Recent Developments in the Area of Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation
Abstract
:Introduction
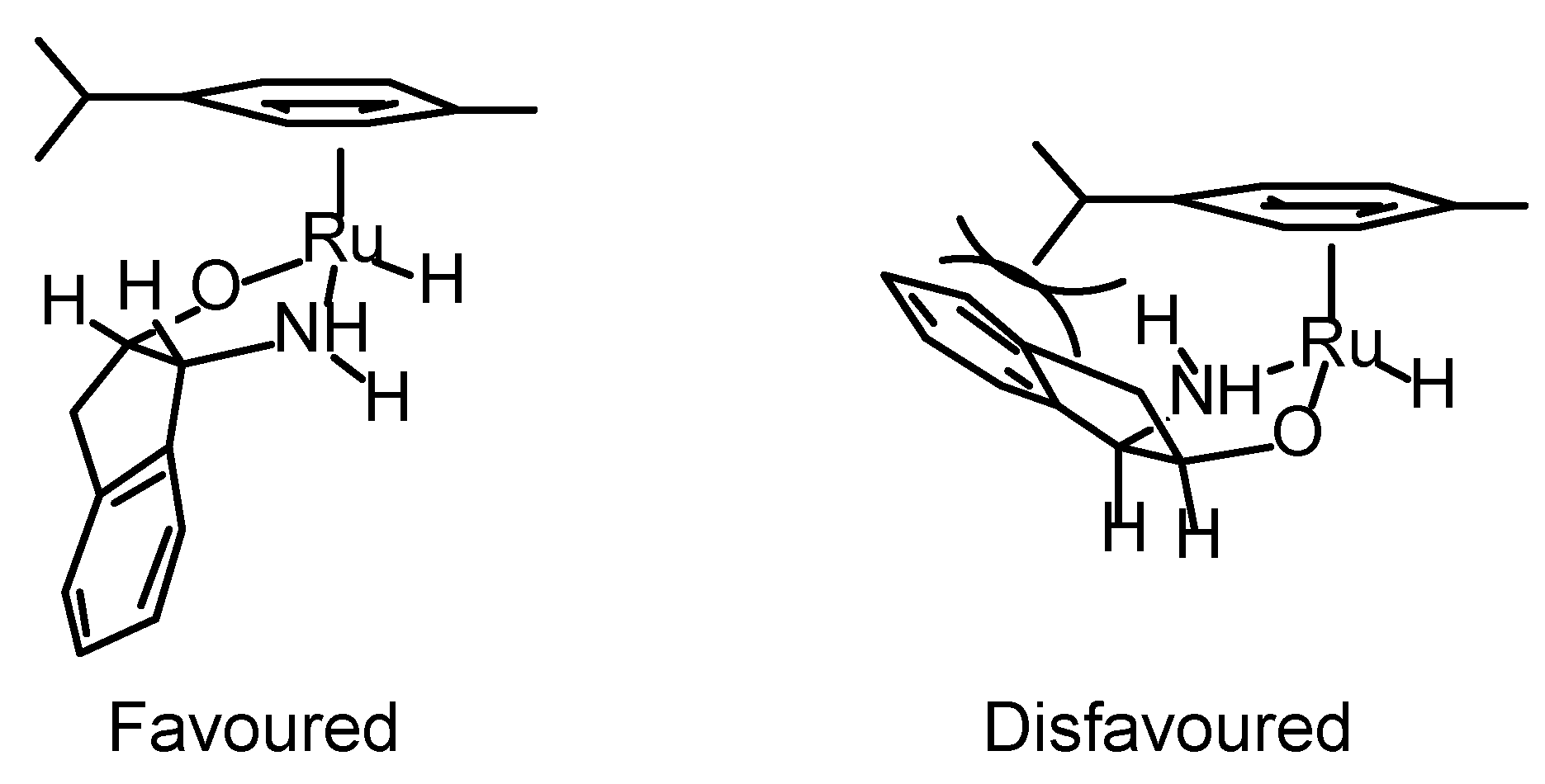
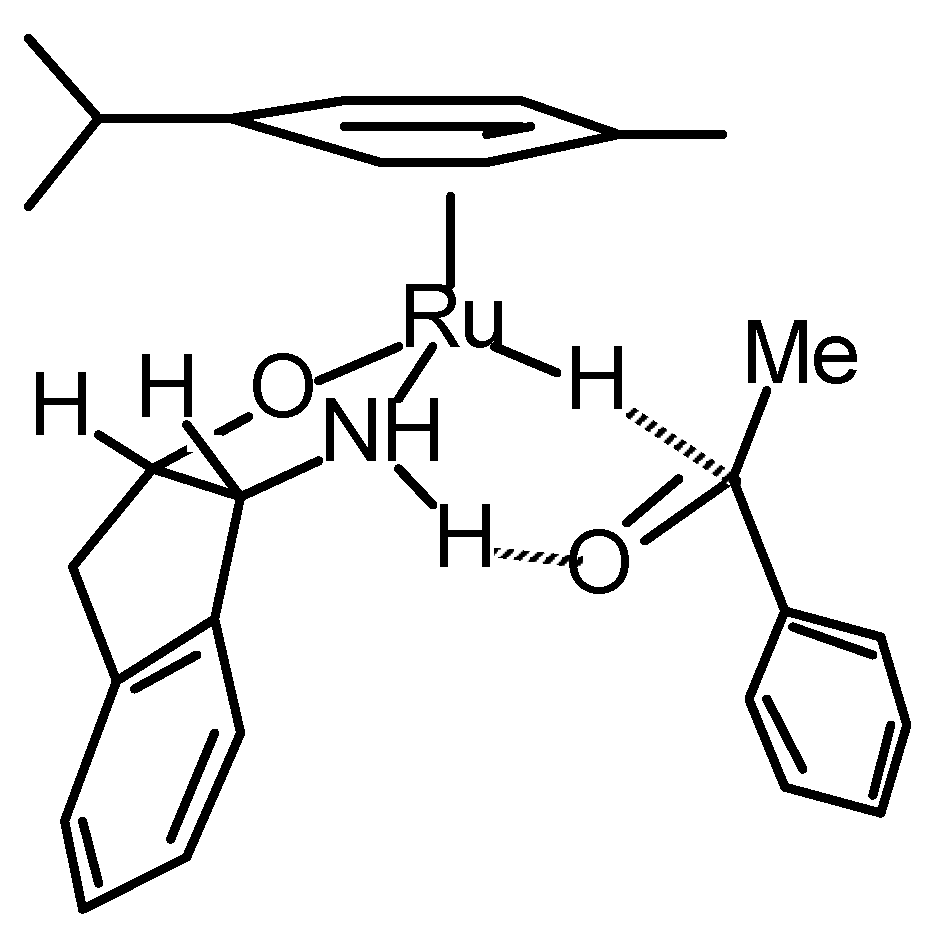
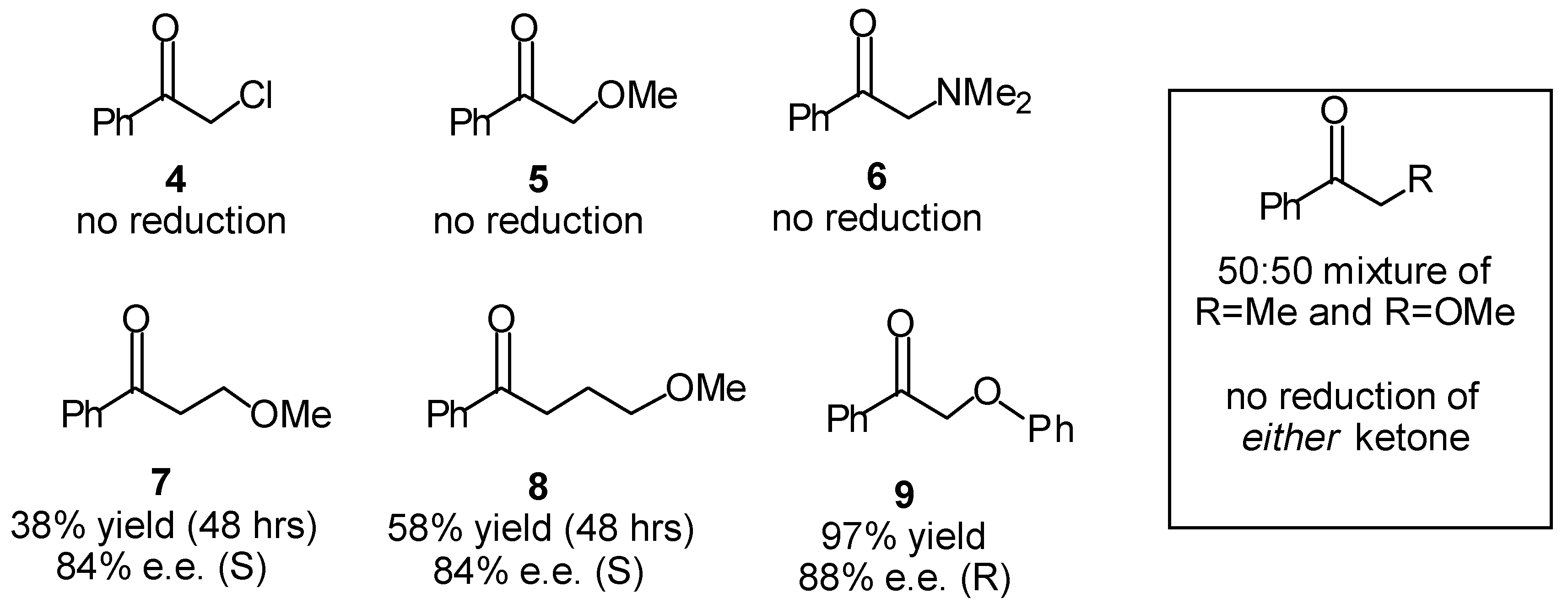
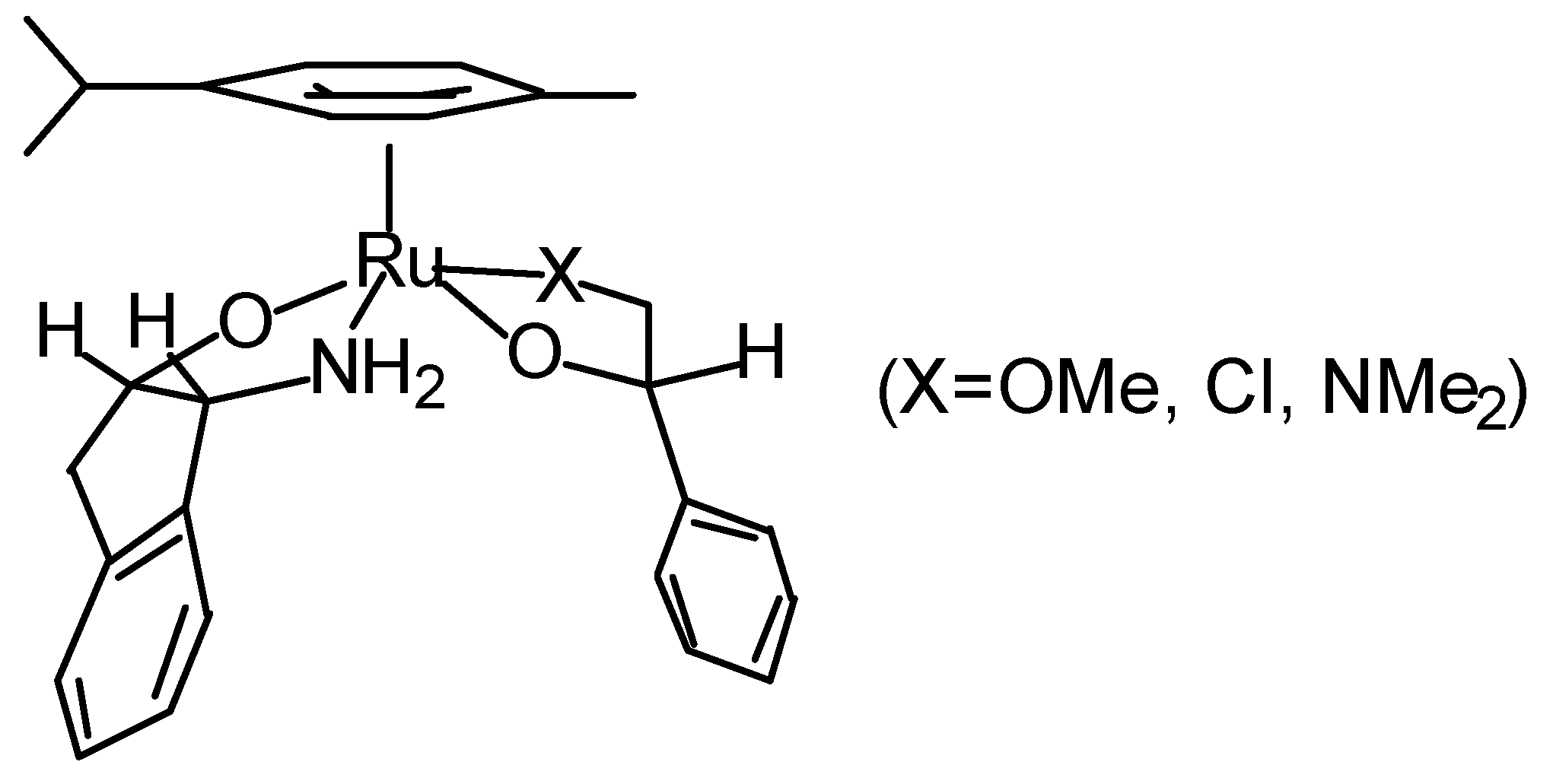
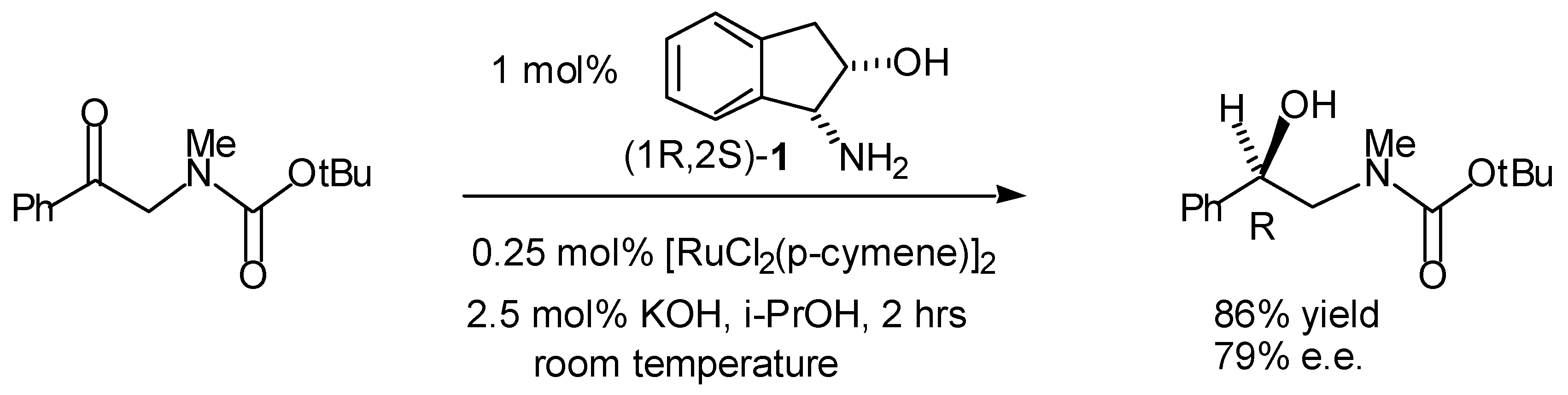
Transfer Hydrogenation of Ketones
Acknowledgements:
References and Notes
- Noyori, R. Asymmetric Catalysis in Organic Synthesis; John Wiley and Sons Ltd: NY, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Ojima, I. Catalytic Asymmetric Synthesis; VCH Press: Berlin, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Noyori, R. Chemical multiplication of chirality - science and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1989, 18, 187–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyori, R.; Takaya, H. BINAP - An efficient chiral element for asymmetric catalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 1990, 23, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaya, H.; Ohno, T.; Noyori, R. Catalytic Asymmetric Synthesis; Ojima, I., Ed.; VCH: New York, 1993; Chapter 1. [Google Scholar]
- Noyori, R. Organometallic ways for the multiplication of chirality. Tetrahedron 1994, 50, 4259–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, M. in Supplement A3: The chemistry of double-bonded functional groups; Patai, S., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons Ltd, 1997; pp. 781–842. [Google Scholar]
- Deloux, L.; Srebnik, M. Asymmetric boron-catalyzed reactions. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 763–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallbaum, S.; Martens, J. Asymmetric syntheses with chiral oxazaborolidines. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 1992, 3, 1475–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkuma, T.; Ooka, H.; Hashiguchi, S.; Ikariya, T.; Noyori, R. Practical enantioselective hydrogenation of aromatic ketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 2675–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkuma, T.; Ooka, H.; Yamakawa, M.; Ikariya, T.; Noyori, R. Stereoselective hydrogenation of simple ketones catalyzed by Ruthenium(II) complexes. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 4872–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkuma, T.; Ikehira, H.; Ikariya, T.; Noyori, R. Asymmetric hydrogenation of cyclic alpha,betaunsaturated ketones to chiral allylic alcohols. Synlett 1997, 467–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkuma, T.; Ooka, H.; Ikariya, T.; Noyori, R. Preferential hydrogenation of aldehydes and ketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 10417–10418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Xiao, D.; Cao, P.; Zhang, X. Highly enantioselective hydrogenation of simple ketones catalyzed by a Rh-PennPhos complex. Angew. Chem., Int. Edn. Engl. 1998, 37, 1100–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
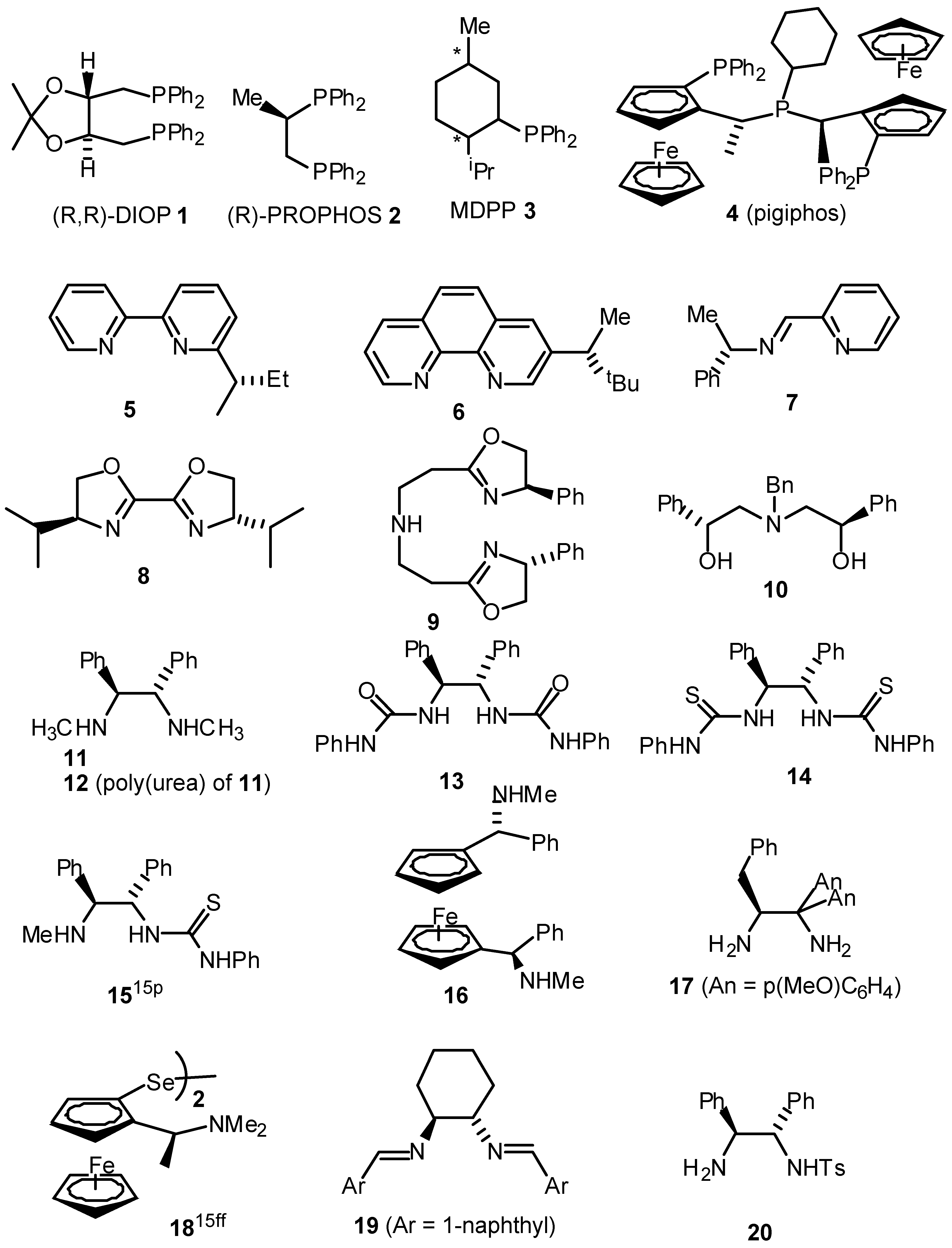
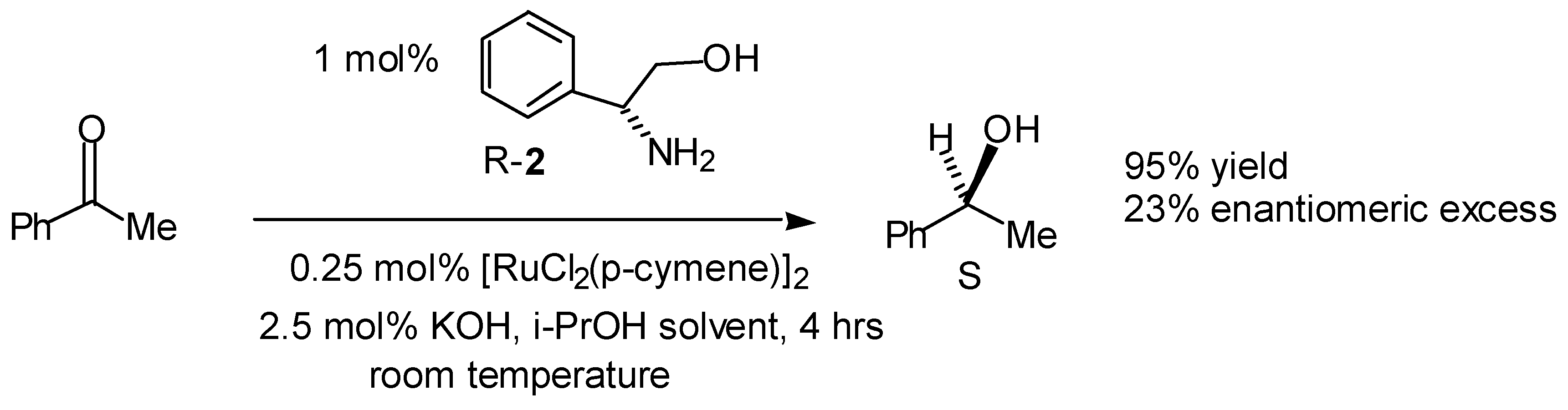
- A summary of ligands (including our own) which have recently been reported for the asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of ketones are given below. For reasons of space the comparison is limited to the reduction of acetophenone.
Table. Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of acetophenone (hydride source / solvent is isopropanol unless otherwise indicated).
Table. Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of acetophenone (hydride source / solvent is isopropanol unless otherwise indicated). Entry Ligand Metal Time, h Temp, °C Yleld, % e.e., % Ref 1 1 Ru(II) 111 120 35 4(S) a 2 2 Rh(I) 3.5 82 60 9(R) b 3 2 Ir(I) 23 82 71 58(S) b 4 2 Ru(II) 0.03 100 80 52(S) b 5 3 Ir(I) 3 82 87 42(S) c 6 4 Ru(II) 120 68 99 72(R) d 7 5 Rh(I) - 82 - 7(R) e 8 6 Rh(I) 4 82 89 63(S) f 9 7 Ir(I) - 82 89 37(S) g 10 8 Ir(I) 3 80 89 58(R) h 11 9 Ru(II) 0.17 82 91 97(S) i 12 10 Sm(III) 2 rt 74 96(R) j 13 11 Rh(I) 168 rt 100 67(R) k 14 12 Rh(I) 24 70 100 60(S) 1 15 13 Rh(I) 163 60 97 43(R) m 16 I4 Ru(II) 9 82 98 87(S) n/o 17 16 Ru(II) 120 -30 98 30(R) p 18 17 Ir(I) 12 rt 74 78(R) q 19 19 Ru(II) 2-8 82 89 28(S) r 20 20 Ru(II) 15 rt 95 97(S) s 21 20* Ru(II) 20 rt 99 98(S) t 22 21 Ru(II) 24 rt 97 56(R) u 23 21* Ru(II) 120 rt 42 83(R) u 24 22* Ru(II) 24 30 99 96(R) u 25 23 Ru(II) 1 rt 94 92(S) 26 24 Ru(II) 1.5 rt 70 91(S) w 27 25 Ru(II) 