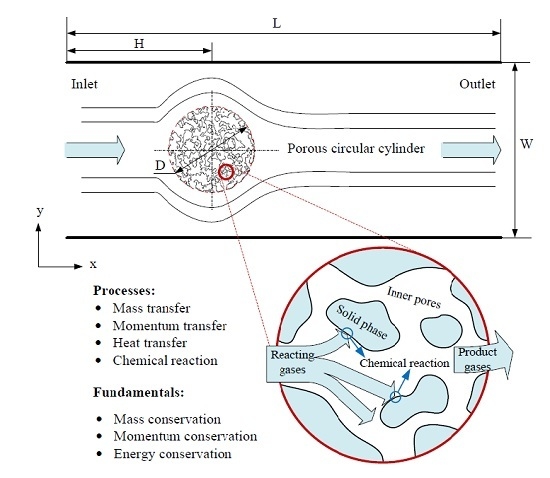
A Lattice Gas Automata Model for the Coupled Heat Transfer and Chemical Reaction of Gas Flow Around and Through a Porous Circular Cylinder
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Simulation Method
2.1. Lattice Gas Automata Model for Heat Transfer and Chemical Reaction


2.2. Chemical Reaction Scheme
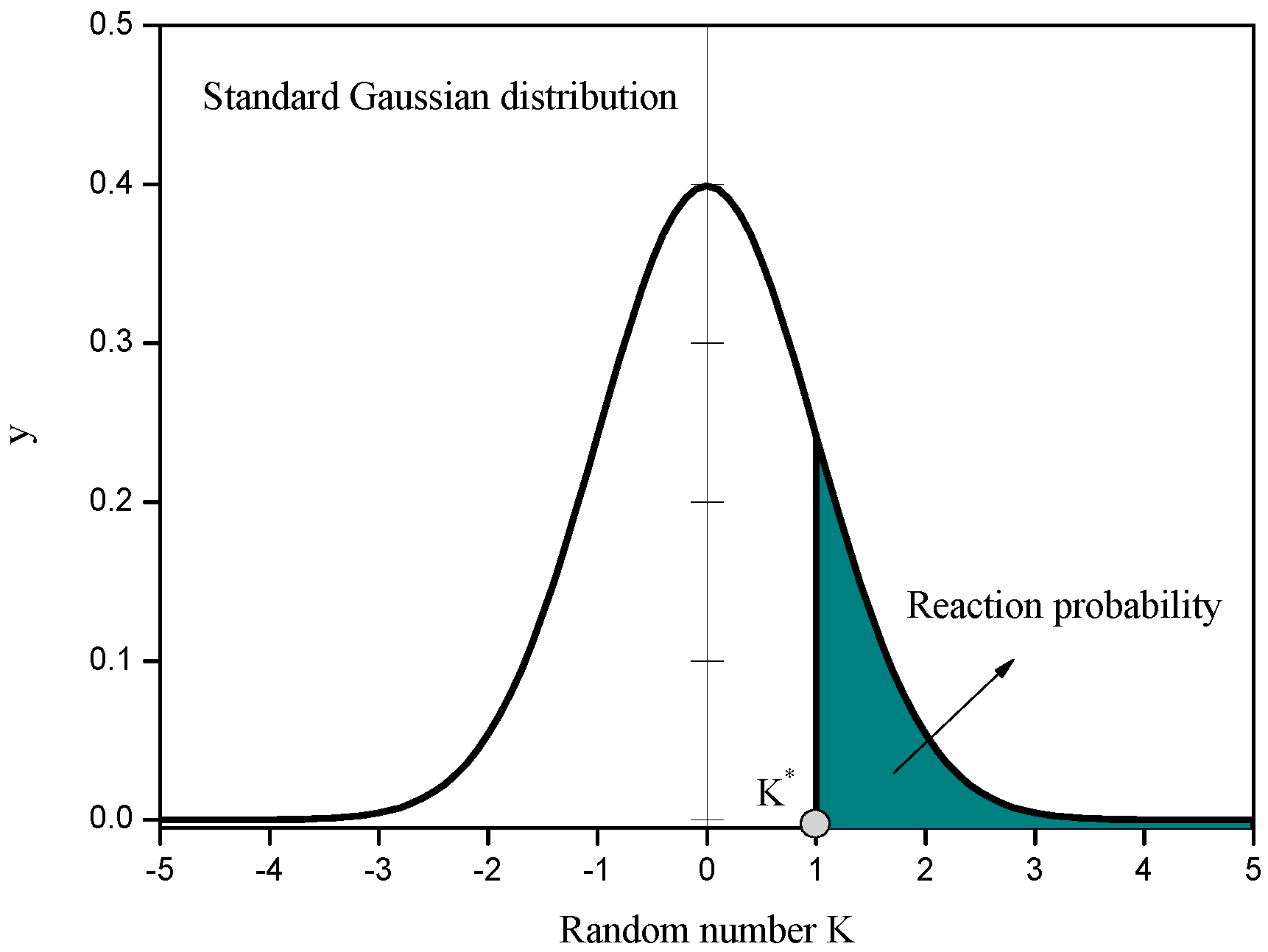
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Validation of the Chemical Reaction Scheme


