MYB Transcription Factors Regulate Glucosinolate Biosynthesis in Different Organs of Chinese Cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Identification of Transcription Factors Involved in GSL Biosynthesis
| Group name | AGI | BrID | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dof1.1 | At1g07640 | Bra031588 (Dof1.1-1) | Skirycz et al. [12] |
| Bra030696 (Dof1.1-2) | |||
| IQD1-1 | At3g09710 | Bra034081 (IQD1-1-1) | Levy et al. [10] |
| Bra001299 (IQD1-1-2) | |||
| MYB28 | At5g61420 | Bra012961 (MYB28-1) | Gigolashvili et al. [14]; Hirai et al. [16] |
| Bra035929 (MYB28-2) | |||
| Bra029311 (MYB28-3) | |||
| MYB29 | At5g07690 | Bra005949 (MYB29) | Gigolashvili et al. [15]; Hirai et al. [16] |
| MYB34 | At5g60890 | Bra013000 (MYB34-1) | Celenza et al. [9] |
| Bra035954 (MYB28-2) | |||
| Bra029350 (MYB28-3) | |||
| Bra029349 (MYB28-4) | |||
| MYB51 | At1g18570 | Bra025666 (MYB51-1) | Gigolashvili et al. [13] |
| Bra031035 (MYB51-2) | |||
| Bra016553 (MYB51-3) | |||
| MYB122 | At1g74080 | Bra015939 (MYB122-1) | Gigolashvili et al. [13] |
| Bra008131 (MYB122-2) |

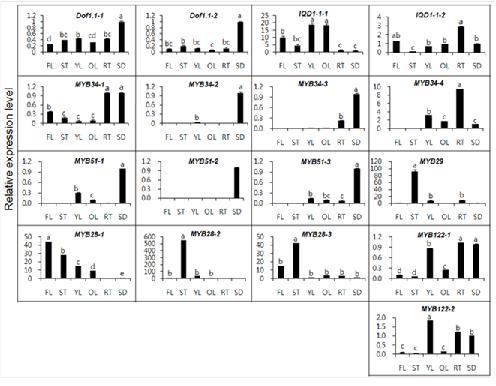
2.2. Gene Expression of MYB TFs in Different Organs


2.3. GSLs Analysis of Different Organs
| Trivial name * | Systematic names | Compound groups | [M+H]+ m/z | Response factor [2, ISO 1992] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Progoitrin | 4-Methylsulfinylbutyl GSL | Aliphatic | 310 | 1.09 |
| Sinigrin | 2-Propenyl GSL | Aliphatic | 280 | 1.00 |
| Glucoalyssin | 5-Methylsufinylpentyl GSL | Aliphatic | 372 | 1.07 |
| Gluconapin | 3-Butenyl GSL | Aliphatic | 294 | 1.11 |
| Glucobrassicanapin | Pent-4-enyl GSL | Aliphatic | 308 | 1.15 |
| Unknown 1 | Unknown | Unknown | 327 | 1.00 |
| Unknown 2 | Unknown | Unknown | 292 | 1.00 |
| Glucobrassicin | 3-Indolymethyl GSL | Indolic | 369 | 0.29 |
| 4-Methoxyglucobrassicin | 4-Methoxy-3-indolylmethyl GSL | Indolic | 399 | 0.25 |
| Neoglucobrasscin | N-Methoxy-3-indolylmethyl GSL | Indolic | 399 | 0.20 |
| Gluconasturtiin | 2-Phenethyl GSL | Aromatic | 344 | 0.95 |
| Trivial name | Flower | Stem | Young leaf | Old leaf | Root | Seed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Progoitrin | 5.53 ± 0.04 | 3.78 ± 0.02 | 4.03 ± 0.10 | 1.11 ± 0.05 | 1.11 ± 0.03 | 3.26 ± 0.21 |
| Sinigrin | 2.23 ± 0.22 | 1.17 ± 0.02 | 0.34 ± 0.03 | 0.11 ± 0.03 | 0.12 ± 0.00 | 3.58 ± 0.79 |
| Glucoalyssin | 0.68 ± 0.22 | 0.18 ± 0.12 | 0.22 ± 0.10 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 0.47 ± 0.21 |
| Gluconapin | 4.51 ± 0.25 | 1.35 ± 0.10 | 1.57 ± 0.19 | 0.34 ± 0.03 | 0.42 ± 0.02 | 60.13 ± 1.76 |
| Glucobrassicanapin | 10.85 ± 0.20 | 4.61 ± 0.18 | 4.32 ± 0.16 | 0.89 ± 0.04 | 1.73 ± 0.04 | 4.92 ± 0.90 |
| Unknown 1 | 1.08 ± 0.11 | 0.99 ± 0.08 | 0.99 ± 0.10 | 0.29 ± 0.04 | 0.62 ± 0.07 | 0.41 ± 0.08 |
| Unknown 2 | 0.52 ± 0.23 | 0.47 ± 0.24 | 0.50 ± 0.22 | 0.16 ± 0.00 | ND | 7.34 ± 1.34 |
| Glucobrassicin | 1.96 ± 0.44 | 0.92 ± 0.14 | 0.43 ± 0.05 | 0.37 ± 0.20 | 0.72 ± 0.05 | 0.90 ± 0.09 |
| 4-Methoxyglucobrassicin | 0.20 ± 0.03 | 0.41 ± 0.05 | 1.14 ± 0.06 | 0.15 ± 0.04 | 0.19 ± 0.02 | 1.27 ± 0.03 |
| Neoglucobrassicin | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 0.08 ± 0.04 | 0.14 ± 0.04 | 0.09 ± 0.04 | 0.30 ± 0.00 | 0.12 ± 0.02 |
| Gluconasturtiin | 2.10 ± 0.13 | 0.80 ± 0.09 | 1.89 ± 0.16 | 0.65 ± 0.23 | 8.42 ± 0.16 | 0.91 ± 0.12 |
| Total | 29.81 ± 0.69 | 14.77 ± 0.53 | 15.59 ± 0.42 | 4.30 ± 0.38 | 13.66 ± 0.23 | 83.38 ± 2.98 |
3. Experimental
3.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
3.2. Bioinformatic Analysis
3.3. cDNA Synthesis and Quantitative Real-time PCR Analysis
3.4. Chemicals
3.5. Extraction of Desulfo-glucosinolates (DS-GSLs) and HPLC Analysis
3.6. LC/ESI-MS Analysis for Quantitation of Desulfoglucosinolates (DS-GSLs)
