On the Chemical Stabilities of Ionic Liquids
Abstract
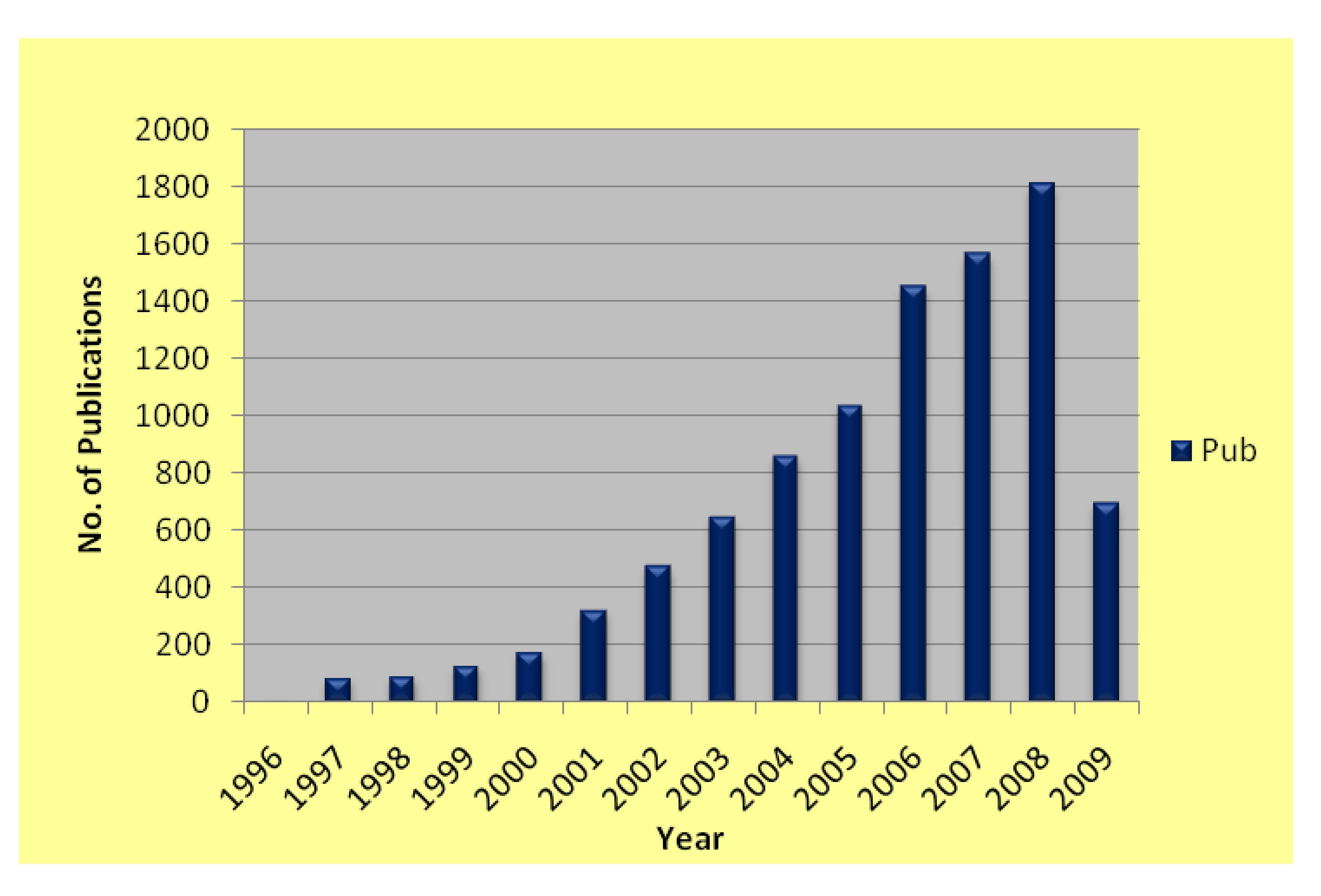
:1. Introduction
2. Scope of This Review


| Property | Organic Solvents | Ionic Liquids | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of solvents | >1,000 | >1,000,000 | |||
| Applicability | Single function | Multifunction | |||
| Catalytic ability | Rare | Common and tunable | |||
| Chirality | Rare | Common and tunable | |||
| Vapour pressure | Obeys the Clausius-Clapeyron Equation | Negligible under normal conditions | |||
| Flammability | Usually flammable | Usually nonflammable | |||
| Solvation | Weakly solvating | Strongly solvating | |||
| Tunability | Limited range of solvents available | Unlimited range means 'designer solvents' | |||
| Polarity | Conventional polarity concepts apply | Polarity concept questionable | |||
| Cost | Normally inexpensive | 2 to 100 times the cost of organic solvents | |||
| Recyclability | Green imperative | Economic imperative | |||
| Viscosity/cP | 0.2-100 | 22-40,000 | |||
| Density/g cm-3 | 0.6-1.7 | 0.8-3.3 | |||
| Refractive index | 1.3-1.6 | 1.5-2.2 |


3. Chemical Stability of Ionic Liquids
3.1. Imidazolium ionic liquids

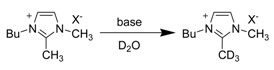
3.1.1. Acidity and deuterium exchange

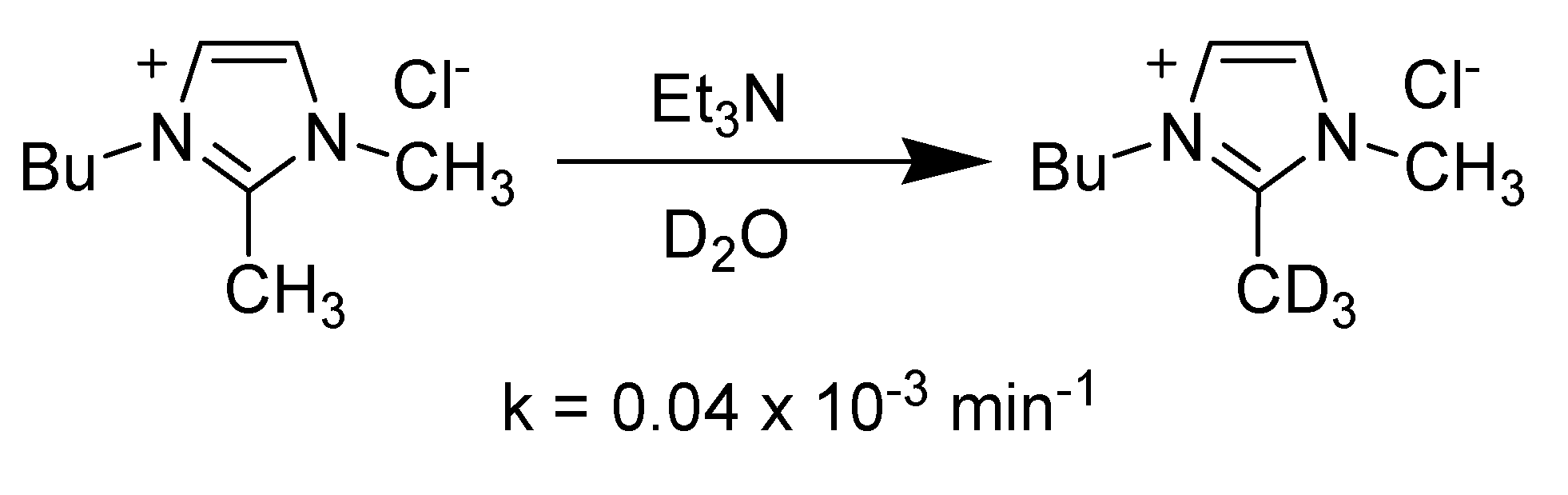
3.1.2. pKa of C2 hydrogen in imidazolium ions
