Consequences of IDH1/2 Mutations in Gliomas and an Assessment of Inhibitors Targeting Mutated IDH Proteins
Abstract
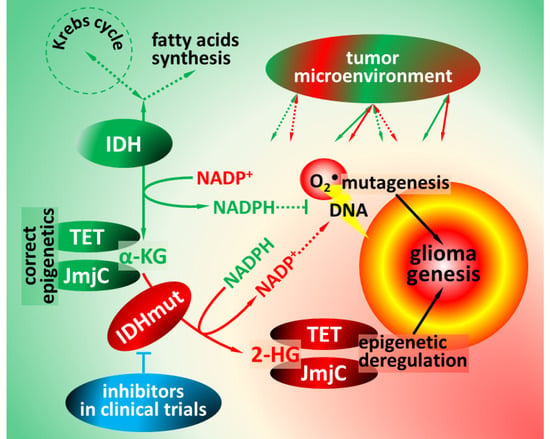
1. Functions of Isocitrate Dehydrogenases
2. Pathophysiology of Isocitrate Dehydrogenase Mutations
3. Detection of IDH Mutations Improves Classification of Gliomas and Predicts Better Survival
4. Impact of IDH Mutations on Glioma Microenvironment
5. Targeting of Mutant IDH1/2 Gliomas with Isoform-Specific Chemical Inhibitors
6. Development of IDH1-R132H Targeting Peptide Vaccines
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parsons, D.W.; Jones, S.; Zhang, X.; Lin, J.C.; Leary, R.J.; Angenendt, P.; Mankoo, P.; Carter, H.; Siu, I.M.; Gallia, G.L.; et al. An integrated genomic analysis of human glioblastoma multiforme. Science 2008, 321, 1807–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mardis, E.R.; Ding, L.; Dooling, D.J.; Larson, D.E.; McLellan, M.D.; Chen, K.; Koboldt, D.C.; Fulton, R.S.; Delehaunty, K.D.; McGrath, S.D.; et al. Recurring mutations found by sequencing an acute myeloid leukemia genome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zhao, J.; Xu, Z.; Peng, B.; Huang, Q.; Arnold, E.; Ding, J. Structures of human cytosolic NADP-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase reveal a novel self-regulatory mechanism of activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 33946–33957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, N.S. Isozymes of Isocitrate Dehydrogenase: Subunit Structure and Intracellular Location. J. Exp. Zool. 1965, 158, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitman, Z.J.; Yan, H. Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 and 2 mutations in cancer: Alterations at a crossroads of cellular metabolism. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2010, 102, 932–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, H.J.; Lee, S.M.; Son, B.G.; Lee, S.H.; Ryoo, Z.Y.; Chang, K.T.; Park, J.W.; Park, D.C.; Song, B.J.; Veech, R.L.; et al. Cytosolic NADP+-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase plays a key role in lipid metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 39968–39974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minard, K.I.; McAlister-Henn, L. Dependence of peroxisomal beta-oxidation on cytosolic sources of NADPH. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 3402–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.M.; Koh, H.J.; Park, D.C.; Song, B.J.; Huh, T.L.; Park, J.W. Cytosolic NADP(+)-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase status modulates oxidative damage to cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 32, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metellus, P.; Colin, C.; Taieb, D.; Guedj, E.; Nanni-Metellus, I.; de Paula, A.M.; Colavolpe, C.; Fuentes, S.; Dufour, H.; Barrie, M.; et al. IDH mutation status impact on in vivo hypoxia biomarkers expression: New insights from a clinical, nuclear imaging and immunohistochemical study in 33 glioma patients. J. Neurooncol. 2011, 105, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleeker, F.E.; Atai, N.A.; Lamba, S.; Jonker, A.; Rijkeboer, D.; Bosch, K.S.; Tigchelaar, W.; Troost, D.; Vandertop, W.P.; Bardelli, A.; et al. The prognostic IDH1(R132) mutation is associated with reduced NADP+-dependent IDH activity in glioblastoma. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metallo, C.M.; Gameiro, P.A.; Bell, E.L.; Mattaini, K.R.; Yang, J.; Hiller, K.; Jewell, C.M.; Johnson, Z.R.; Irvine, D.J.; Guarente, L.; et al. Reductive glutamine metabolism by IDH1 mediates lipogenesis under hypoxia. Nature 2011, 481, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Lin, Y.; Xu, W.; Jiang, W.; Zha, Z.; Wang, P.; Yu, W.; Li, Z.; Gong, L.; Peng, Y.; et al. Glioma-derived mutations in IDH1 dominantly inhibit IDH1 catalytic activity and induce HIF-1alpha. Science 2009, 324, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, P.S.; Patel, J.; Wise, D.R.