero, J.J.; Neria, F.; Albalate, M.; Petkov, V. Alkalinization potentiates vascular calcium deposition in an uremic milieu. J. Nephrol. 2009, 22, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jara, A.; Felsenfeld, A.J.; Bover, J.; Kleeman, C.R. Chronic metabolic acidosis in azotemic rats on a high-phosphate diet halts the progression of renal disease. Kidney Int. 2000, 58, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Newman, A.; Fried, L. Relationship of acid-base status with arterial stiffness in community-living elders: The Health ABC Study. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2018, 33, 1572–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyo, J.; Kang, E.; Ryu, H.; Han, M.; Lee, K.B.; Kim, Y.S.; Sung, S.; Ahn, C.; Oh, K.-H. Metabolic acidosis is associated with pulse wave velocity in chronic kidney disease: Results from the KNOW-CKD Study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabutti, L.; Bianchi, G.; Soldini, D.; Marone, C.; Burnier, M. Haemodynamic consequences of changing bicarbonate and calcium concentrations in haemodialysis fluids. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2009, 24, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raikou, V.; Kyriaki, D. The association between intradialytic hypertension and metabolic disorders in end stage renal disease. Int. J. Hypertens. 2018, 2018, 1681056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballmer, P.E.; McNurlan, M.A.; Hulter, H.N.; Anderson, S.E.; Garlick, P.J.; Krapf, R. Chronic metabolic acidosis decreases albumin synthesis and induces negative nitrogen balance in humans. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 1, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrotra, R.; Kopple, J.D. Nutritional management of maintenance dialysis patients: Why aren’t we doing better? Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2001, 21, 343–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Iorio, B.; Bellasi, A.; Raphael, K.; Santoro, D.; Aucella, F.; Garofano, L.; Ceccarelli, M.; di Lullo, L.; Capolongo, G.; di Iorio, M. Treatment of metabolic acidosis with sodium bicarbonate delays progression of chronic kidney disease: The UBI Study. J. Nephrol. 2019, 32, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alva, S.; Divyashree, M.; Kamath, J.; Prakash, P.S. A Study on Effect of Bicarbonate Supplementation on the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease. Indian J. Nephrol. 2020, 30, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Verove, C.; Maisonneuve, N.; El Azouzi, A.; Boldron, A.; Azar, R. Effect of the correction of metabolic acidosis on nutritional status in elderly patients with chronic renal failure. J. Ren. Nutr. 2002, 12, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizumoto, C.; Kawabata, H.; Uchiyama, T.; Sakamoto, S.; Kanda, J.; Tomosugi, N.; Takaori-Kondo, A. Acidic milieu augments the expression of hepcidin, the central regulator of iron homeostasis. Int. J. Hematol. 