Capacitive Mixing for Harvesting the Free Energy of Solutions at Different Concentrations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The CAPMIX Family
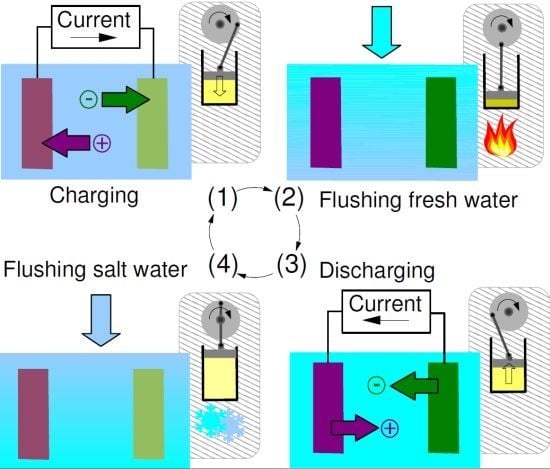
2.1. Capacitive Double Layer Expansion
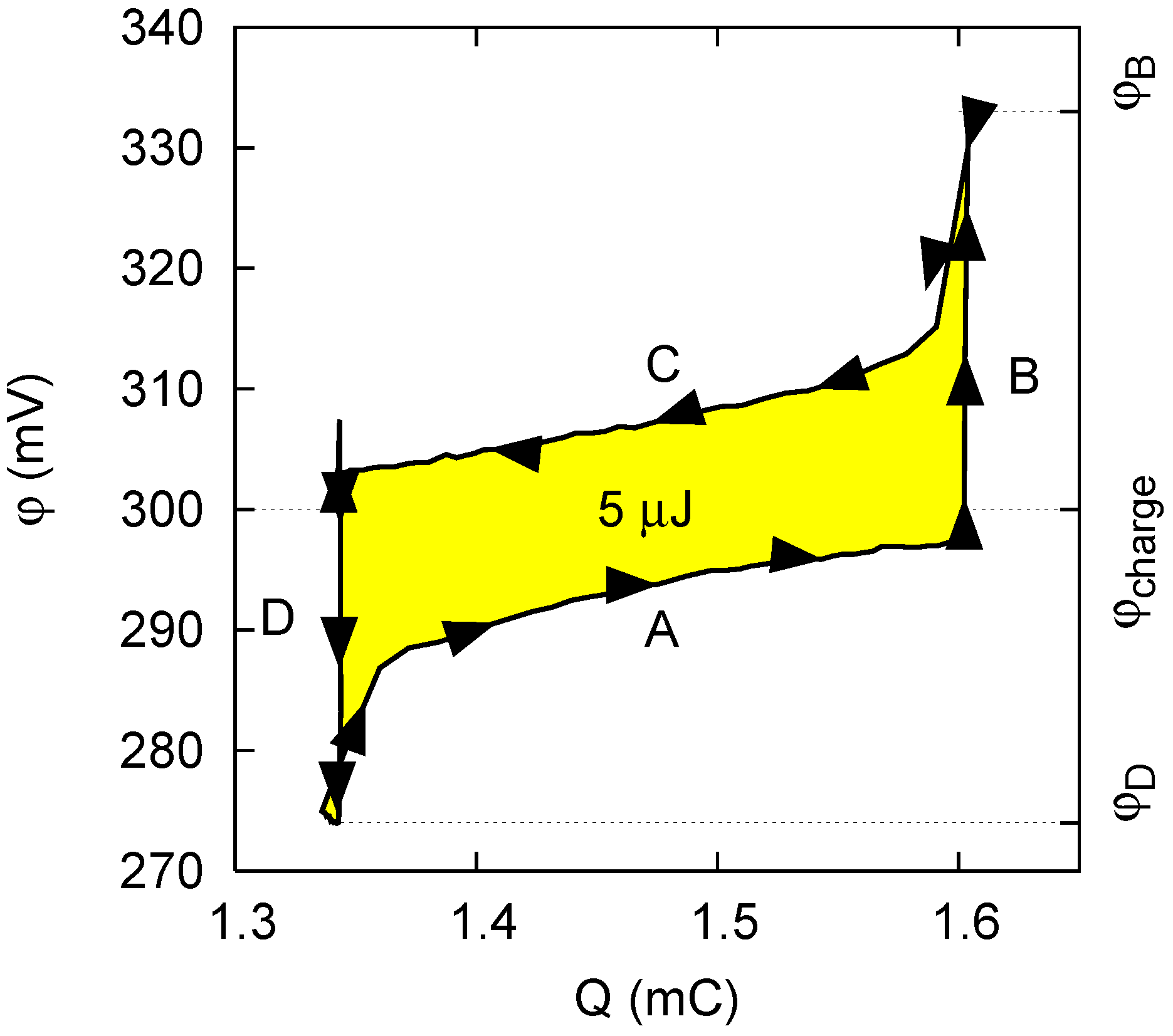
- Phase A: The cell, filled with saltwater, is charged from an initial potential to a final potential through an external load. In this phase energy is stored into the cell.
