Abstract
This study investigated the in vivo effects of microcystins on gene expression of several phosphoprotein phosphatases (PPP) in the freshwater clam Corbicula fluminea with two different exposure scenarios. Clams were exposed for 96 h to 5 μg L−1 of dissolved microcystin-LR and the relative changes of gene expression of three different types of PPP (PPP1, 2 and 4) were analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR. The results showed a significant induction of PPP2 gene expression in the visceral mass. In contrast, the cyanotoxin did not cause any significant changes on PPP1 and PPP4 gene expression. Based on these results, we studied alterations in transcriptional patterns in parallel with enzymatic activity of C. fluminea for PPP2, induced by a Microcystis aeruginosa toxic strain (1 × 105 cells cm−3) during 96 h. The relative changes of gene expression and enzyme activity in visceral mass were analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR and colorimetric assays respectively. The clams exhibited a significant reduction of PPP2 activity with a concomitant enhancement of gene expression. Considering all the results we can conclude that the exposure to an ecologically relevant concentration of pure or intracellular microcystins (-LR) promoted an in vivo effect on PPP2 gene expression in C. fluminea.
1. Introduction
Cyanobacterial blooms often produce toxic metabolites, including cyclic hepatotoxins microcystins (MC). Among more than 80 MC identified, MC-LR is one of the most toxic and commonly detected MC congeners in natural blooms [1,2]. MC-LR enters in the aquatic food web by assimilation of aquatic invertebrates and can be passed to a higher trophic level through accumulation in tissues [3]. These cyclic heptapeptides are strong inhibitors of several serine/threonine (Ser/Thr) protein phosphatases (PP) leading to cell’s metabolism alteration [4]. The reversible phosphorylation of proteins in eukaryotes catalyzed by protein kinases and Ser/Thr PP determines the biological activities of many proteins and is recognized as a major mechanism controlling diverse cellular processes [5]. In mammals, this inhibition mechanism is directly related to MC hepatotoxicity and tumor promotion activity [6–11]. In contrast to mammals, relatively few studies have focused on the uptake and toxicity of MC to aquatic organisms. Although there has been some research examining the capacity of accumulation and depuration of MC [3] by these organisms, there is little information about detrimental effects of exposure to these toxins and their interaction with cell’s targets, in particular with Ser/Thr PP.
Eukaryotic Ser/Thr PP are structurally and functionally diverse enzymes that are classified into three distinct gene families. Phosphoprotein Phosphatases (PPP) is one of those families which are responsible for phosphoserine and phosphothreonine dephosphorylation [12]. The PPP family of Ser/Thr PP comprises seven enzymes (PPP1-7), in a total of 13 catalytic subunits [13]. Ser/Thr PP are closely related in amino acid sequence but can be distinguished functionally based on inhibition by small molecular toxins such as MC-LR [14]. Goldberg et al. [15] found that MC-LR interacts with three regions on the surface of the catalytic subunit of PPP1 α isoform; the hydrophobic moiety, C-terminal moiety and the acidic moiety. MC undergo a two-step interaction with Ser/Thr PP which consists in a rapid and reversible binding followed by a covalent bound after several hours [16]. MC-LR, -LA and -LL were found to interact with PPP2 and PPP1 catalytic subunits by a two-step mechanism involving rapid binding and inactivation of the PP catalytic subunit within minutes, followed by a slower covalent interaction during prolonged reaction-time [16]. The methyl-dehydroalanine (Mdha) residue of the toxin forms a covalent linkage with Cysteine-273 and 269 of PPP1 and PPP2 respectively [15–17]. In mammals, inhibition of Ser/Thr PPs by MC results in the reorganization of cytoskeleton components and disruption of hepatic architecture, leading to severe and irreversible damages and potentially death [18]. Severe effects of MC were also shown in aquatic organisms such as decrease in survival, growth and fecundity, histopathological damage and oxidative stress induction [19–24]. Among this group of organisms, bivalves may be one of the most threatened group of aquatic organisms in the presence of toxic cyanobacteria blooms. Bivalves are sedentary mollusks and filter large amounts of water to handle with nutritional and respiratory needs, being able to accumulate cyanobacterial toxins [3].
One long-standing pitfall in toxicology is to attribute a toxic effect from a sample to a particular compound, without checking that the pure compound actually has that effect, leading to misleading conclusions [25]. Microcystis extracts and toxic cultures have been widely used in oral toxicological studies of MC as effective replicates of natural poisoning for several organisms by toxic cyanobacteria [26]. However, validation of the results with pure MC is in most cases neglected. In this study, we aimed to investigate the in vivo effects of dissolved MC-LR and M. aeruginosa toxic strain cells on gene expression of PPP in the freshwater clam C. fluminea. The assessment of mRNA levels has been used as a reliable method to measure xenobiotic or natural toxins stress [18,27]. We started by investigating several PPP from C. fluminea, identifying PPP1, 2 and 4 transcripts in the freshwater bivalve. Then, the gene expression of PPP1, 2 and 4 in the visceral mass of C. fluminea was evaluated in an exposure assay using purified MC-LR. Finally, we studied alterations in transcriptional patterns in parallel with enzymatic activity of C. fluminea for PPP2, following exposure to a strain of M. aeruginosa producing almost exclusively MC-LR.
2. Results and Discussion
In this work, we showed for the first time the presence of PPP1, PPP2 and PPP4 in C. fluminea. We amplified partial sequences of those genes in this species and the obtained sequences were deposited in GenBank with the accession numbers: JN379818; JN379819; JN379820. In mammals, the main functions of PPP1 are connected to muscle contraction/relaxation, glycogen metabolism, synaptic transmission, gene expression, RNA splicing and cell-cycle progression [13]. PPP2 and PPP4 catalytic subunits are phylogenetically related and have 65% amino acid sequence identity [28]. Although most closely related, PPP2 and PPP4 have individual functions and do not complement each other [29]. PPP2 is mainly cytosolic and plays a role in cell-cycle regulation, cell growth control, cytoskeleton dynamics, cell mobility, metabolism, transcription, translation, RNA splicing, DNA replication, apoptosis, inflammation and differentiation [13]. PPP4 is predominantly nuclear where it seems to play a role in centrosome maturation, microtubule organization, histone phosphorylation and apoptosis [13].
After designing the specific primers for each of the studied genes, gene expression of PPP1, 2 and 4 was evaluated in the visceral mass of C. fluminea in an exposure assay using purified MC-LR. MeOH extractable toxin concentration (unbound MC) was quantified in exposed clam tissues collected during a continuous exposure to 5 μg L−1 of purified MC-LR for 4 days (Figure 1). No free MC were detected in control clams after the intoxication period. In the exposure groups, unbound MC-LR was detected in the clams already after 1.5 h, revealing an immediate uptake of the toxin which was continuous, reaching a mean value of 0.213 μg g−1 DW at 24 h. The mean maximum uptake detectable level was 0.306 μg g−1 DW after 96 h, which reveals an increase of 30% of the accumulated toxin from the end of the first day to the fourth.