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Bennett, B.D.; Coller, H.A.; Cross, J.R.; Fantin, V.R.; Hedvat, C.V.; Perl, A.E.; et al. The common feature of leukemia-associated IDH1 and IDH2 mutations is a neomorphic enzyme activity converting alpha-ketoglutarate to 2-hydroxyglutarate. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, L.; White, D.W.; Gross, S.; Bennett, B.D.; Bittinger, M.A.; Driggers, E.M.; Fantin, V.R.; Jang, H.G.; Jin, S.; Keenan, M.C.; et al. Cancer-associated IDH1 mutations produce 2-hydroxyglutarate. Nature 2009, 462, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, R.; Yeoh, K.K.; Tian, Y.M.; Hillringhaus, L.; Bagg, E.A.; Rose, N.R.; Leung, I.K.; Li, X.S.; Woon, E.C.; Yang, M.; et al. The oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate inhibits histone lysine demethylases. EMBO Rep. 2011, 12, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, H.; Yu, H. Structural insights into histone lysine demethylation. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2010, 20, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turcan, S.; Rohle, D.; Goenka, A.; Walsh, L.A.; Fang, F.; Yilmaz, E.; Campos, C.; Fabius, A.W.; Lu, C.; Ward, P.S.; et al. IDH1 mutation is sufficient to establish the glioma hypermethylator phenotype. Nature 2012, 483, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, P.; Kim, S.H.; Ito, S.; Yang, C.; Wang, P.; Xiao, M.T.; et al. Oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate is a competitive inhibitor of alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Liu, J.; Zhao, S.; Xiong, J.; Mao, Y.; Wang, Y. IDH1 mutations inhibit multiple alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase activities in astroglioma. J. Neurooncol. 2012, 109, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kickingereder, P.; Sahm, F.; Radbruch, A.; Wick, W.; Heiland, S.; Deimling, A.; Bendszus, M.; Wiestler, B. IDH mutation status is associated with a distinct hypoxia/angiogenesis transcriptome signature which is non-invasively predictable with rCBV imaging in human glioma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitman, Z.J.; Jin, G.; Karoly, E.D.; Spasojevic, I.; Yang, J.; Kinzler, K.W.; He, Y.; Bigner, D.D.; Vogelstein, B.; Yan, H. Profiling the effects of isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 and 2 mutations on the cellular metabolome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3270–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, D.; Guan, K.L.; Xiong, Y. Metabolism, Activity, and Targeting of D- and L-2-Hydroxyglutarates. Trends Cancer 2018, 4, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvert, A.E.; Chalastanis, A.; Wu, Y.; Hurley, L.A.; Kouri, F.M.; Bi, Y.; Kachman, M.; May, J.L.; Bartom, E.; Hua, Y.; et al. Cancer-Associated IDH1 Promotes Growth and Resistance to Targeted Therapies in the Absence of Mutation. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 1858–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noushmehr, H.; Weisenberger, D.J.; Diefes, K.; Phillips, H.S.; Pujara, K.; Berman, B.P.; Pan, F.; Pelloski, C.E.; Sulman, E.P.; Bhat, K.P.; et al. Identification of a CpG island methylator phenotype that defines a distinct subgroup of glioma. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 510–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccarelli, M.; Barthel, F.P.; Malta, T.M.; Sabedot, T.S.; Salama, S.R.; Murray, B.A.; Morozova, O.; Newton, Y.; Radenbaugh, A.; Pagnotta, S.M.; et al. Molecular Profiling Reveals Biologically Discrete Subsets and Pathways of Progression in Diffuse Glioma. Cell 2016, 164, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korshunov, A.; Casalini, B.; Chavez, L.; Hielscher, T.; Sill, M.; Ryzhova, M.; Sharma, T.; Schrimpf, D.; Stichel, D.; Capper, D.; et al. Integrated molecular characterization of IDH-mutant glioblastomas. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madala, H.R.; Punganuru, S.R.; Arutla, V.; Misra, S.; Thomas, T.J.; Srivenugopal, K.S. Beyond Brooding on Oncometabolic Havoc in IDH-Mutant Gliomas and AML: Current and Future Therapeutic Strategies. Cancers 2018, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Parsons, D.W.; Jin, G.; McLendon, R.; Rasheed, B.A.; Yuan, W.; Kos, I.; Batinic-Haberle, I.; Jones, S.; Riggins, G.J.; et al. IDH1 and IDH2 mutations in gliomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Bent, M.J.; Dubbink, H.J.; Marie, Y.; Brandes, A.A.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Wesseling, P.; Frenay, M.; Tijssen, C.C.; Lacombe, D.; Idbaih, A.; et al. IDH1 and IDH2 mutations are prognostic but not predictive for outcome in anaplastic oligodendroglial tumors: A report of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Brain Tumor Group. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 1597–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichimura, K.; Pearson, D.M.; Kocialkowski, S.; Backlund, L.M.; Chan, R.; Jones, D.T.; Collins, V.P. IDH1 mutations are present in the majority of common adult gliomas but rare in primary glioblastomas. Neuro-Oncology 2009, 11, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturm, D.; Pfister, S.M.; Jones, D.T.W. Pediatric Gliomas: Current Concepts on Diagnosis, Biology, and Clinical Management. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2370–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waitkus, M.S.; Diplas, B.H.; Yan, H. Isocitrate dehydrogenase mutations in gliomas. Neuro-Oncology 2016, 18, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteller, M.; Garcia-Foncillas, J.; Andion, E.; Goodman, S.N.; Hidalgo, O.F.; Vanaclocha, V.; Baylin, S.B.; Herman, J.G. Inactivation of the DNA-repair gene MGMT and the clinical response of gliomas to alkylating agents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 1350–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balss, J.; Meyer, J.; Mueller, W.; Korshunov, A.; Hartmann, C.; von Deimling, A. Analysis of the IDH1 codon 132 mutation in brain tumors. Acta Neuropathol. 2008, 116, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmiento, J.M.; Mukherjee, D.; Black, K.L.; Fan, X.; Hu, J.L.; Nuno, M.A.; Patil, C.G. Do Long-Term Survivor Primary Glioblastoma Patients Harbor IDH1 Mutations? J. Neurol. Surg. A Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2016, 77, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amelot, A.; De Cremoux, P.; Quillien, V.; Polivka, M.; Adle-Biassette, H.; Lehmann-Che, J.; Francoise, L.; Carpentier, A.F.; George, B.; Mandonnet, E.; et al. IDH-Mutation Is a Weak Predictor of Long-Term Survival in Glioblastoma Patients. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwadate, Y.; Matsutani, T.; Hirono, S.; Ikegami, S.; Shinozaki, N.; Saeki, N. IDH1 mutation is prognostic for diffuse astrocytoma but not low-grade oligodendrogliomas in patients not treated with early radiotherapy. J. Neurooncol. 2015, 124, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellai, M.; Annovazzi, L.; Senetta, R.; Dell’Aglio, C.; Mazzucco, M.; Cassoni, P.; Schiffer, D. Diagnostic revision of 206 adult gliomas (including 40 oligoastrocytomas) based on ATRX, IDH1/2 and 1p/19q status. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 131, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, X. IDH mutation and MGMT promoter methylation are associated with the pseudoprogression and improved prognosis of glioblastoma multiforme patients who have undergone concurrent and adjuvant temozolomide-based chemoradiotherapy. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2016, 151, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Yu, T.; Gong, J.; Nie, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, M.; Xu, M.; Tan, J.; Su, Z.; Zhong, J.; et al. IDH1/2 gene hotspot mutations in central nervous system tumours: Analysis of 922 Chinese patients. Pathology 2016, 48, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakae, S.; Sasaki, H.; Hayashi, S.; Hattori, N.; Kumon, M.; Nishiyama, Y.; Adachi, K.; Nagahisa, S.; Hayashi, T.; Inamasu, J.; et al. PCR-Based Simple Subgrouping Is Validated for Classification of Gliomas and Defines Negative Prognostic Copy Number Aberrations in IDH Mutant Gliomas. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffgens, S.; Wilkens, L.; Brandes, A.A.; Meier, T.; Franceschi, E.; Ermani, M.; Hartmann, C.; Sandalcioglu, I.E.; Dumitru, C.A. Sex-specific clinicopathological significance of novel (Frizzled-7) and established (MGMT, IDH1) biomarkers in glioblastoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 55169–55180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Mao, Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Mao, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Luo, J. An analysis of 170 glioma patients and systematic review to investigate the association between IDH-1 mutations and preoperative glioma-related epilepsy. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 31, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Shan, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ling, M.; Fan, X. IDH1 mutation is associated with a higher preoperative seizure incidence in low-grade glioma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Seizure 2018, 55, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gieryng, A.; Pszczolkowska, D.; Walentynowicz, K.A.; Rajan, W.D.; Kaminska, B. Immune microenvironment of gliomas. Lab. Investig. 2017, 97, 498–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hambardzumyan, D.; Gutmann, D.H.; Kettenmann, H. The role of microglia and macrophages in glioma maintenance and progression. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Jung, T.Y.; Jung, S.; Jang, W.Y.; Moon, K.S.; Kim, I.Y.; Lee, M.C.; Lee, J.J. Tumour-infiltrating T-cell subpopulations in glioblastomas. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2012, 26, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohr, J.; Ratliff, T.; Huppertz, A.; Ge, Y.; Dictus, C.; Ahmadi, R.; Grau, S.; Hiraoka, N.; Eckstein, V.; Ecker, R.C.; et al. Effector T-cell infiltration positively impacts survival of glioblastoma patients and is impaired by tumor-derived TGF-beta. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 4296–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Zhang, C.; Li, Q.; Dong, J.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Wu, A. Tumour-infiltrating CD4(+) and CD8(+) lymphocytes as predictors of clinical outcome in glioma. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 2560–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, L.; Yang, C.; Gao, Q.; Long, Y.; Ge, H.; DeLeon, G.; Jin, L.; Chang, Y.E.; Sayour, E.J.; Ji, J.; et al. CD4+ and Perivascular Foxp3+ T Cells in Glioma Correlate with Angiogenesis and Tumor Progression. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preusser, M.; Lim, M.; Hafler, D.A.; Reardon, D.A.; Sampson, J.H. Prospects of immune checkpoint modulators in the treatment of glioblastoma. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, B.; Jin, R.; Wang, X.; Safaee, M.; Lisiero, D.N.; Yang, I.; Li, G.; Liau, L.M.; Prins, R.M. Monitoring of regulatory T cell frequencies and expression of CTLA-4 on T cells, before and after DC vaccination, can predict survival in GBM patients. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nduom, E.K.; Wei, J.; Yaghi, N.K.; Huang, N.; Kong, L.Y.; Gabrusiewicz, K.; Ling, X.; Zhou, S.; Ivan, C.; Chen, J.Q.; et al. PD-L1 expression and prognostic impact in glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2016, 18, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohanbash, G.; Carrera, D.A.; Shrivastav, S.; Ahn, B.J.; Jahan, N.; Mazor, T.; Chheda, Z.S.; Downey, K.M.; Watchmaker, P.B.; Beppler, C.; et al. Isocitrate dehydrogenase mutations suppress STAT1 and CD8+ T cell accumulation in gliomas. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1425–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garber, S.T.; Hashimoto, Y.; Weathers, S.P.; Xiu, J.; Gatalica, Z.; Verhaak, R.G.; Zhou, S.; Fuller, G.N.; Khasraw, M.; de Groot, J.; et al. Immune checkpoint blockade as a potential therapeutic target: Surveying CNS malignancies. Neuro-Oncology 2016, 18, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berghoff, A.S.; Kiesel, B.; Widhalm, G.; Wilhelm, D.; Rajky, O.; Kurscheid, S.; Kresl, P.; Wohrer, A.; Marosi, C.; Hegi, M.E.; et al. Correlation of immune phenotype with IDH mutation in diffuse glioma. Neuro-Oncology 2017, 19, 1460–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, D.; Dominah, G.; Lobel, G.; Obungu, A.; Lynes, J.; Sanchez, V.; Adamstein, N.; Wang, X.; Edwards, N.A.; Wu, T.; et al. Programmed Death Ligand 1 Is a Negative Prognostic Marker in Recurrent Isocitrate Dehydrogenase-Wildtype Glioblastoma. Neurosurgery 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunse, L.; Pusch, S.; Bunse, T.; Sahm, F.; Sanghvi, K.; Friedrich, M.; Alansary, D.; Sonner, J.K.; Green, E.; Deumelandt, K.; et al. Suppression of antitumor T cell immunity by the oncometabolite (R)-2-hydroxyglutarate. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1192–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amankulor, N.M.; Kim, Y.; Arora, S.; Kargl, J.; Szulzewsky, F.; Hanke, M.; Margineantu, D.H.; Rao, A.; Bolouri, H.; Delrow, J.; et al. Mutant IDH1 regulates the tumor-associated immune system in gliomas. Genes Dev. 2017, 31, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luoto, S.; Hermelo, I.; Vuorinen, E.M.; Hannus, P.; Kesseli, J.; Nykter, M.; Granberg, K.J. Computational Characterization of Suppressive Immune Microenvironments in Glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 5574–5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Sorensen, M.D.; Kristensen, B.W.; Reifenberger, G.; McIntyre, T.M.; Lin, F. D-2-Hydroxyglutarate Is an Intercellular Mediator in IDH-Mutant Gliomas Inhibiting Complement and T Cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 5381–5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieterich, L.C.; Mellberg, S.; Langenkamp, E.; Zhang, L.; Zieba, A.; Salomaki, H.; Teichert, M.; Huang, H.; Edqvist, P.H.; Kraus, T.; et al. Transcriptional profiling of human glioblastoma vessels indicates a key role of VEGF-A and TGFbeta2 in vascular abnormalization. J. Pathol. 2012, 228, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pen, A.; Moreno, M.J.; Martin, J.; Stanimirovic, D.B. Molecular markers of extracellular matrix remodeling in glioblastoma vessels: Microarray study of laser-captured glioblastoma vessels. Glia 2007, 55, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koivunen, P.; Lee, S.; Duncan, C.G.; Lopez, G.; Lu, G.; Ramkissoon, S.; Losman, J.A.; Joensuu, P.; Bergmann, U.; Gross, S.; et al. Transformation by the (R)-enantiomer of 2-hydroxyglutarate linked to EGLN activation. Nature 2012, 483, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; He, L.; Lugano, R.; Roodakker, K.; Bergqvist, M.; Smits, A.; Dimberg, A. IDH mutation status is associated with distinct vascular gene expression signatures in lower-grade gliomas. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20, 1505–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, B.C.; Fathi, A.T.; DiNardo, C.D.; Pollyea, D.A.; Chan, S.M.; Swords, R. Isocitrate dehydrogenase mutations in myeloid malignancies. Leukemia 2017, 31, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, E.; Quivoron, C.; Straley, K.; Lemieux, R.M.; Popovici-Muller, J.; Sadrzadeh, H.; Fathi, A.T.; Gliser, C.; David, M.; Saada, V.; et al. AG-120, an Oral, Selective, First-in-Class, Potent Inhibitor of Mutant IDH1, Reduces Intracellular 2HG and Induces Cellular Differentiation in TF-1 R132H Cells and Primary Human IDH1 Mutant AML Patient Samples Treated Ex Vivo. Blood 2014, 124, 3734. [Google Scholar]