2012, 96, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babitt, J.L.; Lin, H.Y. Mechanism of anaemia Mechanism of anaemia in CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1631–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diskin, C.J.; Stokes, T.J.; Dansby, L.M.; Radcliff, L.; Carter, T.B. Can acidosis and hyperphosphataemia result in increased erythropoietin dosing in haemodialysis patients? Nephrology 2006, 11, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ori, Y.; Zingerman, B.; Bergman, M.; Bessler, H.; Salman, H. The effect of sodium bicarbonate on cytokine secretion in CKD patients with metabolic acidosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2015, 71, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olde Engberink, R.; van den Hoek, T.; van Noordenne, N.; van den Born, B.; Peters-Sengers, H.; Vogt, L. Use of a Single Baseline Versus Multiyear 24-Hour Urine Collection for Estimation of Long-Term Sodium Intake and Associated Cardiovascular and Renal Risk. Circulation 2017, 10, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, I.; Dyer, A.; Chan, Q.; Cogswell, M.; Ueshima, H.; Stamler, J.; Elliott, P.; on behalf of the INTERSALT Co-Operative Research Group. Estimating 24-Hour Urinary Sodium Excretion from Casual Urinary Sodium Concentrations in Western Populations: The INTERSALT Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 11, 1180–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
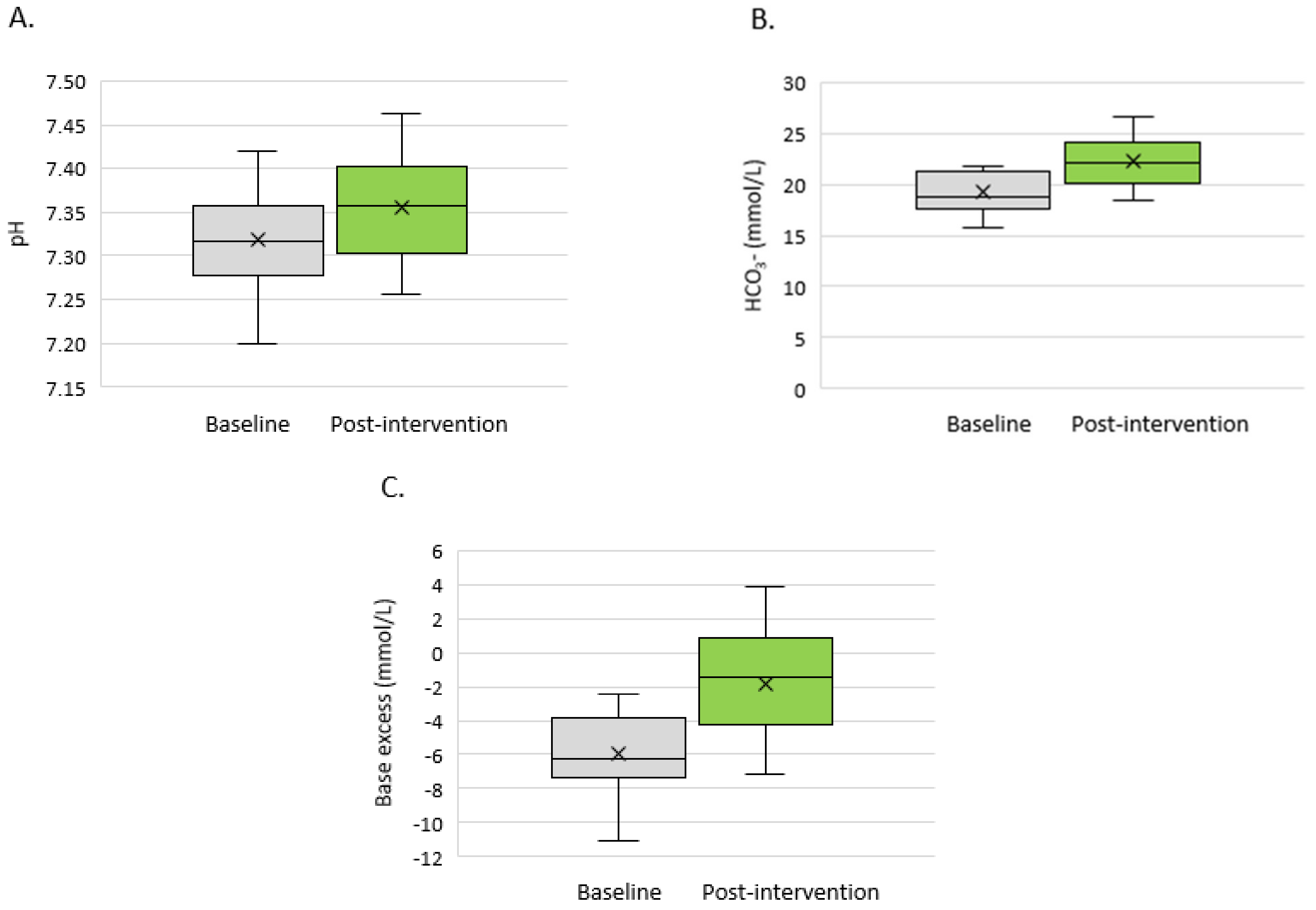

| Visit 0 | Visit 1 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (M/F) | 66.6% (n = 12)/33.3% (n = 6) | - | |
| Age (years) | 66.08 (11.66) | - | |
| Height (cm) | 170.72 (8.60) | - | |
| Weight (kg) | 74.44 (15.96) | 75.67 (16.12) | 0.058 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.83 (22.67–27.12) | 25.11 (23.40–28.40) | 0.051 |
| Visit 0 (n = 18) | Visit 1 (n = 18) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Creatinine (µmol/l) | 313.09 (126.25) | 333.66 (140.03) | 0.057 |
| eGFR (ml/min/1.73 m2) | 19.33 (9.20) | 18.67 (9.97) | 0.360 |
| Na (mmol/l) | 138.29 (3.30) | 139.48 (3.42) | 0.151 |
| K (mmol/l) | 4.91 (0.59) | 4.83 (0.55) | 0.545 |
| Ca (mmol/l) | 2.22 (0.14) | 2.25 (0.18) | 0.317 |
| P (mmol/l) | 1.43 (0.25) | 1.44 (0.33) | 0.688 |
| Albumin (g/l) | 37.26 (5.43) | 39.35 (4.81) | 0.037 * |
| Total protein (g/l) | 62.71 (6.92) | 65.8 (6.22) | 0.013 * |
| NT-proBNP (pmol/l) | 794.70 (291.20–1819.00) | 1247.10 (384.70–4545.00) | 0.006 * |