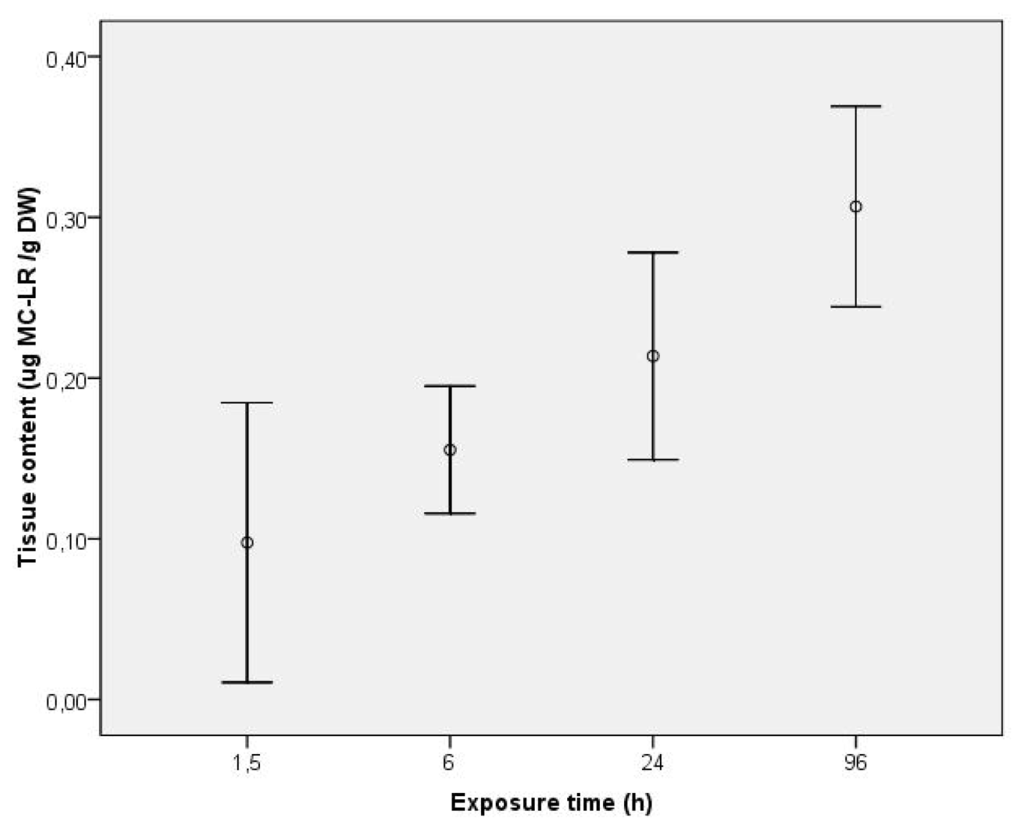
Figure 1.
Tissue content (μg MC-LR g−1 DW) of unbound MC-LR in the visceral mass during exposure of C. fluminea to 5 μg L−1 MC-LR for 96 h. Values represent average of three replicates and bars represent confidence interval for mean level (95%).
During MC-LR exposure, no significant variations were detected for PPP1 and PPP4 transcripts (Figure 2) (same horizontal regression line for controls and exposure groups). However, the regression statistics show significant correlations (p < 0.05) in PPP2 gene expression between treatments (Figure 2). A total of 51.4% of the variation in the PPP2 gene expression in clams may be explained by the significant variable (Treatment) (p < 0.05) in the multiple linear regression analysis (F = 7.175; p = 0.014). As a result, PPP2 gene expression is significantly higher in exposed clams during the 96 h, evidencing the need of the clams to repair cells injuries by protein synthesis. There is no significant variation of results over time regardless the applied treatment, which means that the difference between treatments is constant.
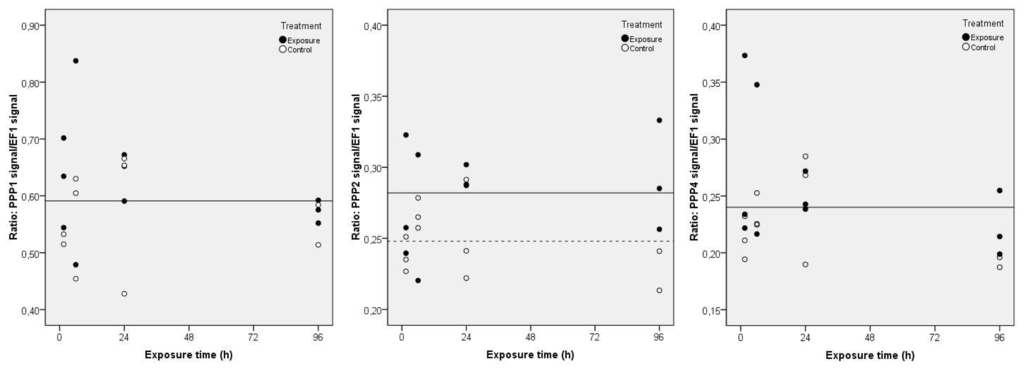
Figure 2.
Projection of the normalized gene expression values of PPP1, PPP2 and PPP4 in C. fluminea visceral mass after exposure to 5 μg L−1 of MC-LR during 96 h, in relation to the studied independent variables, according to the multiple linear regression analysis (Control groups-dashed line; Exposure groups-continuous line). The regression models describing the functions represented in the figure include only the significant regression variables (PPP1: none; PPP2: Treatment; PPP4: none).
Based on these last results, we studied alterations in transcriptional patterns in parallel with enzymatic activity of C. fluminea for PPP2, induced by a cyanobacteria toxic strain. The unbound MC-LReq. tissue concentration was quantified in exposed clams collected during a continuous exposure to a density of 105 cells cm−3 of a M. aeruginosa toxic strain for 4 days (Figure 3). No free MC were detected in control clams after the intoxication period and thus no false positives were detected with ELISA. Unbound MC-LReq. was detected in the clams already in day 1, revealing an immediate uptake of the toxin. In the following days, a decrease of the accumulated free MC-LReq. was verified, particularly between days 2 and 3, with a decrease of nearly 55% of the accumulated toxin. The mean maximum uptake detectable level was 2.77 μg g−1 DW in the first day. At day 4, the clams retained a concentration 62% lower than the mean maximum uptake level.
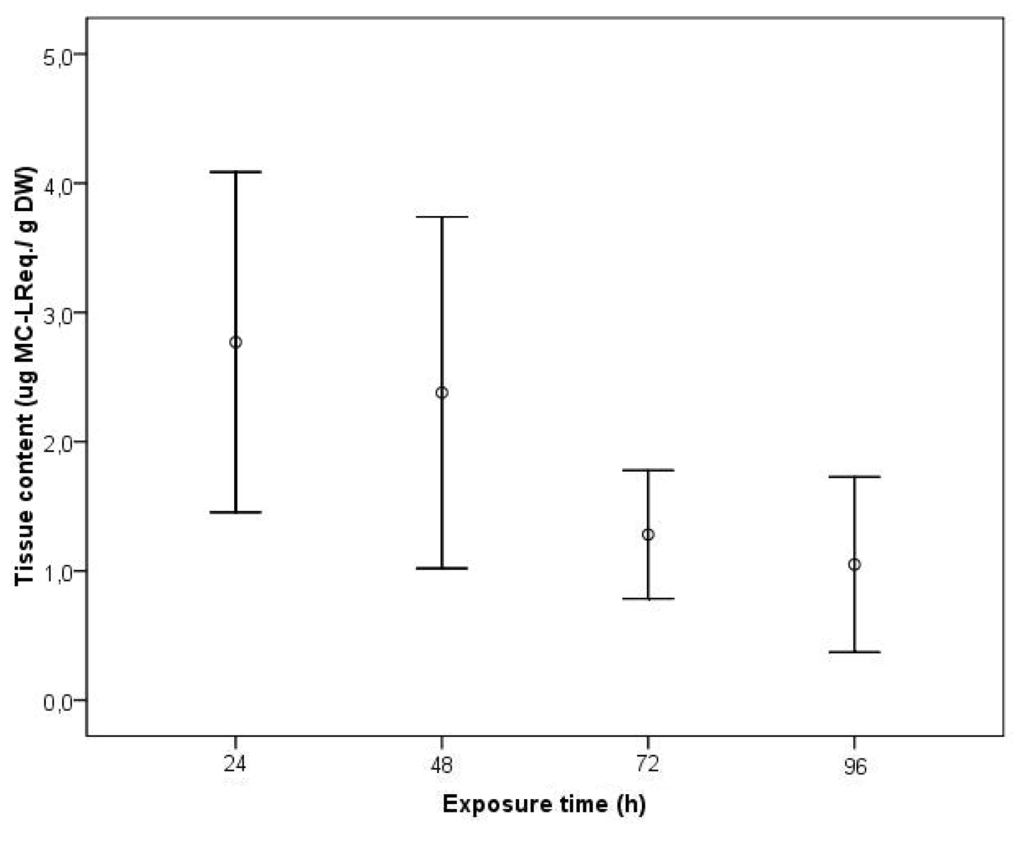
Figure 3.