- Phase B: In open circuit, i.e., at constant charge, the solution in the cell is exchanged with freshwater. The voltage increases to , and the amount of energy stored in the cell also increases, due to the decrease of the capacitance.
- Phase C: The cell is discharged to the potential through an external load. In this phase, energy is extracted from the cell.
- Phase D: Again in open circuit, the solution in the cell is exchanged with saltwater. The voltage decreases to due to the increase of the capacitance.
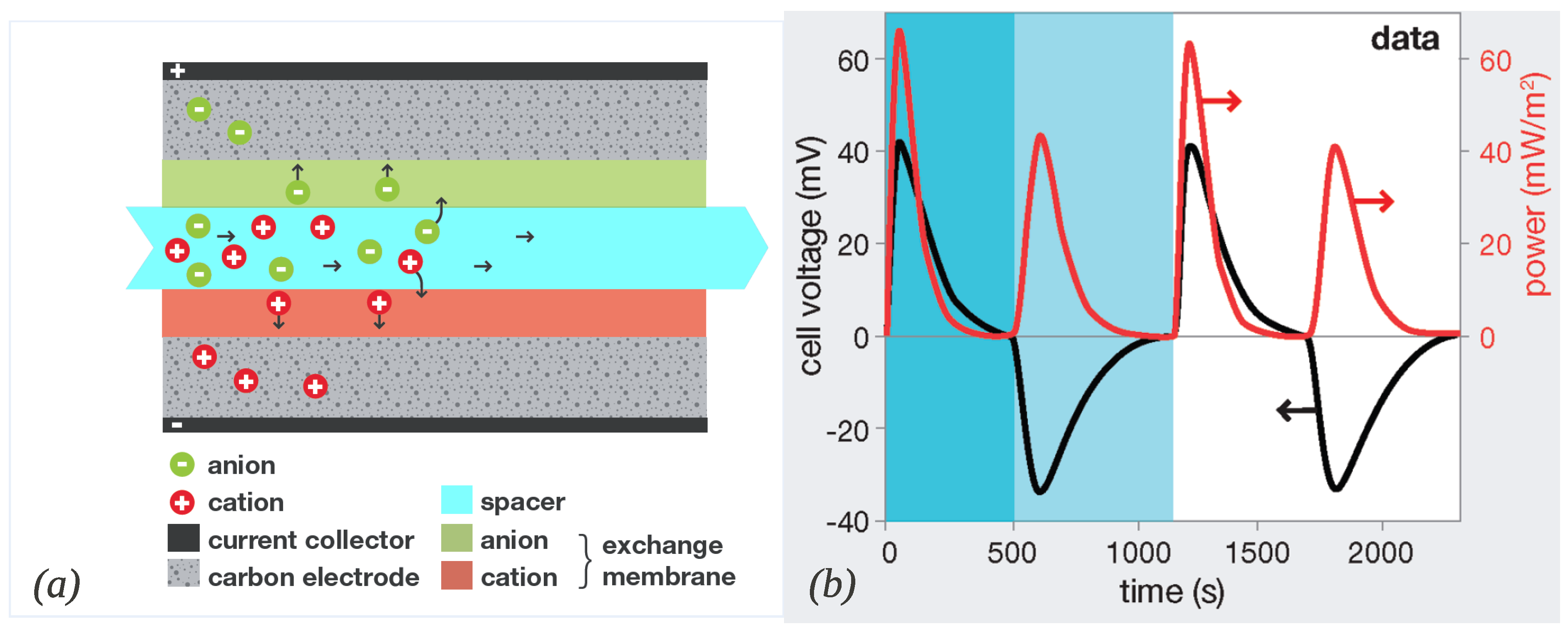
2.2. Capacitive Donnan Potential
2.3. Mixing Entropy Battery
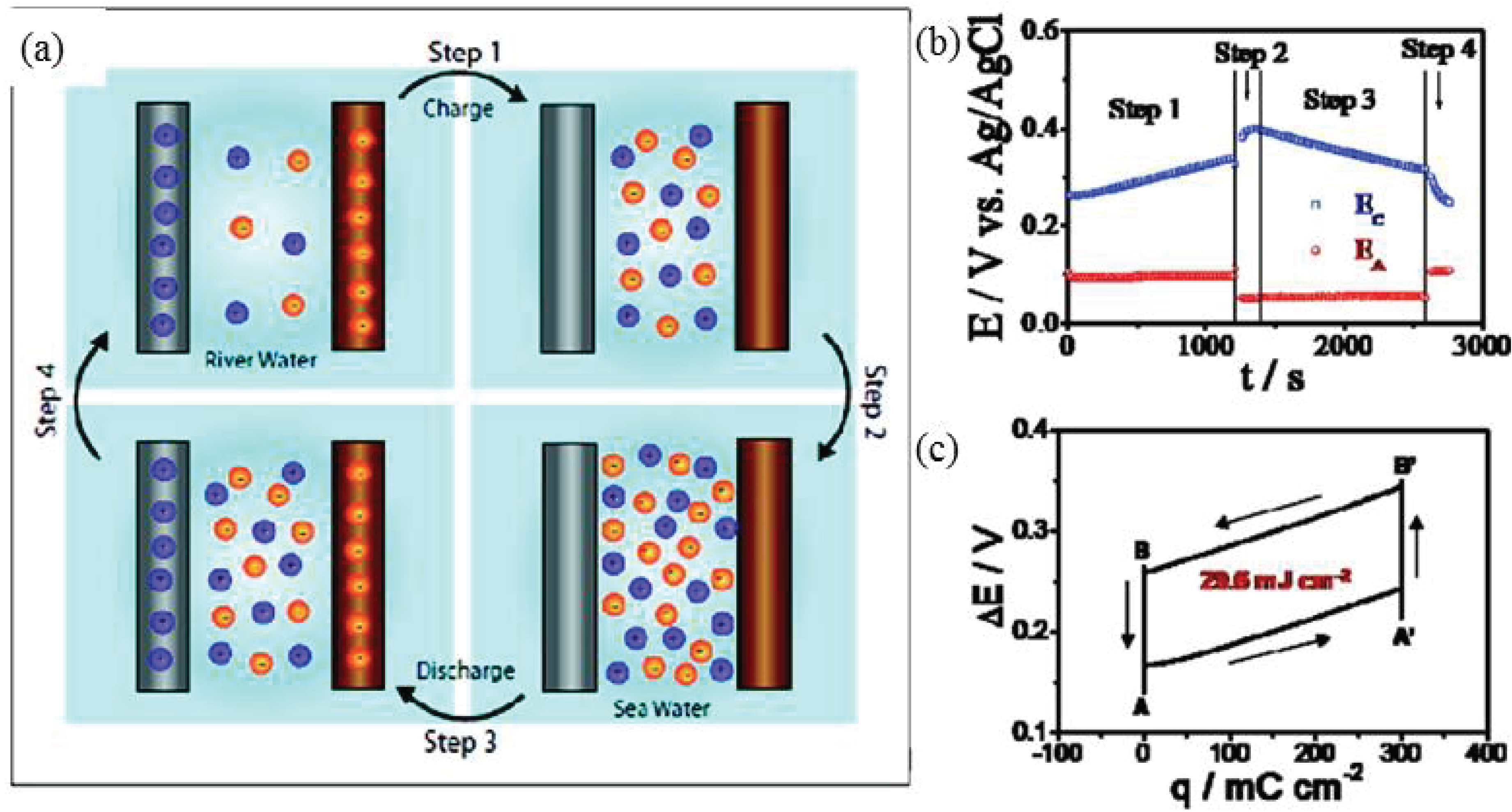
3. Common Features of the CAPMIX Techniques
3.1. Thermodynamics of “Blue Engines” and CAPMIX Cycles
3.2. Ions Transport and Adsorption in a CAPMIX Cell
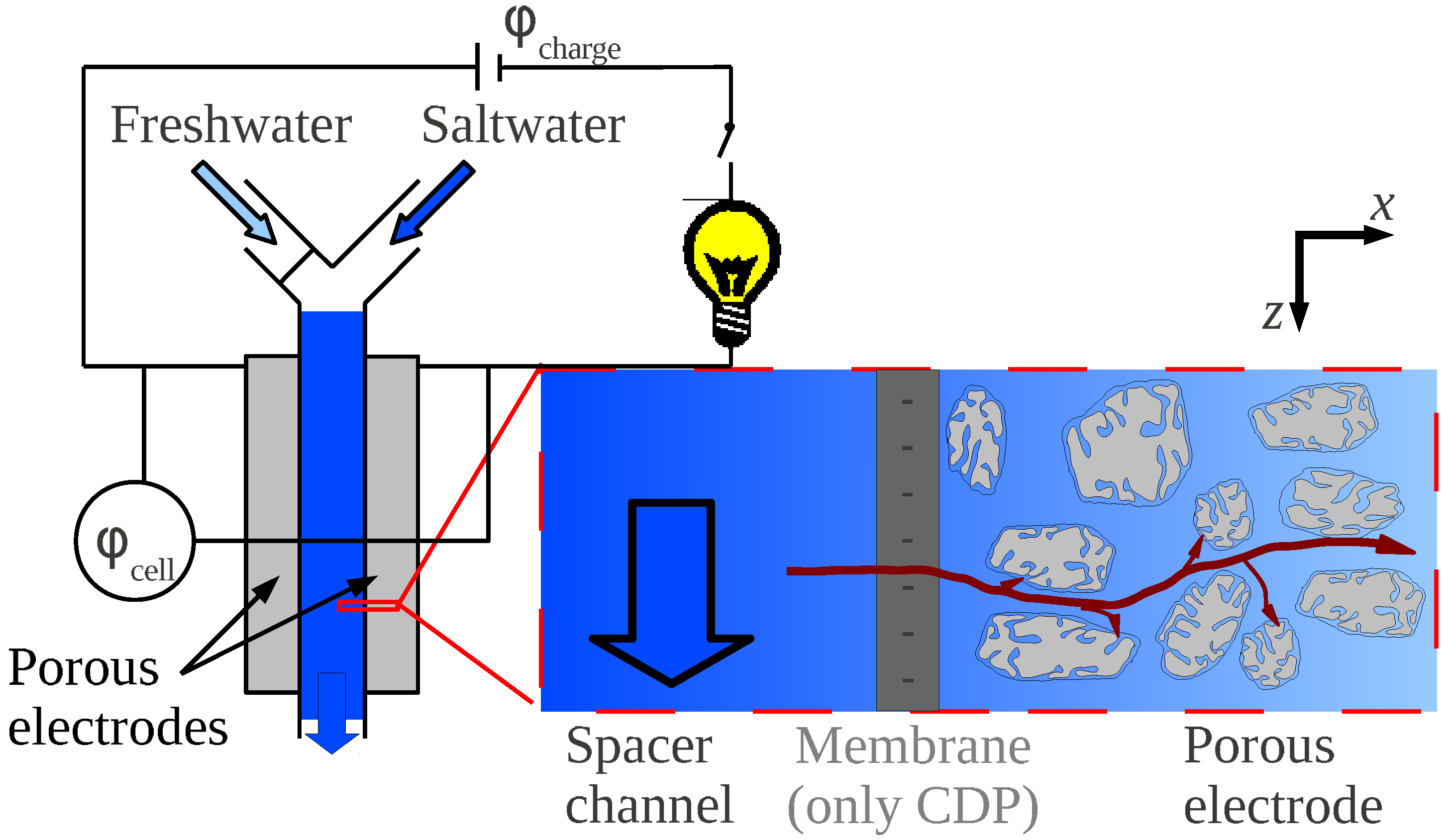
3.3. Key Parameters
4. Recent Advances
4.1. CDLE
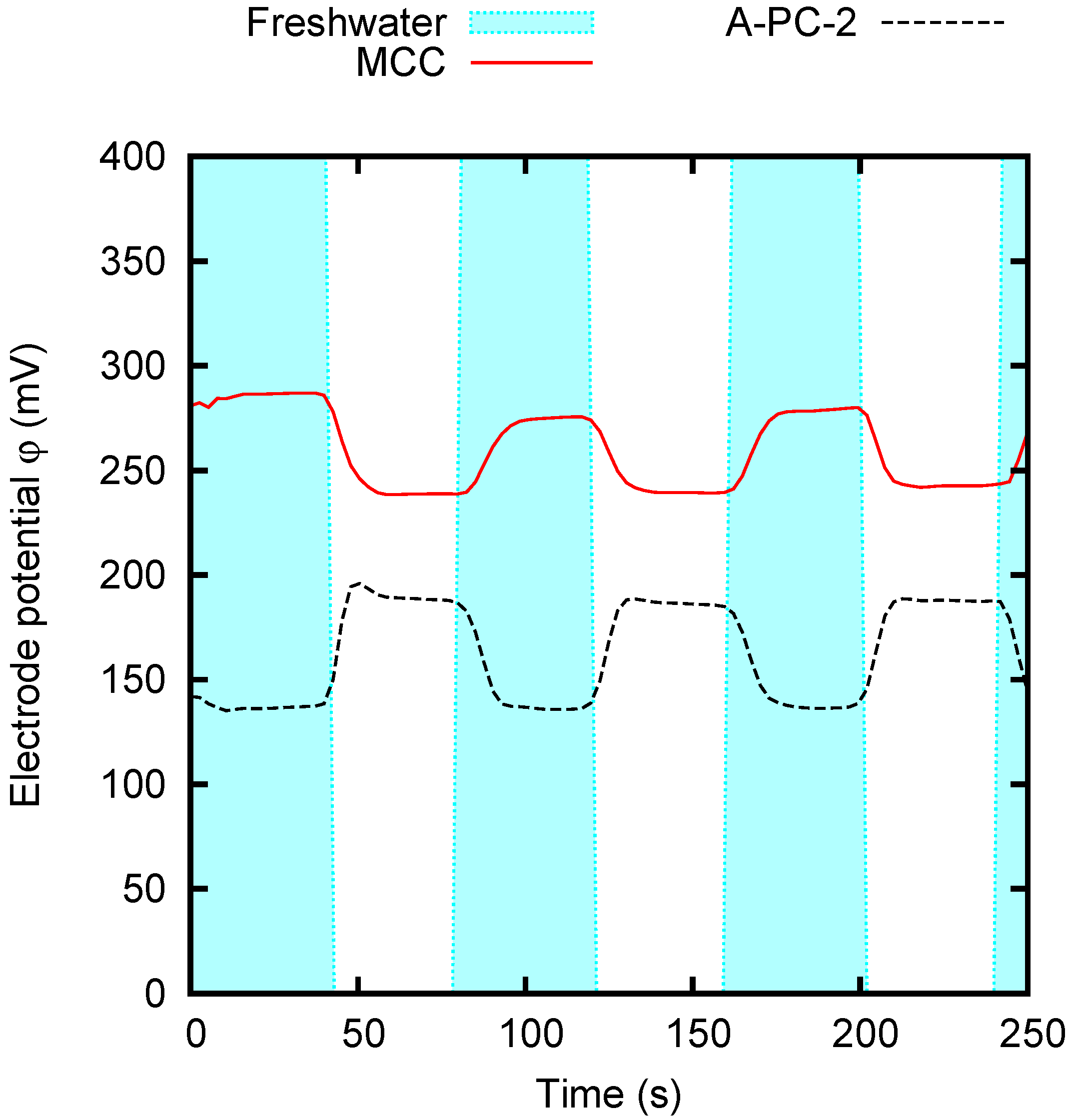
4.2. CDP
5. Perspectives
Acknowledgements
References
- Pattle, R.E. Production of electric power by mixing fresh and salt water in the hydroelectric pile. Nature 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, R.S. Water salination: A source of energy. Science 1974, 186, 350–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levenspiel, O.; de Vevers, N. The osmotic pump. Science 1974, 183, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labrecque, R. Exergy as a useful variable for quickly assessing the theoretical maximum power of salinity gradient energy systems. Entropy 2009, 11, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, N.; van Roij, R. “Blue energy” from ion adsorption and electrode charging in sea and river water. Mol. Phys. 2011, 109, 1229–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, N.Y.; Elimelech, M. Thermodynamic and energy efficiency analysis of power generation from natural salinity gradients by pressure retarded osmosis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 5230–5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, J.W.; Veerman, J.; Hamelers, H.V.M.; Euverink, G.J.W.; Metz, S.J.; Nymeijer, K.; Buisman, C.J.N. Salinity-gradient power: Evaluation of pressure-retarded osmosis and reverse electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 288, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramon, G.Z.; Feinberg, B.J.; Hoek, E.M.V. Membrane-based production of salinity-gradient power. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 4423–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, B.; Elimelech, M. Membrane-based processes for sustainable power generation using water. Nature 2012, 488, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, T.S.; Li, X.; Ong, R.C.; Ge, Q.; Wang, H.; Han, G. Emerging forward osmosis (FO) technologies and challenges ahead for clean water and clean energy applications. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2012, 1, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siria, A.; Poncharal, P.; Biance, A.L.; Fulcrand, R.; Blase, X.; Purcell, S.; Bocquet, L. Giant osmotic energy conversion measured in a single transmembrane boron nitride nanotube. Nature 2013, 494, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, B. Electrochemical Supercapacitors; Kluwer Academic, Plenum Publishers: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kötz, R.; Carlen, M. Principles and applications of electrochemical capacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2000, 45, 2483–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aricò, A.S.; Bruce, P.; Scrosati, B.; Tarascon, J.; van Schalkwijk, W. Nanostructured materials for advanced energy conversion and storage devices. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, P.; Gogotsi, Y. Materials for electrochemical capacitors. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijmans, M.F.M.; Burheim, O.S.; Bryjak, M.; Delgado, A.; Hack, P.; Mantegazza, F.; Tennisson, S.; Hamelers, H.V.M. CAPMIX- Deploying capacitors for salt gradient power extraction. Energy Procedia 2012, 20, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogioli, D.; Ziano, R.; Rica, R.A.; Salerno, D.; Kozynchenko, O.P.; Hamelers, H.V.; Mantegazza, F. Exploiting the spontaneous potential of the electrodes used in capacitive mixing technique for extraction of salinity-difference energy. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 16934–16938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogioli, D. Extracting renewable energy from a salinity difference using a capacitor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 058501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sales, B.B.; Saakes, M.; Post, J.; Buisman, C.J.N.; Biesheuvel, P.M.; Hamelers, H.V.M. Direct power production from a water salinity difference in a membrane-modified supercapacitor flow cell. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 5661–5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Mantia, F.; Pasta, M.; Deshazer, H.D.; Logan, B.E.; Cui, Y. Batteries for efficient energy extraction from a water salinity difference. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 1810–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oren, Y. Capacitive deionization (CDI) for desalination and water treatment- past, present and future (a review). Desalination 2008, 228, 10–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesheuvel, P.M. Thermodynamic cycle analysis for capacitive deionization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 332, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.B.; Park, K.K.; Eum, H.M.; Lee, C.W. Desalination of a thermal power plant wastewater by membrane capacitive deionization. Desalination 2006, 196, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gao, Y.; Pan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Z. Electrosorptive desalination by carbon nanotubes and nanofibres electrodes and ion-exchange membranes. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4923–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasta, M.; Wessells, C.D.; Cui, Y.; La Mantia. A desalination battery. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 839–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rica, R.A.; Ziano, R.; Salerno, D.; Mantegazza, F.; Brogioli, D. Thermodynamic relation between voltage-concentration dependence and salt adsorption in electrochemical cells. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 156103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Roij, R. Electrostatics of Soft and Disordered Matter. In Proceedings of the CECAM Workshop “New challenges in Electrostatics of Soft and Disordered Matter”, Toulouse, France, 7–10 May 2012; Pan Stanford Publishing: Singapore, September 2013. chapter Statistical thermodynamics of supercapacitors and blue engines, In press. [Google Scholar]