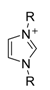 | |||
| Entry | R | Solvent | pKa value |
| 1 | tBu | DMSO | 22.7 |
| 2 | Me | H2O | 23 |
| 3 | Me | DMSO | 21.1 |
| 4 | tBu | DMSO | 22.6 |
| 5 | Ph | DMSO | 16.1 |
| 6 | i Pr(4,5-dimethyl) | DMSO | 24 |
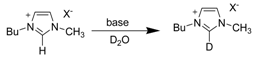 | |||
| Entry | Base | X | Rate (min-1) |
| 1 | None | N(CN)2 | 41 x 10-3 |
| 2 | None | BF4 | 0 |
 | |||
| Entry | Base | X | Rate (min-1) |
| 1 | Et3N | Cl | 0.04 x 10-3 |
| 2 | Et3N | N(CN)2 | 0.04 x 10-3 |
| 3 | KOH | Cl | 2.1 x 10-3 |
| 4 | KOH | N(CN)2 | 1.0 x 10-3 |
 | |||
| Entry | R | X | k (d-1) |
| 1 | mesityl | Cl | 1.06 |
| 2 | isopropyl | Cl | 0.553 |
| 3 | tert-butyl | Cl | << 0.001 |
| 4 | mesityl | Br | 0.176 |
| 5 | isopropyl | Br | << 0.001 |
| 6 | tert-butyl | Br | 0.158 |
3.1.3. Generation and stability of carbenes




3.1.4. Reactions involving C-C bond formation
3.1.4.1. Baylis-Hillman reaction



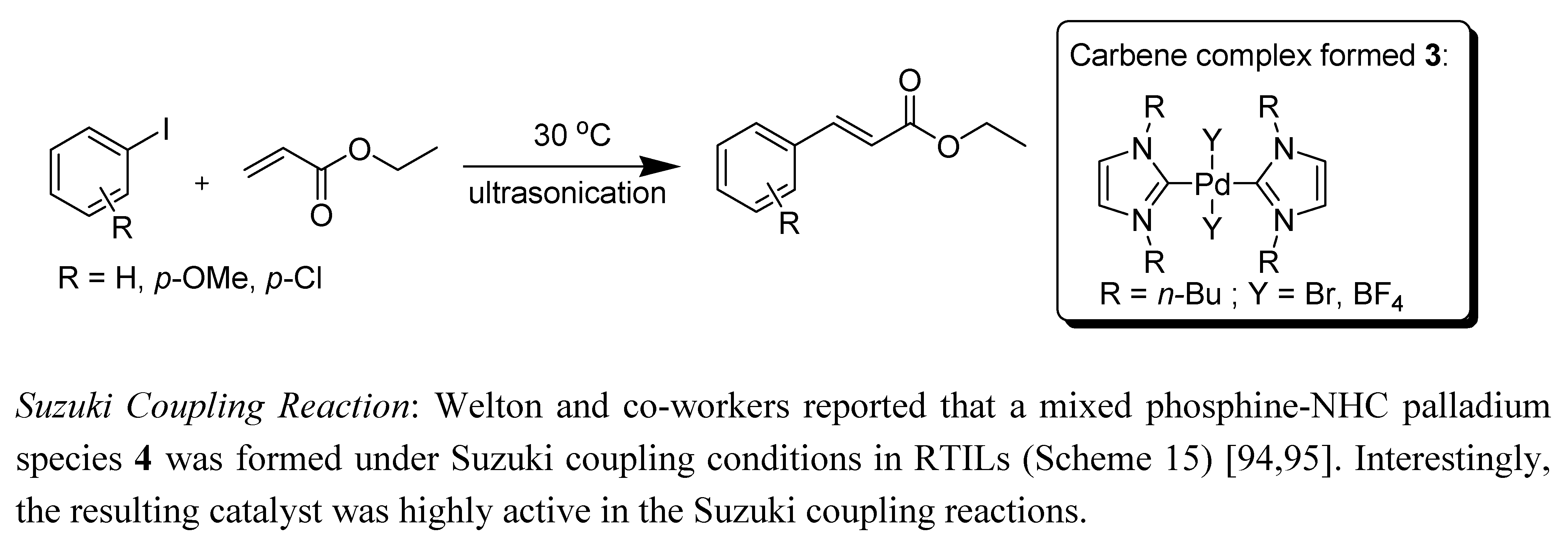
3.1.4.2. Palladium catalysed reactions

| IL | Base | Time (h) | Yield (%)b |
|---|---|---|---|
| [N4,4,4,4][Br] | NaOAc | 18 | 51 |
| [pmim][Br] | NaOAc | 19 | 22 |
| [pbim][Br] | NaOAc | 16 | 11 |
| [bbim][PF6] | NaOAc | 15 | 5 |



| Solvent | System | Time (h) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CH2Cl2 | HNO3 - Ac2O | 1 | 35 |
| [bmim][NTf2] | HNO3 - Ac2O | 1 | 42 |
| [bdmim][NTf2] | HNO3 - Ac2O | 24 | 63 |