Tissue content (μg MC-LReq. g−1 DW) of unbound MC-LReq. in the visceral mass during exposure of C. fluminea to 1 × 105 cells cm−3 of a M. aeruginosa toxic strain for 96 h. Values represent average of three replicates and bars represent confidence interval for mean level (95%).
The clams exposed to the toxic cells of M. aeruginosa showed a different pattern of PPP2 gene expression when compared to pure MC-LR exposure (Figure 4). A total of 95.8% of the variation in the PPP2 gene expression in clams may be explained by the significant variables (time of exposure and treatment) (p < 0.05) in the multiple linear regression analysis (F = 31.240; p = 0.000). As a result of these two factors acting either together or independently, the PPP2 mRNA levels are lower for exposed clams in relation to non-exposed clams, between days one and two, contrary to the last two days. After 96 h, PPP2 mRNA expression levels were 61% higher compared to non-exposed clams. As with purified MC-LR, exposure to Microcystis cells also induced an enhancement of PPP2 mRNA levels, evidencing as well the need of the clams to repair cells injuries through an increase in protein synthesis in both experiments.
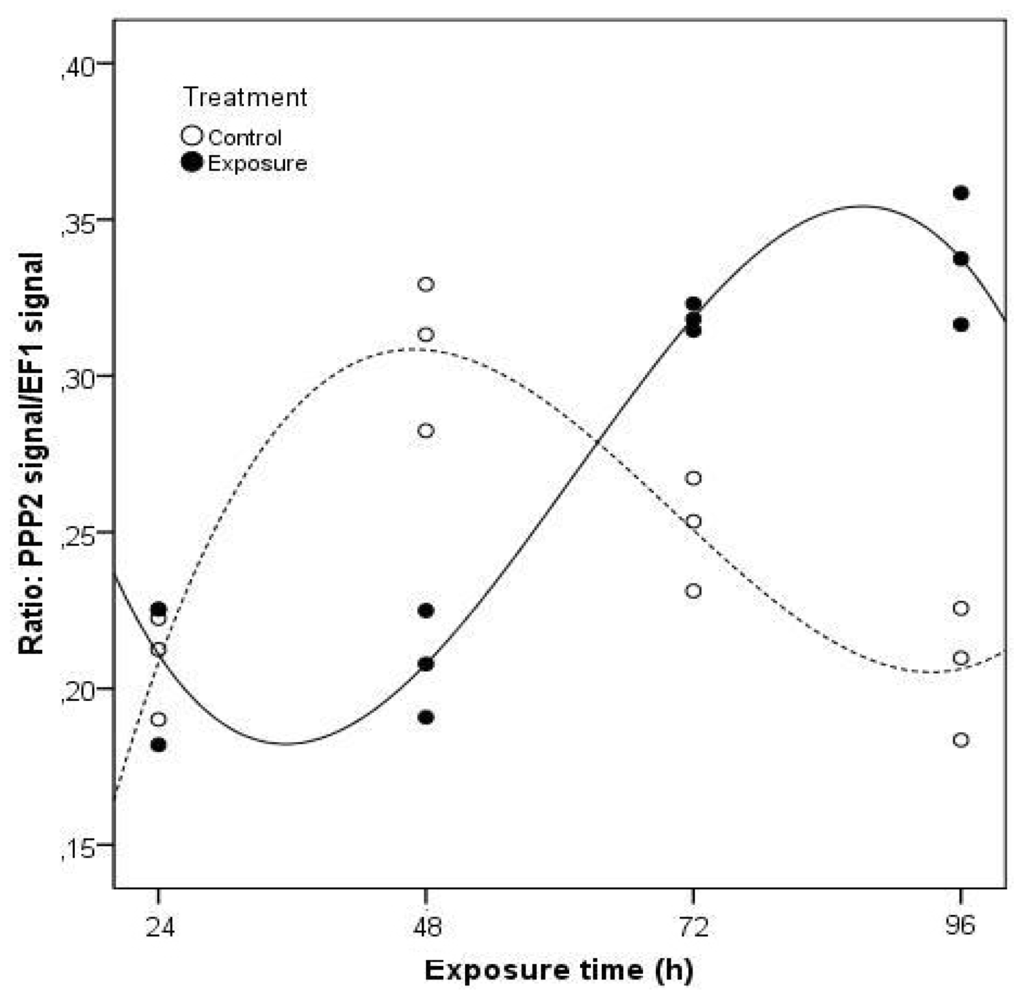
Figure 4.
Projection of the normalized gene expression values of PPP2 in C. fluminea visceral mass after exposure to 1 × 105 cells cm−3 of a M. aeruginosa toxic strain during 96 h, in relation to the studied independent variables, according to the multiple linear regression analysis (Control groups-dashed line; Exposure groups-continuous line). The regression models describing the functions represented in the figure include only the significant regression variables (Treatment, Exposure time, Exposure time squared, Treatment × Exposure time, Treatment × Exposure time squared, Treatment × Exposure time cubed).
The four-day exposure to Microcystis cells was sufficient to produce a reduction in PPP2 enzyme activity present in clams visceral mass (Figure 5). Taking into account all the significant variables (time of exposure and treatment) (p < 0.05) of the multiple linear regression analysis it is possible to explain 93.6% of the total variation in PPP2 enzyme activity in C. fluminea (F = 25.324; p = 0.000). As a result of these two factors, acting either together or independently, the PPP2 enzyme activity in exposed clams is significantly lower during the 96 h of exposure to M. aeruginosa toxic strain. This reduction was especially severe after 96 h, with a lower 91% activity compared to non-exposed clams. This kind of response might be related to a disruption in the signaling pathway leading to protein structural damage.