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodman, J.E.; Karol, K.G.; Price, R.A.; Sytsma, K.J. Molecules, morphology, and Dahlgren’s expanded order Capparales. Syst. Bot. 1996, 21, 289–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, D.B. Glucosinolates, structures and analysis in food. Anal. Methods 2010, 2, 310–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkier, B.A.; Gershenzon, J. Biology and biochemistry of glucosinolates. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 303–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahey, J.W.; Zhang, Y.; Talalay, P. Broccoli sprouts: An exceptionally rich source of inducers of enzymes that protect against chemical carcinogens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 10367–10372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahey, J.W.; Haristoy, X.; Dolan, P.M.; Kensler, T.W.; Scholtus, I.; Stephenson, K.; Talalay, P.; Lozniewski, A. Sulforaphane inhibits extracellular, intracellular, and antibiotic-resistant strains of Helicobacter pylori and prevents benzo[a]pyrene-induced stomach tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7610–7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talalay, P.; Fahey, J.W. Phytochemicals from cruciferous plants protect against cancer by modulating carcinogen metabolism. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 3027S–3033S. [Google Scholar]
- Grubb, C.D.; Abel, S. Glucosinolate metabolism and its control. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittstock, U.; Halkier, B.A. Glucosinolate research in the Arabidopsis era. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celenza, J.L.; Quiel, J.A.; Smolen, G.A.; Merrikh, H.; Silvestro, A.R.; Normanly, J.; Bender, J. The Arabidopsis ATR1Myb transcription factor controls indolic glucosinolate homeostasis. Plant Physiol. 2005, 137, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.; Wang, Q.; Kaspi, R.; Parrella, M.P.; Abel, S. Arabidopsis IQD1, a novel calmodulin-binding nuclear protein, stimulates glucosinolate accumulation and plant defense. Plant J. 2005, 43, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama-Nakashita, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Tohge, T.; Saito, K.; Takahashi, H. Arabidopsis SLIM1 is a central transcriptional regulator of plant sulfur response and metabolism. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 3235–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skirycz, A.; Reichelt, M.; Burow, M.; Birkemeyer, C.; Rolcik, J.; Kopka, J.; Zanor, M.I.; Gershenzon, J.; Strnad, M.; Szopa, J.; Mueller-Roeber, B.; Witt, I. DOF transcription factor AtDof1.1 (OBP2) is part of a regulatory network controlling glucosinolate biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2006, 47, 10–24. [Google Scholar]
- Gigolashvili, T.; Berger, B.; Mock, H.P.; Müller, C.; Weisshaar, B.; Flügge, U.I. The transcription factor HIG1/MYB51 regulates indolic glucosinolate biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2007, 50, 886–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigolashvili, T.; Yatusevich, R.; Berger, B.; Müller, C.; Flügge, U.I. The R2R3-MYB transcription factor HAG1/MYB28 is a regulator of methionine-derived glucosinolate biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2007, 51, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigolashvili, T.; Engqvist, M.; Yatusevich, R.; Müller, C.; Flügge, U.I. HAG2/MYB76 and HAG3/MYB29 exert a specific and coordinated control on the regulation of aliphatic glucosinolate biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol. 2008, 177, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, M.Y.; Sugiyama, K.; Sawada, Y.; Tohge, T.; Obayashi, T.; Suzuki, A.; Araki, R.; Sakurai, N.; Suzuki, H.; Aoki, K.; et al. Omics-based identification of Arabidopsis Myb transcription factors regulating aliphatic glucosinolate biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 6478–6483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sønderby, I.E.; Hansen, B.G.; Bjarnholt, N.; Ticconi, C.; Halkier, B.A.; Kliebenstein, D.J. A systems biology approach identifies a R2R3 MYB gene subfamily with distinct and overlapping functions in regulation of aliphatic glucosinolates. PLoS One 2007, 2, e1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malitsky, S.; Blum, E.; Less, H.; Venger, I.; Elbaz, M.; Morin, S.; Eshed, Y.; Aharoni, A. The transcript and metabolite networks affected by the two clades of Arabidopsis glucosinolate biosynthesis regulators. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 2021–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underhill, E.W.; Wetter, L.R.; Chisholm, M.D. Biosynthesis of glucosinolates. Biochem. Soc. Symp. 1973, 38, 303–326. [Google Scholar]