| [bmpy][NTf2] | HNO3 - Ac2O | 1 | 93 |


3.2. Phosphonium ionic liquids


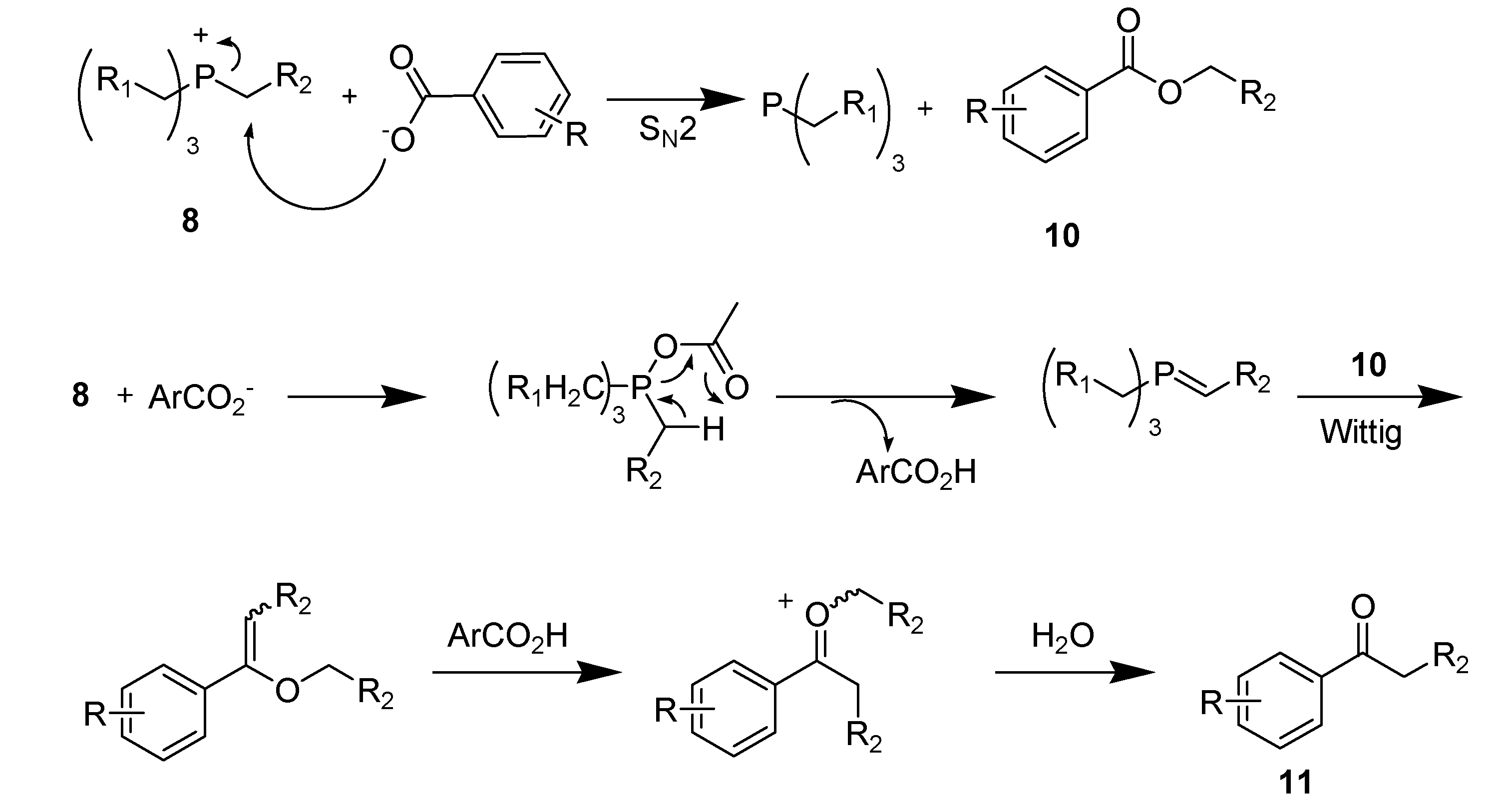
3.3. Quaternary ammonium ionic liquids


3.4. Pyridinium ionic liquids

4. Instability of Anions in Ionic Liquids
 s
s
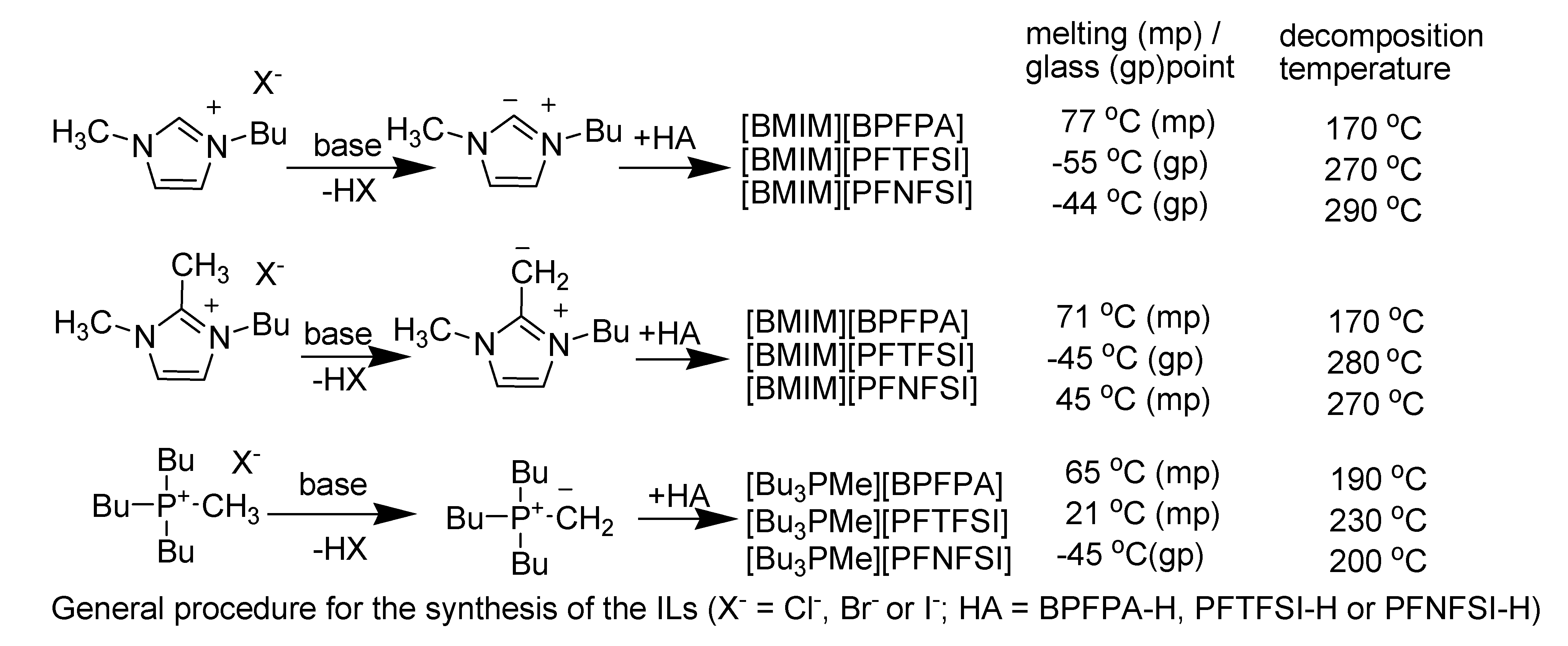
5. Thermal Stability and Decomposition

5.1. Imidazolium ionic liquids
| Ionic liquids | Td range (°C) |
|---|---|
| [bmim][dca], [bmim][Cl], [bmim][Br], [bmim][I], [Bnmim][Cl], [C3mim][Cl], [bmim][Cl], | 240-280 |
| [C5mim][Cl], [eC3mim][I], [mC2mim][Cl], [mC3mim][Cl], [mC4mim][Cl], [mBnmim][Cl] | |
| [bmim][PF6], [bmim][dca], [eC3mim][I], [mBnmim][BF4] | 281-320 |
| [bmim] [BF4], [bmim] [OTf], [bdmim] [PF6], [bdmim][BF4], [C3mim] [BF4], [bmim][BF4], | |
| [Bnmim][BF4], [decmim][BPh4], [eC3mim][BF4], [emim][PF6], [mC2mim][BF4], | 360-400 |
| [mC3mim][BF4], [mC4mim][BF4] | |
| [C5mim][BF4], [bmim][methide], [bmim][NTf2], [emim][BF4], [pmmim][NTf2], [emim][NTf2] | 401-450 |
| [bdmim][N3], [C4mim]2 [ZnBr2Cl2], [pmim][NTf2] | 451-520 |
5.2. Quaternary ammonium ionic liquids
| Entry | Ionic liquid | Td range (o C) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | [NH4][NO3] | 160 |
| 2 | [TMA][BF4] | 688-808 |
| 3 | [TEA][BF4] | 663-745 |
| 4 | [TPA][BF4] | 605-710 |
| 5 | [TBA][BF4] | 598-705 |
5.3. Decomposition
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
- Samples Availability: Not available.