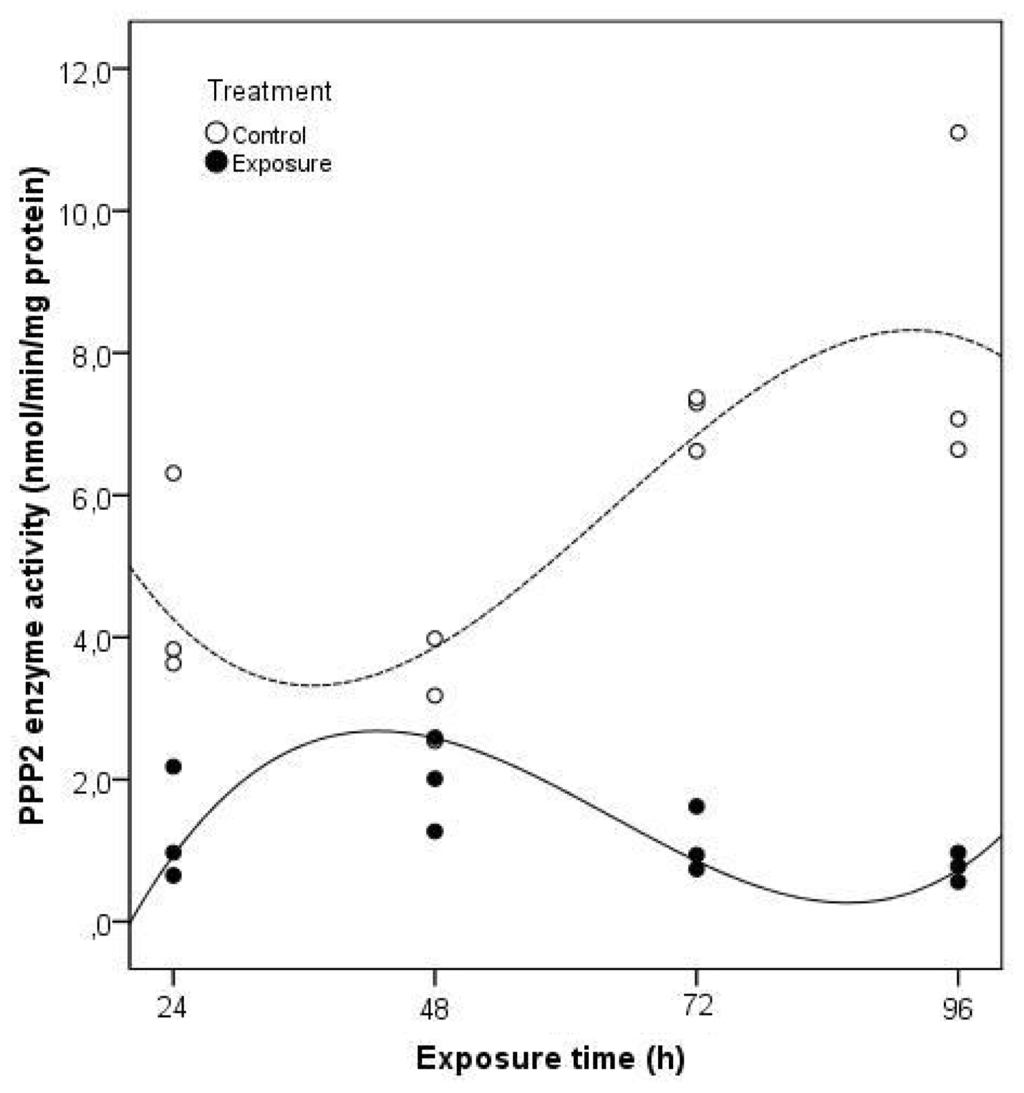
Figure 5.
Projection of enzyme activity values of PPP2 in C. fluminea visceral mass after exposure to 1 × 105 cells mL−1 of a M. aeruginosa toxic strain during 96 h, in relation to the studied independent variables, according to the multiple linear regression analysis (Control groups-dashed line; Exposure groups-continuous line). The regression models describing the functions represented in the figure include only the significant regression variables (Treatment, Exposure time, Treatment × Exposure time, Treatment × Exposure time squared, Treatment × Exposure time cubed).
The results from several field studies demonstrate that bivalves accumulate toxins at sites where toxic cyanobacterial blooms occurred [30,31]. Cyanotoxins accumulation in bivalves can result from ingestion of toxic cyanobacteria or exposure to dissolved toxins released to the water after cells lysis. Generally, healthy bloom populations produce low amounts of extracellular toxin, with values ranging from 0.1 to 10 μg L−1 [32]. However, concentrations of dissolved toxins in the water column are much higher in ageing or collapsing blooms [32]. One of the most frequently found cyanobacterial toxins in blooms from fresh and brackish waters are the hepatotoxins MC.
This study investigated the in vivo effects of MC on gene expression of several PPP in the freshwater clam C. fluminea after exposure to dissolved MC-LR and to toxic M. aeruginosa cells. We observed a difference in cumulative uptake values and patterns amongst the two different exposure scenarios. Our uptake values are limited to free MC and probably also to MC conjugated with glutathione and cysteine [33]. Since MC covalently bind to PP, a significant part of the toxin becomes undetected by the common methods such as ELISA. Conventional methods such as organic extraction only extract the unbound portions of the toxin [34]. Less unbound MC were detected during the dissolved MC-LR exposure compared to cyanobacterial ingestion. After being exposed for 4 days to 5 μg L−1 MC-LR, the clams accumulated a maximum detectable level of 0.306 μg g−1 DW in the fourth day. The accumulation of free MC promoted by the exposure to whole M. aeruginosa toxic strain cells (4.5 μg MC-LReq. L−1) comprehended values between 2.77 and 1.05 μg g−1 DW in the first and fourth days, respectively. Although with higher values, the accumulation of unbound MC promoted by the exposure of the clams to cyanobacterial cells are rather not so significant when compared to results of other laboratory experiments. Amorim and Vasconcelos [26] found MeOH extractable MC-LReq. levels in Mytilus galloprovincialis (whole body) of 10.7 μg g−1 DW, after four days of exposure to a M. aeruginosa toxic strain. In a previous work, Vasconcelos [35] found MeOH extractable MC-LReq. levels in the visceral mass of the same marine bivalve of 27.6 μg g−1 DW, after sixteen days of exposure, also to a M. aeruginosa toxic strain. With Corbicula this is the first laboratory study that addresses MC uptake. The lack of data also exists in what it respects to pure MC uptake by bivalves. In one of the few records, the freshwater bivalve Anodonta grandis simpsoniana did not accumulate MC after exposure to dissolved MC-LR, during three days [36]. In this study, the measurement of MC in the clams exposed to cyanobacterial cells can be overestimated since much of the toxin detected can arise from intact cyanobacteria in the alimentary tract. C. fluminea seems to react to the contact with M. aeruginosa cells with MC by closing their valves so the uptake is limited. After the initial ingestion of cells it seems that the clam decreases their filtering rates, avoiding the toxin producing cells. Studies with gastropods with the same two intoxication routes and taking in account emptiness of their gut contents showed differences in MC accumulation, i.e., 1300 times more important in L. stagnalis after ingestion of toxic cyanobacteria than after dissolved MC-LR exposure [21,37]. These differences in MC accumulation between both scenarios were also found in our study, which may influence the degree of the subsequent pathological effects.