- Yatusevich, R.; Mugford, S.G.; Matthewman, C.; Gigolashvili, T.; Frerigmann, H.; Delaney, S.; Koprivova, A.; Flügge, U.I.; Kopriva, S. Genes of primary sulfate assimilation are part of the glucosinolate biosynthetic network in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2010, 62, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Sun, S.; Liu, B.; Cheng, F.; Sun, R.; Wang, X. Glucosinolate biosynthetic genes in Brassica rapa. Gene 2011, 487, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.; Rost, B. Mimicking cellular sorting improves prediction of subcellular localization. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 348, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, K.L.; Vogel, C.; Textor, S.; Bartram, S.; Hick, A.; Pickett, J.A.; Gershenzon, J. Glucosinolate biosynthesis: demonstration and characterization of the condensing enzyme of the chain elongation cycle in Eruca sativa. Photochemistry 2004, 65, 1073–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Textor, S.; Bartram, S.; Kroymann, J.; Falk, K.L.; Hick, A.; Pickett, J.A.; Gershenzon, J. Biosynthesis of methionine-derived glucosinolates in Arabidopsis thaliana: Recombinant expression and characterization of methylthioalkylmalate synthase, the condensing enzyme of the chain-elongation cycle. Planta 2004, 218, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reintanz, B.; Lehnen, M.; Reichelt, M.; Gershenzon, J.; Kowalczyk, M.; Sandberg, G.; Godde, M.; Uhl, R.; Palme, K. Bus, a bushy Arabidopsis CYP79F1 knockout mutant with abolished synthesis of short-chain aliphatic glucosinolates. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 351–367. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H.; Cominelli, E.; Bailey, P.; Parr, A.; Mehrtens, F.; Jones, J.; Tonelli, C.; Weisshaar, B.; Martin, C. Transcriptional repression by AtMYB4 controls production of UV-protecting sunscreens in Arabidopsis. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 6150–6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubb, C.D.; Zipp, B.J.; Ludwig-Muller, J.; Masuno, M.N.; Molinski, T.F.; Abel, S. Arabidopsisglucosyltranserase UGT74B1 functions in glucosinolate biosynthesis and auxin homeostasis. Plant J. 2004, 40, 893–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, M.D.; Hansen, C.H.; Wittstock, U.; Halkier, B.A. Cytochrome P450cyp79B2 from Arabidopsis catalyzes the conversion of tryptophan to indole-3-acetaldoxime, a precursor of indoleglucosinolates and indole-3-acetic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 33712–33717. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, Y.X.; Kim, H.U.; Kim, J.A.; Lim, M.H.; Jin, M.; Lee, S.C.; Kwon, S.J.; Lee, S.I.; Hong, J.K.; Park, T.H.; Mun, J.H.; Seol, Y.J.; Hong, S.B.; Park, B.S. Genome-wide identification of glucosinolate synthesis genes in Brassica rapa. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 3559–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartea, M.E.; de Haro, A.; Obregon, S.; Soengas, P.; Velasco, P. Glucosinolatevariation in leaves of Brassica rapacrops. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2012, 67, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, G.; Cartea, M.E.; Velasco, P.; Haro, A.; Ordás, A. Variation of glucosinolates in vegetable crops of Brassica rapa. Photochemistry 2007, 68, 536–545. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.K.; Chu, S.M.