Comparison between Multi-Linear- and Radial-Basis-Function-Neural-Network-Based QSPR Models for The Prediction of The Critical Temperature, Critical Pressure and Acentric Factor of Organic Compounds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
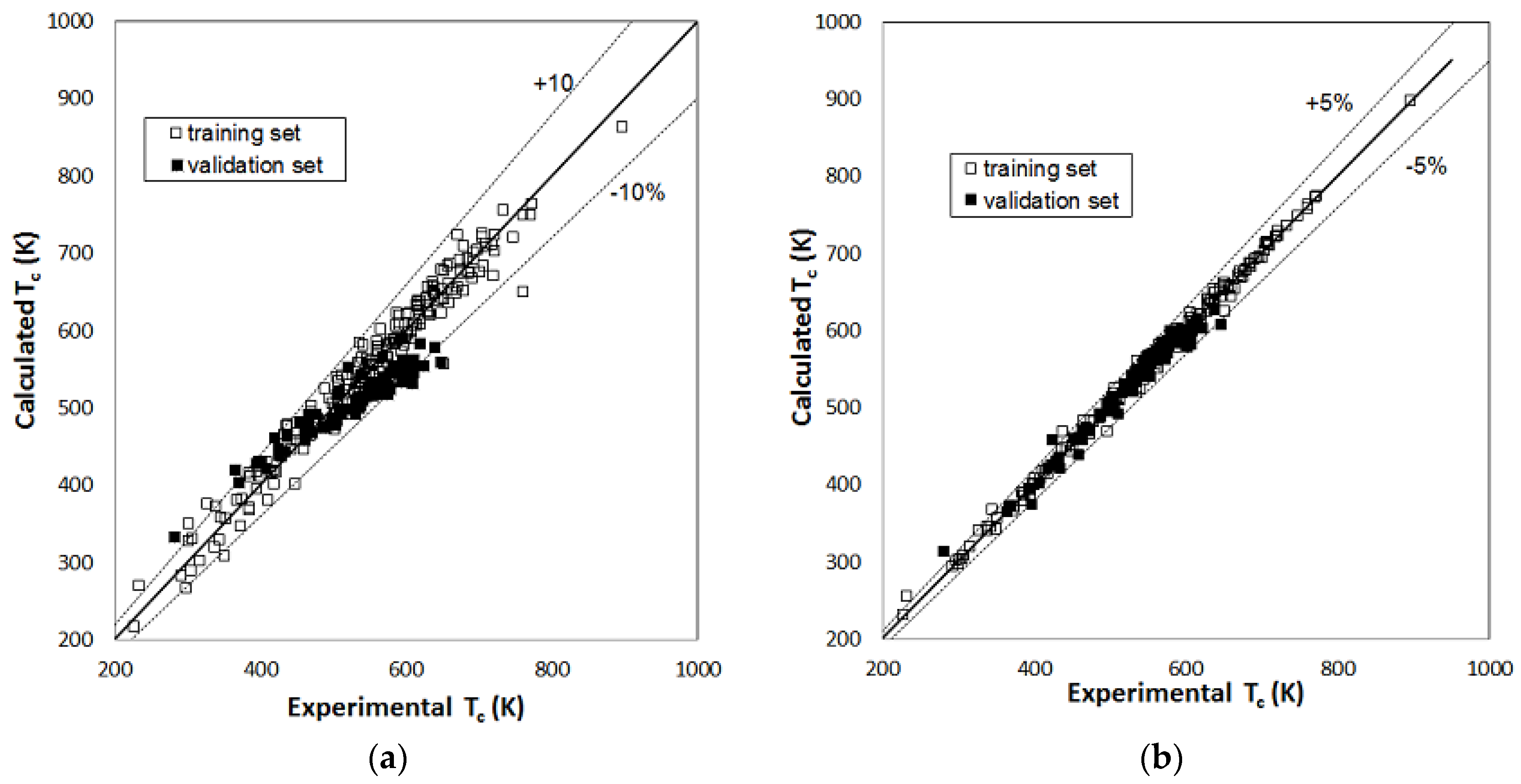
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Database Selection
4.2. Molecular Modelling and Descriptor Generation
4.3. Multi-Linear Regression Correlations
4.4. Radial Basis Function Neural Networks
4.5. Model Validation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| absolute percent relative deviation | |
| average absolute percent deviation | |
| AM1 | Austin Model 1 |
| ANN | artificial neural network |
| GC | group contribution |
| MLR | multi-linear regression |
| NDDO | neglect of diatomic differential overlap |
| QSPR | quantitative structure-property relationship |
| RBFNN | radial basis function neural network |
| root mean square error |
References
- Kontogeorgis, G.M.; Tassios, D.P. Critical constants and acentric factors for long-chain alkanes suitable for corresponding states applications. A critical review. Chem. Eng. J. 1997, 66, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joback, K.G.; Reid, R.C. Estimation of pure-component properties from group-contributions. Chem. Eng. Commun. 1987, 57, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Peng, D.Y. A group-contribution correlation for predicting the acentric factors of organic compounds. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1993, 71, 332–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinou, L.; Gani, R.; O’Connell, J.P. Estimation of the acentric factor and the liquid molar volume at 298 K using a new group contribution method. Fluid Phase Equilib. 1995, 103, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrero, J.; Gani, R. Group-contribution based estimation of pure component properties. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2001, 183–184, 183–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hukkerikara, A.S.; Sarup, B.; Kate, A.T.; Abildskov, J.; Sin, G.; Gani, R. Group-contribution+ (GC+) based estimation of properties of pure components: Improved property estimation and uncertainty analysis. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2012, 321, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katritzky, A.R.; Kuanar, M.; Slavov, S.; Hall, C.D. Quantitative correlation of physical and chemical properties with chemical structure: Utility for prediction. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 5714–5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreyfus, G. Neural Networks: Methodology and Applications, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 1–83. ISBN 978-3-540-22980-3. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Cowan, C.F.N.; Grant, P.M. Orthogonal least squares learning algorithm for radial basis function networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1991, 2, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Egolf, L.M.; Wessel, M.D.; Jurs, P.C. Prediction of boiling points and critical temperatures of industrially important organic compounds from molecular structure. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1994, 34, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katritzky, A.R.; Mu, L.; Karelson, M. Relationships of critical temperatures to calculated molecular properties. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1998, 38, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.E.; Costello, C.L.; Jurs, P.C. Prediction of critical temperatures and pressures of industrially important organic compounds from molecular structure. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1998, 38, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchowicz, P.; Castro, E.A. Prediction of critical temperatures and critical pressures of some industrially relevant organic substances from rather simple topological descriptors. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2002, 72, 1867–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sola, D.; Ferri, A.; Banchero, M.; Manna, L.; Sicardi, S. QSPR prediction of N-boiling point and critical properties of organic compounds and comparison with a group-contribution method. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2008, 263, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobati, M.A.; Abooali, D. Molecular based models for estimation of critical properties of pure refrigerants: Quantitative structure property relationship (QSPR) approach. Thermochim. Acta 2015, 602, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, L.H.; Story, C.T. Boiling point and critical temperature of a heterogeneous data set: QSAR with atom type electrotopological state indices using artificial neural networks. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1996, 36, 1004–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, G.; Yaffe, D.; Arenas, A.; Cohen, Y.; Giralt, F. A fuzzy ARTMAP-based quantitative structure-property relationship (QSPR) for predicting physical properties of organic compounds. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 2757–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godavarthy, S.S.; Robinson, R.L., Jr.; Gasem, K.A.M. Improved structure–property relationship models for prediction of critical properties. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2008, 264, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharagheizi, F.; Mehrpooya, M. Prediction of some important physical properties of sulfur compounds using quantitative structure–properties relationships. Mol. Divers. 2008, 12, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharagheizi, F.; Eslamimanesh, A.; Mohammadi, A.H.; Richon, D. Determination of critical properties and acentric factors of pure compounds using the artificial neural network group contribution algorithm. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2011, 56, 2460–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Liu, M.; Hua, Z.; Fan, B. Radial basis function neural network-based QSPR for the prediction of critical temperature. Chem. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2002, 62, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Liu, M.; Hu, Z.; Fan, B. Radial basis function neural network based QSPR for the prediction of critical pressures of substituted benzenes. Comput. Chem. 2002, 26, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carande, W.H.; Kazakov, A.; Muzny, C.; Frenkel, M. Quantitative structure-property relationship predictions of critical properties and acentric factors for pure compounds. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 60, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokshina, E.G.; Kuz’min, V.E.; Nedostup, V.I. QSPR modeling of critical parameters of organic compounds belonging to different classes in terms of the simplex representation of molecular structure. Russ. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 50, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boozarjomehry, R.B.; Abdolahi, F.; Moosavian, M.A. Characterization of basic properties for pure substances and petroleum fractions by neural network. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2005, 221, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.H.; Afzal, W.; Richon, D. Determination of critical properties and acentric factors of petroleum fractions using artificial neural networks. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 3225–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinifar, P.; Jamshidi, S. Development of a new generalized correlation to characterize physical properties of pure components and petroleum fractions. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2014, 363, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Database of the Project 801 of the Design Institute for Physical Property Data (DIPPR® 801), Electronic Version with Diadem® [CD-ROM], American Institute of Chemical Engineers (AIChE): New York, NY, USA, 2004.