| CRP (mg/l) | 1.30 (0.70–2.93) | 2.75 (1.10–3.10) | 0.025 * |
| PTH (pmol/l) | 21.54 (13.78) | 27.07 (16.29) | 0.006 * |
| RBC (106/µl) | 3.39 (0.60) | 3.61 (0.57) | 0.004 * |
| HGB (g/dl) | 10.24 (1.95) | 10.99 (1.72) | 0.006 * |
| HCT (%) | 31.64 (5.99) | 33.55 (4.80) | 0.009 * |
| ACR (mg/g) | 479.60 (89.50–807.40) | 872.40 (155.70–1412.80) | 0.023 * |
| Urine Na/Cr (mmol/mmol) | 16.52 (5.34) | 18.24 (9.28) | 0.467 |
| Visit 0 (n = 18) | Visit 1 (n = 18) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dipper (yes/no) | 41.2% (7)/58.8% (10) | 41.2% (7)/58.8% (10) | 1.000 |
| SBP mean (mmHg) | 133.00 (14.07) | 138.06 (13.31) | 0.304 |
| DBP mean (mmHg) | 75.75 (11.20) | 80.00 (8.23) | 0.077 |
| HR mean (BPM) | 73 (67–74) | 74 (67–79) | 0.070 |
| SPB day (mmHg) | 134.31 (13.58) | 138.94 (14.63) | 0.386 |
| DBP day (mmHg) | 77.13 (11.67) | 81.38 (8.22) | 0.108 |
| MAP day (mmHg) | 96.19 (11.18) | 100.56 (8.67) | 0.206 |
| SBP night (mmHg) | 129.06 (16.94) | 134.94 (13.94) | 0.168 |
| DBP night (mmHg) | 71.69 (11.61) | 75.75 (11.42) | 0.070 |
| MAP night (mmHg) | 90.37 (11.63) | 89.86 (25.11) | 0.930 |
| NBPF (%) | 5.53 (6.39) | 4.72 (9.93) | 0.679 |
| PWV (m/s) | 9.81 (3.02) | 9.29 (3.78) | 0.464 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szczecińska, K.; Wajdlich, M.; Nowicka, M.; Nowicki, M.; Kurnatowska, I. Effects of Oral Bicarbonate Supplementation on the Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Serum Nutritional Markers in Non-Dialysed Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Medicina 2022, 58, 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58040518
Szczecińska K, Wajdlich M, Nowicka M, Nowicki M, Kurnatowska I. Effects of Oral Bicarbonate Supplementation on the Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Serum Nutritional Markers in Non-Dialysed Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Medicina. 2022; 58(4):518. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58040518
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzczecińska, Katarzyna, Małgorzata Wajdlich, Maja Nowicka, Michał Nowicki, and Ilona Kurnatowska. 2022. "Effects of Oral Bicarbonate Supplementation on the Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Serum Nutritional Markers in Non-Dialysed Chronic Kidney Disease Patients" Medicina 58, no. 4: 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58040518
APA StyleSzczecińska, K., Wajdlich, M., Nowicka, M., Nowicki, M., & Kurnatowska, I. (2022). Effects of Oral Bicarbonate Supplementation on the Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Serum Nutritional Markers in Non-Dialysed Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Medicina, 58(4), 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58040518