- Lyklema, J. Fundamentals of Interface and Colloid Science; Volume 2, Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Lakshminarayanaiah, N. Transport phenomena in artificial membranes. Chem. Rev. 1965, 65, 491–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rica, R.A.; Bazant, M.Z. Electrodiffusiophoresis: Particle motion in electrolytes under direct current. Phys. Fluids 2010, 22, 112109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogioli, D.; Zhao, R.; Biesheuvel, P.M. A prototype cell for extracting energy from a water salinity difference by means of double layer expansion in nanoporous carbon electrodes. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Schaetzle, O.; Sales, B.B.; Saakes, M.; Buisman, C.J.N.; Hamelers, H.V.M. Effect of additional charging and current density on the performance of Capacitive energy extraction based on Donnan Potential. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 8642–8650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burheim, O.; Sales, B.; Schaetzle, O.; Liu, F.; Hamelers, H.V.M. Auto generative capacitive mixing for power conversion of sea and river water by the use of membranes. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazant, M.Z.; Thornton, K.; Ajdari, A. Diffuse-charge dynamics in electrochemical systems. Phys. Rev. E: Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2004, 70, 021506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callen, H.B. Thermodynamics and an Introduction to Thermostatistics; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Biesheuvel, P.M.; Bazant, M.Z. Nonlinear dynamics of capacitive charging and desalination by porous electrodes. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2010, 81, 031502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesheuvel, P.M.; Fu, Y.; Bazant, M.Z. Diffuse charge and Faradaic reactions in porous electrodes. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2011, 83, 061507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmuck, M. Modeling and deriving porous media Stokes-Poisson-Nernst-Planck equations by a Multi-Scale approach. Commun. Math. Sci. 2011, 9, 685–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, A.; Bazant, M.Z. Deionization shocks in microstructures. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 84, 061504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmuck, M. First error bounds for the porous media approximation of the Poisson-Nernst-Planck equations. Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 2012, 92, 304–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, T.R.; Bazant, M.Z. Nonequilibrium thermodynamics of porous electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, A1967–A1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmuck, M.; Berg, P. Homogenization of a catalyst layer model for periodically distributed pore geometries in PEM fuel cells. Math. Phys. 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Biesheuvel, P.; Fu, Y.; Bazant, M. Electrochemistry and capacitive charging of porous electrodes in asymmetric multicomponent electrolytes. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2012, 48, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rica, R.A.; Brogioli, D.; Ziano, R.; Salerno, D.; Mantegazza, F. Ions transport and adsorption mechanisms in porous electrodes during capacitive-mixing double layer expansion (CDLE). J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 16934–16938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rica, R.A.; Ziano, R.; Salerno, D.; Mantegazza, F.; Bazant, M.Z.; Brogioli, D. Electro-diffusion of ions in porous electrodes for capacitive extraction of renewable energy from salinity differences. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 92, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, K.; Epting, W.; Litster, S. Spatially resolved, in situ potential measurements through porous electrodes as applied to fuel cells. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 9492–9498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, K.C.; Whitacre, J.F.; Litster, S. In situ measurements of potential, current and charging current across an EDL capacitance anode for an aqueous sodium hybrid battery. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, A1351–A1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, B.B.; Burheim, O.S.; Liu, F.; Schaetzle, O.; Buisman, C.J.N.; Hamelers, H.V.M. Impact of wire geometry in energy extraction from salinity differences using capacitive technology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 12203–12208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burheim, O.S.; Liu, F.; Sales, B.B.; Schaetzle, O.; Buisman, C.J.N.; Hamelers, H.V.M. Faster time response by the use of wire electrodes in capacitive salinity gradient energy systems. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 19203–19210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Pilon, L. Mesoscale modeling of electric double layer capacitors with three-dimensional ordered structures. J. Power Sources 2013, 221, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazant, M.Z.; Kilic, M.S.; Storey, B.D.; Ajdari, A. Towards an understanding of induced-charge electrokinetics at large applied voltages in concentrated solutions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 152, 48–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiménez, M.L.; Fernández, M.M.; Ahualli, S.; Iglesias, G.; Delgado, A.V. Predictions of the maximum energy extracted from salinity exchange inside porous electrodes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, A.; González-Caballero, F.; Hunter, R.; Koopal, L.; Lyklema, J. Measurement and interpretation of electrokinetic phenomena. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 309, 194–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrique, F.; Arroyo, F.J.; Delgado, A.V. Electrokinetics of concentrated suspensions of spherical colloidal particles with surface conductance, arbitrary zeta potential, and double-layer thickness in static electric fields. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 252, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmiola, J.; Yushin, G.; Gogotsi, Y.; Portet, C.; Simon, P.; Taberna, P.L. Anomalous increase in carbon capacitance at pore sizes less than 1 nanometer. Science 2006, 313, 1760–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Porada, S.; Weinstein, L.; Dash, R.; van der Wal, A.; Bryjak, M.; Gogotsi, Y.; Biesheuvel, P. Water desalination using vapacitive deionization with microporous carbon electrodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 1194–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, B.E. Transition from “supercapacitor” to “battery” behavior in electrochemical energy storage. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1991, 138, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Bae, W.S.; Choi, J.H. Electrode reactions and adsorption/desorption performance related to the applied potential in a capacitive deionization process. Desalination 2010, 258, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, B.B.; Liu, F.; Schaetzle, O.; Buisman, C.J.; Hamelers, H.V. Electrochemical characterization of a supercapacitor flow cell for power production from salinity gradients. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 86, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.B.; van Soestbergen, M.; Mani, A.; Bruus, H.; Biesheuvel, P.M.; Bazant, M.Z. Current-induced membrane discharge. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 108301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porada, S.; Sales, B.B.; Hamelers, H.V.M.; Biesheuvel, P.M. Water desalination with wires. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 1613–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turek, M.; Bandura, B.; Dydo, P. Power production from coal-mine brine utilizing reversed electrodialysis. Desalination 2008, 221, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipollina, A.; Misseri, A.; D’Alí Staiti, G.; Galia, A.; Micale, G.; Scialdone, O. Integrated production of fresh water, sea salt and magnesium from sea water. Desalin. Water Treat. 2012, 49, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermaas, D.; Bajracharya, S.; Bastos, B.; Saakes, M.; Hamelers, H.V.; Nijmeijer, K. Clean energy generation using capacitive electrodes in reverse electrodialysis. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Rica, R.A.; Ziano, R.; Salerno, D.; Mantegazza, F.; Van Roij, R.; Brogioli, D. Capacitive Mixing for Harvesting the Free Energy of Solutions at Different Concentrations. Entropy 2013, 15, 1388-1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/e15041388
Rica RA, Ziano R, Salerno D, Mantegazza F, Van Roij R, Brogioli D. Capacitive Mixing for Harvesting the Free Energy of Solutions at Different Concentrations. Entropy. 2013; 15(4):1388-1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/e15041388
Chicago/Turabian StyleRica, Raúl A., Roberto Ziano, Domenico Salerno, Francesco Mantegazza, Renéa Van Roij, and Doriano Brogioli. 2013. "Capacitive Mixing for Harvesting the Free Energy of Solutions at Different Concentrations" Entropy 15, no. 4: 1388-1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/e15041388