Metabolomic Profiles of Aspergillus oryzae and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens During Rice Koji Fermentation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
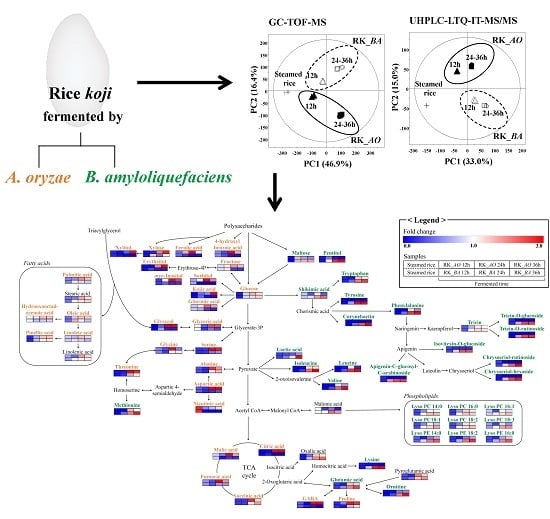
2.1. Multivariate Analysis of Rice Koji Fermented with Different Microorganisms and Fermentation Times
2.2. Different Metabolites and Metabolic Pathway of Rice Koji According to Microorganisms
2.3. Comparison of Bioactivity and Enzymatic Activity in Different Rice Koji Depending on Microorganisms
3. Discussion
3.1. Sugars and Sugar Alcohols
3.2. Organic Acids
3.3. Amino Acids
3.4. Lipid Metabolism
3.5. Phenolic Compounds
3.6. Siderophores
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Inoculum and Rice Koji Fermentation
4.3. Sample Preparation for Metabolite Profiling
4.4. GC-TOF-MS Analysis
4.5. UHPLC-LTQ-IT-MS/MS Analysis
4.6. Data Processing and Multivariate Statistical Analysis
4.7. Determination of Antioxidant Activity and Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Content
4.8. Determination of Enzymatic Activities
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tamang, J.P. Health Benefits of Fermented Foods and Beverages; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Blandino, A.; Al-Aseeri, M.E.; Pandiella, S.S.; Cantero, D.; Webb, C. Cereal-based fermented foods and beverages. Food Res. Int. 2003, 36, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.W.; Jang, E.S.; Moon, B.S.; Lee, J.J.; Lee, D.E.; Lee, C.H.; Shin, C.S. Anti-obesity effects of gochujang products prepared using rice koji and soybean meju in rats. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kum, S.J.; Yang, S.O.; Lee, S.M.; Chang, P.S.; Choi, Y.H.; Lee, J.J.; Hurh, B.S.; Kim, Y.S. Effects of Aspergillus species inoculation and their enzymatic activities on the formation of volatile components in fermented soybean paste (doenjang). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 1401–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.J.; Choi, J.N.; Kim, J.; Yeo, S.H.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, C.H. Metabolomics-based optimal koji fermentation for tyrosinase inhibition supplemented with Astragalus Radix. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2012, 76, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onuma, K.; Kanda, Y.; Suzuki Ikeda, S.; Sakaki, R.; Nonomura, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Osaki, M.; Shikanai, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Okada, F. Fermented brown rice and rice bran with aspergillus oryzae (FBRA) prevents inflammation-related carcinogenesis in mice, through inhibition of inflammatory cell infiltration. Nutrients 2015, 7, 10237–10250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.J.; Choi, J.N.; Kim, J.; Park, S.B.; Yeo, S.H.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, C.H. GC-MS based metabolite profiling of rice koji fermentation by various fungi. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 74, 2267–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechman, A.; Phillips, R.D.; Chen, J. Changes in selected physical property and enzyme activity of rice and barley koji during fermentation and storage. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, M318–M322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiyama, S.I. Selection of micro-organisms for use in the fermentation of soy sauce. Food Microbiol. 1984, 1, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, R.; Roja Rani, S.; Masoodi, T.A.; Shafi, G.; Alharbi, K. Functional analysis and structure determination of alkaline protease from Aspergillus flavus. Bioinformation 2012, 8, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juan, M.Y.; Wu, C.H.; Chou, C.C. Fermentation with Bacillus spp. as a bioprocess to enhance anthocyanin content, the angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory effect, and the reducing activity of black soybeans. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 918–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, D.; Gao, M.; Yang, Y.; Liu, B.; Tian, Z.; Wang, J. Bio-modification of soybean meal with Bacillus subtilis or Aspergillus oryzae. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2012, 1, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S. Metabolomics: Applications to food science and nutrition research. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Oh, D.G.; Lee, S.; Kim, G.R.; Lee, J.S.; Son, Y.K.; Bae, C.H.; Yeo, J.; Lee, C.H. Chemotaxonomic metabolite profiling of 62 Indigenous plant species and its correlation with bioactivities. Molecules 2015, 20, 19719–19734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.Y.; Son, G.H. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-based chemotaxonomic classification of Aspergillus spp. and evaluation of the biological activity of its unique metabolite, neosartorin. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 23, 932–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.C.; Huang, Z.Q.; Zhang, W.; Rao, P.F.; Ni, L. Identification and characterization of filamentous fungi isolated from fermentation starters for Hong Qu glutinous rice wine brewing. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 58, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chutmanop, J.; Chuichulcherm, S.; Chisti, Y.; Srinophakun, P. Protease production by Aspergillus oryzae in solid-state fermentation using agroindustrial substrates. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2008, 83, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Choi, H.J. Physicochemical properties of kochujang prepared by Bacillus sp. koji. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2003, 35, 1174–1181. [Google Scholar]
