Fluctuation-Driven Transport in Biological Nanopores. A 3D Poisson–Nernst–Planck Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Theoretical Calculations
2.2. Experimental Methods
3. Results and Discussion
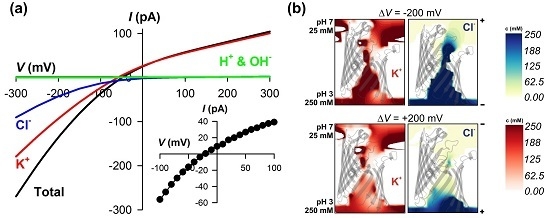
3.1. The Importance of Membrane Charge Asymmetry
3.2. Structural Basis of Ion Pumping
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Westerhoff, H.V.; Tsong, T.Y.; Chock, P.B.; Chen, Y.D.; Astumian, R.D. How enzymes can capture and transmit free energy from an oscillating electric field. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 4734–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astumian, R.D. Thermodynamics and kinetics of a Brownian motor. Science 1997, 276, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdiá-Báguena, C.; Queralt-Martín, M.; Aguilella, V.M.; Alcaraz, A. Protein ion channels as molecular ratchets. Switchable current modulation in Outer Membrane Protein F porin induced by millimolar La3+ ions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 6537–6542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, P.; Ali, M.; Ensinger, W.; Mafe, S. Information processing with a single multifunctional nanofluidic diode. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 133108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, P.; Gomez, V.; Ali, M.; Ensinger, W.; Mafe, S. Net currents obtained from zero-average potentials in single amphoteric nanopores. Electrochem. Commun. 2013, 31, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosgaard, L.D.; Zecchi, K.A.; Heimburg, T.; Budvytyte, R. The effect of the nonlinearity of the response of lipid membranes to voltage perturbations on the interpretation of their electrical properties. A new theoretical description. Membranes 2015, 5, 495–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, M.L.; Queralt-Martín, M.; Alcaraz, A. Stochastic pumping of ions based on colored noise in bacterial channels under acidic stress. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 13422–13428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delcour, A.H. Solute uptake through general porins. Front. Biosci. 2003, 8, D1055–D1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikaido, H. Molecular Basis of Bacterial Outer Membrane Permeability Revisited. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2003, 67, 593–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, J.W. Escherichia coli acid resistance: Tales of an amateur acidophile. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queralt-Martín, M.; Peiró-González, C.; Aguilella-Arzo, M.; Alcaraz, A. Effects of extreme pH on ionic transport through protein nanopores: The role of ion diffusion and charge exclusion. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 21668–21675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queralt-Martín, M.; García-Giménez, E.; Aguilella, V.M.; Ramirez, P.; Mafe, S.; Alcaraz, A. Electrical pumping of potassium ions against an external concentration gradient in a biological ion channel. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 43707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshminarayanaiah, N. Equations of Membrane Biophysics; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Nonner, W.; Eisenberg, B. Ion permeation and glutamate residues linked by Poisson-Nernst-Planck theory in L-type calcium channels. Biophys. J. 1998, 75, 1287–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnikova, M.G.; Coalson, R.D.; Graf, P.; Nitzan, A. A Lattice Relaxation Algorithm for Three-Dimensional Poisson-Nernst-Planck Theory with Application to Ion Transport through the Gramicidin A Channel. Biophys. J. 1999, 76, 642–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.E.; Madura, J.D.; Luty, B.A.; McCammon, J.A. Electrostatics and diffusion of molecules in solution: Simulations with the University of Houston Brownian Dynamics program. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1991, 62, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madura, J.D.; Briggs, J.M.; Wade, R.C.; Davis, M.E.; Luty, B.A.; Ilin, A.; Antosiewicz, J.; Gilson, M.K.; Bagheri, B.; Scott, L.R.; et al. Electrostatics and diffusion of molecules in solution: Simulations with the University of Houston Brownian Dynamics program. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1995, 91, 57–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, S.; Garavito, R.; Jansonius, J.; Jenkins, J.; Karlsson, R.; König, N.; Pai, E.; Pauptit, R.; Rizkallah, P.; Rosenbusch, J.; et al. The structure of OmpF porin in a tetragonal crystal form. Structure 1995, 3, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyer, J.E.; Wheeler, D.; Warren, J.A. FiPy: Partial Differential Equations with Python. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2009, 11, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rossum, G.; Drake, F.L. PYTHON 2. 6 Reference Manual: (Python Documentation MANUAL Part 2); Python Software Foundation: Beaverton, OR, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Marr, J.M.; Li, F.; Petlick, A.R.; Schafer, R.; Hwang, C.-T.; Chabot, A.; Ruggiero, S.T.; Tanner, C.E.; Schultz, Z.D. The Role of Lateral Tension in Calcium-Induced DPPS Vesicle Rupture. Langmuir 2012, 28, 11874–11880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorden, J.; Small, P.L. Acid resistance in enteric bacteria. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Castanie-Cornet, M.P.; Penfound, T.A.; Smith, D.; Elliott, J.F.; Foster, J.W. Control of acid resistance in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 3525–3535. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Lee, I.S.; Frey, J.; Slonczewski, J.L.; Foster, J.W. Comparative analysis of extreme acid survival in Salmonella typhimurium, Shigella flexneri, and Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 4097–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diez-Gonzalez, F.; Russell, J.B. The ability of Escherichia coli O157:H7 to decrease its intracellular pH and resist the toxicity of acetic acid. Microbiology 1997, 143 Pt 4, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, K.N.; Oxford, L.; O’Byrne, C.P. Survival of low-pH stress by Escherichia coli O157:H7: Correlation between alterations in the cell envelope and increased acid tolerance. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 3048–3055. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tyäuble, H.; Teubner, M.; Woolley, P.; Eibl, H. Electrostatic interactions at charged lipid membranes. I. Effects of pH and univalent cations on membrane structure. Biophys. Chem. 1976, 4, 319–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikaido, H.; Vaara, M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol. Rev. 1985, 49, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Meer, G.; Voelker, D.R.; Feigenson, G.W. Membrane lipids: Where they are and how they behave. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcaraz, A.; Ramírez, P.; García-Giménez, E.; López, M.L.; Andrio, A.; Aguilella, V.M. A pH-tunable nanofluidic diode: Electrochemical rectification in a reconstituted single ion channel. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 21205–21209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, W.; Roux, B. Ions and counterions in a biological channel: A molecular dynamics simulation of OmpF porin from Escherichia coli in an explicit membrane with 1 M KCl aqueous salt solution. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 319, 1177–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilella, V.M.; Queralt-Martín, M.; Aguilella-Arzo, M.; Alcaraz, A. Insights on the permeability of wide protein channels: Measurement and interpretation of ion selectivity. Integr. Biol. 2011, 3, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuliński, A.; Grzywna, Z.; Mellor, I.; Siwy, Z.; Usherwood, P. Non-Markovian character of ionic current fluctuations in membrane channels. Phys. Rev. E 1998, 58, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.D.; Marszalek, P.; Chen, Y.D.; Tsong, T.Y. Recognition and processing of randomly fluctuating electric signals by Na,K-ATPase. Biophys. J. 1994, 67, 1247–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danelon, C.; Nestorovich, E.M.; Winterhalter, M.; Ceccarelli, M.; Bezrukov, S.M. Interaction of zwitterionic penicillins with the OmpF channel facilitates their translocation. Biophys. J. 2006, 90, 1617–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui, H.; Il Lee, K.; Pastor, R.W.; Im, W. Molecular dynamics studies of ion permeation in VDAC. Biophys. J. 2011, 100, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, I.H.; Sansom, M.S. Simulations of ion permeation through a potassium channel: Molecular dynamics of KcsA in a phospholipid bilayer. Biophys. J. 2000, 78, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aguilella-Arzo, M.; Queralt-Martín, M.; Lopez, M.-L.; Alcaraz, A. Fluctuation-Driven Transport in Biological Nanopores. A 3D Poisson–Nernst–Planck Study. Entropy 2017, 19, 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19030116
Aguilella-Arzo M, Queralt-Martín M, Lopez M-L, Alcaraz A. Fluctuation-Driven Transport in Biological Nanopores. A 3D Poisson–Nernst–Planck Study. Entropy. 2017; 19(3):116. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19030116
Chicago/Turabian StyleAguilella-Arzo, Marcel, María Queralt-Martín, María-Lidón Lopez, and Antonio Alcaraz. 2017. "Fluctuation-Driven Transport in Biological Nanopores. A 3D Poisson–Nernst–Planck Study" Entropy 19, no. 3: 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19030116