5 83 95 95(S) x 28 26 Ru(II) 0.5 82 74 86(R) y 29 27 Ru(II) 7 28 80 94(R) z 30 28 Ru(II) 24 rt 91 35(R) aa 31 29 Ru(II) 24 rt 96 20(R) bb 32 30 Ru(II) 0.2 80 72 79(R) cc 33 31 Ru(II) 1 45 60 60(R) dd 34 32 Ru(II) 7 45 93 97(R) ee aFormic acid / triethylamine 5/2 used as solvent and hydride source - Bianchi, M.; Matteoli, U.; Menchi, G.; Frediani, P.; Pratesi, S.; Piacenti, F.; Botteghi, C. Use of DIOP in asymmetric transfer hydrogenation. J. Organomet. Chem. 1980, 198, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- a) Spogliarich, R.; Kaspar, J.; Graziani, M.; Morandini, F. Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of ketones catalyzed by phosphine-rhodium(I) and phosphine-iridium(I) complexes. J. Organomet. Chem. 1986, 306, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] b) Genêt, J.- P.; Ratovelomanana-Vidal, V.; Pinel, C. Asymmetric hydrogen transfer reaction of aryl ketones with chiral diphosphine-ruthenium(II) catalysts. Synlett 1993, 478–480. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, H. W.; Bhatnagar, A. K. Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of ketones catalyzed by chiral phosphineiridium complexes. J. Organomet. Chem. 1986, 302, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaro, P.; Bianchini, C.; Togni, A. Synthesis and chracterisation of ruthenium(II) complexes containing chiral bis(ferrocenyl) P3 or P2S ligands. Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of acetophenone. Organometallics 1997, 16, 3004–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botteghi, C.; Chelucci, G.; Chessa, G.; Delogu, G.; Gladiali, S.; Soccolini, F. Optically-active nitrogen ligands. 3. enantioface-discriminating transfer hydrogenation of acetophenone catalyzed by rhodium(I) complexes with chiral 2-(2'-pyridyl)pyridines. J. Organomet. Chem. 1986, 304, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Gladiali, S.; Pinna, L.; Delogu, G.; De Martin, S.; Zassinovich, G.; Mestroni, G. Optically active phenanthrolines in asymmetric catalysis III. Highly efficient enantioselective transfere hydrogenation of acetophenone by chiral Rh(/3-alkyl phenanthroline catalysts. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 1990, 1, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zassinovich, G.; Bettella, R.; Mestroni, G.; Bresciani-Pahor, N.; Geremia, S.; Randaccio, L. Enantioselective hydrogen transfer-reactions from propan-2-ol to ketones catalyzed by pentacoordinate iridium(I) complexes with chiral schiff-bases. J. Organomet. Chem. 1989, 370, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.; Umbricht, G.; Weber, B.; Pfaltz, A. C2 Symmetric 4,4’,5,5’-tetrahydro(oxazoles) and 4,4’,5,5’-tetrahydro-2,2’-methylenebis(oxazoles) as chiral ligands for enantioselective catalysis. Helv. Chim. Acta 1991, 74, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, X. A new chiral bis(oxazolinylmethyl)amine ligand for Ru-catalysed asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of ketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 3817–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D. A.; Nelson, S. G.; Gagné, M. R.; Muci, A. R. A chiral samarium-based catalyst for the asymmetric Meerwein-Ponndorf-Verley reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 9800–9801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- a) Gamez, P.; Fache, F.; Mangeney, P.; Lemaire, M. Enantioselective catalytic reduction of ketones using C2 symmetric diamines as chiral ligands. Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 6897–6898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] b) Gamez, P.; Fache, F.; Lemaire, M. Asymmetric catalytic reduction of carbonyl compounds using C2 symmetric diamines as chiral ligands. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 1995, 6, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] c) Bernard, M.; Guiral, V.; Delbecq, F.; Fache, F.; Sautet, P.; Lemaire, M. Structure of the diamine-Rh(I) precursor in the asymmetric hydride transfer reduction of ketones: A theoretical and experimental approach. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 1441–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] d) ter Halle, R.; Breheret, A.; Schulz, E.; Pinel, C.; Lemaire, M. Chiral nitrogen-metal complexs for the asymmetric reduction of ketones. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 1997, 8, 2101–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamez, P.; Dunjic, B.; Fache, F.; Lemaire, M. C2-Symmetric, psuedo C2 poly(amide) and poly(urea) as chiral inductors in in asymmetric catalysis. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1994, 1417–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamez, P.; Dunjic, B.; Lemaire, M. Diureas as ligands in asymmetric reduction of ketones. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 5196–5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touchard, F.; Gamez, P.; Fache, F.; Lemaire, M. Chiral thiourea as ligand for the asymmetric reduction of prochiral ketones. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 2275–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touchard, F.; Fache, F.; Lemaire, M. Thioureas: new ligands for the metal catalysed asymmetric reduction of carbonyl compounds. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 1997, 8, 3319–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwick, L.; Irelan, T.; Puntener, K.; Knochel, P. New C2-symmetric ferrocenyl diamines as ligands for ruthenium catalysed transfer hydrogenation. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 1998, 9, 1143–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, S. I.; Nomura, K.; Hashiguchi, S.; Noyori, R.; Izawa, Y. Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation catalysed by dimine-iridium(I) complexes. Chem. Lett. 1997, 957–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasik, P.; Alper, H. Schiff-bases as added chiral ligands for the [ru(eta(6)- c6h6)cl2](2) catalyzed hydrogen-transfer reduction of ketones with 2- propanol. Tetrahedron 1994, 50, 4347–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- a) Hashiguchi, S.; Fujii, A.; Takehara, J.; Ikariya, T.; Noyori, R. Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of aromatic ketones catalysed by chiral ruthenium(II) complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 7562–7563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] b) Matsumura, K.; Hashiguchi, S.; Ikariya, T.; Noyori, R. Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of α,β-acetylenic ketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 8738–8739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, A.; Hashiguchi, S.; Uematsu, N.; Ikariya, T.; Noyori, R. Ruthenium(II)-catalysed asymmetric transer hydrogenation of ketones using a formic acid-triethylamine mixture. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 2521–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Püntener, K.; Schwink, L.; Knochel, P. New efficient catalysts for enantioselective transfer hydrogenations. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 8165–8168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takehara, J.; Hashiguchi, S.; Fujii, A.; Inoue, S.; Ikariya, T.; Noyori, R. Amino alcohol effects on the ruthenium(II)-catalysed asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of ketones ion propan-2-ol. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1996, 233–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
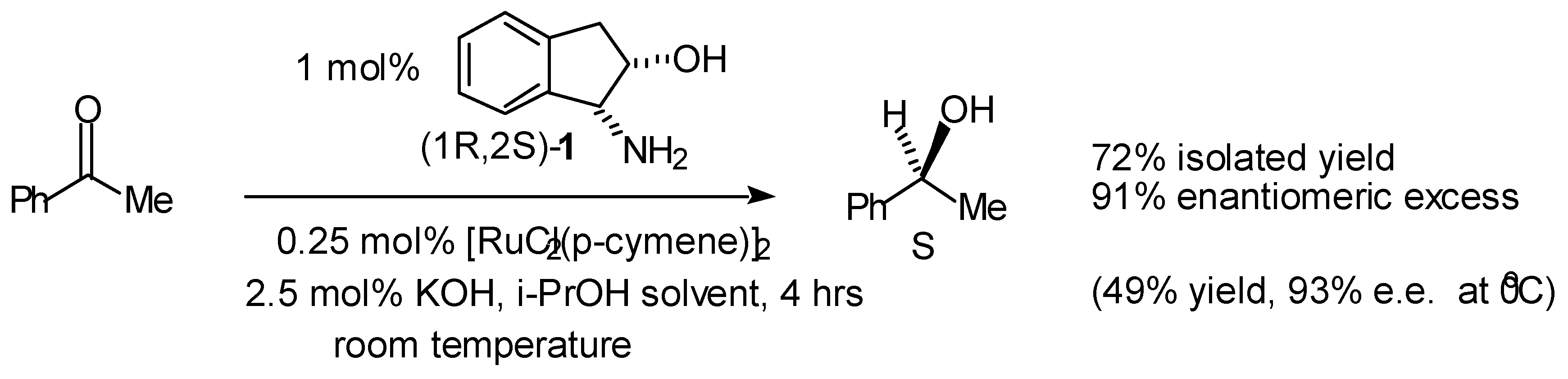
- Palmer, M.; Walsgrove, T.; Wills, M. (1R,2S)-(+)-cis-1-amino-2-indanol: An effective ligand for asymmetric catalysis of transfer hydrogenation of ketones. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 5226–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, D. A.; Guijarro, D.; Pinho, P.; Temme, O.; Andersson, P. G. (1S, 3R, 4R)-2-Azanorbornylmethanol, an efficient ligand for ruthenium-catalysed asymmetric transfer hydrogeantion of ketones. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 2749–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, T.; Helmchen, G. Highly efficient new catalysts for enantioselective transfer hydrogenation of ketones. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 1381–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammakia, T.; Strangeland, E. L. Transfer hydrogenation with ruthenium complexes of chiral (phosphinoferrocenyl)oxazolines. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 6104–6105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Van Plew, D.; Murtuza, S.; Zhang, X. Synthesis of (1R,2R)-2,6-bis(1-diphenylphosphinoethyl)pyridine and its application in asymmetric transfer hydrogenation. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 797–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, X. New chiral ligands for catalytic asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of ketones. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 6565–6568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, X. Highly effective NPN-type tridentate ligands for asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of ketones. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Alvarz-Gressier, M.; Lugan, N.; Mathieu, R. Ruthenium(II) complexes containing optically active hemilabile PNO-tridentate ligands. Organometallics 1997, 16, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.- X.; Ikariya, T.; Noyori, R. A rutenium(II) complex with a C2-symmetric diphosphine/diamine tetradentate ligand for asymmetric trasnfer hydrogenation of aromatic ketones. Organometallics 1996, 15, 1087–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishibayashi, Y.; Singh, J. D.; Arikawa, Y.; Uemura, S.; Hidai, M. Rhodium(I), iridium(I) and ruthenium(II) catalysed asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of ketones using diferrocenyl dichalcogenides as chiral ligands. J. Organomet. Chem. 1997, 531, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- a) Hu, X. M.; Kellogg, R. M. Asymmetric reduction and Meerwein-Ponndorf-Verley reaction of prochiral aromatic ketones in the presence of optically pure 1-aryl- 2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diols. Rec. Trav. Chim. Pays-Bas 1996, 115, 410–418. [Google Scholar] b) Krohn, K.; Knauer, B. Asymmetric induction in kinetically controlled zirconium catalysed Meerwein-Ponndorf-Verley reductions. Rec. Trav. Chim. Pays-Bas 1996, 115, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] c) Knauer, B; Krohn, K. A reinvestigation of the Meerwein-Ponndorf-Verley reduction: a highly efficient variation using zirconium catalysts. Liebigs Ann. 1995, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.; Walsgrove, T.; Wills, M. (1R,2S)-(+)-cis-1-amino-2-indanol: An effective ligand for asymmetric catalysis of transfer hydrogenation of ketones. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 5226–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Wills and J. Kenny, unpublished results.