- Gänzle, M.G. Enzymatic and bacterial conversions during sourdough fermentation. Food Microbiol. 2014, 37, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Lee, J.H.; Vodovotz, Y.; Schwartz, S.J. Changes in distribution of isoflavones and β-glucosidase activity during soy bread proofing and baking. Cereal. Chem. 2004, 81, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.G.; Shim, S.M.; Kwon, D.Y.; Choi, H.K.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, Y.S. Metabolite profiling of Cheonggukjang, a fermented soybean paste, inoculated with various Bacillus strains during fermentation. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 74, 1860–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, S.; Murray, P.G. Metabolic engineering for improved microbial pentose fermentation. Bioeng. Bugs 2010, 1, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrash, J.M. All in the family: Aldose reductase and closely related aldo-keto reductases. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiboth, B.; Gamauf, C.; Pail, M.; Hartl, L.; Kubicek, C.P. The d-xylose reductase of Hypocrea jecorina is the major aldose reductase in pentose and d-galactose catabolism and necessary for beta-galactosidase and cellulase induction by lactose. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 66, 890–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.K.; Kim, S.Y.; Ryu, Y.W.; Seo, J.H.; Kim, J.H. Purification and characterization of a novel erythrose reductase from Candida magnoliae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 3710–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponnusamy, K.; Lee, S.; Lee, C.H. Time-dependent correlation of the microbial community and the metabolomics of traditional barley nuruk starter fermentation. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Lee, S.Y. Production of succinic acid by bacterial fermentation. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2006, 39, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnuson, J.K.; Lasure, L.L. Organic acid production by filamentous fungi. In Advances in Fungal Biotechnology for Industry, Agriculture, and Medicine; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 307–340. [Google Scholar]
- Carlsen, M.; Spohr, A.B.; Nielsen, J.; Villadsen, J. Morphology and physiology of an α-amylase producing strain of Aspergillus oryzae during batch cultivations. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1996, 49, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, D.; Kaplan, N.O. d-and l-lactic acid dehydrogenases in Lactobacillus plantarum. J. Biol. Chem. 1960, 235, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dave, K.K.; Punekar, N.S. Expression of Lactate Dehydrogenase in Aspergillus niger for l-Lactic Acid Production. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licona-Cassani, C.; Lara, A.R.; Cabrera-Valladares, N.; Escalante, A.; Hernandez-Chavez, G.; Martinez, A.; Bolivar, F.; Gosset, G. Inactivation of pyruvate kinase or the phosphoenolpyruvate: Sugar phosphotransferase system increases shikimic and dehydroshikimic acid yields from glucose in Bacillus subtilis. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, B.K.; Ahn, H.J.; van den Berg, F.; Lee, C.H.; Hong, Y.S. Metabolomic insight into soy sauce through 1H NMR spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 6862–6870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ham, S.S.; Choi, K.K.; Cui, C.B.; Lee, B.G.; Joo, D.S.; Lee, D.S. Quality characteristics of soy sauce fermented by Bacillus licheniformis NH20 isolated from traditional meju and Aspergillus oryzae. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2004, 13, 537–543. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.E.; Hwang, G.S.; Lee, C.H.; Hong, Y.S. Metabolomics reveals alterations in both primary and secondary metabolites by wine bacteria. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 10772–10783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutson, S. Structure and function of branched chain aminotransferases. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 2001, 70, 175–206. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H.; Dudareva, N. The shikimate pathway and aromatic amino acid biosynthesis in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2012, 63, 73–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woldman, Y.; Appling, D.R. A general method for determining the contribution of split pathways in metabolite production in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab. Eng. 2002, 4, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikawa, T. Alanine, aspartate, and asparagine metabolism in microorganisms. In Amino Acid Biosynthesis-Pathways, Regulation and Metabolic Engineering; Springer: Berlin, Germany; Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 273–288. [Google Scholar]