Nevertheless the low uptake values, both intoxication routes promoted an effect in gene expression of PPP2, which constitutes, according to the in vitro studies in mammals [13], one of the most sensitive PPP to MC. The low uptake values associated to a lower sensitivity to MC [13] might also be the reasons for the no observed significant changes in PPP1 and 4 gene expressions upon exposure to dissolved MC-LR. For PPP2, gene expression variations during the 4 days of exposure seem to largely depend on MC uptake and accumulation patterns found in our study for the two routes and forms of exposure. During the dissolved MC-LR exposure, PPP2 expression increased remaining relatively constant over time and concomitant to a relatively constant uptake of the toxin between sampling endpoints. In contrast, upon cyanobacterial exposure, PPP2 transcriptional expression levels in the first two days are lower when compared to non-exposed clams, contrary to the last two days. In this case, intracellular MC were immediately incorporated by C. fluminea, but also instantly released. Previous investigations observed as well an immediate uptake and rapid release of MC-LR for D. polymorpha and M. galloprovincialis, although only when mussels were transferred to toxin-free medium [26,38]. The constant decrease of the MC uptake values since day one found in our study can possibly be explained by a filtration reduction activity by the clams, as a result of the closure of their valves [39]. Interestingly, the major increase above control levels of PPP2 expression after 72 and 96 h to M. aeruginosa exposure corresponds to the lower amounts of unbound MC detected during the 4-day exposure, suggesting that most of the accumulated MC at that time is covalently bound. Lance et al. [40] found that 17.7 to 66.7% of the total accumulated MC were found in snails exposed to MC producing toxic strain. Both exposure pathways lead to an enhancement of PPP2 gene expression in the visceral mass of C. fluminea, although with different patterns. Supporting these results, Huang et al. [41] showed that after 7 days of exposure to a cyanobacteria extract (MC-LR, -RR) the expression level of PPP2 in mice liver has increased significantly. For cyanobacterial cells exposure also, the data indicate an increased expression of the PPP2, whereas its activity remains blocked. Several studies show that mRNA levels correlate closely with enzyme activity levels [18,27]. Gehringer et al. [18] suggest that the increase in activity was the result of de novo synthesis, accompanied by an increase in transcription. In bivalves, as in mammals, the inhibition of PPP activity by MC is also a possible relevant phenomenon which can lead to an imbalance phosphorylation state of several key proteins in many cellular pathways. In this study, toxic M. aeruginosa cells producing mostly MC-LR induced a decrease of PPP2 activity in C. fluminea. Malbrouck et al. [42] also reported a decrease in hepatic PPP activity after injecting intraperitoneally the goldfish Carassius auratus with MC-LR.
The major increase above control levels of PPP2 expression detected for both exposure scenarios in this study indicates an enhanced demand for new synthesis of this enzyme. This demand for new synthesis of PPP2 possibly evidences the need of the clams to repair cells injuries. Previously, we showed that a M. aeruginosa toxic strain induced changes in protein expression in the freshwater clam C. fluminea [43]. We have suggested that the almost exclusive identification of cytoskeletal proteins could reflect PPP2 phosphatase inhibition as major role of MC-related toxicity in bivalves [43]. In this study, protein structural damage may be a consequence of the observed emerging reduction in PPP2 enzyme activity since the first day of exposure to the toxic strain.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Test Species and Cultures
For laboratory studies C. fluminea with a size of 25–30 mm were manually collected in Rio Minho estuary (Valença, Portugal). At the time, there was no record of cyanobacterial blooms in the area. Animals were acclimated to laboratory conditions in dechlorinated tap water for one month, prior to exposure experiments. Six hundred bivalves were held in two 60 L storage tanks with aerated water at 18 ± 1 °C. The water was exchanged thrice a week. The animals were fed with an algal suspension (Chlorella vulgaris, 1 × 105 cells mL−1) twice a week. C. vulgaris and M. aeruginosa strain IZANCYA 2 were cultured in 6 L flasks containing 4 L of Z8 medium [44], using cool white fluorescent light (10 μmol m−2 s−1) with a light-dark period of 14–10 h, and a temperature of 25 ± 1 °C. IZANCYA 2 produces MC-LR and low amounts of MC-LA and [d-Asp3]-MC-LR [35]. IZANCYA 2 was regularly analyzed to ensure toxin production characteristics.
3.2. MC Purification
3.2.1. MC-LR Extraction for Analytical HPLC
Subsamples of M. aeruginosa biomass (60–100 mg) were extracted in aqueous methanol (MeOH, HPLC grade) (50%), sonicated in ice bath (60 Hz, 5 min) and the mixture centrifuged (4995 g, 10 min, 4 °C). The supernatant was filtered on GFC 1.2 μm and evaporated in rotavapor until complete dryness. The residue was suspended in aqueous MeOH (50%), filtered on MILLEX®GP 0.22 μm then analyzed by HPLC-PDA.
3.2.2. MC-LR Extraction for Semi-Preparative HPLC
Subsamples of M. aeruginosa biomass (300–500 mg) were extracted in aqueous MeOH (75%), sonicated in ice bath (60 Hz, 5 min) and the mixture centrifuged (4995 g, 20 min, 4 °C). The supernatant was filtered on GFC 1.2 μm and evaporated in rotavapor until completely dryness. The residue was suspended in aqueous MeOH (50%), filtered on MILLEX®GP 0.22 μm then analyzed by HPLC-PDA.
3.2.3. Solid Phase Extraction
The supernatant was transferred to a rounded bottom glass flask (250 mL) and evaporated at 35 °C to about 20 mL using a rotaporator, then applied directly to a Waters Sep-Pak® Vac 6 mL C18–500 mg cartridge, which had been preconditioned by 100% MeOH and distilled water. The column was first washed with 20% MeOH and the toxin then eluted with the 80% MeOH. The MC-containing fraction was evaporated until removing the entire methanol portion. This solution was injected into the HPLC-PDA for analysis.
3.2.4. Quantification of MC-LR
The analytical and semi-preparative analyses of MC-LR were determined according to a modified version of the method applied in Ramanan et al. [45]. The chromatographic system consisted of a Waters Alliance e2695 high-pressure liquid chromatograph equipped with a photodiode array detector 2998. The MC-LR analytical assay was performed using a reversed phase column (Merck Lichrospher RP-18 endcapped (25 cm × 4.6 mm, 5 μm)) equipped with a guard column (Merck Lichrospher RP-18 endcapped (4 × 4 mm, 5 μm)) both were kept at 40 °C. The gradient elution utilized MeOH and water both acidified with 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid (TFA, 99.5%) with a flow rate of 0.9 mL/min. The injected volume was 20 μL. The PDA range was 210–400 nm, with a fixed wavelength at 238 nm. The method linearity (y = 1.45 × 1015 − 1.74 × 102, R2 = 0.995) was achieved between 0.13 and 10 ppm; limit of detection of the instrument was 0.1 ppm (S/R 3). Sets of 6 samples (in duplicate) were analyzed and correspondent concentrations of MC-LR were obtained by a daily two point calibration method. The MC-LR semi-preparative assay was performed to purify MC-LR for the exposure experiments using a reversed phase column (Phenomenex Luna RP-18 (25 cm × 10 mm, 10 μm)) kept at 30 °C. The gradient elution utilized MeOH and water both acidified with 0.1% TFA with a flow rate of 2.5 mL/min. The injected volume was 500 μL. The PDA range was 210–400 nm, with a fixed wavelength at 238 nm. Peak purity and percentage of MC-LR purified was calculated at 214 nm and 238 nm. Fractions were collected and analyzed by analytical HPLC-PDA.
3.3. Exposure Experiments
3.3.1. With Purified MC-LR
Each replicate consisted of five clams exposed in 400 mL of aerated dechlorinated tap water. Both control and treatment were carried out in triplicate. The non-control clams were exposed to 5 μg L−1 of purified MC-LR mixed with C. vulgaris (1 × 104 cells mL−1) to prevent the inhibitory effect by MC alone. Tissues and medium sampling were done after 1.5, 6, 24 and 96 h of exposure to the toxin. The exposure medium was daily renewed. Visceral mass of the collected clams were manually dissected at 4 °C, weighted, frozen with liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C until posterior use.
