Bridging from Brain to Tumor Imaging: (S)-(−)- and (R)-(+)-[18F]Fluspidine for Investigation of Sigma-1 Receptors in Tumor-Bearing Mice †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
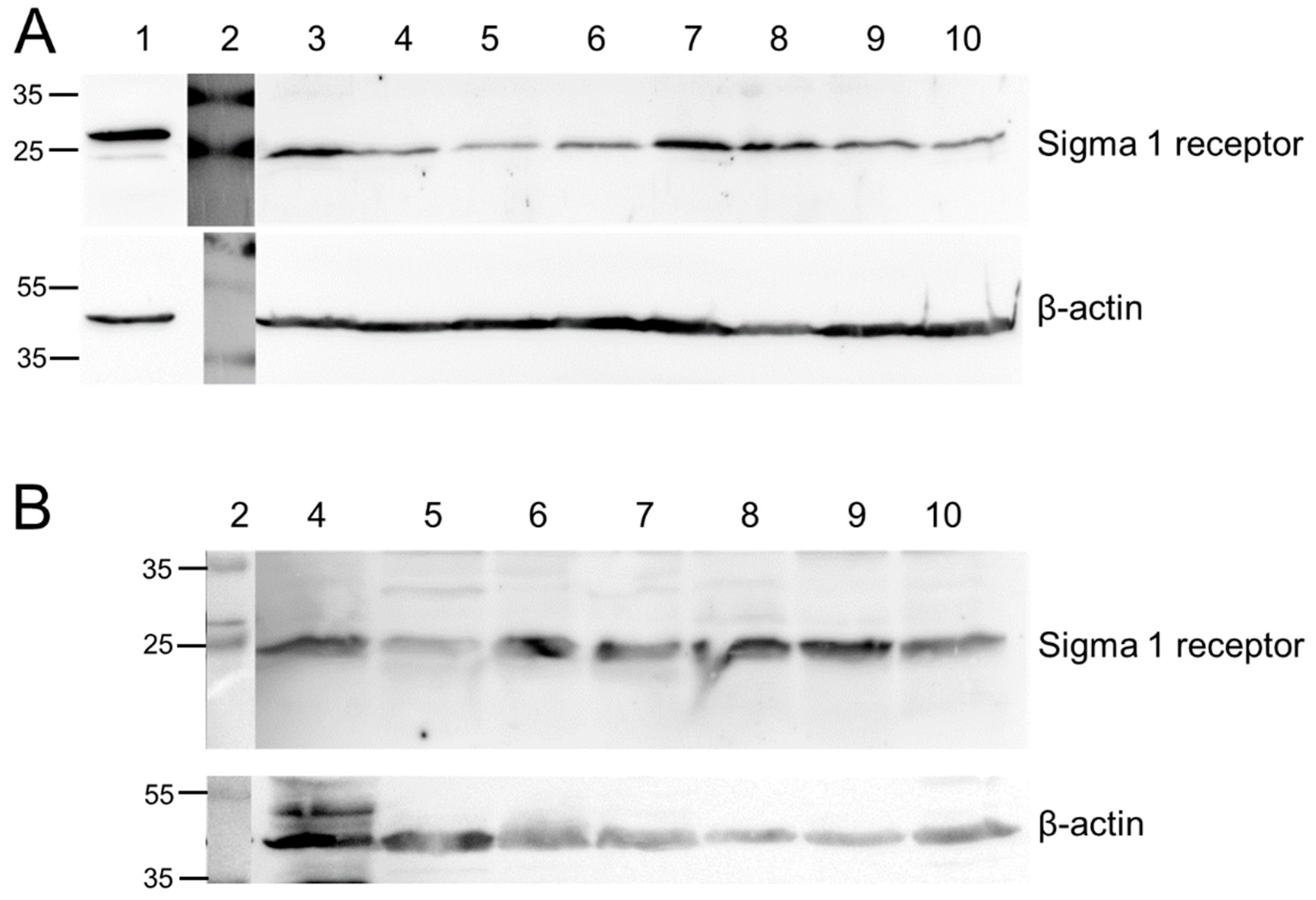
2.1. Cell Specific Expression/Synthesis of Sig1R
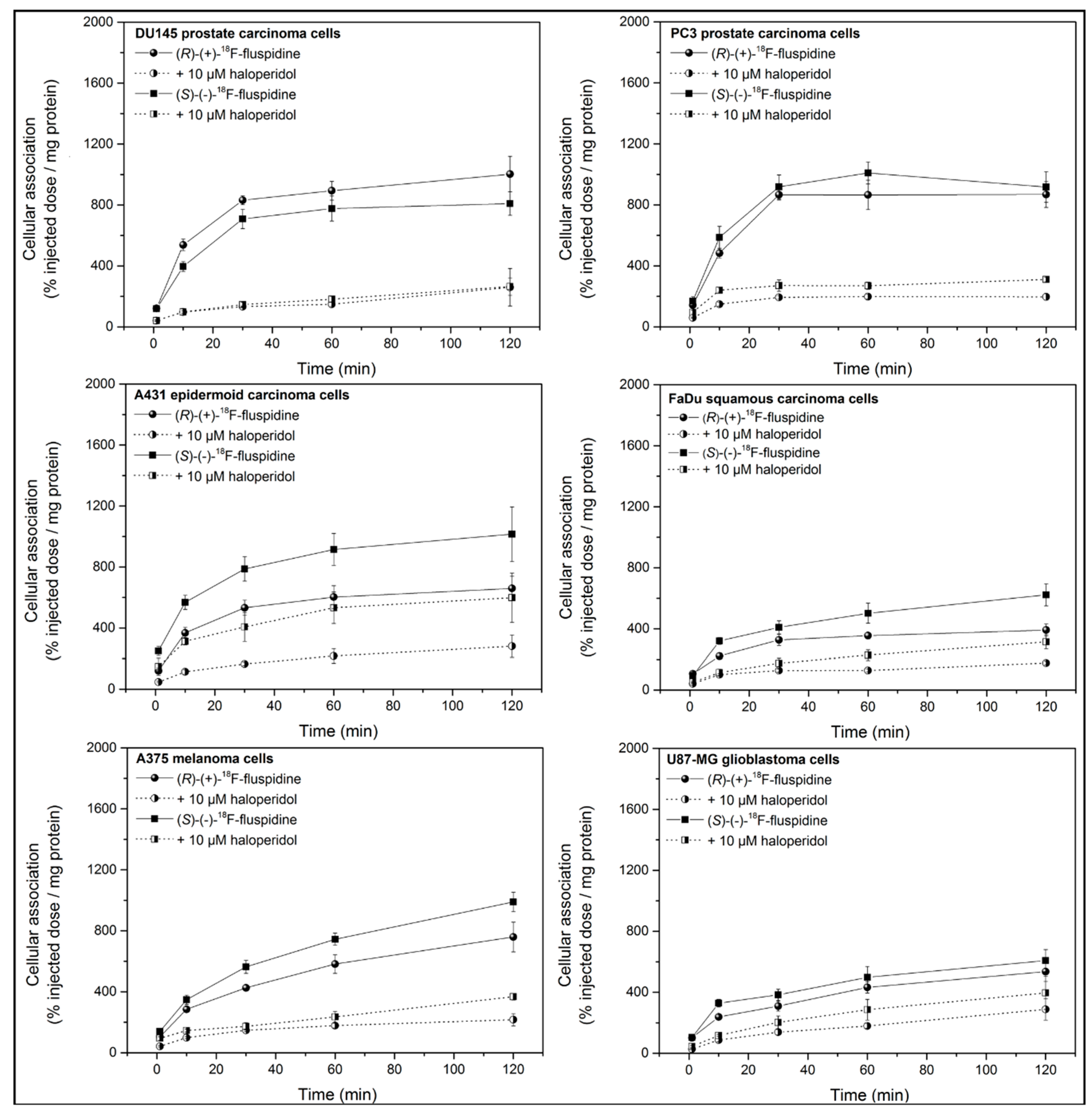
2.2. Cellular Accumulation of [18F]fluspidine
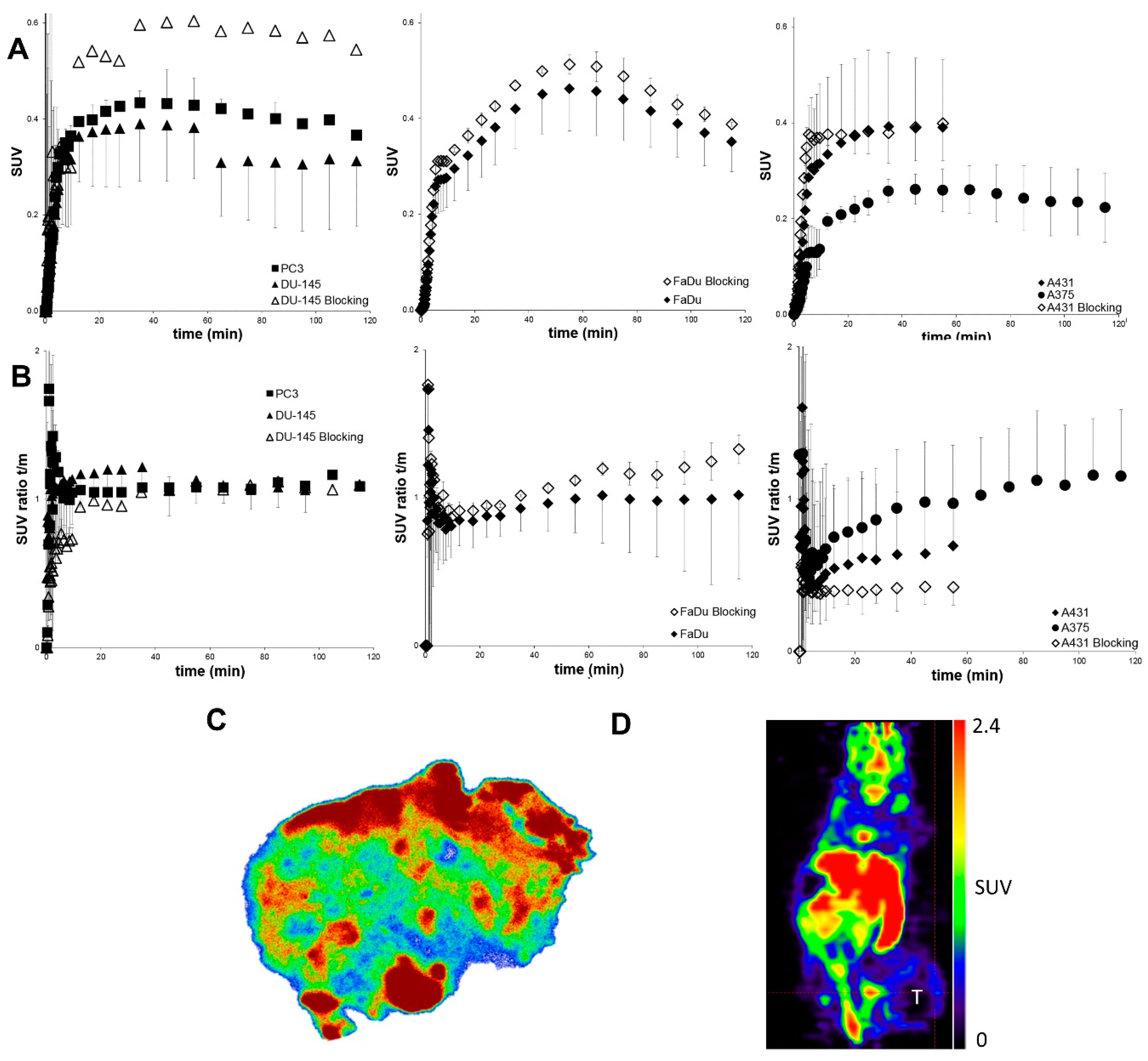
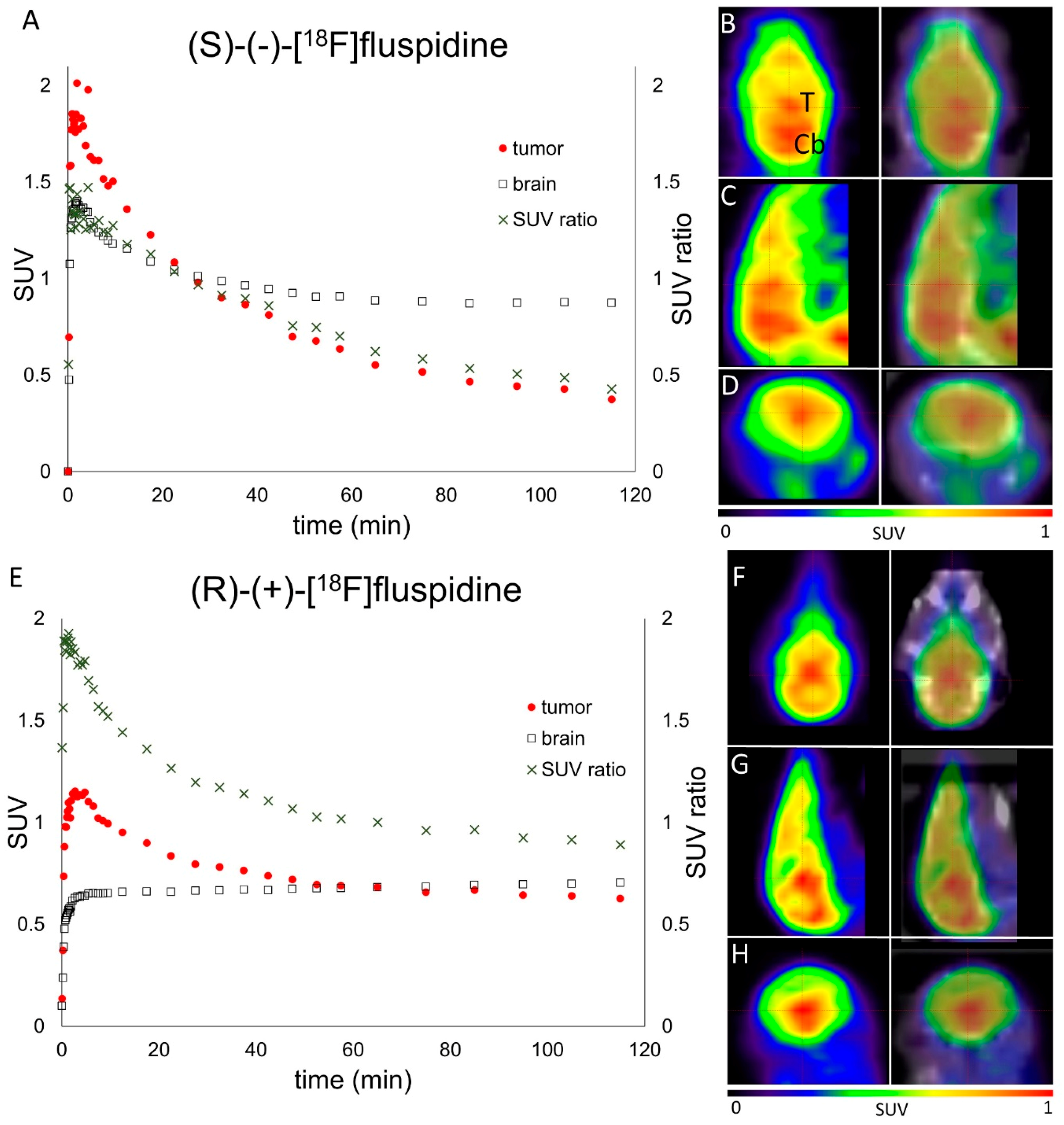
2.3. Small Animal PET Imaging
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Radiochemistry
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Immunoblotting (Western Blot)
4.4. Cellular Accumulation
4.5. Heterotopic Tumor Model and Small Animal PET Imaging
4.6. Orthotopic Brain Tumor Model: Stereotactic Intracranial Tumor Cell Inoculation and PET/CT Imaging
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steel, G.G.; Peckham, M.J. Exploitable mechanisms in combined radiotherapy-chemotherapy: The concept of additivity. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1979, 5, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohren, E.M.; Turkington, T.G.; Coleman, R.E. Clinical applications of PET in oncology. Radiology 2004, 231, 305–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambhir, S.S.; Czernin, J.; Schwimmer, J.; Silverman, D.H.; Coleman, R.E.; Phelps, M.E. A tabulated summary of the FDG PET literature. J. Nucl. Med. 2001, 42, 1S–93S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kukuk, D.; Reischl, G.; Raguin, O.; Wiehr, S.; Judenhofer, M.S.; Calaminus, C.; Honndorf, V.S.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Schönberger, T.; Duchamp, O. Assessment of PET tracer uptake in hormone-independent and hormone-dependent xenograft prostate cancer mouse models. J. Nucl. Med. 2011, 52, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.; Liu, H.; Unterschemmann, K.; Ellinghaus, P.; Liu, S.; Gekeler, V.; Cheng, Z.; Berndorff, D.; Gambhir, S.S. 18F-FAZA PET imaging response tracks the reoxygenation of tumors in mice upon treatment with the mitochondrial complex i inhibitor BAY87-2243. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldherr, C.; Mellinghoff, I.K.; Tran, C.; Halpern, B.S.; Rozengurt, N.; Safaei, A.; Weber, W.A.; Stout, D.; Satyamurthy, N.; Barrio, J.; et al. Monitoring antiproliferative responses to kinase inhibitor therapy in mice with 3'-deoxy-3'-18F-fluorothymidine PET. J. Nucl. Med. 2005, 46, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ekshyyan, O.; Sibley, D.; Caldito, G.C.; Sunderland, J.; Vascoe, C.; Nathan, C.A.O. 18F-fluorodeoxythymidine micro–positron-emission tomography versus 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose micro–positron-emission tomography for in vivo minimal residual disease imaging. Laryngoscope 2013, 123, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruechner, K.; Bergmann, R.; Santiago, A.; Mosch, B.; Yaromina, A.; Hessel, F.; Hofheinz, F.; van den Hoff, J.; Baumann, M.; Beuthien-Baumann, B. Comparison of [18F] FDG uptake and distribution with hypoxia and proliferation in fadu human squamous cell carcinoma (hscc) xenografts after single dose irradiation. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2009, 85, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Ong, L.-C.; Ranganath, S.H.; Zheng, L.; Kee, I.; Zhan, W.; Yu, S.; Chow, P.K.; Wang, C.-H. A dual tracer 18F-fch/18F-FDG PET imaging of an orthotopic brain tumor xenograft model. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witney, T.H.; Pisaneschi, F.; Alam, I.S.; Trousil, S.; Kaliszczak, M.; Twyman, F.; Brickute, D.; Nguyen, Q.-D.; Schug, Z.; Gottlieb, E. Preclinical evaluation of 3-18F-fluoro-2, 2-dimethylpropionic acid as an imaging agent for tumor detection. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 1506–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, J.D.; Schauwecker, D.S.; Davidson, D.; Wenck, S.; Jung, S.H.; Hutchins, G. FDG–PET sensitivity for melanoma lymph node metastases is dependent on tumor volume. J. Surg. Oncol. 2001, 77, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Effert, P.J.; Bares, R.; Handt, S.; Wolff, J.M.; Bull, U.; Jakse, G. Metabolic imaging of untreated prostate cancer by positron emission tomography with sup fluorine-18-labeled deoxyglucose. J. Urol. 1996, 155, 994–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, T.; Takeuchi, H.; Okazawa, H.; Tsujikawa, T.; Fujibayashi, Y. Grading of brain glioma with 1-11 c-acetate PET: Comparison with 18F-FDG PET. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2008, 35, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seltzer, M.A.; Barbaric, Z.; Belldegrun, A.; Naitoh, J.; Dorey, F.; Phelps, M.E.; Gambhir, S.S.; Hoh, C.K. Comparison of helical computerized tomography, positron emission tomography and monoclonal antibody scans for evaluation of lymph node metastases in patients with prostate specific antigen relapse after treatment for localized prostate cancer. J. Urol. 1999, 162, 1322–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Cloughesy, T.; Kamdar, N.; Satyamurthy, N.; Bergsneider, M.; Liau, L.; Mischel, P.; Czernin, J.; Phelps, M.E.; Silverman, D.H. Imaging proliferation in brain tumors with 18f-flt PET: Comparison with 18F-FDG. J. Nucl. Med. 2005, 46, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Basu, S.; Alavi, A. Molecular imaging (PET) of brain tumors. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2009, 19, 625–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydar, E.; Palmer, C.P.; Djamgoz, M.B. Sigma receptors and cancer. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 5029–5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mach, R.; Huang, Y.; Buchheimer, N.; Kuhner, R.; Wu, L.; Morton, T.; Wang, L.-M.; Ehrenkaufer, R.; Wallen, C.; Wheeler, K. [18F] n-4′-fluorobenzyl-4-(3-bromophenyl) acetamide for imaging the sigma receptor status of tumors: Comparison with [18F] FDG and [125I] IUDR. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2001, 28, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, R.H.; Smith, C.R.; Al-Nabulsi, I.; Whirrett, B.R.; Childers, S.R.; Wheeler, K.T. Σ2 receptors as potential biomarkers of proliferation in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vilner, B.J.; John, C.S.; Bowen, W.D. Sigma-1 and sigma-2 receptors are expressed in a wide variety of human and rodent tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al-Nabulsi, I.; Mach, R.; Wang, L.; Wallen, C.; Keng, P.; Sten, K.; Childers, S.; Wheeler, K. Effect of ploidy, recruitment, environmental factors, and tamoxifen treatment on the expression of sigma-2 receptors in proliferating and quiescent tumour cells. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 81, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, K.; Wang, L.; Wallen, C.; Childers, S.; Cline, J.; Keng, P.; Mach, R. Sigma-2 receptors as a biomarker of proliferation in solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 82, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crottès, D.; Guizouarn, H.; Martin, P.; Borgese, F.; Soriani, O. The sigma-1 receptor: A regulator of cancer cell electrical plasticity? Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydar, E.; Onganer, P.; Perrett, R.; Djamgoz, M.B.; Palmer, C.P. The expression and functional characterization of sigma (σ) 1 receptors in breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Lett. 2006, 242, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, K.; Ishiwata, K. Sigma receptor ligands: Possible application as therapeutic drugs and as radiopharmaceuticals. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2006, 12, 3857–3876. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee Collier, T.; O’Brien, J.C.; Waterhouse, R.N. Synthesis of [18f]-1-(3-fluoropropyl)-4-(4-cyanophenoxymethyl)-piperidine: A potential sigma-1 receptor radioligand for PET. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 1996, 38, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Xie, F.; Ye, J.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Cui, B.; Wang, L.; Lu, J.; Steinbach, J.; Brust, P.; Huang, Y. 1-(4-[18F]fluorobenzyl)-4-[(tetrahydrofuran-2-yl) methyl] piperazine: A novel suitable radioligand with low lipophilicity for imaging σ1 receptors in the brain. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 4161–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, K.; Ishiwata, K.; Tajima, H.; Ishii, S.-I.; Matsuno, K.; Homma, Y.; Senda, M. In vivo evaluation of [11C]SA4503 as a PET ligand for mapping cns sigma 1 receptors. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2000, 27, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, M.L.; Shen, B.; Nielsen, C.H.; Behera, D.; Buckmaster, C.L.; Mesangeau, C.; Zavaleta, C.; Vuppala, P.K.; Jamalapuram, S.; Avery, B.A. Evaluation of σ-1 receptor radioligand 18F-FTC-146 in rats and squirrel monkeys using PET. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Bergmann, R.; Kniess, T.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Mamat, C.; Neuber, C.; Liu, B.; Steinbach, J.; Brust, P.; Pietzsch, J. 18F-labeled 1, 4-dioxa-8-azaspiro [4.5] decane derivative: Synthesis and biological evaluation of a σ1 receptor radioligand with low lipophilicity as potent tumor imaging agent. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 5395–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, S.; Wiese, C.; Maestrup, E.G.; Hiller, A.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Scheunemann, M.; Schepmann, D.; Steinbach, J.; Wünsch, B.; Brust, P. Molecular imaging of σ receptors: Synthesis and evaluation of the potent σ1 selective radioligand [18F] fluspidine. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2011, 38, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holl, K.; Falck, E.; Köhler, J.; Schepmann, D.; Humpf, H.U.; Brust, P.; Wünsch, B. Synthesis, characterization, and metabolism studies of fluspidine enantiomers. Chem. Med. Chem. 2013, 8, 2047–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brust, P.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Becker, G.; Patt, M.; Donat, C.K.; Stittsworth, S.; Fischer, S.; Hiller, A.; Wenzel, B.; Dukic-Stefanovic, S. Distinctive in vivo kinetics of the new σ1 receptor ligands (R)-(+)-and (S)-(–)-18F-fluspidine in porcine brain. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 1730–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kranz, M.; Sattler, B.; Wüst, N.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Patt, M.; Meyer, P.M.; Fischer, S.; Donat, C.K.; Wünsch, B.; Hesse, S. Evaluation of the enantiomer specific biokinetics and radiation doses of [18F]fluspidine—A new tracer in clinical translation for imaging of σ1 receptors. Molecules 2016, 21, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, E.; Cai, Z.; Bois, F.; Holden, D.; Lin, S.-F.; Lara-Jaime, T.; Kapinos, M.; Chen, Y.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Fischer, S. PET imaging evaluation of four σ1 radiotracers in nonhuman primates. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.-X.; Li, E.-M.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Liao, L.-D.; Xu, X.-E.; Wu, Z.-Y.; Shen, J.-H.; Xu, L.-Y. Overexpression of sigma1 receptor and its positive associations with pathologic tnm classification in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2012, 60, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, D.; Persaud, L.; Dejoie, J.; Happy, M.; Brannigan, O.; De Jesus, D.; Sauane, M. Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (trail) activates caspases in human prostate cancer cells through sigma 1 receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 470, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, C.S.; Vilner, B.J.; Geyer, B.C.; Moody, T.; Bowen, W.D. Targeting sigma receptor-binding benzamides as in vivo diagnostic and therapeutic agents for human prostate tumors. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 4578–4583. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brune, S.; Schepmann, D.; Lehmkuhl, K.; Frehland, B.; Wünsch, B. Characterization of ligand binding to the σ1 receptor in a human tumor cell line (rpmi 8226) and establishment of a competitive receptor binding assay. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2012, 10, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybczynska, A.A.; de Bruyn, M.; Ramakrishnan, N.K.; de Jong, J.R.; Elsinga, P.H.; Helfrich, W.; Dierckx, R.A.; van Waarde, A. In vivo responses of human A375m melanoma to a σ ligand: 18f-FDG PET imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 2013, 54, 1613–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mégalizzi, V.; Decaestecker, C.; Debeir, O.; Spiegl-Kreinecker, S.; Berger, W.; Lefranc, F.; Kast, R.E.; Kiss, R. Screening of anti-glioma effects induced by sigma-1 receptor ligands: Potential new use for old anti-psychiatric medicines. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 2893–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colabufo, N.A.; Berardi, F.; Contino, M.; Niso, M.; Abate, C.; Perrone, R.; Tortorella, V. Antiproliferative and cytotoxic effects of some σ2 agonists and σ1 antagonists in tumour cell lines. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg Arch. Path. 2004, 370, 106–113. [Google Scholar]
- Moebius, F.F.; Reiter, R.J.; Bermoser, K.; Glossmann, H.; Cho, S.Y.; Paik, Y.-K. Pharmacological analysis of sterol δ8-δ7 isomerase proteins with [3h] ifenprodil. Mol. Pharmacol. 1998, 54, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiese, C.; Maestrup, E.G.; Schepmann, D.; Vela, J.M.; Holenz, J.; Buschmann, H.; Wünsch, B. Pharmacological and metabolic characterisation of the potent σ1 receptor ligand 1′-benzyl-3-methoxy-3h-spiro[[2]benzofuran-1,4′-piperidine]. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2009, 61, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maestrup, E.G.; Wiese, C.; Schepmann, D.; Brust, P.; Wünsch, B. Synthesis, pharmacological activity and structure affinity relationships of spirocyclic σ1 receptor ligands with a (2-fluoroethyl) residue in 3-position. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLarty, K.; Fasih, A.; Scollard, D.A.; Done, S.J.; Vines, D.C.; Green, D.E.; Costantini, D.L.; Reilly, R.M. 18F-FDG small-animal PET/ct differentiates trastuzumab-responsive from unresponsive human breast cancer xenografts in athymic mice. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50, 1848–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, R.K. Normalization of tumor vasculature: An emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science 2005, 307, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cespedes, M.V.; Casanova, I.; Parreño, M.; Mangues, R. Mouse models in oncogenesis and cancer therapy. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2006, 8, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taillandier, L.; Antunes, L.; Angioi-Duprez, K. Models for neuro-oncological preclinical studies: Solid orthotopic and heterotopic grafts of human gliomas into nude mice. J. Neurosci. Methods 2003, 125, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagashira, H.; Bhuiyan, S.; Shioda, N.; Hasegawa, H.; Kanai, H.; Fukunaga, K. Σ 1-receptor stimulation with fluvoxamine ameliorates transverse aortic constriction-induced myocardial hypertrophy and dysfunction in mice. Am. J. Physiol. 2010, 299, H1535–H1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagashira, H.; Matsumoto, T.; Taguchi, K.; Zhang, C.; Han, F.; Ishida, K.; Nemoto, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Fukunaga, K. Vascular endothelial σ1-receptor stimulation with SA4503 rescues aortic relaxation via akt/enos signaling in ovariectomized rats with aortic banding. Circulation 2013, 77, 2831–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, C.; Große Maestrup, E.; Galla, F.; Schepmann, D.; Hiller, A.; Fischer, S.; Ludwig, F.A.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Donat, C.K.; Brust, P. Comparison of in silico, electrochemical, in vitro and in vivo metabolism of a homologous series of (radio) fluorinated σ1 receptor ligands designed for positron emission tomography. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 2445–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kniess, T.; Laube, M.; Bergmann, R.; Sehn, F.; Graf, F.; Steinbach, J.; Wuest, F.; Pietzsch, J. Radiosynthesis of a 18F-labeled 2, 3-diarylsubstituted indole via mcmurry coupling for functional characterization of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in vitro and in vivo. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 3410–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamat, C.; Mosch, B.; Neuber, C.; Köckerling, M.; Bergmann, R.; Pietzsch, J. Fluorine-18 radiolabeling and radiopharmacological characterization of a benzodioxolylpyrimidine-based radiotracer targeting the receptor tyrosine kinase ephb4. ChemMedChem 2012, 7, 