Aloin Suppresses Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Response and Apoptosis by Inhibiting the Activation of NF-κB
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
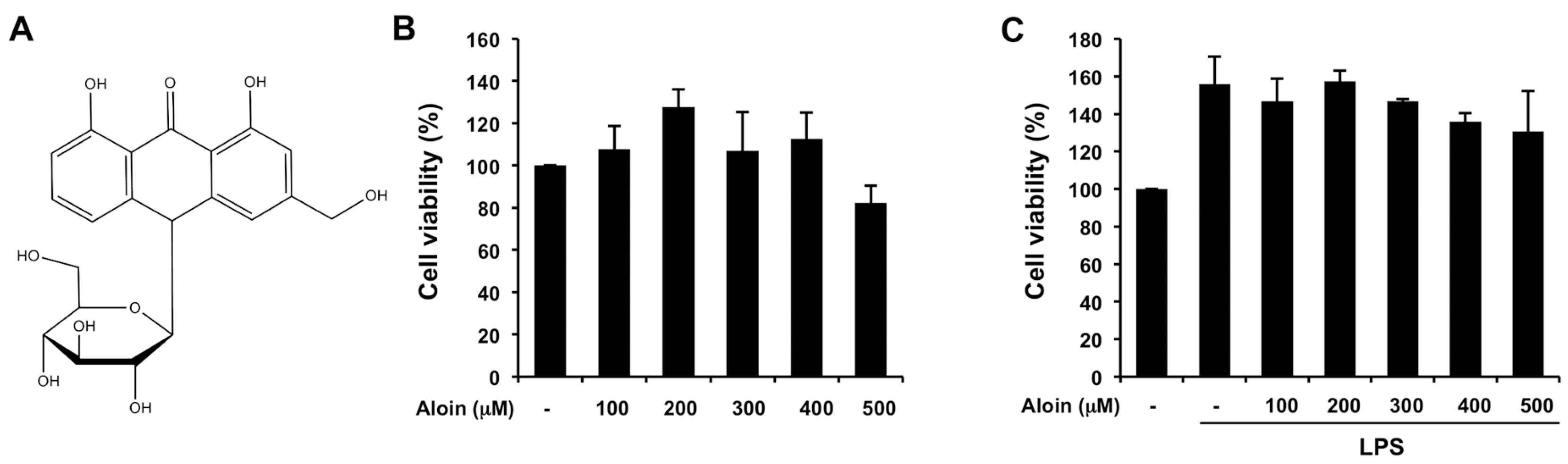
2.1. Effects of Aloin on Cell Viability in Macrophages
2.2. Aloin Inhibits LPS-Induced IL-6 and TNF-α Expression
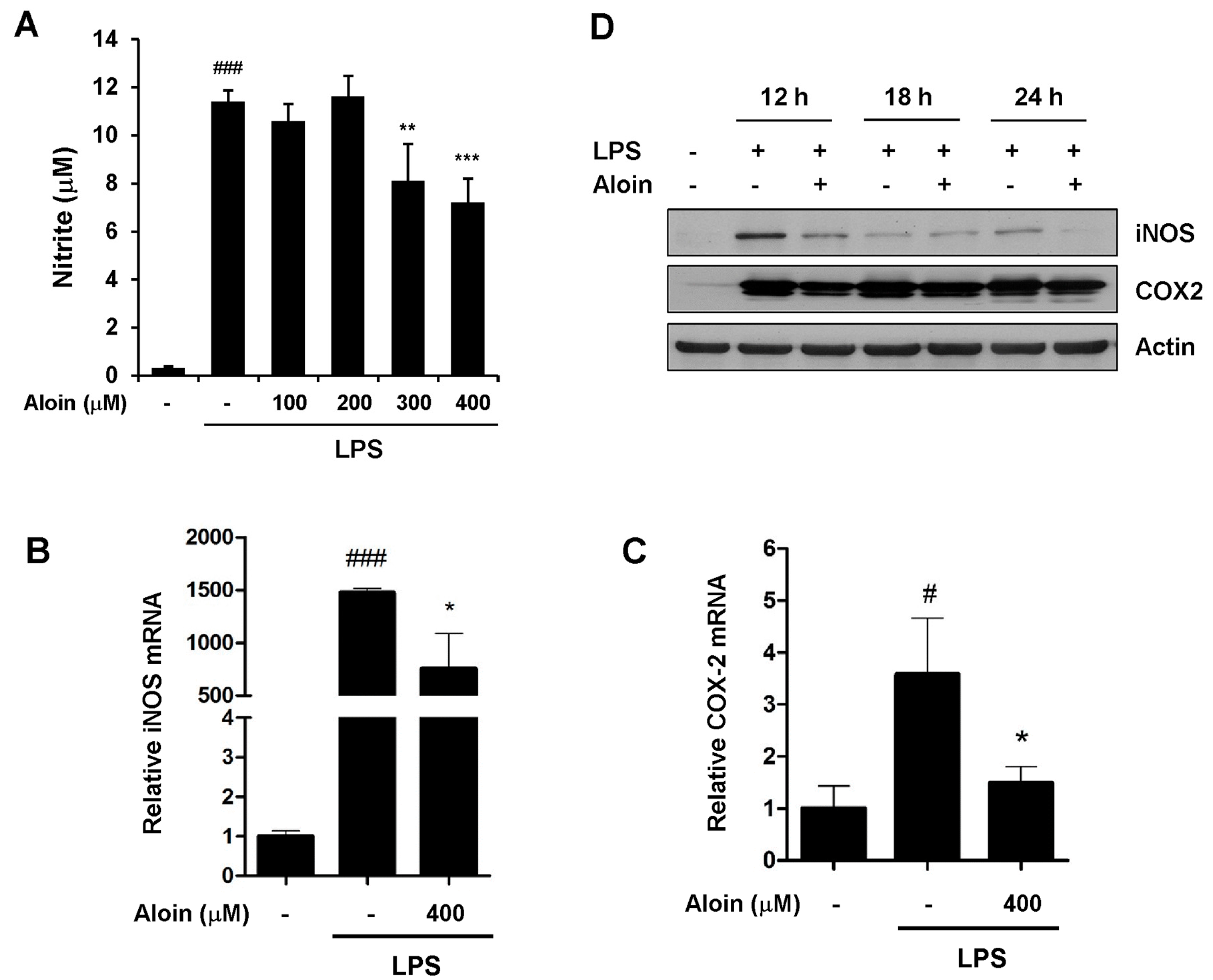
2.3. Aloin Attenuates LPS-Induced NO Production
2.4. Aloin Suppresses iNOS and COX-2 Expression
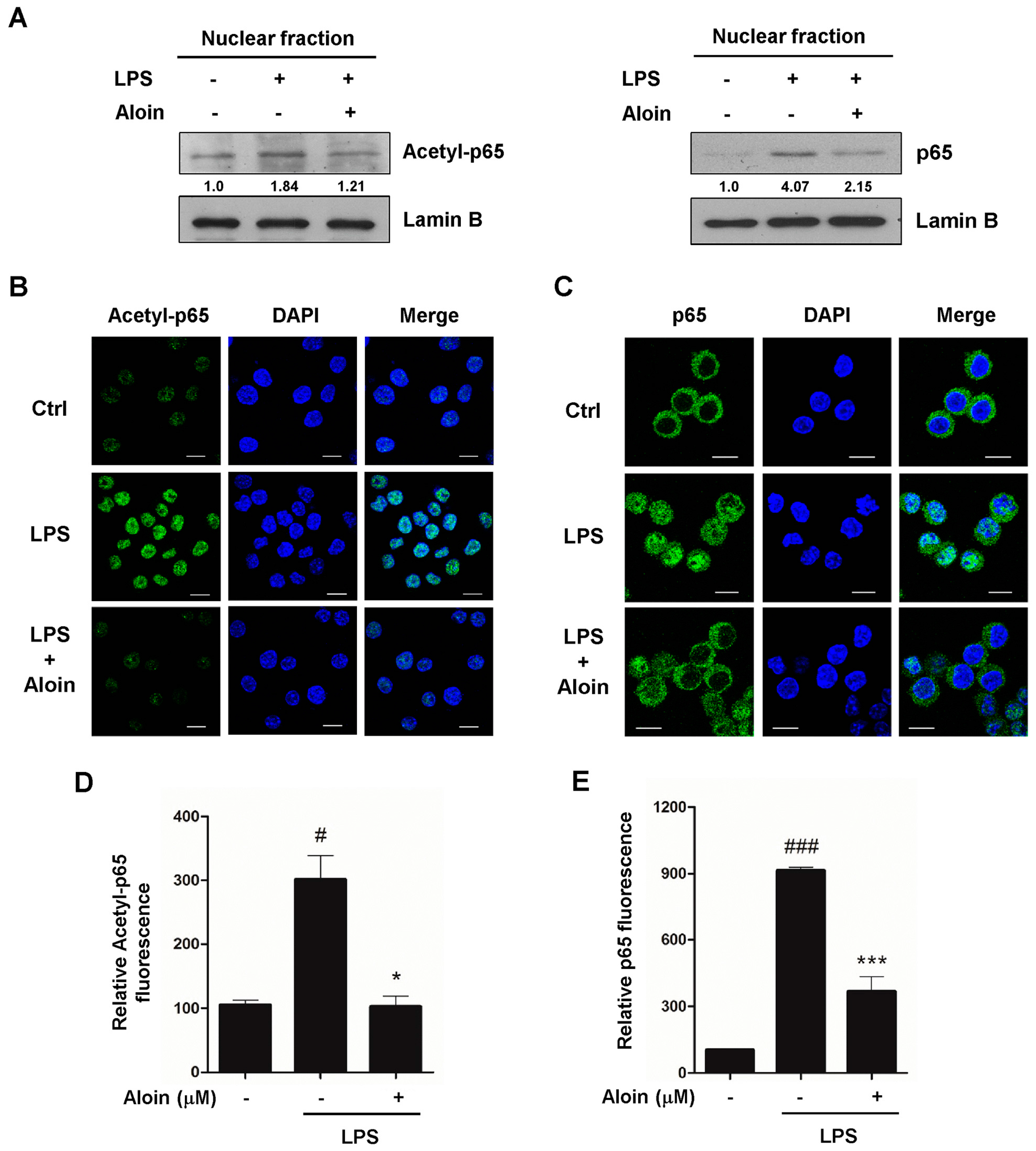
2.5. Aloin Inhibits LPS-Induced p65 Phosphorylation and Acetylation
2.6. Aloin Inhibits LPS-Induced Nuclear Translocation of p65
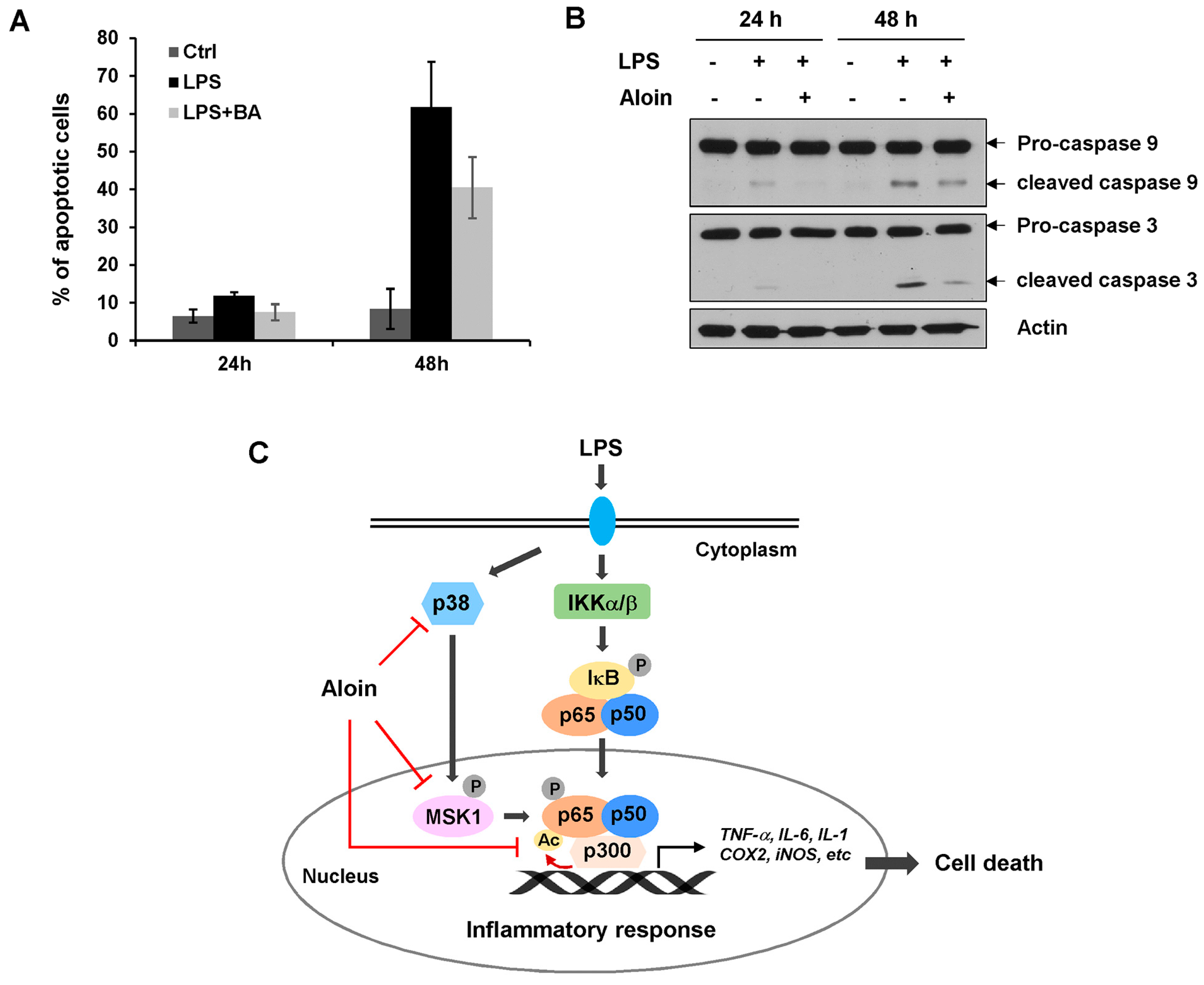
2.7. Aloin Prevents LPS-Induced Apoptotic Cell Death
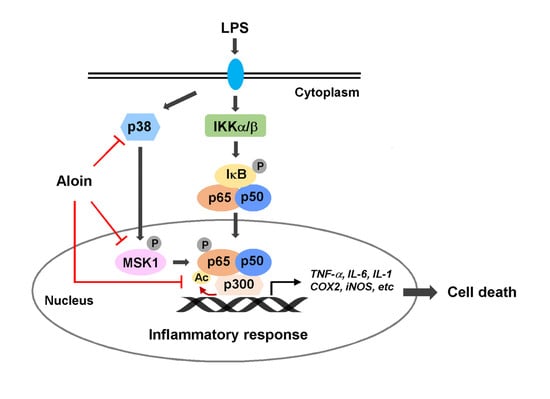
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
4.2. Cell Viability Assay
4.3. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.4. Nitric Oxide Measurement
4.5. Cytokine Measurement
4.6. Western Blot Analysis
4.7. Immunofluorescence
4.8. Flow Cytometry
4.9. Statistical Analyses
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oeckinghaus, A.; Ghosh, S. The NF-kappaB Family of Transcription Factors and Its Regulation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a000034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, A.C.; Konczak, I.; Sze, D.M.; Ramzan, I. Molecular Pathways for Cancer Chemoprevention by Dietary Phytochemicals. Nutr. Cancer 2011, 63, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tak, P.P.; Firestein, G.S. NF-kappaB: A Key Role in Inflammatory Diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neurath, M.F.; Pettersson, S.; Meyer zum Buschenfelde, K.H.; Strober, W. Local Administration of Antisense Phosphorothioate Oligonucleotides to the p65 Subunit of NF-kappa B Abrogates Established Experimental Colitis in Mice. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, T.; Takeuchi, E.; Tomita, N.; Morishita, R.; Kaneko, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Nakase, T.; Seki, H.; Kato, K.; Kaneda, Y.; et al. Suppressed Severity of Collagen-Induced Arthritis by in Vivo Transfection of Nuclear Factor kappaB Decoy Oligodeoxynucleotides as a Gene Therapy. Arthritis Rheumatol. 1999, 42, 2532–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlag, D.M.; Ransone, L.; Tak, P.P.; Han, Z.; Palanki, M.; Barbosa, M.S.; Boyle, D.; Manning, A.M.; Firestein, G.S. The Effect of a T Cell-Specific NF-kappa B Inhibitor on in Vitro Cytokine Production and Collagen-Induced Arthritis. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 1652–1658. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoesel, B.; Schmid, J.A. The Complexity of NF-kappaB Signaling in Inflammation and Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, N.D. Post-Translational Modifications Regulating the Activity and Function of the Nuclear Factor Kappa B Pathway. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6717–6730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christian, F.; Smith, E.L.; Carmody, R.J. The Regulation of NF-kappaB Subunits by Phosphorylation. Cells 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.; May, M.J.; Jimi, E.; Ghosh, S. The Phosphorylation Status of Nuclear NF-kappa B Determines its Association with CBP/p300 or HDAC-1. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Fischle, W.; Verdin, E.; Greene, W.C. Duration of Nuclear NF-kappaB Action Regulated by Reversible Acetylation. Science 2001, 293, 1653–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiernan, R.; Bres, V.; Ng, R.W.; Coudart, M.P.; El Messaoudi, S.; Sardet, C.; Jin, D.Y.; Emiliani, S.; Benkirane, M. Post-Activation Turn-Off of NF-kappaB-Dependent Transcription is Regulated by Acetylation of p65. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 2758–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.F.; Mu, Y.; Greene, W.C. Acetylation of RelA at Discrete Sites Regulates Distinct Nuclear Functions of NF-kappaB. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 6539–6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beppu, H.; Koike, T.; Shimpo, K.; Chihara, T.; Hoshino, M.; Ida, C.; Kuzuya, H. Radical-Scavenging Effects of Aloe Arborescens Miller on Prevention of Pancreatic islet B-cell Destruction in Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 89, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.Y.; Kwon, H.J.; Sung, M.K. Dietary aloin, Aloesin, or Aloe-Gel Exerts anti-Inflammatory Activity in a Rat Colitis model. Life Sci. 2011, 88, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.Y.; Kwon, H.J.; Sung, M.K. Evaluation of Aloin and Aloe-Emodin as Anti-Inflammatory Agents in Aloe by Using Murine Macrophages. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.A.; Trevisan, G.; Hoffmeister, C.; Rossato, M.F.; Boligon, A.A.; Walker, C.I.; Klafke, J.Z.; Oliveira, S.M.; Silva, C.R.; Athayde, M.L.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects of Aloe Saponaria Haw in a Model of UVB-Induced Paw Sunburn in Rats. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2014, 133, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamiza, O.O.; Rehman, M.U.; Khan, R.; Tahir, M.; Khan, A.Q.; Lateef, A.; Sultana, S. Chemopreventive Effects of Aloin Against 1,2-Dimethylhydrazine-Induced Preneoplastic Lesions in the Colon of Wistar Rats. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2014, 33, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niciforovic, A.; Adzic, M.; Spasic, S.D.; Radojcic, M.B. Antitumor Effects of a Natural Anthracycline Analog (Aloin) Involve Altered Activity of Antioxidant Enzymes in HeLaS3 cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2007, 6, 1200–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmat, A.Y.; Tomasetto, C.; Rio, M.C. Cytotoxicity of a Natural Anthraquinone (Aloin) Against Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines with and without ErbB-2: Topoisomerase IIalpha Coamplification. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2006, 5, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmat, A.Y.; El-Gerzawy, S.M.; Rafaat, A. DNA Ploidy and S Phase Fraction of Breast and Ovarian Tumor Cells Treated with a Natural Anthracycline Analog (aloin). Cancer Biol. Ther. 2005, 4, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, L.; Zhang, L.; Fan, K.; Wang, J. Aloin Promotes A549 Cell Apoptosis via the Reactive Oxygen Speciesmitogen Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway and p53 Phosphorylation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 5759–5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Q.; Pan, H.; Lou, H.; Xu, Y.; Tian, L. Inhibition of the Angiogenesis and Growth of Aloin in Human Colorectal Cancer in Vitro and In Vivo. Cancer Cell Int. 2013, 13, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.S.; Jung, H.Y.; Park, E.Y.; Kim, J.; Lee, W.J.; Bae, Y.S. Cutting Edge: Direct Interaction of TLR4 with NAD(P)H Oxidase 4 Isozyme is Essential for Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Production of Reactive Oxygen Species and Activation of NF-kappa B. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 3589–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Shared Principles in NF-kappaB Signaling. Cell 2008, 132, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chen, Z.J. Regulation of NF-kappaB by Ubiquitination. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deak, M.; Clifton, A.D.; Lucocq, L.M.; Alessi, D.R. Mitogen- and Stress-Activated Protein Kinase-1 (MSK1) is Directly Activated by MAPK and SAPK2/p38, and may Mediate activation of CREB. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 4426–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeulen, L.; De Wilde, G.; Van Damme, P.; Vanden Berghe, W.; Haegeman, G. Transcriptional Activation of the NF-kappaB p65 Subunit by Mitogen and Stress-Activated Protein Kinase-1 (MSK1). EMBO J. 2003, 22, 1313–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Hayden, M.S. New Regulators of NF-kappaB in Inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marletta, M.A. Nitric Oxide Synthase Structure and Mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 12231–12234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pautz, A.; Art, J.; Hahn, S.; Nowag, S.; Voss, C.; Kleinert, H. Regulation of the Expression of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase. Nitric Oxide 2010, 23, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.W.; Kashiwabara, Y.; Nathan, C. Role of Transcription Factor NF-kappa B/Rel in Induction of Nitric Oxide Synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 4705–4708. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.S.; Mann, M.; DuBois, R.N. The Role of Cyclooxygenases in Inflammation, Cancer, and Development. Oncogene 1999, 18, 7908–7916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmedtje, J.F., Jr.; Ji, Y.S.; Liu, W.L.; DuBois, R.N.; Runge, M.S. Hypoxia Induces Cyclooxygenase-2 via the NF-kappaB p65 Transcription Factor in Human Vascular Endothelial Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobin, C.; Morteau, O.; Han, D.S.; Balfour Sartor, R. Specific NF-kappaB Blockade Selectively Inhibits Tumour Necrosis Factor-Alpha-Induced COX-2 but not Constitutive COX-1 Gene Expression in HT-29 Cells. Immunology 1998, 95, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.B.; Wong, F.; Harlan, J.M.; Chaudhary, P.M.; Hood, L.; Karsan, A. Lipopolysaccharide Mediates Endothelial Apoptosis by a FADD-Dependent Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 20185–20188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannerman, D.D.; Sathyamoorthy, M.; Goldblum, S.E. Bacterial