3.3.2. With M. aeruginosa Toxic Strain Cells
Exposure experiments were carried out in a continuous flow-through system. In this system, 36 L aquariums containing sand and aerated dechlorinated tap water were used, with 48 clams each. Both control and treatment were carried out in triplicate. Two peristaltic pumps (Gilson Minipuls 3) generated a constant test solution flow of 1500 mL/h. In this way, the aqueous test solution was renewed daily in each aquarium. In the accumulation period, clams were exposed to a constant flow of 25 × 105 cells mL−1 h−1 of the M. aeruginosa strain IZANCYA 2, making a density of 105 cells mL−1 (4.5 μg MC-LReq. L−1) during 4 days. Control group was fed with C. vulgaris. Daily, during these 4 days of the accumulation experiment, 6 animals were randomly collected from each aquarium for toxin analysis, 3 for gene expression and other 3 for enzymatic activity. Visceral mass of the collected clams were manually dissected at 4 °C, weighted, frozen with liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C until posterior use.
3.4. Toxin Analysis in the Clams
In both exposure experiments (pure or intracellular MC-LR), MC quantification was done in the visceral mass of the bivalves. In the visceral mass, two main areas can be distinguished [46]. The digestive tract which comprises various sections including a large dorsal pouch-shaped stomach and a heavily folded intestinal tract showing numerous loops embedded in the digestive gland and the gonadal tissue [46]. Besides the digestive tract, visceral mass is occupied by the hermaphrodite gonad and other internal organs [46]. Extraction of the MC was done using a modified method described in Amorim and Vasconcelos [26]. Corbicula tissues were homogenized in liquid nitrogen until completely disrupted. MC were extracted in 80% methanol (5 mL for 1 g dry weight, 10 °C) with ultrasonication on ice (120 s, 60 Hz). After 24 h, the supernatant was collected and the pellets reextracted with the same procedure. After the 2-day extraction was finished, the two pooled supernatants were combined and centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 30 min. The extracts were diluted (4×) with sterile milliQ water and loaded in a Bond Elut C18 cartridge after being activated with methanol. The cartridge was then rinsed with in sterile Milli-Q water and methanol 20%. Finally, the toxic fraction was recovered with 100% methanol. This solution was completely evaporated and the residues resuspended in Milli-Q water for toxin analysis. For toxin quantification an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used (EnviroGard MCs Plate Kit-Hampshire, UK) with a detection limit of 0.1 ng MC/mL. This assay was already performed using this type of matrix [26]. MC contents in visceral mass of the clams are expressed in μg g−1 DW (dry weight). The values were calculated taking into account an extraction recovery of 75%. This value was defined in a previous study in our laboratory using the same procedure for recovery of the toxins [47].
3.5. Gene Expression
3.5.1. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
RNA isolation was performed in the visceral mass of the bivalves exposed to dissolved MC-LR and to M. aeruginosa toxic strain cells. RNA isolation from C. fluminea tissues (20 mg) was performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions using RNeasy mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), with an additional step of on-column DNA digestion using RNase-Free DNase Set (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). cDNA synthesis was initiated by incubating 1 μg total RNA with 1 μL Oligo (dT)18 primer mix (Bioline, London, UK) and 1 μL deoxynucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs, 10 mM) (Bioline, London, UK) for 10 min at 65 °C. Reverse Trancription was performed using 4 μL 5× RT buffer (Bioline, London, UK), 1 μL RNase inhibitor (10 U/μL) (Bioline, London, UK) and 0.25 μL MMLV reverse transcriptase (200 U/μL) (Bioline, London, UK). The reaction mixture was incubated at 42 °C for 30 min. The reaction was terminated with an incubation step of 15 min at 70 °C.
3.5.2. Primers Design
All primers were obtained from Invitrogen (Carlsbard, USA). For PPP1, degenerate primers were chosen in the PPP1 conserved coding region of several partial sequences of Lottia gigantea built from available EST (Expressed Sequence Tag) records. For PPP2, degenerate primers were chosen in the PPP2 conserved coding region of the five following mollusks: Mytilus californianus, Crassostrea gigas, Crassostrea virginia, Chlamys farreri and Dreissena polymorpha (GenBank accession numbers: GE753752; AM856000.1; EH64803; DT717746; AF508223). For PPP4, degenerate primers were chosen in the PPP4 conserved coding region of the four following mollusks: Crassostrea gigas, Crassostrea virginia, Chlamys farreri, Venerupis philippinarum (GenBank accession numbers: AM854071.1, CD648951.1, DT717768.1, AM872270.1). The same method was applied to amplify others PPP member (PPP3, PPP5, PPP6) although not successfully due to non-specific amplifications. Specific primers were designed according to C. fluminea PPP1, 2 and 4 obtained sequences (Table 1). Specific primers were also designed for elongation factor 1-α (EF1-α) after obtaining C. fluminea EF1-α sequence using specific primers designed for the freshwater mussel D. polymorpha [48]. The PCR products using the specific primers were sent for sequencing to confirm the specificity of the amplified products.

Table 1.
Sequences of primers used for RT-PCR.
3.5.3. Quantitative RT-PCR
Quantitative RT-PCR was performed using a iCycler iQ™ Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad). Specific primers were used to amplify cDNA of PPP1, PPP2 and PPP4. EF1-α cDNA was amplified as a control. EF1-α was used as a control gene for DNA level normalization. The EF1-α was previously used as housekeeping gene in other studies [48,49] and accordingly we observed in the experiment an absence of changes in the expression levels after the treatment. Each reaction mixture consisted of 4 μL cDNA template, 0.25 μM of each primer, 1× IQ SYBR Green Supermix (Bio-Rad) and water to adjust to 20 μL final reaction volume. Reaction mixtures were subjected to the following cycling conditions: 5 min at 95 °C to denature DNA and activate Taq polymerase; 40 cycles of 15 s at 95 °C, 30 s at 58 °C and 30 s at 72 °C. All reactions were run on duplicate in a 96-well plate, including a negative control for each set of primers. Melting curves (81 steps of 30 s, from 55.0 to 95.5 °C, with a temperature gradient increase of 0.5 °C per step) were generated for PCR products to confirm the specificity of the assays and to check the occurrence of primer dimers. A dilution series was also prepared to test the efficiency of PCR amplifications. The PCR efficiency for each gene amplification varied from 96.6% to 110.2%. A standard curve for qPCR was determined as a correlation between gene copy numbers and the cycle threshold (CT). For each gene, standards were prepared with the primers used in the Q-PCR to amplify the cDNA in a normal PCR reaction. The purified PCR products were used as standard samples, and 10-fold serial dilutions of these samples were analyzed by qPCR. Gene copy numbers of the standard samples were determined using the following formula: copy number = [DNA quantity (g) × Avogadro constant (6.022 × 1023 copies mol−1)]/[DNA length (bp) × 660 (g/mol/bp)] [50].
3.6. Enzyme Analysis
PPP2 activity was performed in the visceral mass of the bivalves exposed to M. aeruginosa toxic strain cells according to the manufacturer’s instructions, using Serine/Threonine Phosphatase Assay System Kit (Promega Corporation, Madison, WI). This method determines the amount of free phosphate generated in a reaction by measuring the absorbance of molybdate malachite green: phosphate complex using the synthetic phosphopeptide RRA(pT)VA as substrate. Protein content of the samples was quantified according to Bradford [51].