- Quivoron, C.; David, M.; Straley, K.; Travins, J.; Kim, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, D.; Saada, V.; Bawa, O.; Opolon, P.; et al. AG-221, an Oral, Selective, First-in-Class, Potent IDH2-R140Q Mutant Inhibitor, Induces Differentiation in a Xenotransplant Model. Blood 2014, 124, 3735. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, T.; Khawaja, M.R.; DiNardo, C.D.; Atkins, J.T.; Janku, F. Targeting isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) in cancer. Discov. Med. 2016, 21, 373–380. [Google Scholar]
- DiNardo, C.; de Botton, S.; Pollyea, D.A.; Stein, E.M.; Fathi, A.T.; Roboz, G.J.; Collins, R.; Swords, R.T.; Flinn, I.W.; Altman, J.K.; et al. Molecular Profiling and Relationship with Clinical Response in Patients with IDH1 Mutation-Positive Hematologic Malignancies Receiving AG-120, a First-in-Class Potent Inhibitor of Mutant IDH1, in Addition to Data from the Completed Dose Escalation Portion of the Phase 1 Study. Blood 2015, 126, 1306. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, E.M.; DiNardo, C.; Altman, J.K.; Collins, R.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Sekeres, M.A.; Fathi, A.T.; Flinn, I.W.; Frankel, A.E.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of AG-221, a Potent Inhibitor of Mutant IDH2 That Promotes Differentiation of Myeloid Cells in Patients with Advanced Hematologic Malignancies: Results of a Phase 1/2 Trial. Blood 2015, 126, 323. [Google Scholar]
- Burris, H.; Mellinghoff, I.; Maher, E.; Wen, P.; Beeram, M.; Touat, M.; Faris, J.; Azad, N.; Cloughesy, T.; Gore, L.; et al. The first reported results of AG-120, a first-in-class, potent inhibitor of the IDH1 mutant protein, in a Phase I study of patients with advanced IDH1-mutant solid tumors, including gliomas. In Proceedings of the AACR-NCI-EORTC International Conference: Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics, Boston, MA, USA, 5–9 November 2015; Mol Cancer Ther: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2015. Abstract PL04-05. [Google Scholar]
- Rohle, D.; Popovici-Muller, J.; Palaskas, N.; Turcan, S.; Grommes, C.; Campos, C.; Tsoi, J.; Clark, O.; Oldrini, B.; Komisopoulou, E.; et al. An inhibitor of mutant IDH1 delays growth and promotes differentiation of glioma cells. Science 2013, 340, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Paz, A.C.; Wilky, B.A.; Johnson, B.; Galoian, K.; Rosenberg, A.; Hu, G.; Tinoco, G.; Bodamer, O.; Trent, J.C. Treatment with a Small Molecule Mutant IDH1 Inhibitor Suppresses Tumorigenic Activity and Decreases Production of the Oncometabolite 2-Hydroxyglutarate in Human Chondrosarcoma Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuser, M.; Herbst, L.; Pusch, S.; Klett, L.; Goparaju, R.; Stichel, D.; Kaulfuss, S.; Panknin, O.; Zimmermann, K.; Toschi, L.; et al. Pan-Mutant-IDH1 Inhibitor Bay-1436032 Is Highly Effective Against Human IDH1 Mutant Acute Myeloid Leukemia In Vivo. Blood 2016, 128, 745. [Google Scholar]
- Chaturvedi, A.; Araujo Cruz, M.M.; Jyotsana, N.; Sharma, A.; Yun, H.; Görlich, K.; Wichmann, M.; Schwarzer, A.; Preller, M.; Thol, F.; et al. Mutant IDH1 promotes leukemogenesis in vivo and can be specifically targeted in human AML. Blood 2013, 122, 2877–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, A.; Araujo Cruz, M.M.; Goparaju, R.; Jyotsana, N.; Baehre, H.; Goerlich, K.; Schottmann, R.; Preller, M.; Struys, E.A.; Kloos, A.; et al. A Novel Inhibitor of Mutant IDH1 Induces Differentiation in Vivo and Prolongs Survival in a Mouse Model of Leukemia. Blood 2014, 124, 3598. [Google Scholar]
