Pentacoordinate and Hexacoordinate Mn(III) Complexes of Tetradentate Schiff-Base Ligands Containing Tetracyanidoplatinate(II) Bridges and Revealing Uniaxial Magnetic Anisotropy
Abstract
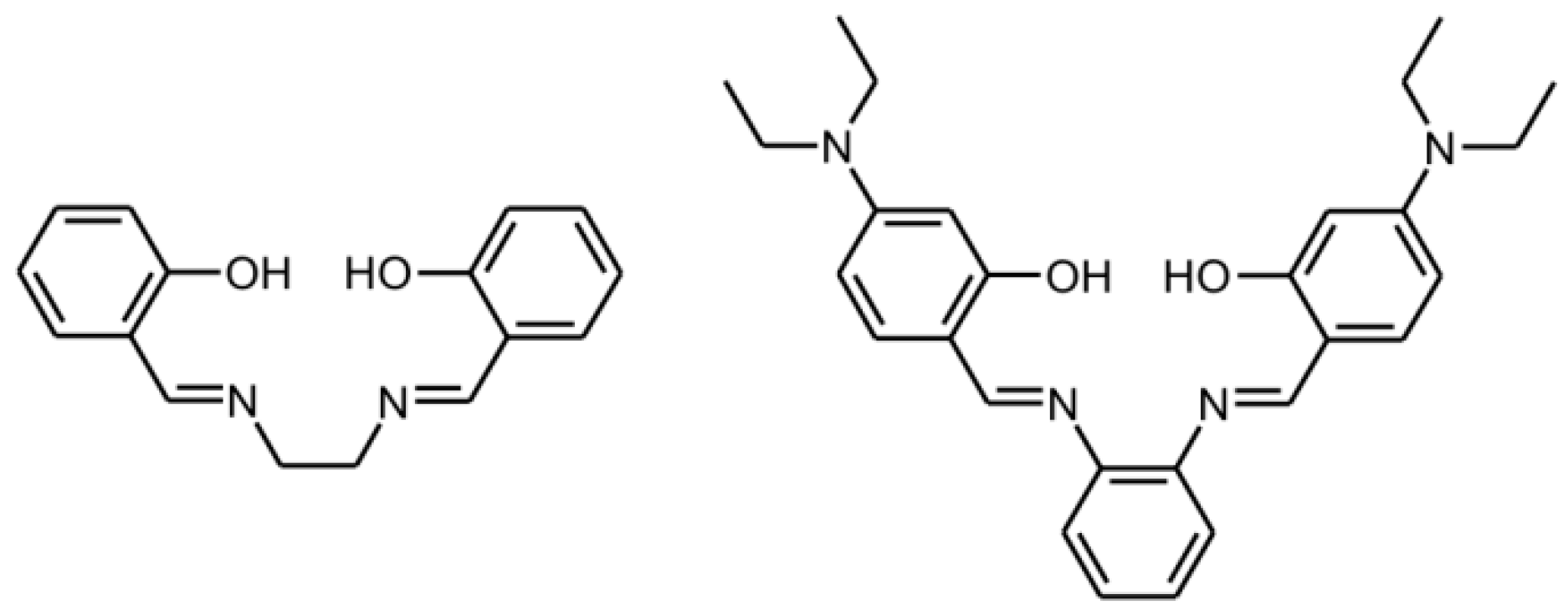
:1. Introduction
2. Results
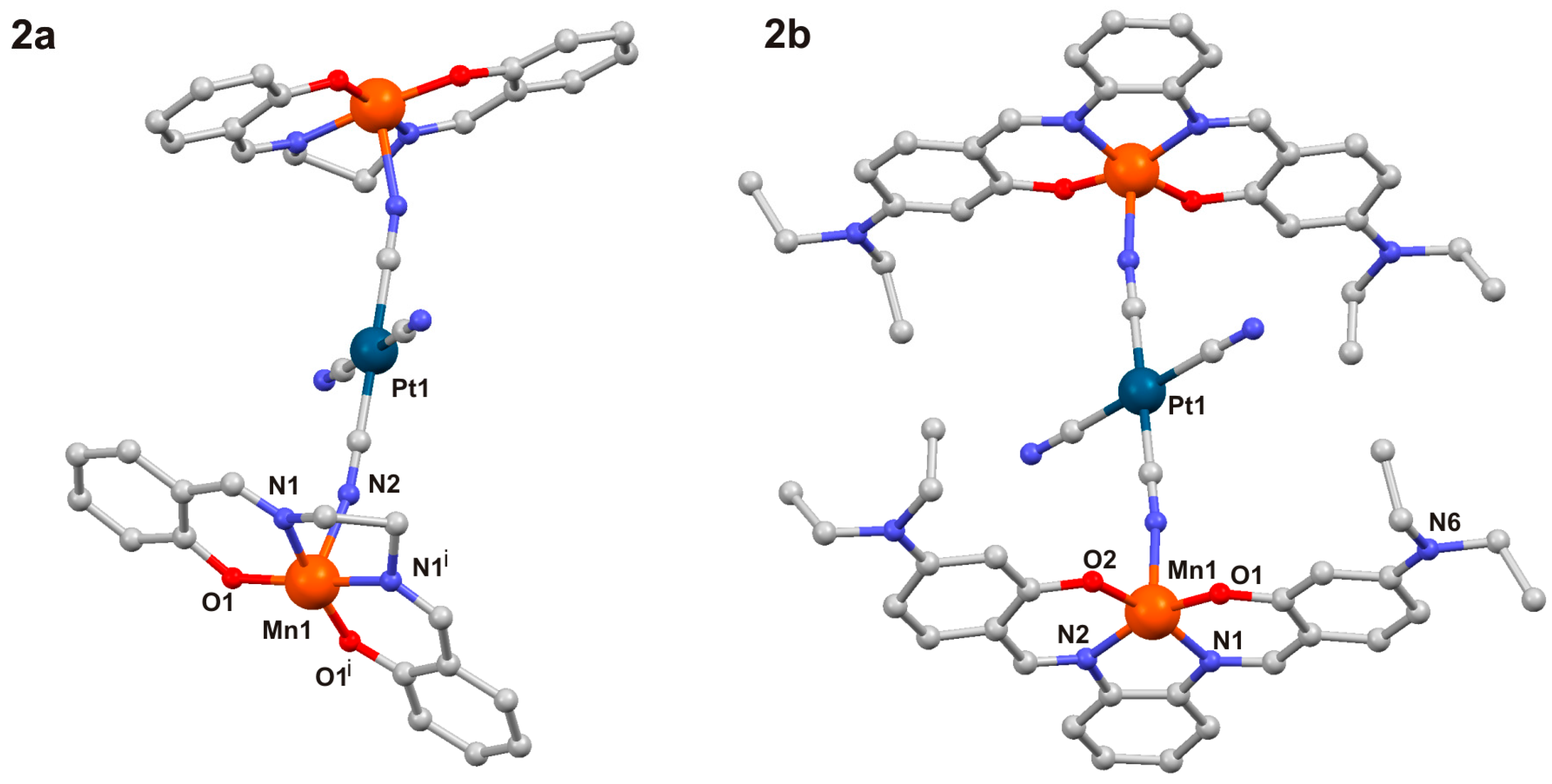
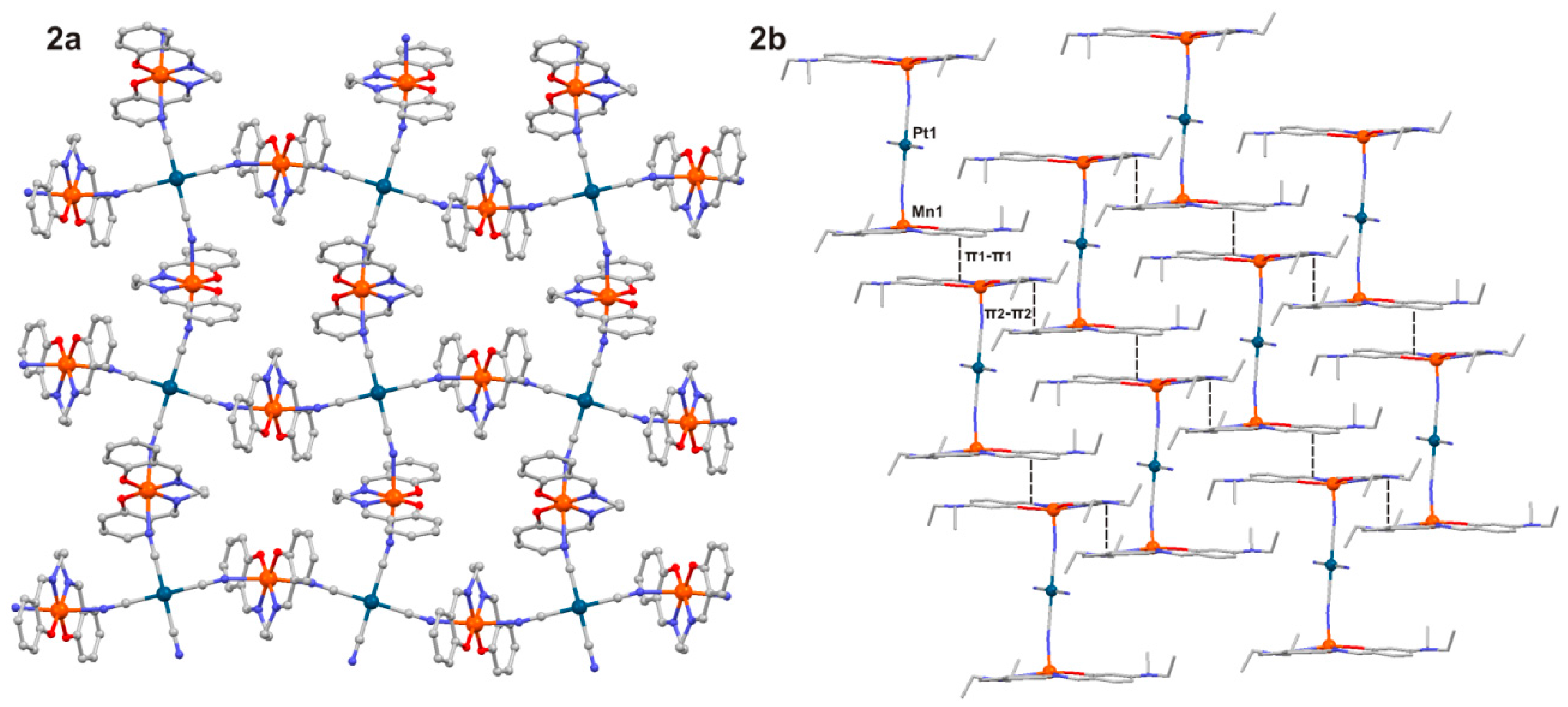
2.1. Crystal Structures
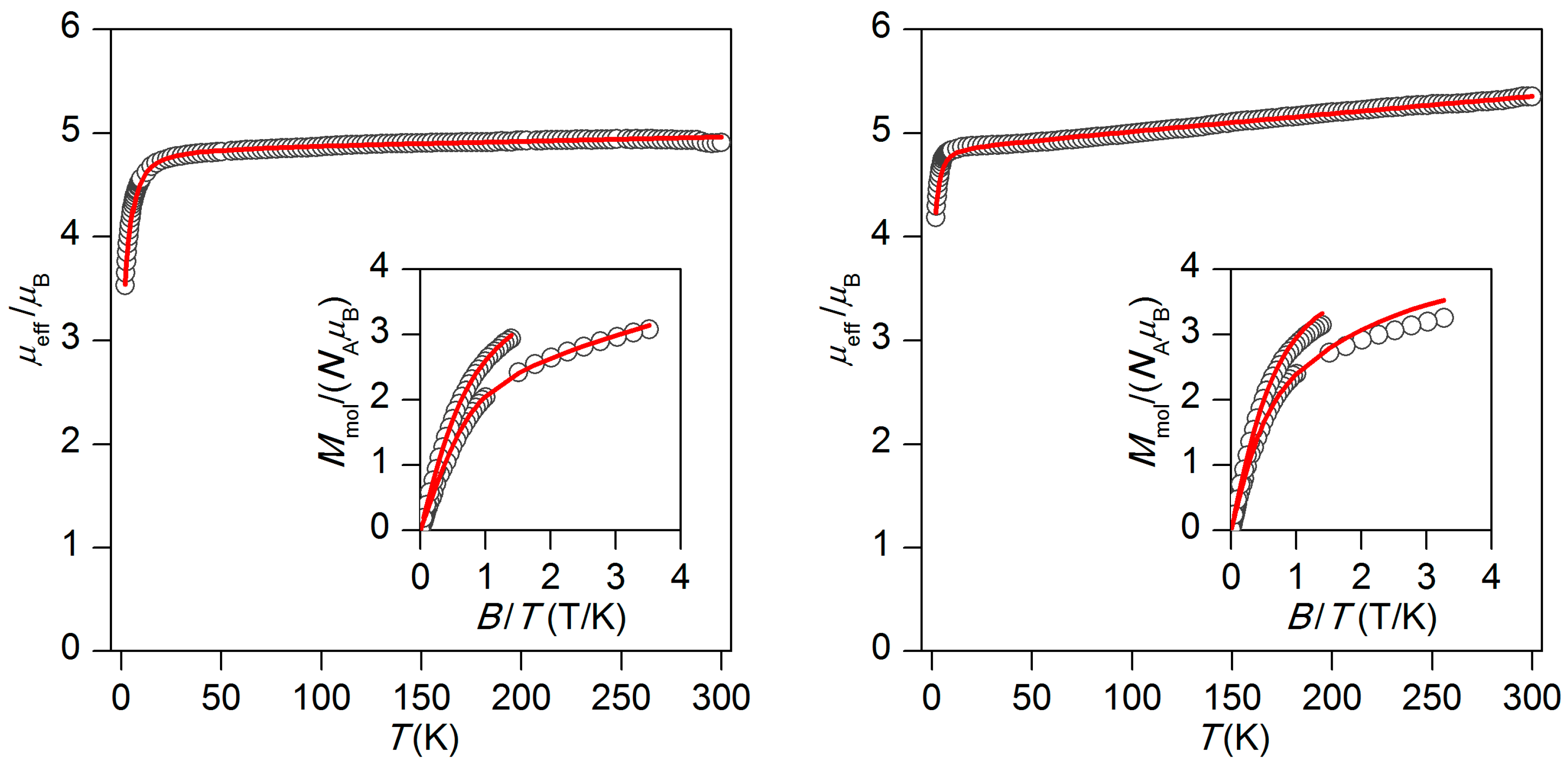
2.2. Magnetic Properties
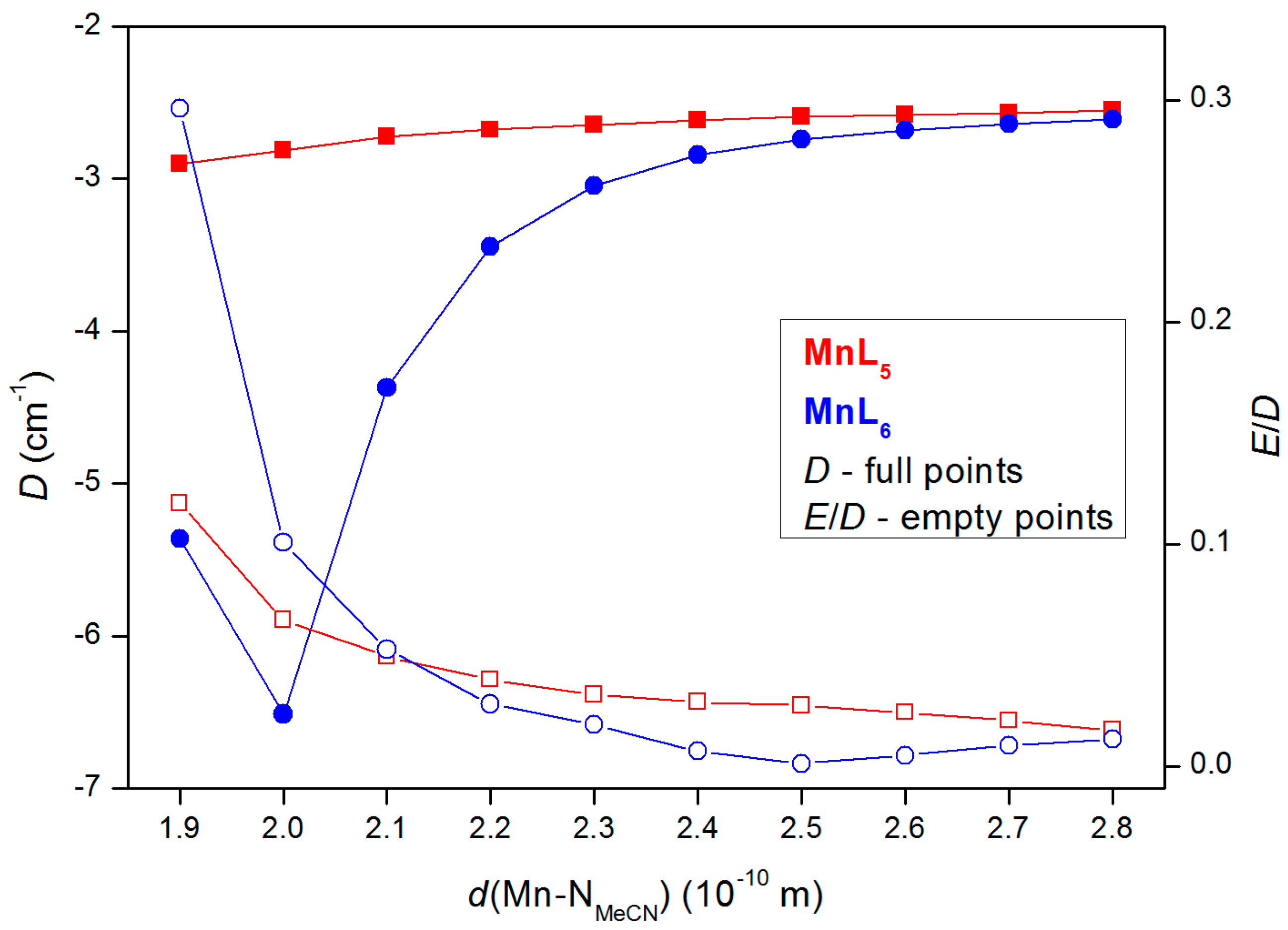
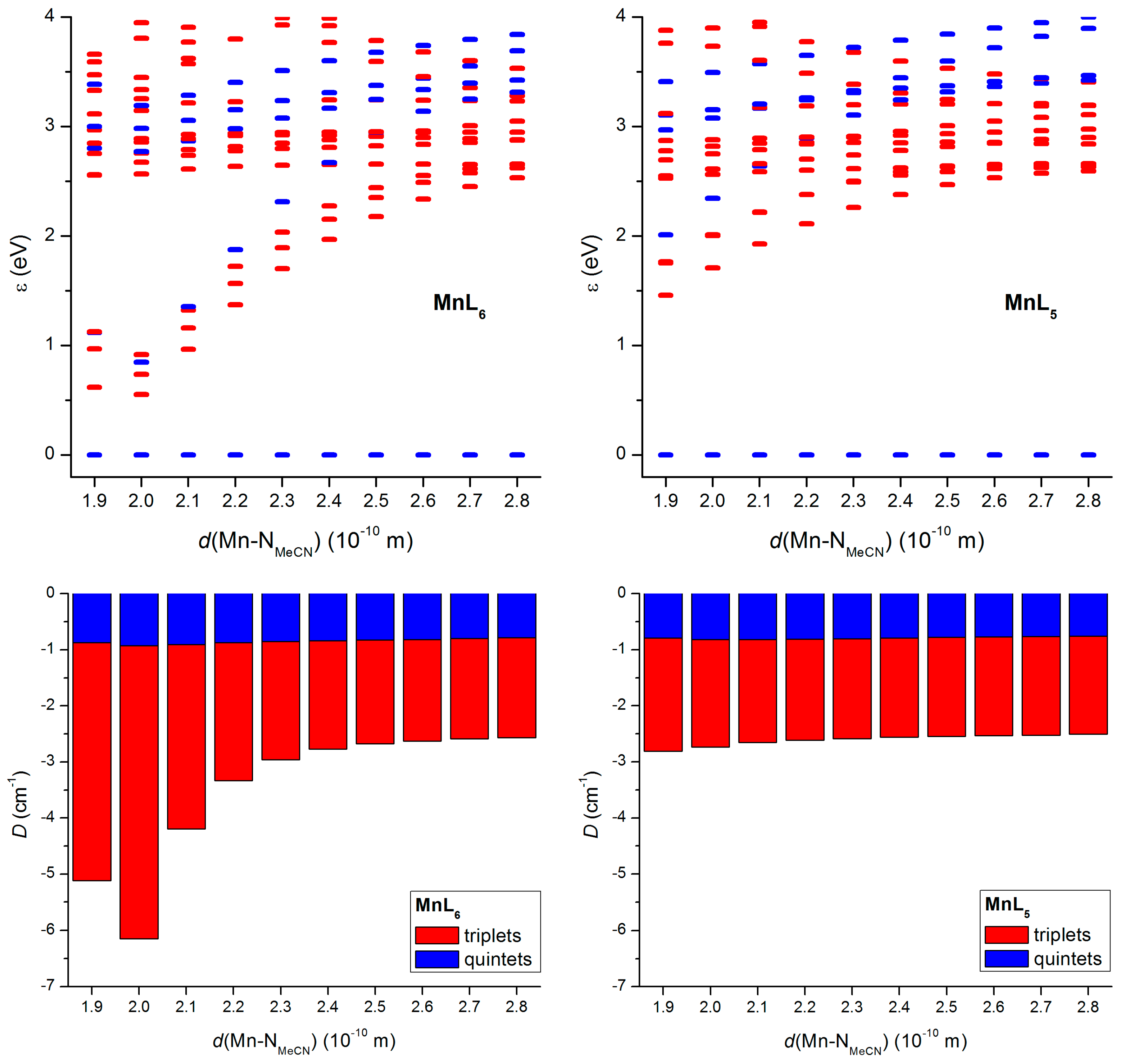
2.3. Theorethical Calculations
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.1.1. Preparation of Ba[Pt(CN)4]
4.1.2. Preparation of [{Mn(L4A)}2{μ4-Pt(CN)4}]n (2a), and [{Mn(L4B)}2{μ-Pt(CN)4}] (2b)
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. General Methods
4.2.2. Single Crystal X-ray Analysis Details
4.2.3. Theoretical Methods
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Miyasaka, H.; Saitoh, A.; Abe, S. Magnetic assemblies based on Mn(III) salen analogues. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2007, 251, 2622–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ding, X.-H.; Li, Y.-H.; Huang, W. Dicyanometalate chemistry: A type of versatile building block for the construction of cyanide-bridged molecular architectures. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 439–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herchel, R.; Váhovská, L.; Potočňák, I.; Trávníček, Z.K. Slow Magnetic Relaxation in Octahedral Cobalt(II) Field-Induced Single-Ion Magnet with Positive Axial and Large Rhombic Anisotropy. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 5896–5898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, K.S.; Bendix, J.; Clerac, R. Single-molecule magnet engineering: Building-block approaches. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 4396–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemec, I.; Herchel, R.; Trávníček, Z.; Šilha, T. Field-induced slow relaxation of magnetization in dinuclear and trinuclear CoIII···MnIII complexes. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 3074–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Vignesh, K.R.; Archana, V.; Rajaraman, G. Theoretical insights into the origin of magnetic exchange and magnetic anisotropy in {ReIV-MII} (M = Mn, Fe, Co, Ni and Cu) single chain magnets. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 8201–8214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ababei, R.; Li, Y.-G.; Roubeau, O.; Kalisz, M.; Brefuel, N.; Coulon, C.; Harte, E.; Liu, X.; Mathoniere, C.; Clerac, R. Bimetallic cyanido-bridged magnetic materials derived from manganese(III) Schiff-base complexes and pentacyanidonitrosylferrate(II) precursor. New J. Chem. 2009, 33, 1237–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Lim, J.H.; Kim, H.C.; Hong, C.S. Cyanide-Bridged Single-Molecule Magnet Constructed by an Octacoordinated [W(CN)6(bpy)]− Anion. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 45, 9613–9615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreiser, J.; Schnegg, A.; Holldack, K.; Pedersen, K.S.; Schau-Magnussen, M.; Nehrkorn, J.; Tregenna-Piggott, P.; Mutka, H.; Weihe, H.; Bendix, J.; et al. Frequency-Domain Fourier-Transform Terahertz Spectroscopy of the Single-Molecule Magnet (NEt4)[Mn2(5-Brsalen)2(MeOH)2Cr(CN)6]. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 7492–7498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, K.S.; Dreiser, J.; Nehrkorn, J.; Gysler, M.; Schau-Magnussen, M.; Schnegg, A.; Holldack, K.; Bittl, R.; Piligkos, S.; Weihe, H.; et al. A linear single-molecule magnet based on [RuIII(CN)6]3−. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 6918–6920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeke, V.; Heidemeier, M.; Krickemeyer, E.; Stammler, A.; Bogge, H.; Schnack, J.; Glaser, T. Structural influences on the exchange coupling and zero-field splitting in the single-molecule magnet [MnIII6MnIII]3+. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 12942–12959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šilha, T.; Nemec, I.; Herchel, R.; Trávníček, Z. Structural and magnetic characterizations of the first manganese(III) Schiff base complexes involving hexathiocyanidoplatinate(IV) bridges. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 5351–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemec, I.; Šilha, T.; Herchel, R.; Trávníček, Z. Investigation of Magnetic Exchange Pathways in Heterotrinuclear Manganese(III) Schiff Base Complexes Involving Tetrathiocyanidoplatinate(II) Bridges. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 2013, 5781–5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemec, I.; Herchel, R.; Šilha, T.; Trávníček, Z. Towards a better understanding of magnetic exchange mediated by hydrogen bonds in Mn(III)/Fe(III) salen-type supramolecular dimers. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 15602–15616. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, A.-H.; Shen, X.-P.; Wu, Q.-J.; Huang, Z.-X.; Xu, Z. Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Magnetic Properties of a Two-Dimensional Heterometallic Assembly [Mn(salen)]∣2∣[Ni(CN)4∣·1/2H2O. J. Coord. Chem. 2002, 55, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, E.A.; Castellano, R.K.; Diederich, F. Interactions with Aromatic Rings in Chemical and Biological Recognition. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 1210–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salonen, L.M.; Ellermann, M.; Diederich, F. Aromatic Rings in Chemical and Biological Recognition: Energetics and Structures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 4808–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinnokrot, M.O.; Sherrill, C.D. High-Accuracy Quantum Mechanical Studies of π−π Interactions in Benzene Dimers. J. Phys. Chem. A 2006, 110, 10656–10668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addison, A.W.; Rao, T.N.; Reedijk, J.; van Rijn, J.; Verschoor, G.C. Synthesis, structure, and spectroscopic properties of copper(II) compounds containing nitrogen-sulphur donor ligands; the crystal and molecular structure of aqua[1,7-bis(N-methylbenzimidazol-2′-yl)-2,6-dithiaheptane]copper(II) perchlorate. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1984, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batsanov, S.S. Van der Waals Radii of Elements. Inorg. Mater. 2001, 37, 871–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boča, R. Theoretical Foundations of Molecular Magnetism; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- The standard deviations of the fitted parameters were calculated as σi = (Pii−1·S/(N − k))−1/2, where Pij = Σ(δμn/δai·δμn/δaj) and S = Σ(μn – μnexp)2 with n = 1 to N; ai and aj are fitted parameters, N is number of experimental points (sum of temperature and field dependent data), μn and μnexp are the calculated and experimental effective magnetic moments for given temperature and magnetic field. The σi was then multiplied by Student’s t95% to provide confidence limits with the 95% probabilities listed in the text.