3.7. Statistical Analysis
Pearson’s coefficient (R Pearson) was calculated to assess the existence of a correlation between the fresh and dry weights of clams (n = 30).
PPP gene expression and enzyme activity responses (dependent variables) were examined with saturated orthogonal multiple linear regression analysis and subsequent variance analysis (ANOVA) [52,53]. The regression model was defined as y (dependent variable) = b0 + b1 × Treatment + b2 × Exposure time + b3 × Exposure time squared + b4 × Exposure time cubed + b5 × Treatment × Exposure time + b6 × Treatment × Exposure time squared + b7 × Treatment × Exposure time cubed. The independent variable Treatment is composed of two modalities or conditions: control group and group of organisms exposed to MC. The independent variable Exposure time is composed of four modalities or times of exposure: 1.5, 6, 24 and 96 h for MC-LR exposure and 24, 48, 72 and 96 h for cyanobacterial cells exposure. The normality of each distribution was verified by Shapiro-Wilk test and variance homogeneity by Levene’s Test of Equality of Error Variances. A significant level (α) of 0.05 was used for the multiple regression analysis, for normality and variance homogeneity tests. All graphics and statistical analysis were carried out using SPSS 11.0 for Windows (Chicago, IL, USA).
4. Conclusions
This paper is the first to sequence PPP1, PPP2 and PPP4 in C. fluminea. The study showed that despite low uptake levels, the exposure of C. fluminea to an environmentally relevant concentration of purified MC-LR resulted in a significant induction of PPP2 gene expression in the visceral mass. In contrast, MC-LR did not cause any significant changes on PPP1 and PPP4. The exposure of C. fluminea to a strain of M. aeruginosa producing mostly MC-LR also caused in vivo induction of PPP2 on the transcript level preceded by an immediate reduction of PPP2 enzyme activity.
Considering all the results we can say that the exposure to an ecologically relevant concentration of pure or intracellular MC (-LR) promoted an in vivo effect on PPP2 gene expression in C. fluminea. The PPP2 expression variations during the four days of exposure seem to largely depend on MC accumulation patterns found in our study for the two routes and forms of exposure.
Apart from the ecological relevance, this study itself may also contribute to the PPP research. Having a major role on MC-related toxicity, further in vivo studies should continue to study how the PP activity and gene expression are affected raising the knowledge about the molecular mechanisms of MC induced toxicity in bivalves.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT) (SFRH/BD/31416/2006).
References
- Chorus, I.; Falconer, I.R.; Salas, H.J.; Bartram, J. Health risks caused by freshwater cyanobacteria in recreational waters. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B 2000, 3, 323–347. [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich, D.; Hoeger, S. Guidance values for microcystins in water and cyanobacterial supplement products (blue-green algal supplements): A reasonable or misguided approach? Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol 2005, 203, 273–289. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, J.C.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Microcystin dynamics in aquatic organisms. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B 2009, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- MacKintosh, C.; Beattie, K.A.; Klumpp, S.; Cohen, P.; Codd, G.A. Cyanobacterial microcystin-LR is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A from both mammals and higher plants. FEBS Lett 1990, 264, 187–192. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Honkanen, R.E. Molecular cloning, expression, and characterization of a novel human serine/threonine protein phosphatase, PP7, that is homologous to Drosophila retinal degeneration C gene product (rdgC). J. Biol. Chem 1998, 273, 1462–1468. [Google Scholar]
- Falconer, I.R. Tumour promotion and liver injury caused by oral consumption of cyanobacteria. Environ. Toxicol. Water Qual 1991, 6, 177–184. [Google Scholar]
- Nishiwaki-Matsushima, R.; Ohta, T.; Nishiwaki, S.; Suganuma, M.; Kohyama, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Carmichael, W.W.; Fujiki, H. Liver tumor promotion by the cyanobacterial cyclic peptide toxin microcystin-LR. J. Cancer Res. Clin 1992, 118, 420–424. [Google Scholar]
- Humpage, A.R.; Hardy, S.J.; Moore, E.J.; Froscio, S.M.; Falconer, I.R. Microcystins (cyanobacterial toxins) in drinking water enhance the growth of aberrant crypt foci in the mouse colon. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2000, 61, 155–165. [Google Scholar]
- Prieto, A.I.; Jos, Á.; Pichardo, S.; Moreno, I.; Cameán, A.M. Differential oxidative stress responses to microcystins LR and RR in intraperitoneally exposed tilapia fish (Oreochromis sp.). Aquat. Toxicol 2006, 77, 314–321. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Xie, P.; Zhang, X. Oxidative stress response after prolonged exposure of domestic rabbit to a lower dosage of extracted microcystins. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol 2009, 27, 195–199. [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki, H.; Suganuma, M. Carcinogenic aspects of protein phosphatase 1 and 2A inhibitors. In Marine Toxins as Research Tools: Progress in Molecular and Subcellular; Spring: Berlin, Germany, 2009; Marine Molecular Biotechnology 46; pp. 221–254. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, L.N. The regulation of protein phosphorylation. Biochem. Soc. Trans 2009, 37, 627–641. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, S.R.; Vasconcelos, V.M.; Antunes, A. The phosphoprotein phosphatase family of Ser/Thr phosphatases as principal targets of naturally occuring toxins. Crit. Rev. Toxicol 2011, 41, 83–110. [Google Scholar]
- Prickett, T.D.; Brautigan, D.L. The α4 regulatory subunit exerts opposing allosteric effects on protein phosphatases PP6 and PP2A. J. Biol. Chem 2006, 281, 30503–30511. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, J.; Huang, H.B.; Kwon, Y.G.; Greengard, P.; Nairn, A.C.; Kuriyan, J. Three dimensional structure of the catalytic subunit of protein serine/threonine phosphatase-1. Nature 1995, 376, 745–753. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, M.; Luu, H.A.; McCready, T.L.; Williams, D.; Andersen, R.J.; Holmes, C.F. Molecular mechanisms underlying he interaction of motuporin and microcystins with type-1 and type-2A protein phosphatases. Biochem. Cell Biol 1996, 74, 569–578. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Chao, Y.; Lin, Z.; Li, Z.; Strack, S.; Stock, J.B.; Shi, Y. Structure of protein phosphatase 2A core enzyme bound to tumor-inducing toxins. Cell 2006, 127, 341–353. [Google Scholar]
- Gehringer, M.M.; Shephard, E.G.; Downing, T.G.; Wiegand, C.; Neilan, B.A. An investigation into the detoxification of microcystin-LR by the glutathione pathway in Balb/c mice. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol 2004, 36, 931–941. [Google Scholar]
- Malbrouck, C.; Kestemont, P. Effects of microcystin on fish. Environ. Toxicol. Chem 2005, 25, 72–86. [Google Scholar]
- Pinho, G.L.L.; Rosa, C.M.; Maciel, F.E.; Bianchini, A.; Yunes, J.S.; Proença, L.A.O.; Monserrat, J.M. Antioxidant responses and oxidative stress after microcystin exposure in the hepatopancreas of an estuarine crab species. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf 2005, 61, 353–360. [Google Scholar]
