Expression, Purification, and Characterization of a Novel Hybrid Peptide with Potent Antibacterial Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Construction of Expression Plasmids
2.2. Expression of Fusion Protein SUMO–C–L
2.3. Purification and Cleavage of Fusion Protein SUMO–C–L
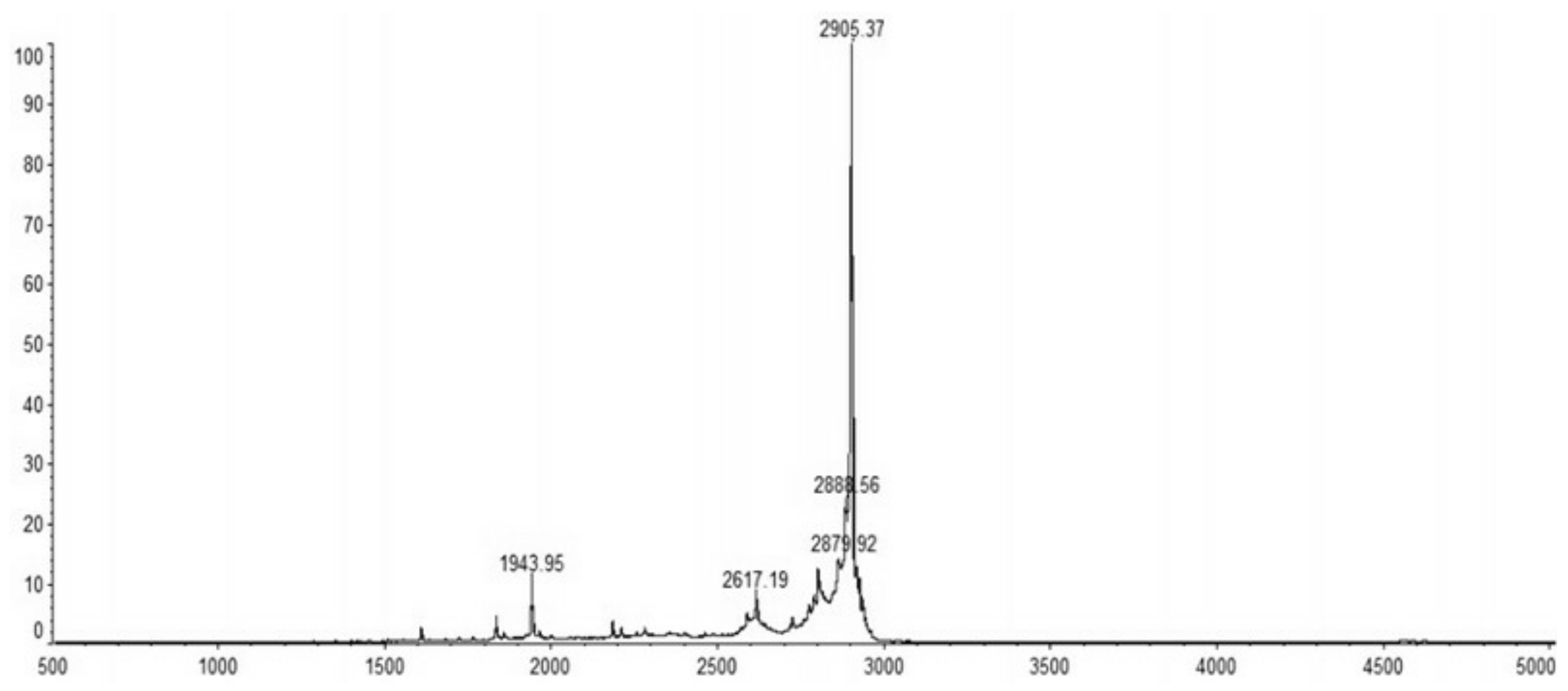
2.4. Purification of Recombinant C–L
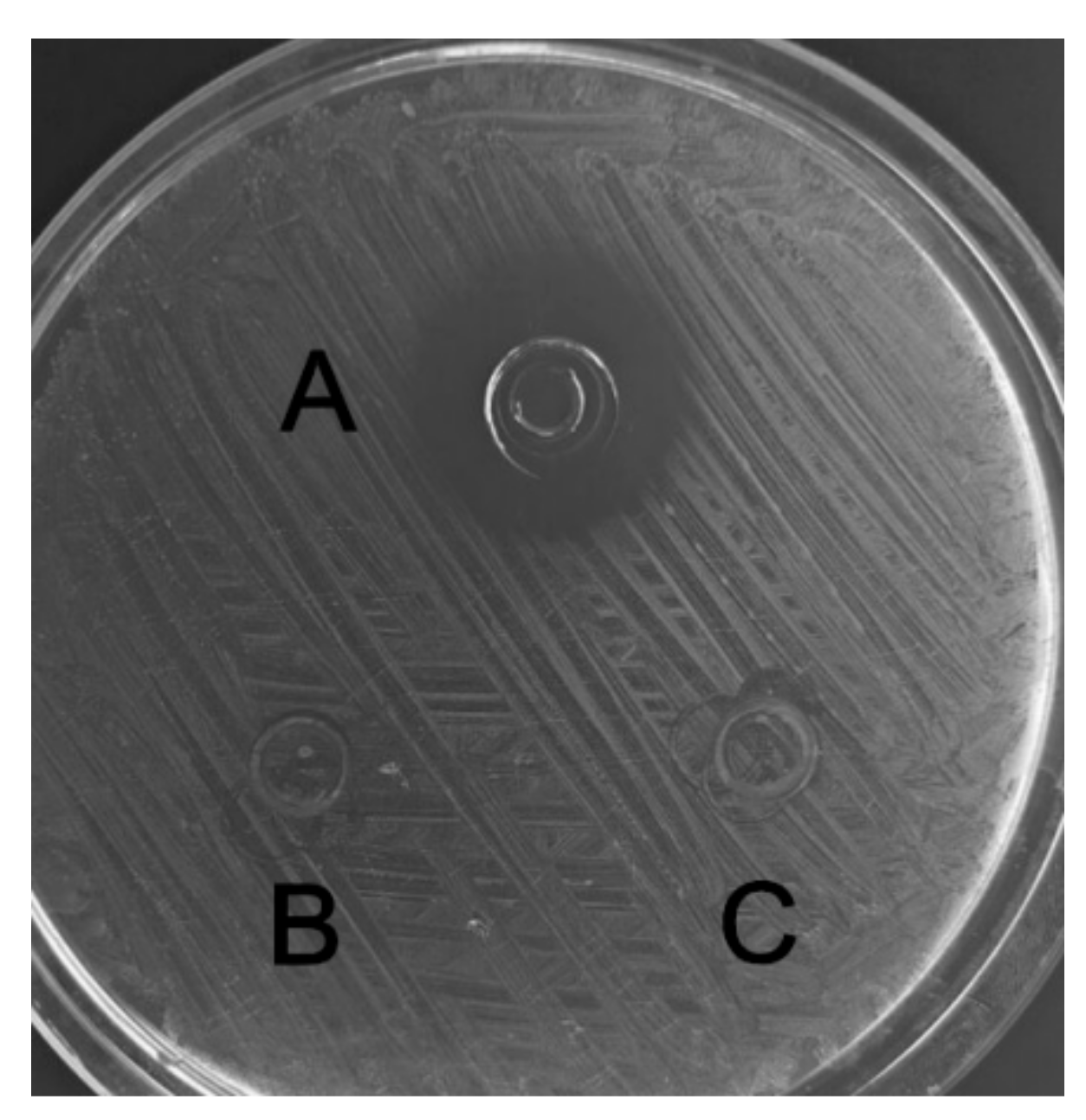
2.5. Antibacterial and Hemolytic Activity of C, L, and C–L
2.6. Effect of Temperature, pH and Proteinases on C–L Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids, and Enzymes
4.2. Synthesis of Hybrid Peptide
4.3. PCR Amplification and Construction of Expression Vectors
4.4. Expression of SUMO–C–L Fusion Protein
4.5. Purification of SUMO–C–L Fusion Protein
4.6. Cleavage of SUMO–C–L Fusion Protein and Purification the Recombinant C–L
4.7. Antibacterial Studies
4.8. Hemolytic Asssay
4.9. Assessment of Stability
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santos, N.A.; Fernandes, R.S.; Sgardioli, B.F.; Ramos, M.A.S.; Piccoli, J.P.; Camargo, I.L.B.C.; Bauab, T.M.; Cilli, E.M. Antibacterial activity of the non-cytotoxic peptide (p-BthTX-I)(2) and Its serum degradation product against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Molecules 2017, 22, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.B.; Wu, R.J.; Si, D.Y.; Liao, X.D.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhang, R.J. Novel hybrid peptide cecropin A (1-8)-LL37(17-30) with potential antibacterial activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.P.; Gallo, R.L. AMPed up immunity: How antimicrobial peptides have multiple roles in immune defense. Trends Immunol. 2008, 30, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deptula, M.; Wardowska, A.; Dzierzynska, M.; Rodziewicz-Motowidlo, S.; Pikula, M. Antibacterial peptides in dermatology-strategies for evaluation of allergic potential. Molecules 2018, 23, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantic, J.M.; Jovanovic, I.P.; Radosavljevic, G.D.; Arsenijevic, N.N.; Conlon, J.M.; Lukic, M.L. The potential of frog skin-derived peptides for development into therapeutically-valuable immunomodulatory agents. Molecules 2017, 22, 2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeaman, M.R.; Yount, N.Y. Mechanisms of antimicrobial peptide action and resistance. Pharmacol. Rev. 2003, 55, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.V.R.; Yedery, R.D.; Aranha, C. Antimicrobial peptides: Premises and promises. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2004, 24, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brogden, K.A. Antimicrobial peptides: Pore formers or metabolic inhibitors in bacteria? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.S.; Mishra, B.; Epand, R.F.; Epand, R.M. High-quality 3D structures shine light on antibacterial, anti-biofilm and antiviral activities of human cathelicidin LL-37 and its fragments. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2014, 1838, 2160–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, R.; Silva, J.P.; Rodrigues, A.C.; Costa, R.; Guardao, L.; Schmitt, F.; Soares, R.; Vilanova, M.; Domingues, L.; Gama, M. Wound healing activity of the human antimicrobial peptide LL37. Peptides 2011, 32, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thennarasu, S.; Tan, A.M.; Penumatchu, R.; Shelburne, C.E.; Heyl, D.L.; Ramamoorthy, A. Antimicrobial and membrane disrupting activities of a peptide derived from the human cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide LL37. Biophys. J. 2010, 98, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacalum, M.; Radu, M. Cationic antimicrobial peptides cytotoxicity on mammalian cells: An analysis using therapeutic index integrative concept. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2015, 21, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacometti, A.; Cirioni, O.; Kamysz, W.; Amato, G.; Silvestri, C.; Del Prete, M.S.; Lukasiak, J.; Scalise, G. Comparative activities of cecropin A, melittin, and cecropin A–melittin peptide CA(1–7)M(2–9)NH2 against multidrug-resistant nosocomial isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. Peptides 2003, 24, 1315–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.T.; Wu, D.; Li, W.Z.; Zheng, X.; Li, W.F.; Shan, A.S. High specific selectivity and membrane-active mechanism of synthetic cationic hybrid antimicrobial peptides based on the peptide FV7. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saugar, J.M.; Rodriguez-Hernandez, M.J.; de la Torre, B.G.; Pachon-Ibanez, M.E.; Fernandez-Reyes, M.; Andreu, D.; Pachon, J.; Rivas, L. Activity of cecropin A-melittin hybrid peptides against colistin-resistant clinical strains of Acinetobacter baumannii: Molecular basis for the differential mechanisms of action. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1251–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bommarius, B.; Jenssen, H.; Elliott, M.; Kindrachuk, J.; Pasupuleti, M.; Gieren, H. Cost-effective expression and purification of antimicrobial and host defense peptides in Escherichia coli. Peptides 2010, 31, 1957–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.Q.; Li, L.X.; Ding, J.X.; Wen, L.Z.; Shen, Z.L. High-level expression and novel purification strategy of recombinant thanatin analog in Escherichia coli. Curr. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demonte, D.; Dundas, C.M.; Park, S. Expression and purification of soluble monomeric streptavidin in Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 986, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomala, M.; Lavrentieva, A.; Moretti, P.; Rinas, U.; Kasper, C.; Stahl, F. Preparation of bioactive soluble human leukemia inhibitory factor from recombinant Escherichia coli using thioredoxin as fusion partner. Protein Expr. Purif. 2010, 73, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, C.; Zhang, H.W.; Song, D.G.; Xie, Y.G.; Feng, J.; Wang, Y.Z. Expressing antimicrobial peptide cathelicidin-BF in Bacillus subtilis using SUMO technology. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 3651–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.N.; Quan, C.S.; Liu, B.Q.; Xu, Y.B.; Zhao, P.C.; Xiong, W.; Fan, S.D. Green fluorescent protein (GFP)-based overexpression screening and characterization of AgrC, a receptor protein of quorum sensing in Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 18470–18487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Hwang, S.W.; Lee, W.J.; Yoon, H.K.; Lee, H.S. High-level expression of antimicrobial peptide mediated by a fusion partner reinforcing formation of inclusion bodies. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 277, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias-Figueroa, B.; Valdiviezo-Godina, N.; Siqueiros-Cendon, T.; Sinagawa-Garcia, S.; Arevalo-Gallegos, S.; Rascon-Cruz, Q. High-level expression of recombinant bovine lactoferrin in Pichia pastoris with antimicrobial activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Zhang, S.Q.; Li, B.C.; Qiu, W.; Jiao, B.; Zhang, J. Expression of a cytotoxic cationic antibacterial peptide in Escherichia coli using two fusion partners. Protein Expr. Purif. 2008, 57, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, T.R.; Edavettal, S.C.; Hall, J.P.; Mattern, M.R. SUMO fusion technology for difficult-to-express proteins. Protein Expr. Purif. 2005, 43, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.C.; Zhang, S.Q.; Dan, W.B.; Chen, Y.Q.; Cao, P. Expression in Escherichia coli and purification of bioactive antibacterial peptide ABP-CM4 from the Chinese silk worm, Bombyx mori. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 29, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.Y.; Henzler-Wildman, K.A.; Ramamoorthy, A. Expression and purification of a recombinant LL-37 from Escherichia coli. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2006, 1758, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Jin, F.; Yu, X.; Ji, S.; Wang, J.; Cheng, H. Expression and purification of a recombinant antibacterial peptide, cecropin, from Escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2007, 53, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Jin, F.; Yu, X.; Ren, S.; Hu, J.; Zhang, W. High-level expression of the recombinant hybrid peptide cecropinA(1–8)-magainin2(1–12) with an ubiquitin fusion partner in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2007, 55, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.H.; Hancock, R. Interaction of the cyclic antimicrobial cationic peptide bactenecin with the outer and cytoplasmic membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 274, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, P.; Hong, Y.; Liu, W. Fusion expression of cecropin B-like antibacterial peptide in Escherichia coli and preparation of its antiserum. Biotechnol. Lett. 2010, 32, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacey, B.; Hamrita, TK.; Lacy, M.P.; Van Wicklen, G.L.; Czarick, M. Monitoring deep body temperature responses of broilers using biotelemetry. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2000, 9, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warriss, P.D.; Pope, S.J.; Brown, S.N.; Wilkins, L.J.; Knowles, T.G. Estimating the body temperature of groups of pigs by thermal imaging. Vet. Rec. 2006, 158, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snoeck, V.; Cox, E.; Verdonck, F.; Joensuu, J.J.; Goddeeris, B.M. Influence of porcine intestinal pH and gastric digestion on antigenicity of F4 fimbriae for oral immunisation. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 98, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, A.G. The activity of pepsin, chymotrypsin and trypsin during 24 h periods in the small intestine of growing pigs. Br. J. Nutr. 1982, 48, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mantovani, H.C.; Hu, H.J.; Worobo, R.W.; Russell, J.B. Bovicin HC5, a bacteriocin from Streptococcus bovis HC5. Microbiology 2002, 148, 3347–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Osnes, T.; Sandstad, O.; Skar, V.; Osnes, M.; Kierulf, P. Total protein in common duct bile measured by acetonitrile precipitation and a micro bicinchoninic acid (BCA) method. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 1993, 53, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papo, N.; Shai, Y. A molecular mechanism for lipopolysaccharide protection of gram-negative bacteria from antimicrobial peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 10378–10387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds antibacterial peptides are available from the authors. |





| Indicated Strains | MIC (μg/mL) | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | L | Recombinant C–L | Synthesized C–L | ||
| E. coli CVCC 245 | 4.2 ± 0.35 c | 85.2 ± 2.00 a | 7.2 ± 0.14 b | 7.0 ± 0.21 b | <0.01 |
| S. aureus ATCC 25923 | 198 ± 10.1 a | 58.0 ± 2.56 b | 2.2 ± 0.05 c | 2.0 ± 0.02 c | <0.01 |
| L. mono. CVCC 1599 | 64.5 ± 3.20 a | 13.4 ± 0.50 b | 2.1 ± 0.03 c | 2.2 ± 0.05 c | <0.01 |
| Indicated cell | HC50 (μg/mL) | p-Value | |||
| C | L | Recombinant C–L | Synthesized C–L | ||
| Sheep erythrocyte cell | 169 ± 8.20 b | 32 ± 1.20 c | 221 ± 3.45 a | 219 ± 2.98 a | <0.01 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, X.; Wu, R.; Zhang, L.; Ahmad, B.; Si, D.; Zhang, R. Expression, Purification, and Characterization of a Novel Hybrid Peptide with Potent Antibacterial Activity. Molecules 2018, 23, 1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061491
Wei X, Wu R, Zhang L, Ahmad B, Si D, Zhang R. Expression, Purification, and Characterization of a Novel Hybrid Peptide with Potent Antibacterial Activity. Molecules. 2018; 23(6):1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061491
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Xubiao, Rujuan Wu, Lulu Zhang, Baseer Ahmad, Dayong Si, and Rijun Zhang. 2018. "Expression, Purification, and Characterization of a Novel Hybrid Peptide with Potent Antibacterial Activity" Molecules 23, no. 6: 1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061491
APA StyleWei, X., Wu, R., Zhang, L., Ahmad, B., Si, D., & Zhang, R. (2018). Expression, Purification, and Characterization of a Novel Hybrid Peptide with Potent Antibacterial Activity. Molecules, 23(6), 1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061491