References and Notes
- Xue, H.; Verma, R.; Shreeve, J.M. Review of ionic liquids with fluorine-containing anions. J. Fluorine Chem. 2006, 127, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Verma, R.D.; Meshri, D.T.; Shreeve, J.M. Energetic nitrogen-rich salts and ionic liquids. Angew.Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 3584–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, D.R.; Pringle, J.M.; Johansson, K.M.; Forsyth, S.A.; Forsyth, M. Lewis base ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 2006, 1905–1917. [Google Scholar]
- Canal, J.P.; Ramnial, T.; Dickie, D.A.; Clyburne, J.A.C. From the reactivity of N-heterocyclic carbenes to new chemistry in ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 2006, 1809–1818. [Google Scholar]
- Abedin, S.Z.E.; Endres, F. Ionic liquids: The link to high-temperature molten salts? Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, R.D.; Voth, G.A. Ionic liquids. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 1077–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welton, T. Room-temperature ionic liquids. Solvents for synthesis and catalysis. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2071–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserscheid, P.; Keim, W. Ionic liquids - New “Solutions” for transition metal catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 3772–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, C.M. New developments in catalysis using ionic liquids . Appl. Catal. A. 2001, 222, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Wu, M.; Kou, Y.; Min, E. Ionic liquids: applications in catalysis. Catal.Today 2002, 74, 157–189. [Google Scholar]
- Dupont, J.; de Souza, R.F.; Suarez, P.A.Z. Ionic liquid (molten salt) phase organometallic catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 3667–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plechkova, N.V.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic liquids: "Designer" solvents for green chemistry. In Methods and Reagents for Green Chemistry; Tundo, P., Perosa, A., Zecchini, F., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA,, 2007; pp. 103–130. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, R.D.; Seddon, K.R.; Volkov, S. In Green Industrial Applications of Ionic Liquids,1st ed.; Springer: Norwell, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Earle, M.J.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic liquids. Green solvents for the future. Pure Appl. Chem. 2000, 72, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haumann, M.; Riisager, A. Hydroformylation in room temperature ionic liquids (RTILs): Catalyst and process developments. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 1474–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvulescu, V.I.; Hardacre, C. Catalysis in ionic liquids. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2615–2665. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, M.A.P.; Frizzo, C.P.; Moreira, D.N.; Zanatta, N.; Bonacorso, H.G. Ionic liquids in heterocyclic synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2015–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, W.; Chan, T.H. Ionic-liquid-supported synthesis: A novel liquid-phase strategy for organic synthesis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2006, 39, 897–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Armstrong, D.W. Ionic liquids in separations. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xia, S.; Ma, P. Use of ionic liquids as ‘green’ solvents for extractions. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2005, 80, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, A.E.; Swatloski, R.P.; Reichert, W.M.; Mayton, R.; Sheff, S.; Wierzbicki, A.; Davis, J.H.; Rogers, R.D. Task-specific ionic liquids incorporating novel cations for the coordination and extraction of Hg2+ and Cd2+: Synthesis, characterization, and extraction studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2523–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huddleston, J.G.; Rogers, R.D. Room temperature ionic liquids as novel media for ‘clean’ liquid-liquid extraction. Chem. Commun. 1998, 16, 1765–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapiot, P.; Lagrost, C. Electrochemical reactivity in room-temperature ionic liquids. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2238–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M.; Howlett, P.C.; Pringle, J.M.; Sun, J.; Annat, G.; Neil, W.; Izgorodina, E.I. Ionic liquids in electrochemical devices and processes: Managing interfacial electrochemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, T.; Yoshio, M.; Hamasaki, A.; Mukai, T.; Ohno, H.; Kato, T. Self- organization of room-temperature ionic liquids exhibiting liquid-crystalline bicontinuous cubic phases: Formation of nano-ion channel networks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 10662–10663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, K.; Rao, C.N.R. Use of ionic liquids in the synthesis of nanocrystals and nanorods of semiconducting metal chalcogenides. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 6123–6129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, H. Synthesis of CoPt nanorods in ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 5316–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, W.; Qi, R.; Hu, X. Microwave-assisted synthesis of single-crystalline Tellurium nanorods and nanowires in ionic liquids. Angew.Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 1410–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantwijk, F.V.; Sheldon, R.A. Biocatalysis in ionic liquids. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2757–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, T.L.; Drummond, C.J. Protic ionic liquids: Properties and applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 206–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Hawkins, T.; Rosander, M.; Vaghjiani, G.; Chambreau, S.; Drake, G. Ionic liquids as hypergolic fuels. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 2871–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H. Innovative applications of ionic liquids as “GREEN” engineering liquids. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2006, 193, 1660–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.E. Immobilisation of chiral catalysts: easy recycling of catalyst and improvement of catalytic efficiencies. Ann. Rep. Prog. Chem. Sect. C 2005, 101, 143–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.E. Methodologies in Asymmetric Catalysis; Malhotra, S.V., Ed.; ACS Symposium Series 880; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; pp. 145–160. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.E. Enantioselective chemo- and bio-catalysis in ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 2004, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Mohan, R.S.; Scott, J.L. Reactivity of ionic liquids. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 2363–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennis, E.; Handy, S.T. The chemistry of the C2 position of imidazolium room temperature ionic liquids. Curr.Org. Syn. 2007, 4, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, E.A.; Abraham, M.; Kini, V.; Al-Ghafri, M.; Abushaban, A. Cytotoxicity of the ionic liquid, 1-N-butyl-3-methyl imidazolium chloride. Res. Commun. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2002, 7, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Holbrey, J.D.; Seddon, K.R. ionic liquids. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 1999, 1, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, K.R. Ionic liquids for clean technology. J. Chem. Tech. Biotech. 1997, 68, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R. Catalytic reactions in ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 2001, 2399–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, C.M. New developments in catalysis using ionic liquids. Appl. Catal.A. 2001, 222, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helene, O.B; Magna, L. Ionic liquids: Perspectives for organic and catalytic reactions. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2002, 182, 419–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, J.; de Souza, R.F.; Suarez, P.A.Z. Ionic liquid (Molten Salt) phase organometallic catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 3667–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walden, P. Ueber die Molekulargrösse und elektrische Leitfähigkeit einiger geschmolzenen salze. Bull. Acad. Imper. Sci. St. Petersburg 1914, 8, 405–422. [Google Scholar]
- Chum, H.L.; Koch, V.R.; Miller, L.L.; Osteryoung, R.A. Electrochemical scrutiny of organometallic iron complexes and hexamethylbenzene in a room temperature molten salt. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975, 97, 3264–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, J.S.; Levisky, J.A.; Wilson, R.A.; Hussey, C.L. Electron transfer. 52. Reactions of dihydroriboflavin with metal-center oxidants. Inorg. Chem. 1982, 21, 1236–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, J.S.; Zaworotko, M.J. Air and water stable 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium based ionic liquids. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1992, 965–967. [Google Scholar]
- Natalia, V.P; Seddon, K.R. Applications of ionic liquids in the chemical industry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, M. Green Chemistry: An Introductory Text; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkes, J.S. A short history of ionic liquids-from molten salts to neoteric solvents. Green Chem. 2002, 4, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freemantle, M. Ionic liquids in organic synthesis. Chem. Eng. News 2004, 82, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- .