- Todeschini, R.; Consonni, V. Molecular Descriptors for Chemoinformatics, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2009; Volume I, pp. 109–117, 161, 598. ISBN 978-3-527-31852-0. [Google Scholar]
- Balaban, A.T.; Ivanciuc, O. Historical development of topological indices. In Topological Indices and Related Descriptors in QSAR and QSPR, 1st ed.; Devillers, J., Balaban, A.T., Eds.; Gordon and Breach Science Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 21–57. ISBN 90-5699-239-2. [Google Scholar]
- Basak, S.C. Information theoretic indices of neighborhood complexity and their applications. In Topological Indices and Related Descriptors in QSAR and QSPR, 1st ed.; Devillers, J., Balaban, A.T., Eds.; Gordon and Breach Science Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 563–593. ISBN 90-5699-239-2. [Google Scholar]
- Katritzky, A.R.; Petrukhin, R.; Jain, R.; Karelson, M. QSPR analysis of flash points. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2001, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zefirov, N.S.; Kirpichenok, M.A.; Izmailov, F.F.; Trofimov, M.I. Scheme for the calculation of the electronegativities of atoms in a molecule in the framework of Sanderson’s principle. Dokl. Akad. Nauk. SSSR 1987, 296, 883–887. [Google Scholar]
- AMPAC 8.15, Semichem, Inc.: Shawnee, KS, USA, 2004.
- Dewar, M.J.S.; Zoebisch, E.G.; Healy, E.F.; Stewart, J.J.P. AM1: A new general purpose quantum mechanical molecular model. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 3902–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, C.J. Essentials of Computational Chemistry: Theories and Models: Theories and Models, 2nd ed.; Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2004; pp. 145–146. ISBN 978-0-470-09182-1. [Google Scholar]
- CODESSA 2.642, Semichem, Inc.: Shawnee, KS, USA, 1995.
- MATLAB 9.2.0, The MathWorks, Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2017.


| MLR Model | RBFNN Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training Set | Validation Set | Training Set | Validation Set | ||
| Tc | total number of compounds | 215 | 91 | 215 | 91 |
| compounds with AD% > 10% | 8 | 9 | - | 1 | |
| compounds with AD% < 5% | 184 | 49 | 203 | 80 | |
| AAD% | 3.2% | 6.2% | 0.92% | 1.7% | |
| RMSE (K) | 22.0 | 37.4 | 7.2 | 11.9 | |
| Pc | total number of compounds | 215 | 91 | 215 | 91 |
| compounds with AD% > 10% | 40 | 25 | - | 3 | |
| compounds with AD% < 5% | 124 | 45 | 171 | 60 | |
| AAD% | 6.1% | 8.5% | 1.9% | 3.5% | |
| RMSE (MPa) | 0.40 | 0.47 | 0.11 | 0.18 | |
| ω | total number of compounds | 215 | 91 | 215 | 91 |
| compounds with AD% > 10% | 65 | 45 | 1 | 7 | |
| compounds with AD% < 5% | 98 | 25 | 168 | 39 | |
| AAD% | 8.7% | 12.2% | 2.0% | 4.8% | |
| RMSE (−) | 0.040 | 0.066 | 0.0086 | 0.023 | |
| Tc | Pc | ω | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE for MLR models | Egolf and coworkers [10] | 12 K | - | - |
| Katritzky and coworkers [11] | 15 K | - | - | |
| Turner and coworkers [12] | 7.7 K | 0.16 MPa | - | |
| Sola and coworkers [14] | 12 K | 0.25 MPa | - | |
| Sobati and Abooali [15] | 16.3 K | 0.27 MPa | - | |
| this work (1) | 27.5 K | 0.42 MPa | 0.049 | |
| RMSE for ANN models | Espinosa and coworkers [17] | 5.6 K | 0.08 MPa | - |
| Gharagheizi and Mehrpooya [19] | 18 K | 0.17 MPa | 0.032 | |
| Yao and coworkers [21] | 14 K | - | - | |
| Yao and coworkers [22] | 0.15 MPa | - | ||
| this work (1) | 8.8 K | 0.13 MPa | 0.015 | |