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, D.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Lim, S.H.; Ha, S.H.; Kweon, S.J.; Cho, H.S. Variation of glucosinolates in vegetable crops of Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuelsson, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. Locating proteins in the cell using TargetP, SignalP and related tools. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 953–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, H.; Keun-Joon, P.; Takeshi, O.; Naoya, F.; Hajime, H.; Adams-Collier, C.J.; Kenta, N. WoLF PSORT: Protein localization predictor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W585–W587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumakov, K.M.; Yushmanov, S.V. The maximum topological similarity principle in molecular systematic. Mol. Genet. Microbiol. Virusol. 1988, 3, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Triinu, K.; Maido, R. Enhancements and modifications of primer design program Primer3. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1289–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.L.; Bolitho, K.; Garryn, K.; Kortstee, A.; Karunairetnam, S.; McGhie, T.K.; Espley, R.V.; Hellens, R.P.; Allan, A.C. An R2R3 MYB transcription factor associated with regulation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway in Rosaceae. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.Z.; Hu, F.C.; Hu, G.B.; Li, X.J.; Huang, X.M.; Wang, H.C. Differential expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes in relation to anthocyanin accumulation in pericarp of Litchi Chinensis Sonn. PLoS One 2011, 6, e19455. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Chiu, L.W.; Li, L. Transcriptional regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in red cabbage. Planta 2009, 230, 1141–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Kawaharada, C.; Jin, S.; Hashimoto, M.; Ishii, G.; Yamauchi, H. Structural elucidation of 4-(cystein-S-yl) butyl glucosinolate from the leaves of Eruca sativa. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007, 71, 114–121. [Google Scholar]
- International Standards Organization (ISO), Part 1: Method using high performance liquid chromatography. In ISO 9167–1 (E). Rapeseed: Determination of Glucosinolates Content; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1992; pp. 1–9.
- Sample Availability: In general, samples of the compounds analyzed herein are unavailable from the authors due to their isolation on a small scale. They are readily analyzed using the procedures described.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.B.; Li, X.; Kim, S.-J.; Kim, H.H.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Park, S.U. MYB Transcription Factors Regulate Glucosinolate Biosynthesis in Different Organs of Chinese Cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis). Molecules 2013, 18, 8682-8695. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18078682
Kim YB, Li X, Kim S-J, Kim HH, Lee J, Kim H, Park SU. MYB Transcription Factors Regulate Glucosinolate Biosynthesis in Different Organs of Chinese Cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis). Molecules. 2013; 18(7):8682-8695. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18078682
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yeon Bok, Xiaohua Li, Sun-Ju Kim, Haeng Hoon Kim, Jeongyeo Lee, HyeRan Kim, and Sang Un Park. 2013. "MYB Transcription Factors Regulate Glucosinolate Biosynthesis in Different Organs of Chinese Cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis)" Molecules 18, no. 7: 8682-8695. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18078682
APA StyleKim, Y. B., Li, X., Kim, S.-J., Kim, H. H., Lee, J., Kim, H., & Park, S. U. (2013). MYB Transcription Factors Regulate Glucosinolate Biosynthesis in Different Organs of Chinese Cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis). Molecules, 18(7), 8682-8695. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18078682