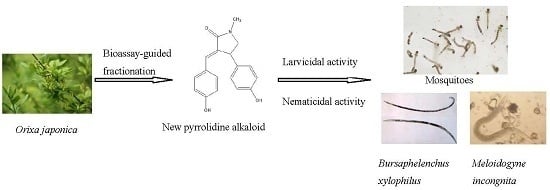
Bioactivities of a New Pyrrolidine Alkaloid from the Root Barks of Orixa japonica
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
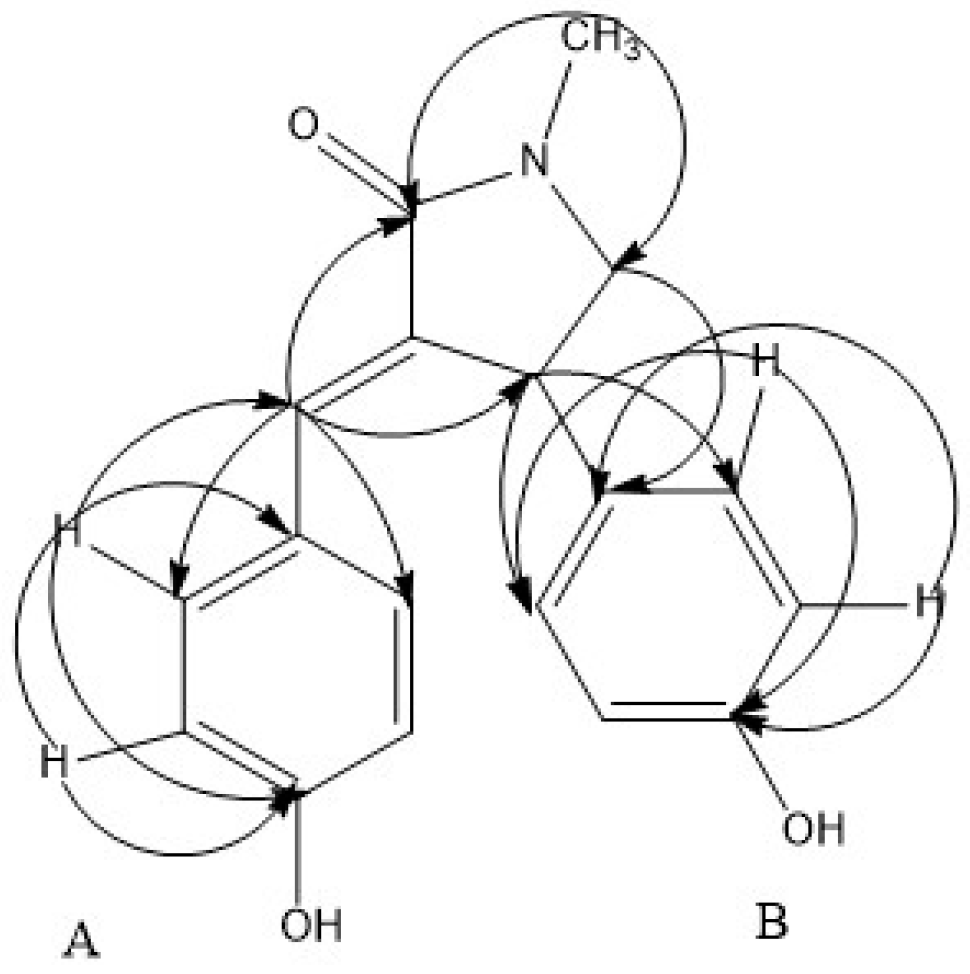
2.1. Isolated Bioactive Compound
2.2. Bioactivities
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General
3.2. Mosquitoes
3.3. Nematodes
3.4. Plant Material
3.5. Extraction and Isolation
3.6. Bioactivity Assays
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perumalsamy, H.; Jang, M.J.; Kim, J.R.; Kadarkarai, M.; Ahn, Y.J. Larvicidal activity and possible mode of action of four flavonoids and two fatty acids identified in Millettia pinnata seed toward three mosquito species. Parasite Vector 2015, 8, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, V.; Sanila, D.; Shetty, N.J. Insecticide susceptibility status in three medically important species of mosquitoes, Anopheles stephensi, Aedes aegypti and Culex quinquefasciatus, from Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike, Karnataka, India. Pest Manag. Sci. 2013, 69, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Malaria Report 2010; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- Sun, L.; Dong, H.; Guo, C.; Qian, J.; Sun, J.; Ma, L.; Zhu, C. Larvicidal activity of extracts of Ginkgo biloba exocarp for three different strains of Culex pipiens pallens. J. Med. Entomol. 2006, 43, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.L.; Liu, Q.Z.; Du, S.S.; Deng, Z.W. Mosquito larvicidal activity of alkaloids and limonoids derived from Evodia rutaecarpa unripe fruits against Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae). Parasitol. Res. 2012, 111, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, M. Current options in integrated management of plant-parasitic nematodes. Integ. Pest Manag. Rev. 1997, 2, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Jin, H.; Liu, Q.; Yan, Z.; Ding, L.; Qin, B. Nematicidal metabolites from roots of Stellera chamaejasme against Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and Bursaphelenchus mucronatus. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caboni, P.; Saba, M.; Oplos, C.; Aissani, N.; Maxia, A. Nematicidal activity of furanocoumarins from parsley against Meloidogyne spp. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 71, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neville, C.F.; Grundon, M.F.; Ramachandran, V.N.; Reisch, J. Quinoline alkaloids. Part 27. Synthesis of the Ptelea alkaloids pteleflorine, neohydroxylunine, O-methylhydroxyluninium salt and hydroxylunine. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1991, 2, 259–262. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, C.; Itoigawa, M.; Furukawa, A.; Hirano, T.; Murata, T.; Kaneda, N.; Hisada, Y.; Okuda, K.; Furukawa, H. Quinolone alkaloids with nitric oxide production inhibitory activity from Orixa japonica. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1800–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.C.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Z.L. Laboratory evaluation of larvicidal activity of the essential oil of Allium tuberosum roots and its selected major constituent compounds against Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2015, 52, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.C.; Liu, Q.; Chen, X.B.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Z.L. Larvicidal activity of the essential oil from Tetradium glabrifolium fruits and its constituents against Aedes albopictus. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 71, 1582–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, N.H.; Kwon, H.R.; Son, S.W.; Choi, Y.H.; Jang, K.S.; Lee, S.O.; Choi, J.E.; Ngoc, L.H.; Kim, J.C. Nematicidal activity of malabaricones isolated from Myristica malabarica fruitrinds against Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Nematology 2008, 10, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, J.M.S.; Barbosa, P.; Bennett, R.N.; Mota, M.; Figueiredo, A.C.S. Bioactivity against Bursaphelenchus xylophilus: Nematotoxics from essential oils, essential oils fractions and decoction waters. Phytochemistry 2013, 94, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Peter, H.R.; Hong, D.Y. Orixa japonica, Flora of China. Available online: http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=2&taxon_id=200012465 (accessed on 25 October 2016).
- He, Q.S.; Feng, Y.; Peng, Q.C.; Yang, Z.N. Analysis of volatile chemical constituents in entire plants of Orixa japonica by GC-MS spectrometry. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Form. 2010, 16, 83–87. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kang, C.H.; Choi, Y.H.; Choi, I.W.; Lee, J.D.; Kim, G.Y. Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced iNOS, COX-2, and TNF-α expression by aqueous extract of Orixa japonica in RAW 264.7 cells via suppression of NF-κB activity. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2011, 10, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Ono, H.; Kuwahara, Y.; Nishida, R. Hydroxybenzoic acid derivatives in a nonhostrutaceous plant, Orixa japonica, deter both oviposition and larval feeding in a Rutaceae-feeding swallowtail butterfly, Papilio xuthus L. J. Chem. Ecol. 2004, 30, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; Sharma, V.K.; Seo, S.Y. Screening of some medicinal plants for anti-lipase activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 97, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.N.; Pei, Y.H.; Chen, G.; Cong, H.; Liu, J.C. Two new compounds from Dictamnus dasycarpus. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 14, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crucianelli, E.; Galeazzi, R.; Martelli, G.; Orena, M.; Rinaldi, S.; Sabatino, P. A novel conformationally restricted analogue of 3-methylaspartic acid via stereoselective methylation of chiral pyrrolidin-2-ones. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dade, J.M.E.; Irie-N’Guessan, G.; Komlaga, G.; Say, M.; Okpekon, T.A.; Boti, J.B.; Kablan, B.J.; Bamba, E.H.S. Pyrrolidine alkaloids and their glycosylated derivatives from the root bark of Dichrostachys cinerea (L.) Wight & Arn. (Fabaceae). Phytochem. Lett. 2016, 16, 268–276. [Google Scholar]
- Majik, M.S.; Naik, D.; Bhat, C.; Tilve, S.; Tilvi, S.; D’Souza, L. Synthesis of (R)-norbgugaine and its potential as quorum sensing inhibitor against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 2353–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girgis, A.S. Regioselective synthesis of dispiro[1H-indene-2,3′-pyrrolidine-2′,3′′-[3H]indole]-1,2′′(1′′H)-diones of potential antitumor properties. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreño Otero, A.L.; Vargas Méndez, L.Y.; Duque, L.J.E.; Kouznetsov, V.V. Design, synthesis, acetylcholinesterase inhibition and larvicidal activity of girgensohnine analogs on Aedes aegypti, vector of dengue fever. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 78, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, T.H.; Blum, M.S.; Andersen, A.N.; Fales, H.M.; Escoubas, P. Novel 2-ethyl-5-alkylpyrrolidines in the venom of an Australian ant of the genus Monomorium. J. Chem. Ecol. 1988, 14, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizushina, Y.; Xu, X.; Asano, N.; Kasai, N.; Kato, A.; Takemura, M.; Asahara, H.; Linn, S.; Sugawara, F.; Yoshida, H.; et al. The inhibitory action of pyrrolidine alkaloid, 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-ribitol, on eukaryotic DNA polymerases. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 304, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Viglierchio, D.R.; Schmitt, R.V. On the methodology of nematode extraction from field samples: Baermann funnel modifications. J. Nematol. 1983, 15, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meyer, S.L.; Zasada, I.A.; Roberts, D.P.; Vinyard, B.T.; Lakshman, D.K.; Lee, J.K.; Chitwood, D.J.; Carta, L.K. Plantago lanceolata and Plantago rugelii extracts are toxic to Meloidogyne incognita but not to certain microbes. J. Nematol. 2006, 38, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Report of the WHO Informal Consultation on the “Evaluation and Testing of Insecticides”; Technical Report Number: CTD/WHOPES/IC/96.1; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996; pp. 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Caboni, P.; Ntalli, N.G.; Aissani, N.; Cavoski, I.; Angioni, A. Nematicidal activity of (E,E)-2,4-decadienal and (E)-2-decenal from Ailanthus altissima against Meloidogyne javanica. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the crude extracts and pure compounds are available from the authors.
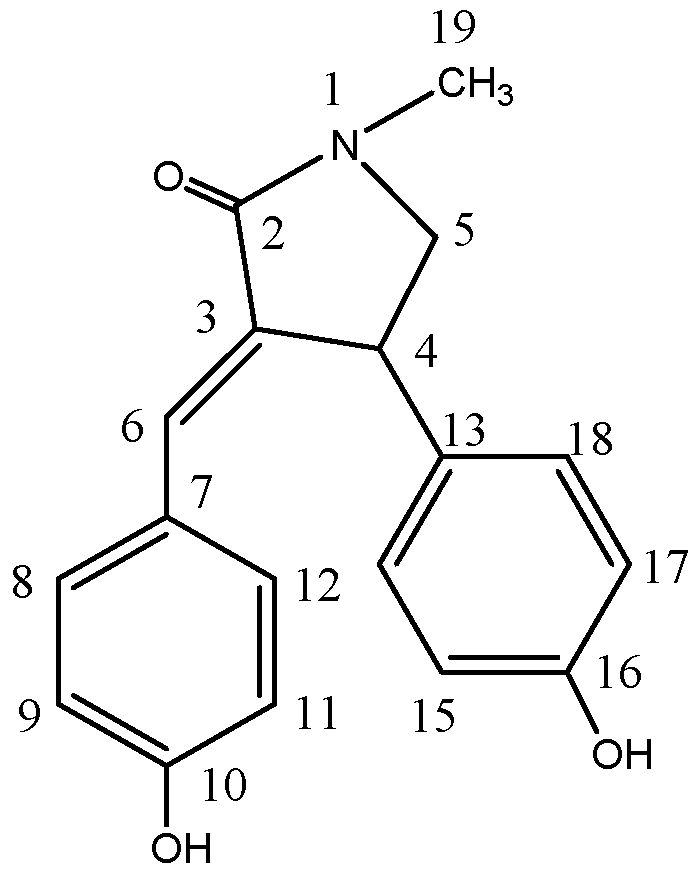