- Smiglak, M.; Reichert, W.M.; Holbrey, J.D.; Wilkes, J.S.; Sun, L.; Thrasher, J.S.; Kirichenko, K.; Singh, S.; Katritzky, A.R.; Rogers, R.D. Combustible ionic liquids by design: is laboratory safety another ionic liquid myth? Chem. Commun. 2006, 2554–2556. [Google Scholar]
- Holbrey, J.D.; Seddon, K.R. he phase behaviour of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborates; Ionic liquids and ionic liquid crystals. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1999, 2133–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionic Liquids in Synthesis; Wasserscheid, P.; Welton, T. (Eds.) Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003.
- Ranu, B.C.; Banerjee, S. . Ionic liquid as catalyst and reaction medium. The dramatic influence of a task-specific ionic liquid, [bmIm]OH, in Michael addition of active methylene compounds to conjugated ketones, carboxylic esters, and nitriles. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 3049–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Yang, X.; Fei, Z.; Li, Y.; Kou, Y.; Dyson, P.J. Solvent-enhanced coupling of sterically hindered reagents and aryl chlorides using functionalized ionic liquids. Organometallics 2009, 28, 937–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, S.T. Room temperature ionic liquids: Different classes and physical properties. Curr. Org. Chem. 2005, 9, 959–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canal, J.P.; Ramnial, T.; Dickie, D.A.; Clyburne, J.A.C. From the reactivity of N-heterocyclic carbenes to new chemistry in ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 2006, 1809–1818. [Google Scholar]
- Olofson, R.A.; Thompson, W.R.; Michelman, J.S. Heterocyclic nitrogen ylides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1964, 86, 1865–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, S.T.; Okello, M. The 2-position of imidazolium ionic liquids: Substitution and exchange. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 1915–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alder, R.W.; Allen, P.R.; Williams, S.J. Stable carbenes as strong bases. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1995, 1267–1268. [Google Scholar]
- Amyes, T.L.; Diver, S.T.; Richard, J.P.; Rivas, F.M.; Toth, K. Formation and stability of N-heterocyclic carbenes in water: The carbon acid pKa of imidazolium cations in aqueous solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 4366–4374. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.J.; Streitwieser, A. Basicity of a stable carbene, 1,3-Di-tert-butylimidazol-2-ylidene, in THF. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 5757–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magill, A.M.; Cavell, K.J.; Yates, B.F. Basicity of nucleophilic carbenes in aqueous and nonaqueous solvents theoretical predictions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 8717–8724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahlbusch, T.; Frank, M.; Schatz, J.; Schuehle, D.T. Kinetic acidity of supramolecular imidazolium salts-effects of substituent, preorientation, and counterions on H/D exchange rates. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 1688–1691. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.Y.; Chu, Y.H. 1-Butyl-2,3-trimethyleneimidazolium bis(trifluoromethyl sulfonyl) imide ([b-3C-im][NTf2]): a new, stable ionic liquid. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 1575–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, R.R.; Mansour, T.S.; Savard, S. Acidity measurements in THF. V. Heteroaromatic compounds containing 5-membered rings. Can. J. Chem. 1985, 63, 3505–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanzlick, H.W.; Schikora, E. Ein neuer Zugang zur Carben-Chemie. Angew.Chem. 1960, 72, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduengo, A.J., III; Harlow, R.L.; Kline, M. A stable crystalline carbene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 361–363. [Google Scholar]
- Arduengo, A.J., III. Looking for stable carbenes: The difficulty in starting anew. Acc. Chem. Res. 1999, 32, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amyes, T.L.; Diver, S.T.; Richard, J.P.; Rivas, F.M.; Toth, K. Formation and stability of N-heterocyclic carbenes in water: The carbon acid pKa of imidazolium cations in aqueous solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 4366–4374. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Justes, D.R.; Cooks, G.R. Proton affinities of N-heterocyclic carbene super bases. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 3949–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduengo, A.J.; Goerlich, J.R.; Marshall, W.J. A stable diaminocarbene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 11027–11028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcarazo, M.; Roseblade, S.J.; Alonso, E.; Fernandez, R.; Alvarez, E.; Lahoz, F.J.; Lassaletta, J.M. 1,3-Bis(N,N-dialkylamino)imidazolin-2-ylidenes: Synthesis and reactivity of a new family of stable N-heterocyclic carbenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 13242–13243. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, J.N.; Afonso, C.A.M.; Santos, A.G. Ionic liquids as a recyclable reaction medium for the Baylis-Hillman reaction. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 4189–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, V.K.; Emme, I.; Mereu, A. Unexpected side reactions of imidazolium-based ionic liquids in the base-catalysed Baylis–Hillman reaction. Chem. Commun. 2002, 1612–1613. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, J.N.; Afonso, C.A.M.; Santos, A.G. Ionic liquids as a recyclable reaction medium for the Baylis-Hillman reaction. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 4189–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.C.; Yen, Y.H.; Ch, Y.H. Baylis–Hillman reaction in [bdmim][PF6] ionic liquid. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 4673–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, T.; Kude, K.; Hayase, S.; Kawatsura, M. Design of ionic liquids as a medium for the Grignard reaction. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 7774–7777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurcik, V.; Wilhelm, R. An imidazolinium salt as ionic liquid for medium and strong bases. Green Chem. 2005, 7, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, S.T. Grignard reactions in imidazolium ionic liquids. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 4659–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennis, E.; Handy, S.T. The chemistry of the C2 position of imidazolium room temperature ionic liquids. Curr.Org. Synt. 2007, 4, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, G.; Schiehser, S.; Potthast, A.; Rosenau, T. Side reaction of cellulose with common 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium-based ionic liquids. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 7322–7324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, A.J.; Earle, M.J.; Holbrey, J.D.; McCormac, P.B.; Seddon, K.R. The Heck Reaction in ionic liquids: A multiphasic catalyst system. Org. Lett. 1999, 1, 997–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, W.A.; Böhm, V.P.W. Heck reaction catalyzed by phospha-palladacycles in non-aqueous ionic liquids. J. Organomet. Chem. 1999, 572, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, V.P.W.; Herrmann, W.A. Nonaqueous ionic liquids: Superior reaction media for the catalytic Heck-vinylation of chloroarenes. Chem. Eur. J. 2000, 6, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chen, W.; Xiao, J. Heck reaction in ionic liquids and the in situ identification of N-heterocyclic carbene complexes of Palladium. Organometallics 2000, 19, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, W.A.; Bohm, V.P.W.; Reisinger, C.P. Application of palladacycles in Heck type reactions. J. Organomet. Chem. 1999, 576, 23–41. [Google Scholar]
- Gründeman, S.; Kovacevic, A.; Albrecht, M.; Faller, J.W.; Crabtree, R.H. Abnormal ligand binding and reversible ring hydrogenation in the reaction of imidazolium salts with IrH5(PPh3)2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 10473–10481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuiness, D.S.; Cavell, K.J.; Skelton, B.W.; White, A.H. Zerovalent palladium and nickel complexes of heterocyclic carbenes: Oxidative addition of organic halides, carbon-carbon coupling processes, and the Heck reaction. Organometallics 1999, 18, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, R.R.; Rajagopal, R.; Srinivasan, K.V. Ultrasound promoted C-C bond formation: Heck reaction at ambient conditions in room temperature ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 2001, 1544–1545. [Google Scholar]
- Mathews, C.J.; Smith, P.J.; Welton, T.; White, A.J.P.; Williams, D.J. In situ formation of mixed phosphine-imidazolylidene Palladium complexes in room-temperature ionic liquids. Organometallics 2001, 20, 3848–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLachlan, F.; Mathews, C.J.; Smith, P.J.; Welton, T. Palladium-catalyzed Suzuki cross-coupling reactions in ambient temperature ionic liquids: Evidence for the importance of palladium imidazolylidene complexes. Organometallics 2003, 22, 5350–5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.; Han, S.; Livingston, A.G. The effect of ionic liquids on product yield and catalyst stability. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 1338–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirieix, J.; Ossberger, M.; Betzemeier, B.; Knochel, P. Palladium catalyzed cross-couplings of organozincs in ionic liquids. Synlett. 2000, 1613–1615. [Google Scholar]
- Law, M.C.; Wong, K.Y.; Chan, T.H. Organometallic reactions in ionic liquids. Alkylation of aldehydes with diethylzinc. Green Chem. 2004, 6, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
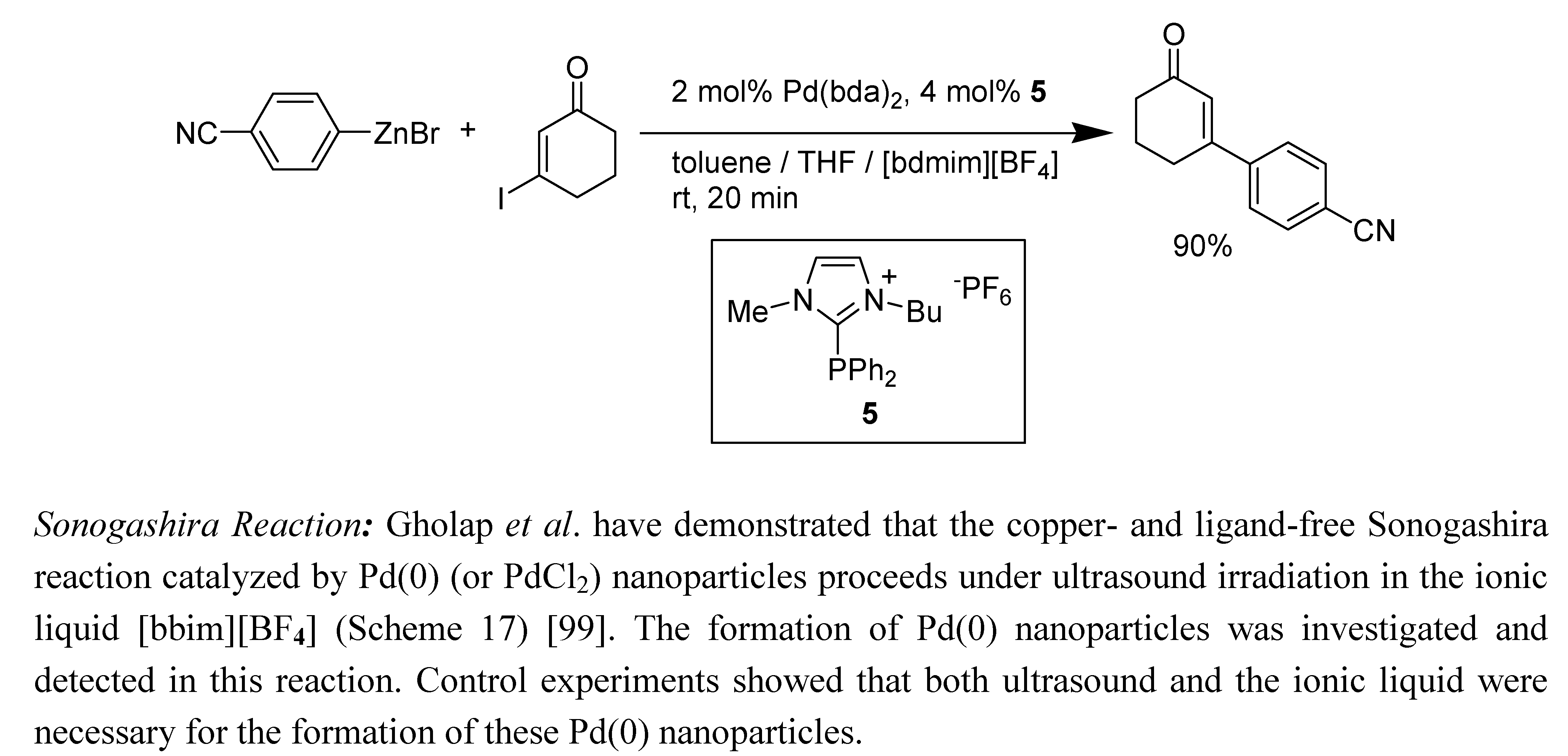
- Gholap, A.R.; Venkatesan, K.; Pasricha, R.; Daniel, T.; Lahoti, R.; Srinivasan, K.V. Copper- and ligand-free Sonogashira reaction catalyzed by Pd(0) nanoparticles at ambient conditions under ultrasound irradiation. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 4869–4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magna, L.; Chauvin, Y.; Niccolai, G.P.; Basset, J.M. The importance of imidazolium substituents in the use of imidazolium-based room-temperature ionic liquids as solvents for Palladium-catalyzed telomerization of butadiene with methanol. Organometallics 2003, 22, 4418–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, M.J.; Katdare, S.P.; Seddon, K.R. Paradigm confirmed: The first use of ionic liquids to dramatically influence the outcome of chemical reactions. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, N.L.; Llopis-Mestre, V. Aromatic nitrations in ionic liquids: The importance of cation choice. Chem. Commun. 2003, 2812–2813. [Google Scholar]
- Chiappe, C.; Capraro, D.; Conte, V.; Pieraccini, D. Stereoselective halogenations of alkenes and alkynes in ionic liquids. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 1061–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, M.C.; Liang, Y.M.; Chu, Y.H. Synthesis of fused tetrahydro-β-carbolinequinoxalinones in 1-n-butyl-2,3-dimethylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethyl sulfonyl) imide ([bdmim][NTf2]) and 1-n-butyl-2,3-dimethylimidazolium perfluorobutylsulfonate ([bdmim][PFBuSO3]) ionic liquids. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 6131–6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, H.C.; Tseng, M.C.; Chu, Y.H. Bicyclic imidazolium-based ionic liquids: synthesis and characterization. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 1644–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.L.; Cheng, J.Y.; Chu, Y.H. Microwave-accelerated Claisen rearrangement in bicyclic imidazolium [b-3C-im][NTf2] ionic liquid. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 10949–10957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNulty, J.; Capretta, A.; Wilson, J.; Dyck, J.; Adjabeng, G.; Robertson, A.J. Suzuki cross-coupling reactions of aryl halides in phosphonium salt ionic liquid under mild conditions. Chem. Commun. 2002, 1986–1987. [Google Scholar]
