Proteomic Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid in a Fulminant Case of Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
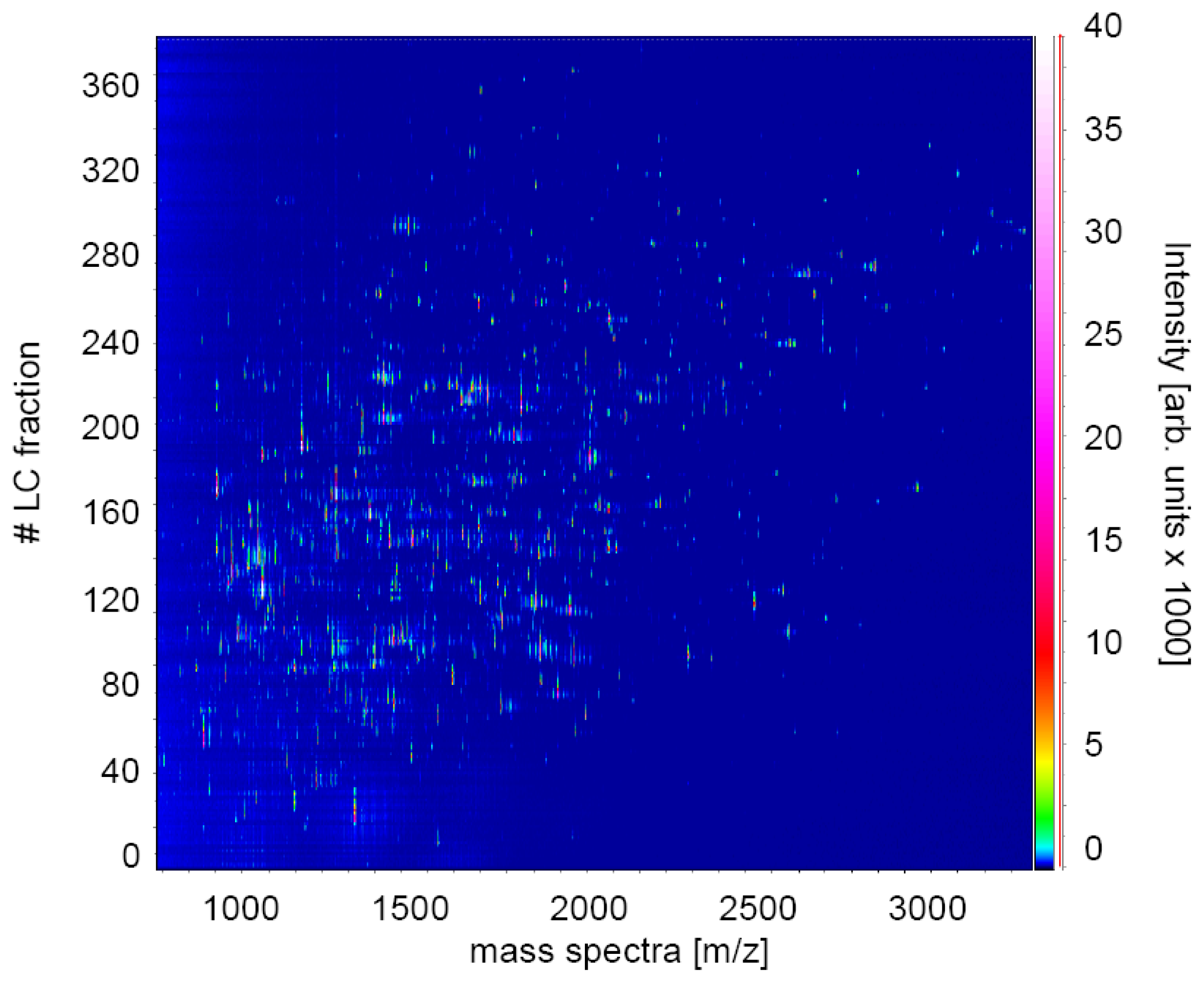
2.1. Experimental Design for MS Analysis
2.2. Protein-Identification by Combined Database Search
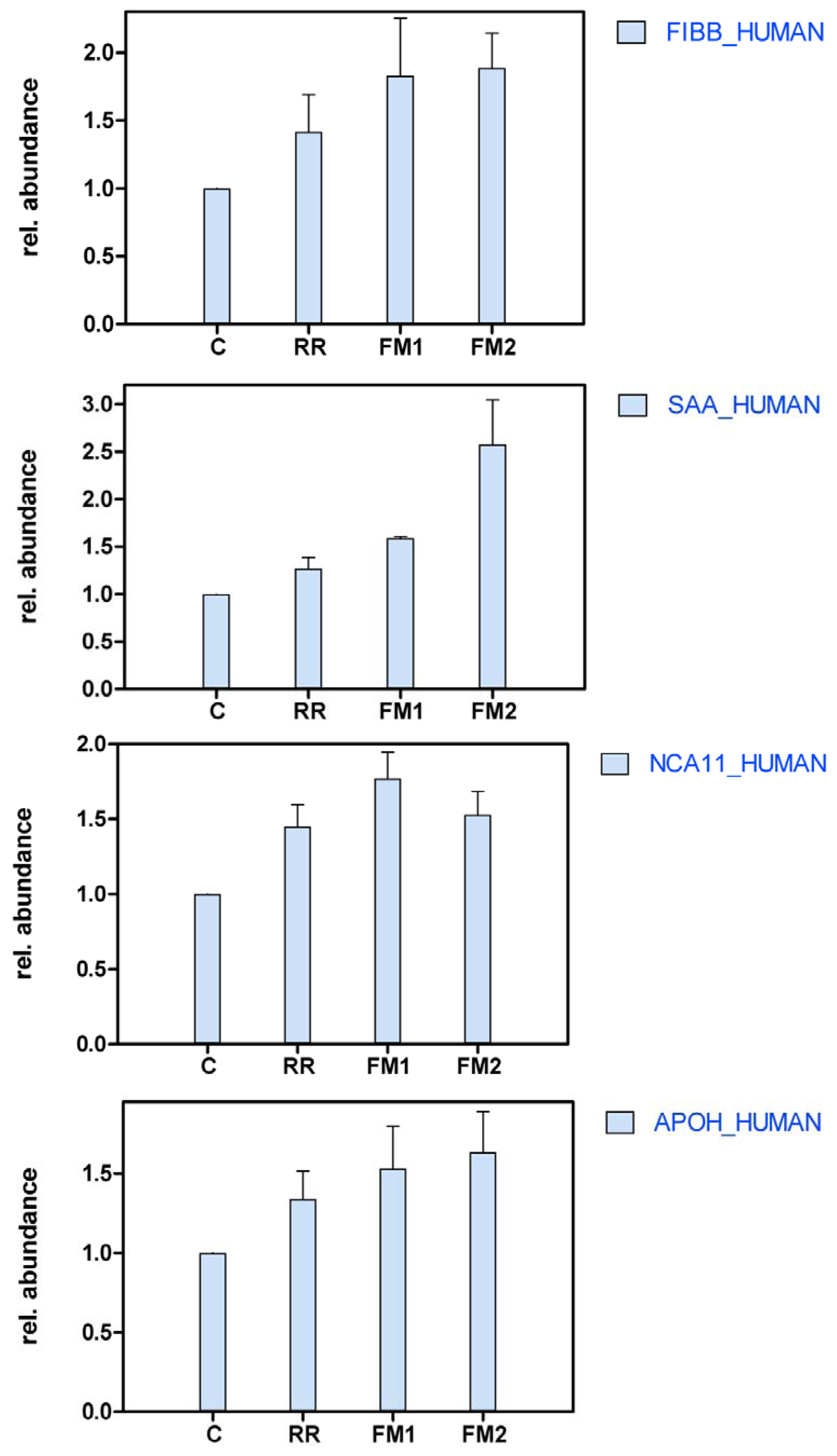
2.3. Differential Protein Profiles
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
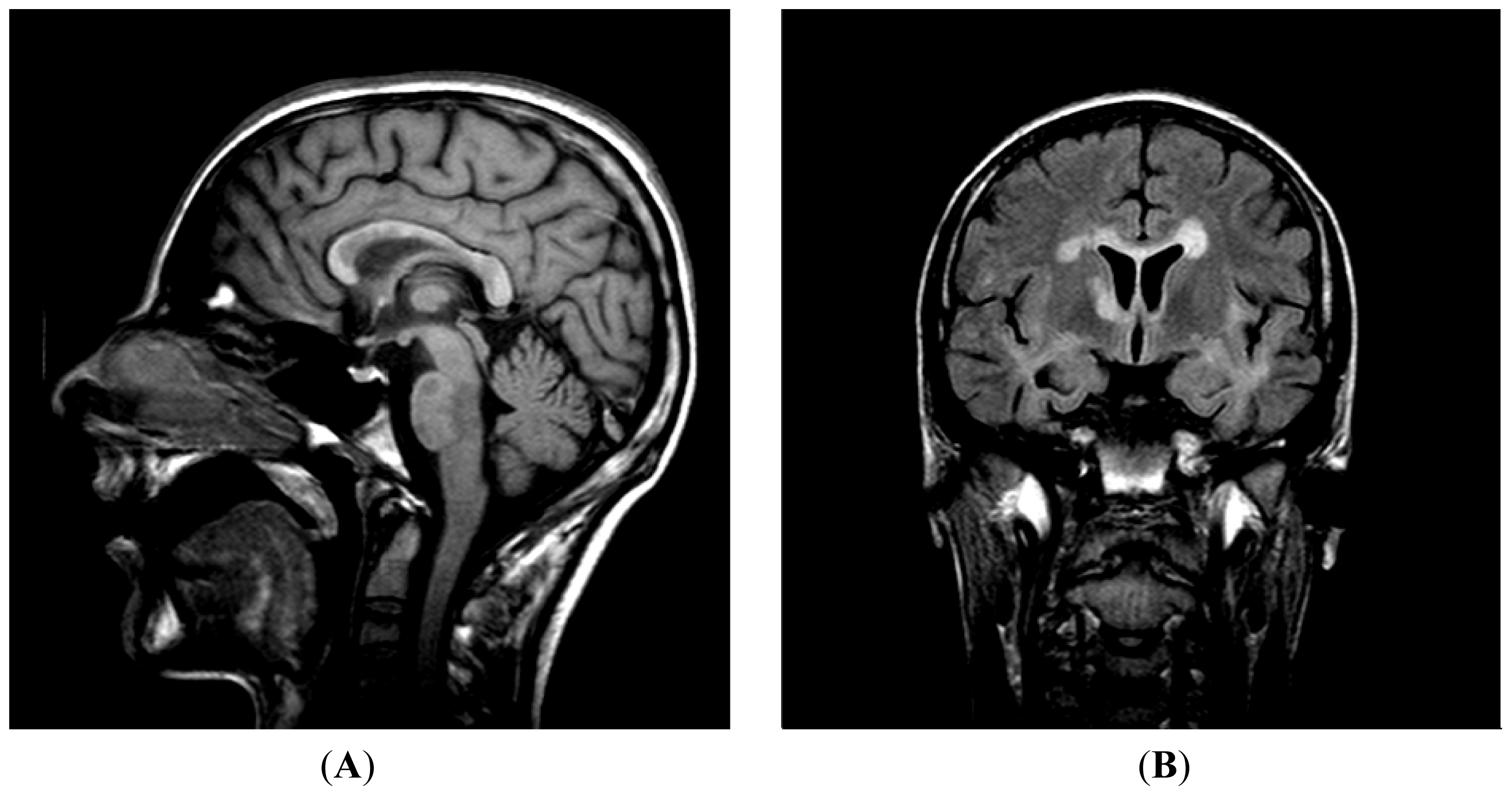
4.1. Patient Case History and Outcome
4.1.1. Examinations
4.1.2. Electrophysiology
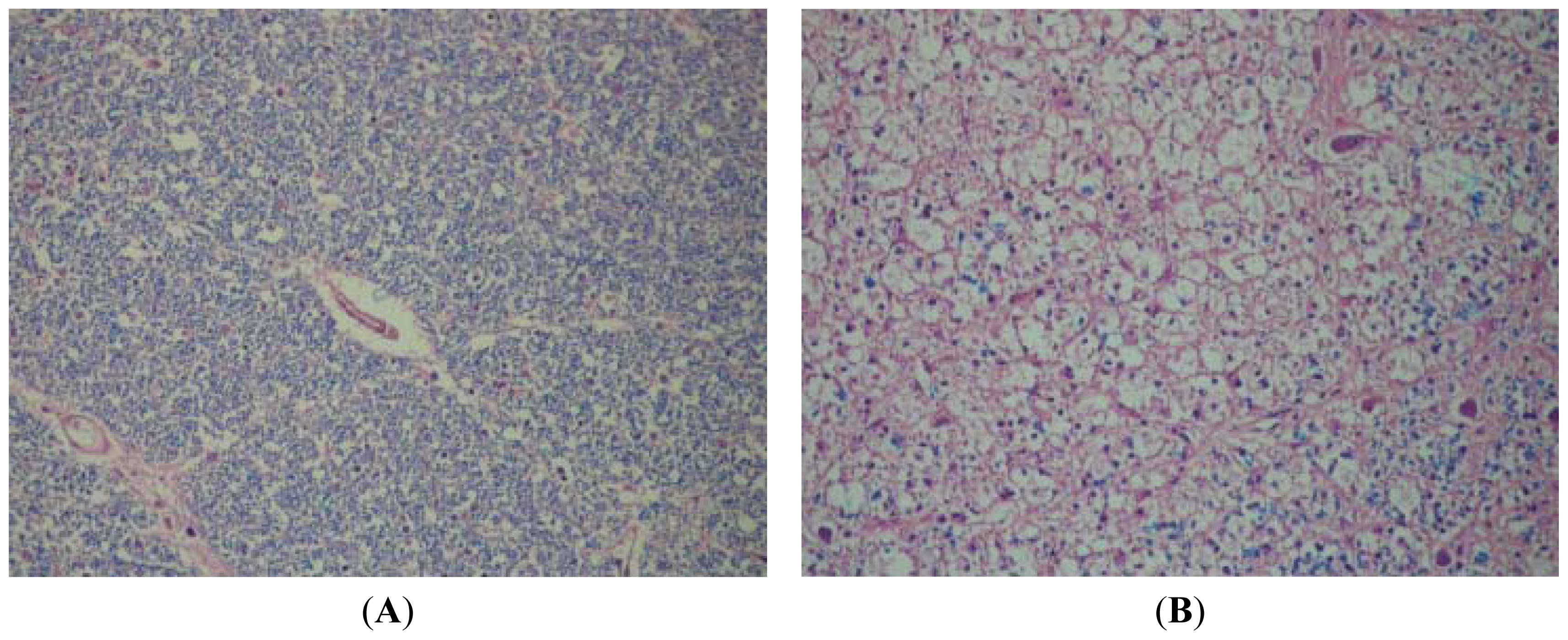
4.1.3. Pathology
4.2. Sampling
4.3. Ethics
4.4. Chemicals and Reagents
4.5. Protein Digestion and Isobaric Tag Labeling Procedure
4.6. Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Anderson, N.L.; Anderson, N.G. Proteome and proteomics: New technologies, new concepts, and new words. Electrophoresis 1998, 19, 1853–1861. [Google Scholar]
- Gygi, S.P.; Aebersold, R. Mass spectrometry and proteomics. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol 2000, 4, 489–494. [Google Scholar]