| Tc | Pc | ω | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAD% | MLR model (1) | 4.1% | 6.8% | 9.7% |
| RBFNN model (1) | 1.2% | 2.3% | 2.8% | |
| Gani’s GC method (2) | 2.7% | 8.5% | 14.1% | |
| RMSE | MLR model (1) | 27.5 K | 0.42 MPa | 0.049 |
| RBFNN model (1) | 8.8 K | 0.13 MPa | 0.015 | |
| Gani’s GC method (2) | 31.1 K | 0.48 MPa | 0.099 | |
| Descriptor | Group | |
|---|---|---|
| Tc | Relative number of F atoms | Constitutional descriptor |
| Number of aromatic bonds | Constitutional descriptor | |
| Relative number of rings | Constitutional descriptor | |
| Relative molecular weight | Constitutional descriptor | |
| Moment of inertia B | Geometrical descriptor | |
| HASA2/TMSA 1/2 | Electrostatic descriptor | |
| HDCA2/TMSA | Electrostatic descriptor | |
| Topographic electronic index (all pairs) | Electrostatic descriptor | |
| Randic index (order 1) | Topological descriptor | |
| Structural Information content (order 0) | Topological descriptor | |
| Pc | Number of Cl atoms | Constitutional descriptor |
| Relative number of rings | Constitutional descriptor | |
| Molecular volume | Geometrical descriptor | |
| Moment of inertia C | Geometrical descriptor | |
| HASA1 | Electrostatic descriptor | |
| HDSA1/TMSA | Electrostatic descriptor | |
| FPSA3 | Electrostatic descriptor | |
| Relative negative charged SA | Electrostatic descriptor | |
| Relative positive charged SA | Electrostatic descriptor | |
| count of H-donors sites | Electrostatic descriptor | |
| ω | Relative number of double bonds | Constitutional descriptor |
| Molecular surface area | Geometrical descriptor | |
| Gravitation index (all bonds) | Geometrical descriptor | |
| HDCA2 | Electrostatic descriptor | |
| PNSA3 | Electrostatic descriptor | |
| Polarity parameter (Qmax − Qmin) | Electrostatic descriptor | |
| count of H-donors sites | Electrostatic descriptor | |
| Topographic electronic index (all bonds) | Electrostatic descriptor | |
| Structural Information content (order 0) | Topological descriptor | |
| Kier & Hall index (order 2) | Topological descriptor |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Banchero, M.; Manna, L. Comparison between Multi-Linear- and Radial-Basis-Function-Neural-Network-Based QSPR Models for The Prediction of The Critical Temperature, Critical Pressure and Acentric Factor of Organic Compounds. Molecules 2018, 23, 1379. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061379
Banchero M, Manna L. Comparison between Multi-Linear- and Radial-Basis-Function-Neural-Network-Based QSPR Models for The Prediction of The Critical Temperature, Critical Pressure and Acentric Factor of Organic Compounds. Molecules. 2018; 23(6):1379. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061379
Chicago/Turabian StyleBanchero, Mauro, and Luigi Manna. 2018. "Comparison between Multi-Linear- and Radial-Basis-Function-Neural-Network-Based QSPR Models for The Prediction of The Critical Temperature, Critical Pressure and Acentric Factor of Organic Compounds" Molecules 23, no. 6: 1379. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061379
APA StyleBanchero, M., & Manna, L. (2018). Comparison between Multi-Linear- and Radial-Basis-Function-Neural-Network-Based QSPR Models for The Prediction of The Critical Temperature, Critical Pressure and Acentric Factor of Organic Compounds. Molecules, 23(6), 1379. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061379