- Gerritsma, D.A.; Robertson, A.; McNulty, A.; Capretta, A. Heck reactions of aryl halides in phosphonium salt ionic liquids: library screening and applications. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 7629–7631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradaric, C.J.; Downard, A.; Kennedy, C.; Robertson, A.J.; Zhou, Y. Industrial preparation of phosphonium ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2003, 5, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Varma, R.S. Tetrahaloindate(III)-based ionic liquids in the coupling reaction of carbon dioxide and epoxides to generate cyclic carbonates: H-bonding and mechanistic studies. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 7882–7891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramnial, T.; Daisuke, D.I.; Clyburne, J.A.C. Phosphonium ionic liquids as reaction media for strong bases. Chem. Commun. 2005, 325–327. [Google Scholar]
- Gorodetsky, B.; Ramnial, T.; Branda, N.R.; Clyburne, J.A.C. Electrochemical reduction of an imidazolium cation: a convenient preparation of imidazol-2-ylidenes and their observation in an ionic liquid. Chem. Commun. 2004, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar]
- Ramnial, T.; Taylor, S.A.; Bender, M.L.; Gorodetsky, B.; Lee, P.T.K.; Dickie, D.A.; McCollum, B.M.; Pye, C.C.; Walsby, C.J.; Clyburne, J.A.C. Carbon-centered strong bases in phosphonium ionic liquids. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 801–812. [Google Scholar]
- Ramnial, T.; Ino, D.D.; Clyburne, J.A.C. Phosphonium ionic liquids as reaction media for strong bases. 2005. [Google Scholar]
- .
- Tseng, M.C.; Kan, H.C.; Chu, Y.H. Reactivity of trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium chloride, a room-temperature phosphonium ionic liquid. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 9085–9089. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, S.J.; Criddle, W.J. Pyrolysis-gas chromatography of quaternary phosphonium compounds. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 1985, 7, 337–349. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, S.J.; Criddle, W.J. Anion effects in the pyrolysis-gas chromatography of quaternary phosphonium compounds. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 1985, 9, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel, S.; Weiner, J. Ueber einige Abkömmlinge des Propylamins. Ber. 1888, 21, 2669–2679. [Google Scholar]
- Walden, P. Ueber die Molekulargrösse und elektrische Leitfähigkeit einiger geschmolzenen salze. Bull. Acad. Sci. St. Petersburg 1914, 405–422. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, T.; Maruo, T.; Marukane, S.; Takagi, K. Ionic liquids containing carbonate solvent as electrolytes for lithium ion cells. J. Power Sources 2004, 138, 253–261. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, H.; Sakaebe, H.; Tatsumi, K. Preparation of room temperature ionic liquids based on aliphatic onium cations and asymmetric amide anions and their electrochemical properties as a lithium battery electrolyte. J. Power Sources 2005, 146, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.B.; Takeda, M.; U, M. New hydrophobic ionic liquids based on perfluoroalkyltrifluoroborate anions. J. Fluor. Chem. 2004, 125, 471–476. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.B.; Matsumoto, H.; Tatsumi, K. Low-melting, low-viscous, hydrophobic ionic liquids: Aliphatic quaternary ammonium salts with perfluoroalkyltrifluoroborates. Chem. Eur. J. 2005, 11, 752–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.B.; Matsumoto, H.; Tatsumi, K. A new class of hydrophobic ionic liquids: Trialkyl(2-methoxyethyl)ammonium perfluoroethyltrifluoroborate. Chem. Lett. 2004, 33, 886–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.B.; Matsumoto, H.; Tatsumi, K. Cyclic quaternary ammonium ionic liquids with perfluoroalkyltrifluoroborates: Synthesis, characterization, and properties. Chem. Eur. J. 2006, 12, 2196–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calò, V.; Nacci, A.; Monopoli, A. Effects of ionic liquids on Pd-catalysed carbon-carbon bond formation. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 3791–3802. [Google Scholar]
- Calò, V.; Nacci, A.; Monopoli, A.; Lopez, L.; di Cosmo, A. Heck reaction of β-substituted acrylates in ionic liquids catalyzed by a Pd-benzothiazole carbene complex. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 6071–6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calò, V.; Nacci, A.; Monopoli, A.; Laera, S.; Cioffi, N. Pd nanoparticles catalyzed stereospecific synthesis of β-aryl cinnamic esters in ionic liquids. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 2929–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.E. Fused organic salts. III. Chemical stability of molten tetra-n-alkylammonium salts. Medium effects on thermal R4N+X- decomposition. RBr + I- = RI + Br- equilibrium constant in fused salt medium. J. Org. Chem. 1965, 30, 2760–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolthoff, I.M.; Bruckenstein, S.; Chantooni, M.K. Acid-base equilibria in acetonitrile. spectrophotometric and conductometric determination of the dissociation of various acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1961, 83, 3927–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.O. Correlation of relative rates and equilibria with a double basicity scale. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1954, 76, 1540–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magna, L.; Chauvin, Y.; Niccolai, G.P.; Basset, J.M. The importance of imidazolium substituents in the use of imidazolium-based room-temperature ionic liquids as solvents for Palladium-catalyzed telomerization of butadiene with methanol. Organometallics 2003, 22, 4418–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutney, J.P.; Greenhouse, R. The protection and deprotection of the pyridine nitrogen. Synth. Commun. 