- Gygi, S.P.; Corthals, G.L.; Zhang, Y.; Rochon, Y.; Aebersold, R. Evaluation of two-dimensional gel electrophoresis-based proteome analysis technology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 9390–9395. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, R.D. Probing proteomes—seeing the whole picture? Nat. Biotechnol 2000, 18, 1041–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Calvo, K.R.; Liotta, L.A.; Petricoin, E.F. Clinical proteomics: From biomarker discovery and cell signaling profiles to individualized personal therapy. Biosci. Rep 2005, 25, 107–125. [Google Scholar]
- Brancia, F.L. Mass spectrometry based strategies in quantitative proteomics. Curr. Anal. Chem 2006, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, P.L.; Huang, Y.N.; Marchese, J.N.; Williamson, B.; Parker, K.; Hattan, S.; Khainovski, N.; Pillai, S.; Dey, S.; Daniels, S.; et al. Multiplexed protein quantitation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using amine-reactive isobaric tagging reagents. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2004, 3, 1154–1169. [Google Scholar]
- Hanrieder, J.; Nyakas, A.; Naessen, T.; Bergquist, J. Proteomic analysis of human follicular fluid using an alternative bottom-up approach. J. Proteome Res 2008, 7, 443–449. [Google Scholar]
- UniProt Home Page. Available online: http://www.uniprot.org accessed on 6 January 2012.
- Hammack, B.N.; Fung, K.Y.; Hunsucker, S.W.; Duncan, M.W.; Burgoon, M.P.; Owens, G.P.; Gilden, D.H. Proteomic analysis of multiple sclerosis cerebrospinal fluid. Mult. Scler 2004, 10, 245–260. [Google Scholar]
- Dumont, D.; Noben, J.P.; Raus, J.; Stinissen, P.; Robben, J. Proteomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid from multiple sclerosis patients. Proteomics 2004, 4, 2117–2124. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmensiek, V.; Sussmuth, S.D.; Tauscher, G.; Brettschneider, J.; Felk, S.; Gillardon, F.; Tumani, H. Cerebrospinal fluid proteome profile in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler 2007, 13, 840–849. [Google Scholar]
- Stoop, M.P.; Dekker, L.J.; Titulaer, M.K.; Burgers, P.C.; Sillevis Smitt, P.A.; Luider, T.M.; Hintzen, R.Q. Multiple sclerosis-related proteins identified in cerebrospinal fluid by advanced mass spectrometry. Proteomics 2008, 8, 1576–1585. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.H.; Hwang, S.I.; Roy, D.B.; Lundgren, D.H.; Price, J.V.; Ousman, S.S.; Fernald, G.H.; Gerlitz, B.; Robinson, W.H.; Baranzini, S.E.; et al. Proteomic analysis of active multiple sclerosis lesions reveals therapeutic targets. Nature 2008, 451, 1076–1081. [Google Scholar]