- Gérard, C.; Poullain, V. Variation in the response of the invasive species Potamopyrgus antipodarum (Smith) to natural (cyanobacterial toxin) and anthropogenic (herbicide atrazine) stressors. Environ. Pollut 2005, 138, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Gérard, C.; Brient, L.; Le Rouzic, B. Variation in the response of juvenile and adult gastropods (Lymnaea stagnalis) to cyanobacterial toxin (microcystin-LR). Environ. Toxicol 2005, 20, 592–596. [Google Scholar]
- Lance, E.; Paty, C.; Bormans, M.; Brient, L.; Gérard, C. Interactions between cyanobacteria and gastropods II. Impact of toxic Planktothrix agardhii on the life-history traits of Lymnaea stagnalis. Aquat. Toxicol 2007, 81, 389–396. [Google Scholar]
- Zurawell, R.W.; Goldberg, J.I.; Holmes, C.F.B.; Prepas, E.E. Tissue distribution and oral dose effects of microcystin in the freshwater pulmonate snail Lymnaea stagnalis jugularis (Say). J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2007, 70, 620–626. [Google Scholar]
- Falconer, I.R. Cyanobacterial toxins present in Microcystis aeruginosa extracts—More than microcystins! Toxicon 2007, 50, 585–588. [Google Scholar]
- Amorim, A.; Vasconcelos, V. Dynamics of microcystins in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxicon 1999, 37, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Buetler, T.M.; Gallagher, E.P.; Wang, C.; Stahl, D.L.; Hayes, J.D.; Eaton, D.L. Induction of phase I and phase II drug-metabolizing enzyme mRNA, protein, and activity by BHA, ethoxyquin and oltipraz. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol 1995, 135, 45–57. [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings, B.A.; Adams-Pearson, C.; Maurer, F.; Müller, P.; Goris, J.; Merlevede, W.; Hofsteenge, J.; Stone, S.R. Alpha- and beta-forms of the 65-kDa subunit of protein phosphatase 2A have a similar 39 amino acid repeating structure. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 3166–3173. [Google Scholar]
- Stark, M.J. Yeast protein serine/threonine phosphatases: Multiple roles and diverse regulation. Yeast 1996, 12, 1647–1675. [Google Scholar]
- Gkelis, S.; Lanaras, T.; Sivonen, K. The presence of microcystins and other cyanobacterial bioactive peptides in aquatic fauna collected from Greek freshwaters. Aquat. Toxicol 2006, 78, 32–41. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, S.A.; Briggs, L.R.; Sprosen, J.; Ruck, J.G.; Wear, R.G.; Holland, P.T.; Bloxham, M. Changes in concentrations of microcystins in rainbow trout, freshwater mussels, and cyanobacteria in Lakes Rotoiti and Rotoehu. Environ. Toxicol 2006, 21, 205–222. [Google Scholar]
- Apeldoorn, M.E.; Egmond, H.P.; Speijers, G.J.A.; Bakker, G.J.I. Toxins of cyanobacteria. Mol. Nutr. Food Res 2007, 51, 7–60. [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf, J.S.; Beattie, K.A.; Pflugmacher, S.; Codd, G.A. Immuno-crossreactivity and toxicity assessment of conjugation products of the cyanobacterial toxin, microcystin-LR. FEMS Microbiol. Lett 2000, 189, 155–158. [Google Scholar]
- Ott, J.L.; Carmichael, W.W. LC/ESI/MS method development for the analysis of hepatotoxic cyclic peptide microcystins in animal tissues. Toxicon 2006, 47, 734–741. [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos, V.M. Uptake and depuration of the heptapeptide toxin microcystin-LR in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Aquat. Toxicol 1995, 32, 227–237. [Google Scholar]
- Prepas, E.E.; Kotak, B.G.; Campbell, L.M.; Evans, J.C.; Hrudey, S.E.; Holmes, C.F.B. Accumulation and elimination of cyanobacterial hepatotoxins by the freshwater clam Anodonta grandis simpsoniana. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci 1997, 54, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Lance, E.; Brient, L.; Bormans, M.; Gérard, C. Interactions between cyanobacteria and Gastropods I. Ingestion of toxic Planktothrix agardhii by Lymnaea stagnalis and the kinetics of microcystin bioaccumulation and detoxification. Aquat. Toxicol 2006, 79, 140–148. [Google Scholar]
- Pires, L.M.D.; Karlsson, K.M.; Meriluoto, J.A.O.; Kardinaal, E.; Visser, P.M.; Siewertsen, K.; Donk, E.V.; Ibelings, B.W. Assimilation and depuration of microcystin-LR by the zebra mussel Dreissena polymorpha. Aquat. Toxicol 2004, 69, 385–396. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, P.; Wu, X. Grazing on toxic and non-toxic Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7820 by Unio douglasiae and Corbicula fluminea. Limnology 2009, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lance, E.; Neffling, M.; Gérard, C.; Meriluoto, J.; Bormans, M. Accumulation of free and covalently bound microcystins in tissues of Lymnaea stagnalis (Gastropoda) following toxic cyanobacteria or dissolved microcystin-LR exposure. Environ. Pollut 2010, 158, 674–680. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, P.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, L. Oral administration of cyanobacterial bloom extract induced the altered expression of the PP2A, Bax, and Bcl-2 in mice. Environ. Toxicol 2008, 23, 688–693. [Google Scholar]
- Malbrouck, C.; Trausch, G.; Devos, P.; Kestemont, P. Effect of microcystin-LR on protein phosphatase activity in fed and fasted juvenile goldfish Carassius auratus L. Toxicon 2004, 43, 295–301. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, J.C.; Leão, P.N.; Vasconcelos, V. Differential protein expression in Corbicula fluminea upon exposure to a Microcystis aeruginosa toxic strain. Toxicon 2009, 53, 409–416. [Google Scholar]
- Kotai, J. Instruction for Preparation of Modified Nutrient Solution Z8 for Algae, Publication B-11/69; Norwegian Institute for Water Research: Oslo, Norway, 1972; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Ramanan, S.; Tang, J.; Velayudhan, A. Isolation and preparative purification of microcystin variants. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 883, 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire-Gony, S.; Boudou, A. Mantle and gill fine structure in the freshwater Asiatic clam, Corbicula fluminea (Müller). Ann. Limnol. Int. J. Limnol 1997, 33, 163–178. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, S. Biodisponibilidade de cianotoxinas em bivalves. PhD Thesis, University of Porto, Porto, Portugal, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Contardo-Jara, V.; Pflugmacher, S.; Wiegand, C. Multi-xenobiotic-resistance a possible explanation for the insensitivity of bivalves towards cyanobacterial toxins. Toxicon 2008, 52, 936–943. [Google Scholar]
- Morga, B.; Arzul, I.; Faury, N.; Renault, T. Identification of genes from flat oyster Ostrea edulis as suitable housekeeping genes for quantitative real time PCR. Fish Shellfish Immunol 2010, 29, 937–945. [Google Scholar]
- Whelan, J.A.; Russell, N.B.; Whelan, M.A. A method for the absolute quantification of cDNA using real-time PCR. J. Immunol. Methods 2003, 278, 261–269. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar]
- Box, G.E.P.; Hunter, W.G.; Hunter, J.S.; Hunter, W.G. Statistics for Experimenter: An Introduction to Design, Data Analysis and Model Building; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1978; p. 653. [Google Scholar]
- Tomassone, R.; Lesquoy, E.; Millier, C. La Regression-Nouveaux Regards Sur Une Ancienne Method Statistique; Masson: Paris, France, 1983; p. 180. [Google Scholar]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).