- Noyori, R.; Hashiguchi, S. Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation Catalysed by Chiral Ruthenium Complexes. Acc. Chem. Res. 1997, 30, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
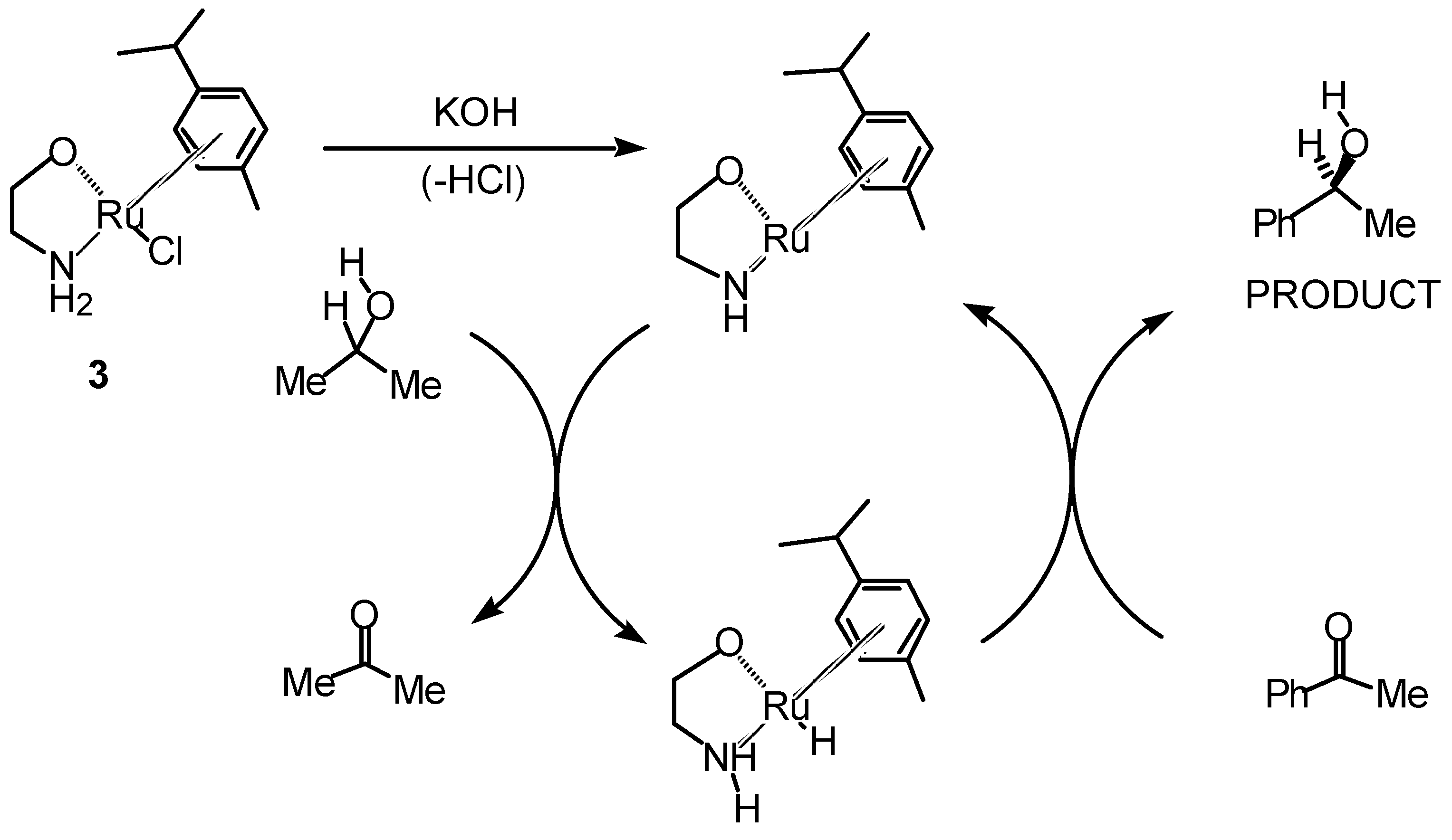
- Haack, K.-J.; Hashiguchi, S.; Fujii, A.; Ikariya, T.; Noyori, R. The catalyst precursor, catalyst, and intermediate in the Ru-II- promoted asymmetric hydrogen transfer between alcohols and ketones. Angew. Chem., Int. Edn. Engl. 1997, 36, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Wills and A. Smith, unpublished results.
- Bayston, D. J.; Travers, C. B.; Polywka, M. E. C. Synthesis and evaluation of a chiral heterogeneous transfer hydrogenation catalyst. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 1998, 9, 2015–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- a) Uematsu, N.; Fujii, A.; Hashiguchi, S.; Ikariya, T.; Noyori, R. Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of imines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 4916–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] b) Wang, G.- Z.; Bäckvall, J.-E. Ruthenium-catalyzed transfer hydrogenation of imines by propan- 2-ol. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1992, 980–982. [Google Scholar] c) Ahn, K. H.; Ham, C.; Kim, S.-K.; Cho, C.-W. Practical synthesis of chiral sultam auxiliaries: 3-substituted 1,2-benzisothiazoline 1,1-dioxides. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 7047–7048. [Google Scholar]
- a) ter Halle, R.; Schulz, E.; Lemaire, M. Heterogeneous enentioselective catalytic reduction of ketones. Synlett 1997, 1257–1258. [Google Scholar] b) Breysse, E.; Pinel, C.; Lemaire, M. Use of heterogenized dialdimine ligands in asymmetric transfer hydrogenation. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 1998, 9, 897–900. [Google Scholar]
- Hashiguchi, S.; Fujii, A.; Haack, K.-J.; Matsumura, K.; Ikariya, T.; Noyori, R. Kinetic resolution of racemis secondary alcohols by Ru(II)-catalysed hydrogen transfer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1997, 36, 288–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samples Availability: available from the authors.


© 2000 by MDPI (http://www.mdpi.org). Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.
Share and Cite
Wills, M.; Palmer, M.; Smith, A.; Kenny, J.; Walsgrove, T. Recent Developments in the Area of Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation. Molecules 2000, 5, 4-18. https://doi.org/10.3390/50100004
Wills M, Palmer M, Smith A, Kenny J, Walsgrove T. Recent Developments in the Area of Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation. Molecules. 2000; 5(1):4-18. https://doi.org/10.3390/50100004
Chicago/Turabian StyleWills, Martin, Matthew Palmer, Athene Smith, Jennifer Kenny, and Tim Walsgrove. 2000. "Recent Developments in the Area of Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation" Molecules 5, no. 1: 4-18. https://doi.org/10.3390/50100004
APA StyleWills, M., Palmer, M., Smith, A., Kenny, J., & Walsgrove, T. (2000). Recent Developments in the Area of Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation. Molecules, 5(1), 4-18. https://doi.org/10.3390/50100004