Stabilisation and Growth of Metastable Form II of Fluconazole in Amorphous Solid Dispersions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Formation of Fluconazole (FLU) Hydrate and FLU Form II
2.3. Preparation of Solid Dispersions by the Fusion Method
2.4. Preparation of Solid Dispersions by the Spray Drying Technique
2.5. Powder X-ray Diffraction (PXRD)
2.6. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.7. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.8. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.9. Dissolution Study
2.10. High Pressure Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
2.11. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.12. Stability Studies
2.13. True Density of FLU and SOL
2.14. Theoretical Calculation of the Glass Transition Temperature (Tg) of Fluconazole (FLU):SOL Binary Systems using the Gordon-Taylor Equation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Stability and Recrystalisation Behaviour of Amorphous Fluconazole
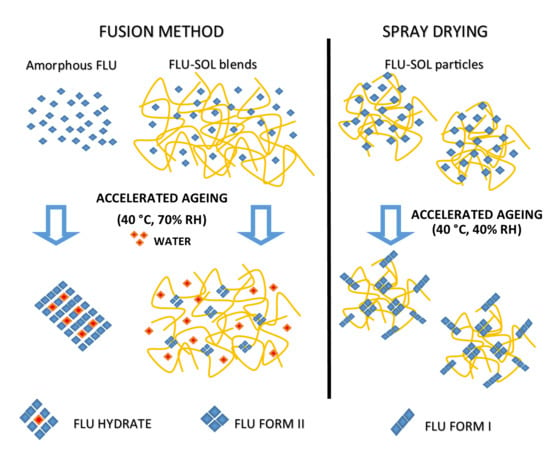
3.2. Stabilisation and Crystallisation Behaviour of an Amorphous Fluconazole (FLU) in the SOL Polymer Matrix Prepared by Fusion Method
The Effect of Elevated Humidity on the Formation of FLU Form II Embedded in the SOL Polymer Matrix and the Stability of an Amorphous Drug in Solid Dispersions
3.3. Stability and Crystallisation Behaviour of Amorphous FLU in Spray Dried Solid Dispersions
3.3.1. The Effect of Materials Composition on Morphology of Spray Dried Solid Dispersions
3.3.2. The Effect of the Drug:Polymer Ratio on Stability and Crystallisation Behaviour of an Amorphous FLU in Spray Dried Solid Dispersions
3.3.3. The Effect of the Material Composition on the Dissolution Rate of Spray Dried Solid Dispersions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Atkinson, R.M.; Bedford, C.; Child, K.J.; Tomich, E.G. Effect of Particle Size on Blood Griseofulvin-Levels in Man. Nature 1962, 193, 588–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T. Drug Solubilization by Complexation. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pudipeddi, M.; Serajuddin, A.T.M. Trends in Solubility of Polymorphs. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, N.J.; Nangia, A. Solubility Advantage of Amorphous Drugs and Pharmaceutical Cocrystals. Cryst. Growth Des. 2011, 11, 2662–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jornada, D.; dos Santos Fernandes, G.; Chiba, D.; de Melo, T.; dos Santos, J.; Chung, M. The Prodrug Approach: A Successful Tool for Improving Drug Solubility. Molecules 2016, 21, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leuner, C. Improving Drug Solubility for Oral Delivery Using Solid Dispersions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sareen, S.; Joseph, L.; Mathew, G. Improvement in Solubility of Poor Water-Soluble Drugs by Solid Dispersion. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2012, 2, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ford, J.L. The Current Status of Solid Dispersions. Pharm. Acta Helv. 1986, 61, 69–88. [Google Scholar]
- Censi, R.; Di Martino, P. Polymorph Impact on the Bioavailability and Stability of Poorly Soluble Drugs. Molecules 2015, 20, 18759–18776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Broman, E.; Khoo, C.; Taylor, L.S. A Comparison of Alternative Polymer Excipients and Processing Methods for Making Solid Dispersions of a Poorly Water Soluble Drug. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 222, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docoslis, A.; Huszarik, K.L.; Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Bikiaris, D.; Stergiou, A.; Georgarakis, E. Characterization of the Distribution, Polymorphism, and Stability of Nimodipine in Its Solid Dispersions in Polyethylene Glycol by Micro-Raman Spectroscopy and Powder X-Ray Diffraction. AAPS J. 2007, 9, E361–E370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Q.; Taylor, L.S.; Harris, M.T. Evaluation of the Microstructure of Semicrystalline Solid Dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Ohárriz, M.; Martín, C.; Goñi, M.; Rodríguez-Espinosa, C.; Tros-Ilarduya, M.; Zornoza, A. Influence of Polyethylene Glycol 4000 on the Polymorphic Forms of Diflunisal. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 8, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telford, R.; Seaton, C.C.; Clout, A.; Buanz, A.; Gaisford, S.; Williams, G.R.; Prior, T.J.; Okoye, C.H.; Munshi, T.; Scowen, I.J. Stabilisation of Metastable Polymorphs: The Case of Paracetamol Form III. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 12028–12031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Duong, T.; Lüdeker, D.; Van Bockstal, P.J.; De Beer, T.; Van Humbeeck, J.; Van Den Mooter, G. Polymorphism of Indomethacin in Semicrystalline Dispersions: Formation, Transformation, and Segregation. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 1037–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yam, N.; Li, X.; Jasti, B.R. Interactions of Topiramate with Polyethylene Glycol 8000 in Solid State with Formation of New Polymorph. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 411, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zein, H.; Riad, L.; El-Bary, A.A. Enhancement of Carbamazepine Dissolution: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 168, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naima, Z.; Siro, T.; Juan-Manuel, G.-D.; Chantal, C.; René, C.; Jerome, D. Interactions between Carbamazepine and Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) 6000: Characterisations of the Physical, Solid Dispersed and Eutectic Mixtures. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 12, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.; Gonen, S.; Hoag, S.W. Influence of Polyethylene Glycol and Povidone on the Polymorphic Transformation and Solubility of Carbamazepine. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 240, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nartowski, K.P.; Malhotra, D.; Hawarden, L.E.; Fábián, L.; Khimyak, Y.Z. Nanocrystallization of Rare Tolbutamide Form V in Mesoporous MCM-41 Silica. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 4926–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nartowski, K.P.; Tedder, J.; Braun, D.E.; Fábián, L.; Khimyak, Y.Z. Building Solids inside Nano-Space: From Confined Amorphous through Confined Solvate to Confined ‘Metastable’ Polymorph. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 24761–24773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Srinarong, P.; de Waard, H.; Frijlink, H.W.; Hinrichs, W.L.J. Improved Dissolution Behavior of Lipophilic Drugs by Solid Dispersions: The Production Process as Starting Point for Formulation Considerations. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2011, 8, 1121–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adibkia, K.; Barzegar-Jalali, M.; Maheri-Esfanjani, H.; Ghanbarzadeh, S.; Shokri, J.; Sabzevari, A.; Javadzadeh, Y. Physicochemical Characterization of Naproxen Solid Dispersions Prepared Via Spray Drying Technology. Powder Technol. 2013, 246, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhamis, K.A.; Obaidat, A.A.; Nuseirat, A.F. Solid-State Characterization of Fluconazole. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2002, 7, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, S.R.; Shaikh, M.M.; Dharwadkar, S.R. Thermoanalytical Study of Polymorphic Transformation in Fluconazole Drug. Thermochim. Acta 2003, 399, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caira, M.R.; Alkhamis, K.A.; Obaidat, R.M. Preparation and Crystal Characterization of a Polymorph, a Monohydrate, and an Ethyl Acetate Solvate of the Antifungal Fluconazole. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karanam, M.; Dev, S.; Choudhury, A.R. New Polymorphs of Fluconazole: Results from Cocrystallization Experiments. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, P.A.; Martinez-Oharriz, M.C.; Rubios, M.; Irache, J.M.; Espuelas, S. Fluconazole Encapsulation in PLGA Microspheres by Spray-Drying. J. Microencapsul. 2004, 21, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Bikiaris, D.; Kanaze, F.I.; Karavas, E.; Stergiou, A.; Georgarakis, E. Tailoring the Release Rates of Fluconazole Using Solid Dispersions in Polymer Blends. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2008, 34, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.; Taylor, J.S. Ideal Copolymers and the Second-Order Transitions of Synthetic Rubbers. I. non-Crystalline Copolymers. J. Appl. Chem. 2007, 2, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, K.; Thilak Kumar, R. Structural, Spectral, Thermodynamical, NLO, HOMO, LUMO and NBO Analysis of Fluconazole. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 150, 974–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavra, Z.M.M.; Pereira de Santana, D.; Ré, M.I. Solubility and Dissolution Performances of Spray-Dried Solid Dispersion of Efavirenz in Soluplus. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, P.; Krupa, A.; Kubat, K.; Węgrzyn, A.; Harańczyk, H.; Ciułkowska, A.; Jachowicz, R. Water Vapour Sorption in Tadalafil-Soluplus Co-Milled Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Powder Technol. 2019, 346, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djuris, J.; Nikolakakis, I.; Ibric, S.; Djuric, Z.; Kachrimanis, K. Preparation of Carbamazepine–Soluplus® Solid Dispersions by Hot-Melt Extrusion, and Prediction of Drug–Polymer Miscibility by Thermodynamic Model Fitting. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 84, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, G.P.; Zhai, H.; Tipping, S.; Jones, D.S. Characterisation of the Thermal, Spectroscopic and Drug Dissolution Properties of Mefenamic Acid and Polyoxyethylene–Polyoxypropylene Solid Dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 4545–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Rudraraju, V.S. A Systematic Approach to Design and Prepare Solid Dispersions of Poorly Water-Soluble Drug. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2014, 15, 641–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehta, M.; Kothari, K.; Ragoonanan, V.; Suryanarayanan, R. Effect of Water on Molecular Mobility and Physical Stability of Amorphous Pharmaceuticals. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasanthavada, M.; Tong, W.-Q.; Joshi, Y.; Kislalioglu, M.S. Phase Behavior of Amorphous Molecular Dispersions II: Role of Hydrogen Bonding in Solid Solubility and Phase Separation Kinetics. Pharm. Res. 2005, 22, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Pui, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; Su, C.C.; Hageman, M.; Hussain, M.; Haskell, R.; Stefanski, K.; Foster, K.; et al. Moisture-Induced Amorphous Phase Separation of Amorphous Solid Dispersions: Molecular Mechanism, Microstructure, and Its Impact on Dissolution Performance. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Obaidat, R.M.; Alkhamis, K.A.; Salem, M.S. Determination of Factors Affecting Kinetics of Solid-State Transformation of Fluconazole Polymorph II to Polymorph I Using Diffuse Reflectance Fourier transform Spectroscopy. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2010, 36, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gift, A.D.; Luner, P.E.; Luedeman, L.; Taylor, L.S. Manipulating Hydrate Formation During High Shear Wet Granulation Using Polymeric Excipients. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 4670–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, V.; Dantuluri, A.K.; Kumar, M.; Karar, N.; Bansal, A.K. Wettability and Surface Chemistry of Crystalline and Amorphous Forms of a Poorly Water Soluble Drug. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 40, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Drooge, D.J.; Hinrichs, W.L.J.; Frijlink, H.W. Anomalous Dissolution Behaviour of Tablets Prepared from Sugar Glass-Based Solid Dispersions. J. Control. Release 2004, 97, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langham, Z.A.; Booth, J.; Hughes, L.P.; Reynolds, G.K.; Wren, S.A.C. Mechanistic Insights into the Dissolution of Spray-Dried Amorphous Solid Dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 2798–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meulenaar, J.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Nuijen, B. Slow Dissolution Behaviour of Amorphous Capecitabine. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 441, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nowak, M.; Gajda, M.; Baranowski, P.; Szymczyk, P.; Karolewicz, B.; Nartowski, K.P. Stabilisation and Growth of Metastable Form II of Fluconazole in Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010012
Nowak M, Gajda M, Baranowski P, Szymczyk P, Karolewicz B, Nartowski KP. Stabilisation and Growth of Metastable Form II of Fluconazole in Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleNowak, Maciej, Maciej Gajda, Przemysław Baranowski, Patrycja Szymczyk, Bożena Karolewicz, and Karol P. Nartowski. 2020. "Stabilisation and Growth of Metastable Form II of Fluconazole in Amorphous Solid Dispersions" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010012
APA StyleNowak, M., Gajda, M., Baranowski, P., Szymczyk, P., Karolewicz, B., & Nartowski, K. P. (2020). Stabilisation and Growth of Metastable Form II of Fluconazole in Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Pharmaceutics, 12(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010012