- DiNardo, C.D.; Schimmer, A.D.; Yee, K.W.L.; Hochhaus, A.; Kraemer, A.; Carvajal, R.D.; Janku, F.; Bedard, P.; Carpio, C.; Wick, A.; et al. A Phase I Study of IDH305 in Patients with Advanced Malignancies Including Relapsed/Refractory AML and MDS That Harbor IDH1R132 Mutations. Blood 2016, 128, 1073. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Travins, J.; DeLaBarre, B.; Penard-Lacronique, V.; Schalm, S.; Hansen, E.; Straley, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Liu, W.; Gliser, C.; et al. Targeted inhibition of mutant IDH2 in leukemia cells induces cellular differentiation. Science 2013, 340, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kernytsky, A.; Wang, F.; Hansen, E.; Schalm, S.; Straley, K.; Gliser, C.; Yang, H.; Travins, J.; Murray, S.; Dorsch, M.; et al. IDH2 mutation-induced histone and DNA hypermethylation is progressively reversed by small-molecule inhibition. Blood 2015, 125, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Travins, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, H.; Straley, K.; Choe, S.; Dorsch, M.; Schenkein, D.P.; Agresta, S.; Biller, S.; et al. AG-221 Offers a Survival Advantage in a Primary Human IDH2 Mutant AML Xenograft Model. Blood 2013, 122, 240. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, E.; Altman, J.K.; Collins, R.; DeAngelo, D.; Fathi, A.; Flinn, I.; Frankel, A.; Levine, R.; Medeiros, B.; et al. AG-221, an oral, selective, first-in-class, potent inhibitor of the IDH2 mutant enzyme, induced durable responses in a phase 1 study of IDH2 mutation-positive advanced hematologic malignancies. Blood 2014, 124, 115. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, B.; Chen, Y.; Wang, F.; Yen, K.; Utley, L.; Almon, C.; Straley, K.; Attar, E.; Bowden, C.; Biller, S.; et al. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) evaluation of AG-221, a potent mutant IDH2 inhibitor, from a phase 1 trial of patients with IDH2-mutation positive hematologic malignancies. Haematologica 2015, 100 (Suppl. 1), E948. [Google Scholar]
- de Botton, S. Targeting isocitrate dehydrogenase-1 (IDH1) and IDH2 mutations. Clinical results in advanced hematologic malignancies. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, Abstract ii15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, T.; Bunse, L.; Pusch, S.; Sahm, F.; Wiestler, B.; Quandt, J.; Menn, O.; Osswald, M.; Oezen, I.; Ott, M.; et al. A vaccine targeting mutant IDH1 induces antitumour immunity. Nature 2014, 512, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegatta, S.; Valletta, L.; Corbetta, C.; Patane, M.; Zucca, I.; Riccardi Sirtori, F.; Bruzzone, M.G.; Fogliatto, G.; Isacchi, A.; Pollo, B.; et al. Effective immuno-targeting of the IDH1 mutation R132H in a murine model of intracranial glioma. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2015, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platten, M.; Schilling, D.; Bunse, L.; Wick, A.; Bunse, T.; Riehl, D.; Green, E.; Sanghvi, K.; Karapanagiotou-Schenkel, I.; Harting, I.; et al. ATIM-33. NOA-16: A first-in-man multicenter phase I clinical trial of the german neurooncology working group evaluating a mutation-specific peptide vaccine targeting IDH1R132H in patients with newly diagnosed malignant astrocytomas. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20, vi8–vi9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, M.; Bunse, L.; Wick, W.; Platten, M. Perspectives of immunotherapy in isocitrate dehydrogenase-mutant gliomas. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2018, 30, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Zou, F.; Pusch, S.; Xu, Y.; von Deimling, A.; Zha, X. Inhibitors of Mutant Isocitrate Dehydrogenases 1 and 2 (mIDH1/2): An Update and Perspective. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 8981–9003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Inhibitor | Target | Cancer | Current Status of Clinical Trials | Identifier at ClinicalTrials.Gov | Company | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AG-120 | Mutant IDH1 | Cholangiocarcinoma, chondrosarcoma, glioma and advanced solid tumors | Phase I | NCT02073994 | Agios Pharmaceuticals Inc./Celgene Corporation | [71,73,85] |