| Position | δH | δC |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 170.8 | |
| 3 | ||
| 4 | 4.48, d, J = 7.8 Hz | 40.3 |
| 5α | 3.98, d, J = 9.3 Hz | 57.0 |
| 5β | 3.27, d, J = 9.9 Hz | |
| 6 | 7.39, s | 132.2 |
| 7 | 125.9 | |
| 8 | 7.23, d, J = 8.2 Hz | 131.8 |
| 9 | 6.66, d, J = 8.1 Hz | 114.9 |
| 10 | 158.2 | |
| 11 | 6.66, d, J = 8.1 Hz | 114.9 |
| 12 | 7.23, d, J = 8.2 Hz | 131.8 |
| 13 | 133.5 | |
| 14 | 7.05, d, J = 8.0 Hz | 127.7 |
| 15 | 6.72, d, J =8.0 Hz | 115.3 |
| 16 | 156.1 | |
| 17 | 6.72, d, J =8.0 Hz | 115.3 |
| 18 | 7.05, d, J = 8.0 Hz | 127.7 |
| 19 | 2.98, s | 29.0 |
| Mosquitoes | Treatment | LC50 (μg/mL) (95% CL) | LC90 (μg/mL) (95% CL) | Slope ± SD | χ2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ae. aegypti | Compound | 232.09 (209.05–254.74) | 293.19 (265.30–321.58) | 12.63 ± 1.43 | 8.69 | 0.0130 * |
| Rotenone | 3.75 (3.39–4.11) | 9.64 (8.64–10.56) | 3.22 ± 0.33 | 18.20 | 0.0001 * | |
| An. sinensis | Compound | 49.91 (45.61–54.51) | 82.31 (74.12–90.46) | 5.90 ± 0.68 | 11.05 | 0.0040 * |
| Rotenone | 0.73 (0.66–0.80) | 1.13 (1.02–1.24) | 4.00 ± 0.51 | 10.55 | 0.0051 * | |
| C. pipiens pallens | Compound | 161.10 (145.37–177.04) | 211.80 (192.01–232.97) | 10.78 ± 1.24 | 9.28 | 0.0097 * |
| Rotenone | 1.88 (1.69–2.01) | 3.74 (3.38–4.09) | 6.90 ± 0.88 | 15.80 | 0.0004 * |
| Nematodes | Treatment | LC50 (μg/mL) (95% CL) | LC90 (μg/mL) (95% CL) | Slope ± SD | χ2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. xylophilus | Compound | 391.50 (353.90–429.18) | >500 | 2.37 ± 0.20 | 15.15 | 0.0005 * |
| Avermectin | 0.071 (0.068–0.075) | 0.24 (0.22–0.26) | 2.45 ± 0.20 | 14.76 | 0.0006 * | |
| M. incongnita | Compound | 134.51 (121.91–146.24) | >500 | 1.18 ± 0.12 | 12.00 | 0.0025 * |
| Avermectin | 0.025 (0.023–0.027) | 0.13 (0.12–0.14) | 2.08 ± 0.16 | 28.21 | 0.0000 * |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.C.; Lai, D.; Liu, Q.Z.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Z.L. Bioactivities of a New Pyrrolidine Alkaloid from the Root Barks of Orixa japonica. Molecules 2016, 21, 1665. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21121665
Liu XC, Lai D, Liu QZ, Zhou L, Liu Q, Liu ZL. Bioactivities of a New Pyrrolidine Alkaloid from the Root Barks of Orixa japonica. Molecules. 2016; 21(12):1665. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21121665
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xin Chao, Daowan Lai, Qi Zhi Liu, Ligang Zhou, Qiyong Liu, and Zhi Long Liu. 2016. "Bioactivities of a New Pyrrolidine Alkaloid from the Root Barks of Orixa japonica" Molecules 21, no. 12: 1665. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21121665
APA StyleLiu, X. C., Lai, D., Liu, Q. Z., Zhou, L., Liu, Q., & Liu, Z. L. (2016). Bioactivities of a New Pyrrolidine Alkaloid from the Root Barks of Orixa japonica. Molecules, 21(12), 1665. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21121665