- Maurice, R.; de Graaf, C.; Guihéry, N. Magnetostructural relations from a combined ab initio and ligand field analysis for the nonintuitive zero-field splitting in Mn(III) complexes. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 133, 084307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciringh, Y.; Gordon-Wylie, S.W.; Norman, R.E.; Clark, G.R.; Weintraub, S.T.; Horwitz, C.P. Multinuclear paramagnetic NMR spectra and solid state X-ray crystallographic characterization of manganese(III) Schiff-base complexes. Inorg. Chem. 1997, 36, 4968–4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Cryst. C 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. WinGX suite for small-molecule single-crystal crystallography. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1999, 32, 837–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spek, A. Structure validation in chemical crystallography. Acta Cryst. Section D 2009, 65, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, Y. MISSYM1.1—A flexible new release. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1988, 21, 983–984. [Google Scholar]
- Malmqvist, P.-Å.; Roos, B.O. The CASSCF state interaction method. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1989, 155, 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Angeli, C.; Cimiraglia, R.; Evangelisti, S.; Leininger, T.; Malrieu, J.P. Introduction of n-electron valence states for multireference perturbation theory. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 114, 10252–10264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neese, F. The ORCA program system. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2012, 2, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lenthe, E.; Baerends, E.J.; Snijders, J.G. Relativistic regular two-component Hamiltonians. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 99, 4597–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wüllen, C. Molecular density functional calculations in the regular relativistic approximation: Method, application to coinage metal diatomics, hydrides, fluorides and chlorides, and comparison with first-order relativistic calculations. J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 109, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantazis, D.A.; Chen, X.-Y.; Landis, C.R.; Neese, F. All-Electron Scalar Relativistic Basis Sets for Third-Row Transition Metal Atoms. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2008, 4, 908–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neese, F.; Wennmohs, F.; Hansen, A. Efficient and accurate local approximations to coupled-electron pair approaches: An attempt to revive the pair natural orbital method. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 13, 114108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganyushin, D.; Neese, F. First-principles calculations of zero-field splitting parameters. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 125, 024103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neese, F. Efficient and accurate approximations to the molecular spin-orbit coupling operator and their use in molecular g-tensor calculations. J. Chem. Phys. 2005, 122, 034107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurice, R.; Bastardis, R.; Graaf, C.; Suaud, N.; Mallah, T.; Guihéry, N. Universal Theoretical Approach to Extract Anisotropic Spin Hamiltonians. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2009, 5, 2977–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klamt, A.; Schuurmann, G. COSMO: A new approach to dielectric screening in solvents with explicit expressions for the screening energy and its gradient. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1993, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional exchange-energy approximation with correct asymptotic behavior. Phys. Rev. A 1988, 38, 3098–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Yang, W.T.; Parr, R.G. Development of the Colle-Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, P.J.; Devlin, F.J.; Chabalowski, C.F.; Frisch, M.J. Ab Initio Calculation of Vibrational Absorption and Circular Dichroism Spectra Using Density Functional Force Fields. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 11623–11627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors.

| 2a | 2b | |
|---|---|---|
| Formula | C36H28Mn2N8O4Pt | C30H32MnN6O2Pt0.50 |
| Mr | 941.62 | 661.10 |
| Space group | P4/ncc | P-1 |
| Crystal system | tetragonal | triclinic |
| a/Å | 14.7755(3) | 10.6904(4) |
| b/Å | 14.7755(3) | 12.6273(3) |
| c/Å | 16.7105(5) | 13.2804(3) |
| α/° | 90 | 70.773(2) |
| β/° | 90 | 79.588(2) |
| γ/° | 90 | 67.676(3) |
| V/Å3 | 3648.2(2) | 1562.69(9) |
| T/K | 150(2) | 150(2) |
| DC/g cm−3 | 1.717 | 1.405 |
| μ/mm−1 | 4.568 | 2.684 |
| F(000) | 1846.0 | 668.0 |
| Reflections collected/unique | 1612/1435 | 5396/4748 |
| Data/restraints/parameters | 1612/1/115 | 5396/0/361 |
| Goodness of fit (GOF) on F2 | 1.307 | 1.004 |
| R1, wR2 (I > 2δ(I)) a,b | 0.0500/0.1166 | 0.0368/0.0817 |
| R1, wR2 (all data) a,b | 0.0544/0.1166 | 0.0425/0.0829 |
| CCDC number | 1510379 | 1510378 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nemec, I.; Herchel, R.; Trávníček, Z. Pentacoordinate and Hexacoordinate Mn(III) Complexes of Tetradentate Schiff-Base Ligands Containing Tetracyanidoplatinate(II) Bridges and Revealing Uniaxial Magnetic Anisotropy. Molecules 2016, 21, 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21121681
Nemec I, Herchel R, Trávníček Z. Pentacoordinate and Hexacoordinate Mn(III) Complexes of Tetradentate Schiff-Base Ligands Containing Tetracyanidoplatinate(II) Bridges and Revealing Uniaxial Magnetic Anisotropy. Molecules. 2016; 21(12):1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21121681
Chicago/Turabian StyleNemec, Ivan, Radovan Herchel, and Zdeněk Trávníček. 2016. "Pentacoordinate and Hexacoordinate Mn(III) Complexes of Tetradentate Schiff-Base Ligands Containing Tetracyanidoplatinate(II) Bridges and Revealing Uniaxial Magnetic Anisotropy" Molecules 21, no. 12: 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21121681