- Stoop, M.P.; Singh, V.; Dekker, L.J.; Titulaer, M.K.; Stingl, C.; Burgers, P.C.; Sillevis Smitt, P.A.; Hintzen, R.Q.; Luider, T.M. Proteomics comparison of cerebrospinal fluid of relapsing remitting and primary progressive multiple sclerosis. PLoS One 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottervald, J.; Franzen, B.; Nilsson, K.; Andersson, L.I.; Khademi, M.; Eriksson, B.; Kjellstrom, S.; Marko-Varga, G.; Vegvari, A.; Harris, R.A.; et al. Multiple sclerosis: Identification and clinical evaluation of novel CSF biomarkers. J. Proteomics 2010, 73, 1117–1132. [Google Scholar]
- Cantorna, M.T.; Mahon, B.D. Mounting evidence for vitamin D as an environmental factor affecting autoimmune disease prevalence. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2004, 229, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar]
- Raghuwanshi, A.; Joshi, S.S.; Christakos, S. Vitamin D and multiple sclerosis. J. Cell. Biochem 2008, 105, 338–343. [Google Scholar]
- Myhr, K.M. Vitamin D treatment in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci 2009, 286, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, R.A.; Bauer, J.; Flick, M.J.; Sikorski, S.L.; Nuriel, T.; Lassmann, H.; Degen, J.L.; Akassoglou, K. The fibrin-derived gamma377-395 peptide inhibits microglia activation and suppresses relapsing paralysis in central nervous system autoimmune disease. J. Exp. Med 2007, 204, 571–582. [Google Scholar]
- Ristori, G.; Laurenti, F.; Stacchini, P.; Gasperini, C.; Buttinelli, C.; Pozzilli, C.; Salvetti, M. Serum amyloid A protein is elevated in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol 1998, 88, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Boylan, M.T.; Crockard, A.D.; Duddy, M.E.; Armstrong, M.A.; McMillan, S.A.; Hawkins, S.A. Interferon-beta1a administration results in a transient increase of serum amyloid A protein and C-reactive protein: Comparison with other markers of inflammation. Immunol. Lett 2001, 75, 191–197. [Google Scholar]
- Lucchinetti, C.F.; Bruck, W.; Rodriguez, M.; Lassmann, H. Distinct patterns of multiple sclerosis pathology indicates heterogeneity on pathogenesis. Brain Pathol 1996, 6, 259–274. [Google Scholar]