3.2. Heat Transfer and Reaction across a Porous Circular Cylinder


| Case No. | Parameters of QSGS | r | u | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Di | P | |||
| 1 | 0.02 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1587 | 1.0 |
| 2 | 0.02 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.1587 | 1.0 |
| 3 | 0.035 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1587 | 1.0 |
| 4 | 0.02 | 0.35 | 0.2 | 0.1587 | 1.0 |
| 5 | 0.02 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.0668 | 1.0 |
| 6 | 0.02 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3085 | 1.0 |
| 7 | 0.02 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1587 | 0.5 |
| 8 | 0.02 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1587 | 0.8 |
3.2.1. Effect of Inner Porous Structure





3.2.2. Effect of Reaction Probability


3.2.3. Effect of Inlet Gas Velocity


4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, C.; Thovert, J.-F.; Debenest, G. Upscaling of mass and thermal transports in porous media with heterogeneous combustion reactions. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 84, 862–875. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmud, S.; Fraser, R.A. Free convection and irreversibility analysis inside a circular porous enclosure. Entropy 2003, 5, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Patil, P.R.; Narusawa, U. On Darcy-Brinkman equation: Viscous flow between two parallel plates packed with regular square arrays of cylinders. Entropy 2007, 9, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makinde, O.D.; Eegunjobi, A.S. Entropy generation in a couple stress fluid flow through a vertical channel filled with saturated porous media. Entropy 2013, 15, 4589–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Z. Effect of endothermic reaction mechanisms on the coupled heat and mass transfers in a porous packed bed with Soret and Dufour effects. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 67, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cai, J.; Xin, F.; Huai, X.; Guo, J. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of endothermal catalytic reaction in catalyst porous media. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 50, 1194–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, R. Numerical simulations of surface reaction in porous media with lattice Boltzmann. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 69, 628–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, F.; Li, X.-F.; Xu, M.; Huai, X.-L.; Cai, J.; Guo, Z.-X. Simulation of gas exothermic chemical reaction in porous media reactor with lattice Boltzmann method. J. Therm. Sci. 2013, 22, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf-Gladrow, D.A. Lattice-Gas Cellular Automata and Lattice Boltzmann Models; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- McNamara, G.R.; Garcia, A.L.; Alder, B.J. Stabilization of thermal lattice Boltzmann models. J. Statist. Phys. 1995, 81, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, J.F. Flow through arrays of cylinders: Lattice gas cellular automata simulations. Phys. Fluids 1994, 6, 435–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogeler, A.; Wolf-Gladrow, D.A. Pair interaction lattice gas simulations: Flow past obstacles in two and three dimensions. J. Statist. Phys. 1993, 71, 163–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissler, W.; Drtina, P.; Frohn, A. Cellular automata simulation of flow around chains of cylinders. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1992, 34, 773–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dab, D.; Lawniczak, A.; Boon, J.-P.; Kapral, R. Cellular-automaton model for reactive systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1990, 64, 2462–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boon, J.P.; Dab, D.; Kapral, R.; Lawniczak, A. Lattice gas automata for reactive systems. Phys. Rep. 1996, 273, 55–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weimar, J.R. Cellular automata for reaction-diffusion systems. Parallel Comput. 1997, 23, 1699–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seybold, P.G.; Kier, L.B.; Cheng, C.-K. Simulation of first-order chemical kinetics using cellular automata. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1997, 37, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seybold, P.G.; Kier, L.B.; Cheng, C.-K. Stochastic cellular automata models of molecular excited-state dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. A 1998, 102, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seybold, P.G.; Kier, L.B.; Cheng, C.-K. Aurora borealis: Stochastic cellular automata simulations of the excited-state dynamics of oxygen atoms. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 1999, 75, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuforth, A.; Seybold, P.G.; Kier, L.B.; Cheng, C.-K. Cellular automata models of kinetically and thermodynamically controlled reactions. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 2000, 32, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.D.; Caserio, M.C. Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry, 2nd ed.; WA Benjamin: Menlo Park, CA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, K.-C. Understanding product optimization: Kinetic versus thermodynamic control. J. Chem. Educ. 1988, 65, 857–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingsworth, C.A.; Seybold, P.G.; Kier, L.B.; Cheng, C.-K. First-order stochastic cellular automata simulations of the Lindemann mechanism. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 2004, 36, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindemann, F.A.; Arrhenius, S.; Langmuir, I.; Dhar, N.R.; Perrin, J.; McC. Lewis, W.C. Discussion on “the radiation theory of chemical action”. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1922, 17, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, U.; d’Humières, D.; Hasslacher, B.; Lallemand, P.; Pomeau, Y.; Rivet, J.-P. Lattice gas hydrodynamics in two and three dimensions. Complex Syst. 1987, 1, 649–707. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Gao, X. Lattice gas automata method for modeling fluid flow and heat transfer in metallurgical porous media. Acta Met. Sin. 2000, 36, 433–437. [Google Scholar]
- Bresolin, C.S.; Oliveira, A.A.M. An algorithm based on collision theory for the lattice Boltzmann simulation of isothermal mass diffusion with chemical reaction. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2012, 183, 2542–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baercor, T.; Mayer, P.M. Statistical Rice–Ramsperger–Kassel–Marcus quasiequilibrium theory calculations in mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1997, 8, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.H.; Oh, J.Y.; Kim, M.S. A systematic and efficient method to estimate the vibrational frequencies of linear peptide and protein ions with any amino acid sequence for the calculation of Rice–Ramsperger–Kassel–Marcus rate constant. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 17, 1749–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.H.; Sun, M.; Kim, M.S. Efficient and reliable calculation of Rice–Ramsperger–Kassel–Marcus unimolecular reaction rate constants for biopolymers: Modification of Beyer–Swinehart algorithm for degenerate vibrations. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 18, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wichura, M.J. Algorithm as 241: The percentage points of the normal distribution. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1988, 37, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecca, P.; Laurenzi, I.; Jord, F. Deterministic Versus Stochastic Modelling in Biochemistry and Systems Biology; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Bi, X.T. Simulation of flow and heat transfer around a heated stationary circular cylinder by lattice gas automata. Powder Technol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Pan, N.; Chen, S. Mesoscopic predictions of the effective thermal conductivity for microscale random porous media. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 75, 036702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wu, G.; Holby, E.F.; Zelenay, P.; Tao, W.-Q.; Kang, Q. Lattice Boltzmann pore-scale investigation of coupled physical-electrochemical processes in C/Pt and non-precious metal cathode catalyst layers in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 158, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, S.; Ogata, S.; Koga, J.; Matsumoto, S. Gas–solid reaction model for a shrinking spherical particle with unreacted shrinking core. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 4971–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, E.E. Reaction of porous solids. AIChE J. 1957, 3, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Bi, X.T. A Lattice Gas Automata Model for the Coupled Heat Transfer and Chemical Reaction of Gas Flow Around and Through a Porous Circular Cylinder. Entropy 2016, 18, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/e18010002
Chen H, Zheng Z, Chen Z, Bi XT. A Lattice Gas Automata Model for the Coupled Heat Transfer and Chemical Reaction of Gas Flow Around and Through a Porous Circular Cylinder. Entropy. 2016; 18(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/e18010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Hongsheng, Zhong Zheng, Zhiwei Chen, and Xiaotao T. Bi. 2016. "A Lattice Gas Automata Model for the Coupled Heat Transfer and Chemical Reaction of Gas Flow Around and Through a Porous Circular Cylinder" Entropy 18, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/e18010002
APA StyleChen, H., Zheng, Z., Chen, Z., & Bi, X. T. (2016). A Lattice Gas Automata Model for the Coupled Heat Transfer and Chemical Reaction of Gas Flow Around and Through a Porous Circular Cylinder. Entropy, 18(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/e18010002