Lipopolysaccharide Disrupts Endothelial Monolayer Integrity and Survival Signaling Events Through Caspase Cleavage of Adherens Junction Proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 35371–35380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, Y.; Morikawa, A.; Sugiyama, T.; Koide, N.; Jiang, G.Z.; Lwin, T.; Yoshida, T.; Yokochi, T. Augmentation of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Thymocyte Apoptosis by Interferon-Gamma. Cell Immunol. 1997, 177, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xaus, J.; Comalada, M.; Valledor, A.F.; Lloberas, J.; Lopez-Soriano, F.; Argiles, J.M.; Bogdan, C.; Celada, A. LPS Induces Apoptosis in Macrophages mostly through the Autocrine Production of TNF-alpha. Blood 2000, 95, 3823–3831. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Parrillo, J.E. Pathogenetic Mechanisms of Septic Shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, M.M.; Shelhamer, J.H.; Natanson, C.; Alling, D.W.; Parrillo, J.E. Serial Cardiovascular Variables in Survivors and Nonsurvivors of Human Septic Shock: Heart Rate as an early Predictor of Prognosis. Crit. Care Med. 1987, 15, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albina, J.E.; Cui, S.; Mateo, R.B.; Reichner, J.S. Nitric Oxide-Mediated Apoptosis in Murine Peritoneal Macrophages. J. Immunol. 1993, 150, 5080–5085. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sarih, M.; Souvannavong, V.; Adam, A. Nitric Oxide Synthase Induces Macrophage Death by Apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 191, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Isatsu, K.; Nishihara, T.; Aiuchi, T.; Nakaya, K.; Hasegawa, K. Mechanisms Involved in Apoptosis of Human Macrophages Induced by Lipopolysaccharide from Actinobacillus Actinomycetemcomitans in the Presence of Cycloheximide. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 1856–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwabara, T.; Imajoh-Ohmi, S. LPS-Induced Apoptosis is Dependent upon Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Apoptosis 2004, 9, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.; Liu, L.; Lao, Y.; Liao, W.; Liao, M.; Luo, X.; Wu, J.; Xie, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, N. MicroRNA-181a Suppresses Parkin-Mediated Mitophagy and Sensitizes Neuroblastoma Cells to Mitochondrial Uncoupler-Induced Apoptosis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 42274–42287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Aloin is available from the authors. |


© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, X.; Zhang, H.; Wei, X.; Shi, M.; Fan, P.; Xie, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, N. Aloin Suppresses Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Response and Apoptosis by Inhibiting the Activation of NF-κB. Molecules 2018, 23, 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030517
Luo X, Zhang H, Wei X, Shi M, Fan P, Xie W, Zhang Y, Xu N. Aloin Suppresses Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Response and Apoptosis by Inhibiting the Activation of NF-κB. Molecules. 2018; 23(3):517. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030517
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Xuan, Haowei Zhang, Xiduan Wei, Mengjuan Shi, Ping Fan, Weidong Xie, Yaou Zhang, and Naihan Xu. 2018. "Aloin Suppresses Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Response and Apoptosis by Inhibiting the Activation of NF-κB" Molecules 23, no. 3: 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030517
APA StyleLuo, X., Zhang, H., Wei, X., Shi, M., Fan, P., Xie, W., Zhang, Y., & Xu, N. (2018). Aloin Suppresses Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Response and Apoptosis by Inhibiting the Activation of NF-κB. Molecules, 23(3), 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030517