Preparation of (S)-1-Halo-2-octanols Using Ionic Liquids and Biocatalysts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
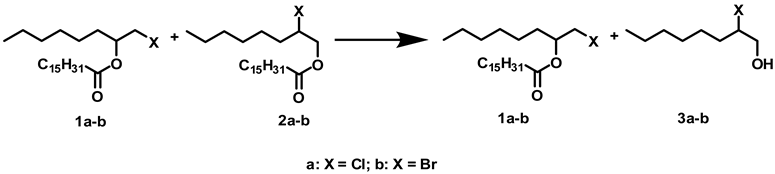
2.1. Influence of Solvents and Biocatalysts on the Regioselectivity of the Process
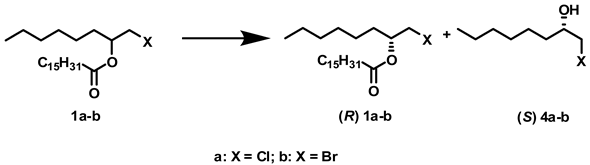
2.2. Influence of Solvents and Biocatalysts on the Enantioselectivity of the Process
3. Experimental
3.1. General Procedures
3.2. Procedure for the Syntheses of Halohydrin Palmitates
3.3. Procedure for the Syntheses of Halohydrin Standards
3.4. General Procedure for Optimizing the Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Halohydrin Esters
3.5. Procedure for Preparing (S)-2-Chloro-1-octanol (4a)
3.6. Procedure for Preparing (S)-2-Bromo-1-octanol (4b)
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References and Notes
- Ranu, B.C.; Banerjee, S. Ionic liquid as reagent. A green procedure for the regioselective conversion of epoxides to vicinal-halohydrins using [AcMIm]X under catalyst- and solvent-free conditions. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 4517–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oromí-Farrús, M.; Eras, J.; Villorbina, G.; Torres, M.; Llopis-Mestre, V.; Welton, T.; Canela, R. [BMIM][PF6] promotes the synthesis of halohydrin esters from diols using potassium halides. Anal. Sci. 2008, 24, 1341–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méndez, J.; Oromí, M.; Cerveró, M.; Balcells, M.; Torres, M.; Canela, R. Combining regio- and enantioselectivity of lipases for the preparation of (R)-4-chloro-2-butanol. Chirality 2007, 19, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotticci, D.; Orrenius, C.; Hult, K.; Norin, T. Enantiomerically enriched bifunctional sec–alcohols prepared by Candida antarctica lipase B catalysis. Evidence of non-steric interactions. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 1997, 8, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umezawa, J.; Furuhashi, K. Preparation of optically active 1-halo-2-alkanols. JP Pat. 01070423, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, T.; Kawanaka, Y.; Kasamatsu, E.; Ohta, C.; Nakabayashi, K.; Okamoto, M.; Hamano, M.; Takahashi, K.; Ohuchida, S.; Hamada, Y. A new process for synthesis of the astrocyte activation suppressor, ONO-2506. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2005, 9, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuegg, J.; Honig, H.; Schrag, J.D.; Cygler, M. Selectivity of lipases: Conformational analysis of suggested intermediates in ester hydrolysis of chiral primary and secondary alcohols. J. Mol. Catal. B-Enzym. 1997, 3, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeller, K.M.; Wong, C.H. Enzymes for chemical synthesis. Nature 2001, 409, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, W.; Wei, L.W.; Mei, Z.Y.; Huaping, W. Do we understand the recyclability of ionic liquids? Chem.-Eur. J. 2009, 15, 1804–1810. [Google Scholar]
- Ranke, J.; Stolte, S.; Stoermann, R.; Arning, J.; Jastorff, B. Design of Sustainable Chemical Products - The Example of Ionic Liquids. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2183–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, A.R.; Smith, P.; Srinivasan, N.; Welton, T. Ionic liquids as solvents for organic synthesis. In Green Industrial Applications of Ionic Liquids; Rogers, R.D., Seddon, K.R., Volkov, S., Eds.; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003; NATO Science Series II: Mathematics, Physics and Chemistry; Volume 92, pp. 457–464. [Google Scholar]
- Erbeldinger, M.; Mesiano, A.J.; Russell, A.J. Enzymatic catalysis of formation of Z-aspartame in ionic liquid—An alternative to enzymatic catalysis in organic solvents. Biotechnol. Prog. 2000, 16, 1129–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, R.M.; van Rantwijk, F.; Seddon, K.R.; Sheldon, R.A. Lipase-catalyzed reactions in ionic liquids. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 4189–4191. [Google Scholar]
- Schofer, S.H.; Kaftzik, N.; Wasserscheid, P.; Kragl, U. Enzyme catalysis in ionic liquids: lipase catalysed kinetic resolution of 1-phenylethanol with improved enantioselectivity. Chem. Commun. 2001, 425–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknam, K.; Nasehi, T. Cleavage of epoxides into halohydrins with elemental iodine and bromine in the presence of 2,6-bis[2-(o-aminophenoxy)methyl]-4-bromo-1-methoxybenzene (BABMB) as catalyst. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 10259–10261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharghi, H.; Eskandari, M.M. Conversion of epoxides to halohydrins with elemental halogen catalyzed by phenylhydrazine. Synthesis 2002, 1519–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rantwijk, F.; Sheldon, R.A. Biocatalysis in Ionic Liquids. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2757–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkessel, A.; Rollmann, C.; Chamouleau, F.; Labs, S.; May, O.; Groeger, H. A practical and versatile access to dihydrosalen (salalen) ligands: highly enantioselective titanium in situ catalysts for asymmetric epoxidation with aqueous hydrogen peroxide. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007, 349, 2697–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhindsa, A.S.; Bryce, M.R.; Petty, M.C.; Kobayashi, K.; Tukada, H. Synthesis of tetrathiafulvalene (TTF) derivatives substituted with two and four hydrophobic alkyl chains. Synth. Met. 1989, 31, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pueschel, F.; Kaiser, C. Higher-molecular-weight aliphatic sulfonic acids. I. 2-Hydroxy-n-alkane-1-sulfonic acids. Chem. Ber. 1964, 97, 2903–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Settimo, F.; Primofiore, G.; La Motta, C.; Taliani, S.; Simorini, F.; Marini, A.M.; Mugnaini, L.; Lavecchia, A.; Novellino, E.; Tuscano, D.; Martini, C. Novel, Highly Potent Adenosine Deaminase Inhibitors Containing the Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine Ring System. Synthesis, Structure-Activity Relationships, and Molecular Modeling Studies. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 5162–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haak, R.M.; Tarabiono, C.; Janssen, Dick B.; Minnaard, A.J.; de Vries, J.G.; Feringa, B.L. Synthesis of enantiopure chloroalcohols by enzymatic kinetic resolution. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Träff, A.; Bogár, K.; Warner, M.; Bäckvall, Jan-E. Highly efficient route for enantioselective preparation of chlorohydrins via dynamic kinetic resolution. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 4807–4810. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano, P.; De Diego, T.; Carrie, D.; Vaultier, M.; Iborra, J.L. Enzymatic ester synthesis in ionic liquids. J. Mol. Catal. B-Enzym. 2003, 21, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, W.Y.; Zong, M.H. Efficient kinetic resolution of (R, S)-1-trimethylsilylethanol via lipase-mediated enantioselective acylation in ionic liquids. Chirality 2006, 18, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal, A.; Chouhan, G. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of enantiomerically pure 1,2-diols employing immobilized lipase in the ionic liquid [bmim][ PF6]. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 8801–8805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nara, S.J.; Harjani, J.R.; Salunkhe, M.M. Lipase-catalysed transesterification in ionic liquids and organic solvents: a comparative study. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 2979–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakels, J.L.L.; Straathof, A.J.J.; Heijnen, J.J. A simple method to determine the enantiomeric ratio in enantioselective biocatalysis. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1993, 15, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eras, J.; Méndez, J.J.; Balcells, M.; Canela, R. Chlorotrimethylsilane: A suitable reagent for the synthesis of chlorohydrin esters. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 8631–8634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilen, S.H.; Delguzzo, L.; Saferstein, R. Experimental-Evidence for Aco-7 Neighboring Group Participation. Tetrahedron 1987, 43, 5089–5094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nara, S.J.; Mohile, S.S.; Harjani, J.R.; Naik, P.U.; Salunkhe, M.M. Influence of ionic liquids on the rates and regioselectivity of lipase-mediated biotransformations on 3,4,6-tri-O-acetyl-D-glucal. J. Mol. Catal. B-Enzym. 2004, 28, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 1a, 1b, 2a, 2b, (S)-4a, (S)-4b are available from the authors. |
| Entry | Biocatalyst | Solvent | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| t-Butanol | [OMIM][BF4] | [BMIM][PF6] | ||
| 1a | R. oryzae | 13 | ||
| 2a | R. oryzae | 100 | ||
| 1a | Lipozyme | 8 | 5 | |
| 2a | Lipozyme | 100 | 89 | |
| 1a | Novozym | 57 | 43 | 51* |
| 2a | Novozym | 100 | 85 | 53* |
| 1b | R. oryzae | 57 | ||
| 2b | R. oryzae | 100 | ||
| 1b | Lipozyme | 54 | 1 | |
| 2b | Lipozyme | 100 | 90 | |
| 1b | Novozym | 52 | 15 | 35* |
| 2b | Novozym | 100 | 91 | 52* |
| Entry | Biocatalyst | Solvent | % Hydrolysis | eesa | Ea |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | Novozym | t-Butanol | 57 | 90 | 40 |
| 1a | Novozym | [OMIM][BF4] | 43 | 98 | 220 |
| 1a | Novozym | [BMIM][PF6]* | 51 | 98 | 360 |
| 1b | R. oryzae | [OMIM][BF4] | 57 | 47 | 4 |
| 1b | Lipozyme | t-Butanol | 54 | 48 | 4 |
| 1b | Novozym | t-Butanol | 52 | 90 | 50 |
| 1b | Novozym | [BMIM][PF6]* | 35 | > 99 | > 340 |
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Oromí-Farrús, M.; Eras, J.; Sala, N.; Torres, M.; Canela, R. Preparation of (S)-1-Halo-2-octanols Using Ionic Liquids and Biocatalysts. Molecules 2009, 14, 4275-4283. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14104275
Oromí-Farrús M, Eras J, Sala N, Torres M, Canela R. Preparation of (S)-1-Halo-2-octanols Using Ionic Liquids and Biocatalysts. Molecules. 2009; 14(10):4275-4283. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14104275
Chicago/Turabian StyleOromí-Farrús, Mireia, Jordi Eras, Núria Sala, Mercè Torres, and Ramon Canela. 2009. "Preparation of (S)-1-Halo-2-octanols Using Ionic Liquids and Biocatalysts" Molecules 14, no. 10: 4275-4283. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14104275
APA StyleOromí-Farrús, M., Eras, J., Sala, N., Torres, M., & Canela, R. (2009). Preparation of (S)-1-Halo-2-octanols Using Ionic Liquids and Biocatalysts. Molecules, 14(10), 4275-4283. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14104275