| Advanced hematologic malignancies: relapsed or refractory AML, untreated AML, other hematologic malignancies | Phase I | NCT02074839 | Agios Pharmaceuticals Inc./Celgene Corporation | |||
| Newly diagnosed AML, untreated AML, AML arising from MDS, AML arising from antecedent hematologic disorder, AML arising after exposure to genotoxic injury | Phase I | NCT02632708 | Agios Pharmaceuticals Inc./Celgene Corporation | |||
| Newly diagnosed AML | Phase Ib/II | NCT02677922 | Agios Pharmaceuticals Inc./Celgene Corporation | |||
| AG-221 (Enasidenib) | Mutant IDH2 | Advanced hematologic malignancies | Phase I/II | NCT01915498 | Agios Pharmaceuticals Inc./Celgene Corporation | [72,82,83,84,85] |
| Advanced solid tumors including glioma, angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma chondrosarcoma | Phase I/II | NCT02273739 | Agios Pharmaceuticals Inc./Celgene Corporation | |||
| Late-stage AML | Phase III | NCT02577406 | Agios Pharmaceuticals Inc./Celgene Corporation | |||
| Newly diagnosed AML, untreated AML, AML arising from MDS, AML arising from AHD, AML arising after exposure to genotoxic injury | Phase I | NCT02632708 | Agios Pharmaceuticals Inc./Celgene Corporation | |||
| Newly diagnosed AML | Phase Ib/II | NCT02677922 | Agios Pharmaceuticals Inc./Celgene Corporation | |||
| AG-881 | Mutant IDH1 and IDH2 | Advanced hematologic malignancies: AML, MDS | Phase I | NCT02492737 | Agios Pharmaceuticals Inc./Celgene Corporation | [67,70] |
| Advanced solid tumors: cholangiocarcinoma chondrosarcoma, gliomas | Phase I | NCT02481154 | Agios Pharmaceuticals Inc./Celgene Corporation | |||
| AGI-6780 | Mutant IDH2 | AML | - | - | Agios Pharmaceuticals Inc. | [80,81] |
| AGI-5198 | Mutant IDH1 | Chondrosarcoma, low-grade WHO glioma | - | - | Xcess Biosciences Inc. | [74,75] |
| BAY-1436032 | Mutant IDH1 | Advanced solid tumors, including anaplastic glioma, glioblastoma, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | Phase I | NCT02746081 | Bayer | [76] |
| FT-2102 | Mutant IDH1 | AML, high-risk MDS | Phase I/Ib | NCT02719574 | Forma Therapeutics Inc. | [67] |
| HMS-101 | Mutant IDH1 | AML | - | - | Ascenion GmnH | [78] |
| IDH305 | Mutant IDH1 | II or III WHO glioma | Phase II | NCT02977689 | Novartis AG Pharmaceuticals | [79] |
| Low-grade glioma | Phase II | NCT02987010 | ||||
| AML and advanced solid tumors including cholangiocarcinoma and glioma | Phase I | NCT02381886 | ||||
| AML | Phase I | NCT02826642 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaminska, B.; Czapski, B.; Guzik, R.; Król, S.K.; Gielniewski, B. Consequences of IDH1/2 Mutations in Gliomas and an Assessment of Inhibitors Targeting Mutated IDH Proteins. Molecules 2019, 24, 968. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050968
Kaminska B, Czapski B, Guzik R, Król SK, Gielniewski B. Consequences of IDH1/2 Mutations in Gliomas and an Assessment of Inhibitors Targeting Mutated IDH Proteins. Molecules. 2019; 24(5):968. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050968
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaminska, Bozena, Bartosz Czapski, Rafal Guzik, Sylwia Katarzyna Król, and Bartlomiej Gielniewski. 2019. "Consequences of IDH1/2 Mutations in Gliomas and an Assessment of Inhibitors Targeting Mutated IDH Proteins" Molecules 24, no. 5: 968. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050968
APA StyleKaminska, B., Czapski, B., Guzik, R., Król, S. K., & Gielniewski, B. (2019). Consequences of IDH1/2 Mutations in Gliomas and an Assessment of Inhibitors Targeting Mutated IDH Proteins. Molecules, 24(5), 968. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050968