- Moongngarm, A.; Saetung, N. Comparison of chemical compositions and bioactive compounds of germinated rough rice and brown rice. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, K.; Nishimura, K.; Iwahara, M. Purification and characterization of glutamate decarboxylase from Aspergillus oryzae. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2003, 9, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.B.; Oh, S.H. Enhancement of γ-aminobutyric acid production in Chungkukjang by applying a Bacillus subtilis strain expressing glutamate decarboxylase from Lactobacillus brevis. Biotechnol. Lett. 2006, 28, 1459–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, J.; Jiang, S.; Pan, L.; Zhang, Y. Purification, characterization and application of a cold-adapted phospholipase A1 from Bacillus cereus sp. AF-1. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2013, 27, 3972–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Choi, J.N.; John, K.M.; Kusano, M.; Oikawa, A.; Saito, K.; Lee, C.H. GC–TOF-MS-and CE–TOF-MS-based metabolic profiling of cheonggukjang (fast-fermented bean paste) during fermentation and its correlation with metabolic pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9746–9753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.X.; Yang, H.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Li, T.; Zhu, B.Q.; Zhang, B.L. Polyphenolic compositions and chromatic characteristics of bog bilberry syrup wines. Molecules 2015, 20, 19865–19877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, C.M.P.; Delabona Pda, S.; Lima, D.J.; Paixao, D.A.A.; Pradella, J.G.; Farinas, C.S. Addition of feruloyl esterase and xylanase produced on-site improves sugarcane bagasse hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 170, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topakas, E.; Vafiadi, C.; Christakopoulos, P. Microbial production, characterization and applications of feruloyl esterases. Process Biochem. 2007, 42, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, N.T.; van Camp, J.; Smagghe, G.; Raes, K. Improved release and metabolism of flavonoids by steered fermentation processes: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 19369–19388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rao, A.S.; Reddy, S.G.; Babu, P.P.; Reddy, A.R. The antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of methanolic extracts from Njavara rice bran. BMC Complem. Altern. Med. 2010, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.H.; Koumoutsi, A.; Scholz, R.; Schneider, K.; Vater, J.; Süssmuth, R.; Piel, J.; Borriss, R. Genome analysis of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 reveals its potential for biocontrol of plant pathogens. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 140, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertlein, G.; Müller, S.; Garcia-Gonzalez, E.; Poppinga, L.; Süssmuth, R.D.; Genersch, E. Production of the catechol type siderophore bacillibactin by the honey bee pathogen Paenibacillus larvae. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terabayashi, Y.; Sano, M.; Yamane, N.; Marui, J.; Tamano, K.; Sagara, J.; Dohmoto, M.; Oda, K.; Ohshima, E.; Tachibana, K.; et al. Identification and characterization of genes responsible for biosynthesis of kojic acid, an industrially important compound from Aspergillus oryzae. Fungal. Genet. Biol. 2010, 47, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WAGENINGEN. Available online: http://www.metalign.nl (accessed on 2 April 2016).
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, W.B. Determination of flavanones in citrus fruits. Anal. Chem. 1947, 19, 476–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, A.; Mavi, A.; Kara, A.A. Determination of antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Rumex crispus L. extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4083–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.





© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.E.; Lee, S.; Jang, E.S.; Shin, H.W.; Moon, B.S.; Lee, C.H. Metabolomic Profiles of Aspergillus oryzae and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens During Rice Koji Fermentation. Molecules 2016, 21, 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21060773
Lee DE, Lee S, Jang ES, Shin HW, Moon BS, Lee CH. Metabolomic Profiles of Aspergillus oryzae and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens During Rice Koji Fermentation. Molecules. 2016; 21(6):773. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21060773
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Da Eun, Sunmin Lee, Eun Seok Jang, Hye Won Shin, Byoung Seok Moon, and Choong Hwan Lee. 2016. "Metabolomic Profiles of Aspergillus oryzae and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens During Rice Koji Fermentation" Molecules 21, no. 6: 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21060773
APA StyleLee, D. E., Lee, S., Jang, E. S., Shin, H. W., Moon, B. S., & Lee, C. H. (2016). Metabolomic Profiles of Aspergillus oryzae and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens During Rice Koji Fermentation. Molecules, 21(6), 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21060773