1991–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reissenweber, B.; Mosch, B.; Pietzsch, J. Experimental hypoxia does not influence gene expression and protein synthesis of eph receptors and ephrin ligands in human melanoma cells in vitro. Melanoma Res. 2013, 23, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, R.; Ruffani, A.; Graham, B.; Spiccia, L.; Steinbach, J.; Pietzsch, J.; Stephan, H. Synthesis and radiopharmacological evaluation of 64Cu-labeled bombesin analogs featuring a bis(2-pyridylmethyl)-1,4,7-triazacyclononane chelator. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 70, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Kong, D.K.; Zheng, M.-Q.; Murikinati, S.; Ma, C.; Yuan, P.; Li, L.; Tian, D.; Cai, Q.; Ye, C. Increased nanoparticle delivery to brain tumors by autocatalytic priming for improved treatment and imaging. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4209–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kranz, M.; Bergmann, R.; Kniess, T.; Belter, B.; Neuber, C.; Cai, Z.; Deng, G.; Fischer, S.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Y.; et al. Bridging from Brain to Tumor Imaging: (S)-(−)- and (R)-(+)-[18F]Fluspidine for Investigation of Sigma-1 Receptors in Tumor-Bearing Mice. Molecules 2018, 23, 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030702
Kranz M, Bergmann R, Kniess T, Belter B, Neuber C, Cai Z, Deng G, Fischer S, Zhou J, Huang Y, et al. Bridging from Brain to Tumor Imaging: (S)-(−)- and (R)-(+)-[18F]Fluspidine for Investigation of Sigma-1 Receptors in Tumor-Bearing Mice. Molecules. 2018; 23(3):702. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030702
Chicago/Turabian StyleKranz, Mathias, Ralf Bergmann, Torsten Kniess, Birgit Belter, Christin Neuber, Zhengxin Cai, Gang Deng, Steffen Fischer, Jiangbing Zhou, Yiyun Huang, and et al. 2018. "Bridging from Brain to Tumor Imaging: (S)-(−)- and (R)-(+)-[18F]Fluspidine for Investigation of Sigma-1 Receptors in Tumor-Bearing Mice" Molecules 23, no. 3: 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030702
APA StyleKranz, M., Bergmann, R., Kniess, T., Belter, B., Neuber, C., Cai, Z., Deng, G., Fischer, S., Zhou, J., Huang, Y., Brust, P., Deuther-Conrad, W., & Pietzsch, J. (2018). Bridging from Brain to Tumor Imaging: (S)-(−)- and (R)-(+)-[18F]Fluspidine for Investigation of Sigma-1 Receptors in Tumor-Bearing Mice. Molecules, 23(3), 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030702