1975, 5, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deady, L.W.; Finlayson, W.L.; Korytky, O.L. Steric effects in forward and reverse Menschutkin reactions of some pyridines, quinolines and thiazoles. Aust. J. Chem. 1979, 32, 1735–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strehmel, V.; Laschewsky, A.; Wetzel, H.; Görnitz, E. Free radical polymerization of n-butyl methacrylate in ionic liquids. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrey, J.D.; Reichert, W.M.; Swatloski, R.P.; Broker, G.A.; Pitner, W.R.; Seddon, K.R.; Rogers, R.D. Efficient, halide free synthesis of new, low cost ionic liquids: 1,3-dialkylimida-zolium salts containing methyl and ethyl sulfate anions. Green Chem. 2002, 4, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserscheid, P.; Hal, V.R.; Bösmann, A. 1-n-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium ([bmim]) octylsulfate-an even ‘greener’ ionic liquid. Green Chem. 2002, 4, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huddleston, J.G.; Visser, A.E.; Reichert, W.M.; Willauer, H.D.; Broker, G.A.; Rogers, R.D. Characterization and comparison of hydrophilic and hydrophobic room temperature ionic liquids incorporating the imidazolium cation. Green Chem. 2001, 3, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- .
- Swatloski, R.P.; Holbrey, J.D.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic liquids are not always green: hydrolysis of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate. Green Chem. 2003, 5, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, T.; Sundermeyer, J. Three novel anions based on pentafluorophenyl amine combined with two new synthetic strategies for the synthesis of highly lipophilic ionic liquid. Chem. Commun. 2009, 2914–2916. [Google Scholar]
- Scammells, P.J.; Scott, J.L.; Singer, R.D. Ionic liquids: The neglected issues. Aust. J. Chem. 2005, 58, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Sesto, R. E.; McCleskey, T.M.; Macomber, C.; Ott, K.C.; Koppisch, A.T.; Baker, G.A.; Burrell, A.K. Limited thermal stability of imidazolium and pyrrolidinium ionic liquids. Thermochim.Acta 2009, 491, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, B.K.M.; Chang, N.H.; Grimmett, M.R. The synthesis and thermolysis of imidazole quaternary salts. Aust. J. Chem. 1977, 30, 2005–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busi, S.; Lahtinen, M.; Kärnä, M.; Valkonen, J.; Kolehmainen, E.; Rissanen, K. Synthesis, characterization and thermal properties of nine quaternary dialkyldiaralkylammonium chlorides. J. Mol. Struct. 2006, 787, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredlake, C.P.; Crosthwaite, J.M.; Hert, D.G.; Aki, S.N.V.K.; Brennecke, J.F. Thermophysical properties of imidazolium-based ionic liquids. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2004, 49, 954–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Varma, R.S. Tetrahaloindate(III)-based ionic liquids in the coupling reaction of carbon dioxide and epoxides to generate cyclic carbonates: H-bonding and mechanistic studies. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 7882–7891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooster, T.J.; Johanson, K.M.; Fraser, K.J.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Scott, J.L. Thermal degradation of cyano containing ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, M.R.R.; Krishnan, K.; Ninan, K.N.; Krishnamurthy, V.N. Thermal decomposition of tetraalkyl ammonium tetrafluoroborates. Thermochim. Acta 1997, 297, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, B.K.M.; Chang, N.; Grimmett, M.R. The synthesis and thermolysis of imidazole quaternary salts. Aust. J. Chem. 1977, 30, 2005–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, H.; Ishimura, S.; Kumai, M. Thermal decomposition behaviors of imidazolium-type ionic liquids studied by pyrolysis-gas chromatography. Anal. Sci. 2008, 24, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxley, J.D.; Prozorov, T.; Suslick, K.S. Sonochemistry and sonoluminescence of room-temperature ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 11138–11139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, S.U. A systematic study of the thermal decomposition of tetraalkylammonium haloborates. J. Thermal Anal. 1980, 18, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambiar, P.R.; Jain, S.R. Thermal characterization of tetramethylphosphonium perchlorate, nitrate and picrate. Thermochim. Acta 1974, 9, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambiar, P.R.; Verneker, V.R.P.; Jain, S.R. Explosive sensitivity of methylammonium perchlorates. J. Thermal Anal. 1975, 8, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernak, J.; Sobaszkiewicz, K.; Foksowicz-Flaczyk, J. Ionic liquids with symmetrical dialkoxymethyl-substituted imidazolium cations. Chem. Eur. J. 2004, 10, 3479–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernak, J.; Goc, I.; Mirska, I. Anti-microbial activities of protic ionic liquids with lactate anion. Green Chem. 2004, 6, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkrob, I.A.; Chemerisov, S.D. The initial stages of radiation damage in ionic liquids and ionic liquid-based extraction systems. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 11786–11793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepnowski, P.; Zaleska, A. Comparison of different advanced oxidation processes for the degradation of room temperature ionic liquids. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2004, 170, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Sowmiah, S.; Srinivasadesikan, V.; Tseng, M.-C.; Chu, Y.-H. On the Chemical Stabilities of Ionic Liquids. Molecules 2009, 14, 3780-3813. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14093780
Sowmiah S, Srinivasadesikan V, Tseng M-C, Chu Y-H. On the Chemical Stabilities of Ionic Liquids. Molecules. 2009; 14(9):3780-3813. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14093780
Chicago/Turabian StyleSowmiah, Subbiah, Venkatesan Srinivasadesikan, Ming-Chung Tseng, and Yen-Ho Chu. 2009. "On the Chemical Stabilities of Ionic Liquids" Molecules 14, no. 9: 3780-3813. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14093780