- Mahad, D.; Ziabreva, I.; Lassmann, H.; Turnbull, D. Mitochondrial defects in acute multiple sclerosis lesions. Brain 2008, 131, 1722–1735. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, W.I.; Compston, A.; Edan, G.; Goodkin, D.; Hartung, H.P.; Lublin, F.D.; McFarland, H.F.; Paty, D.W.; Polman, C.H.; Reingold, S.C.; et al. Recommended diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: Guidelines from the International Panel on the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol 2001, 50, 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzke, J.F. Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: An expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 1983, 33, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar]
- Hanrieder, J.; Wetterhall, M.; Enblad, P.; Hillered, L.; Bergquist, J. Temporally resolved differential proteomic analysis of human ventricular CSF for monitoring traumatic brain injury biomarker candidates. J. Neurosci. Methods 2009, 177, 469–478. [Google Scholar]
- Abdi, F.; Quinn, J.; Jankovic, J.; McIntosh, M.; Leverenz, J.; Peskind, E. Detection of biomarkers with a multiplex quantitative proteomic platform in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with neurodegenerative disorders. J. Alzheimers Dis 2006, 9, 293–348. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, M.; Alvarez-Cermeno, J.; Bernardi, G.; Cogato, I.; Fredman, P.; Frederiksen, J.; Fredrikson, S.; Gallo, P.; Grimaldi, L.M.; Gronning, M.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: A consensus report. J. Neurol. Neurosurg Psychiatry 1994, 57, 897–902. [Google Scholar]
- Bergquist, J. FTICR mass spectrometry in proteomics. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther 2003, 5, 310–314. [Google Scholar]
- Ramstrom, M.; Palmblad, M.; Markides, K.E.; Hakansson, P.; Bergquist, J. Protein identification in cerebrospinal fluid using packed capillary liquid chromatography Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Proteomics 2003, 3, 184–190. [Google Scholar]
- Ramstrom, M.; Ivonin, I.; Johansson, A.; Askmark, H.; Markides, K.E.; Zubarev, R.; Hakansson, P.; Aquilonius, S.M.; Bergquist, J. Cerebrospinal fluid protein patterns in neurodegenerative disease revealed by liquid chromatography-Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Proteomics 2004, 4, 4010–4018. [Google Scholar]
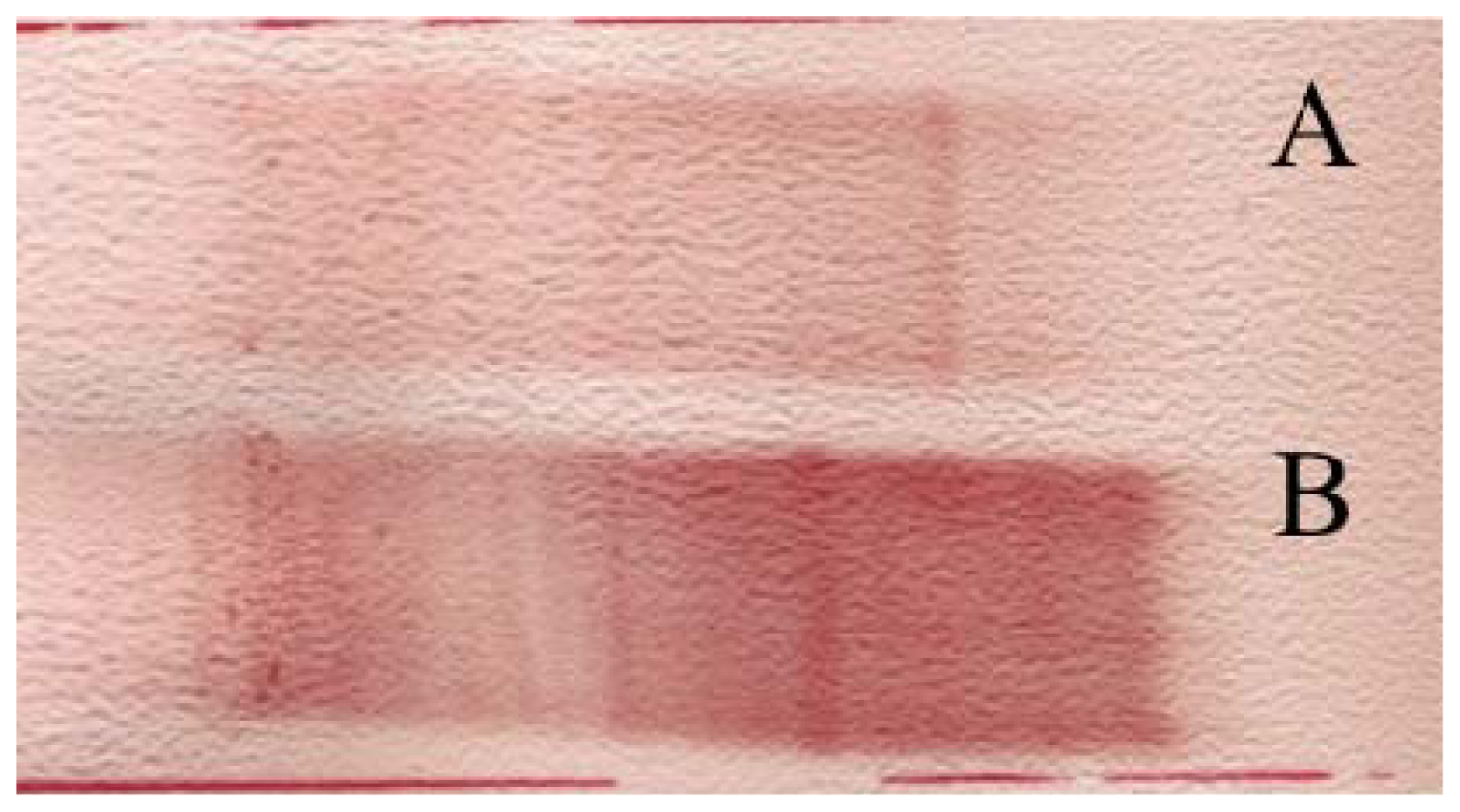


| # | Protein Name | Database Entry a | Mascot score b | Number of Pep. c | MW d | Function | C | RR | Δ | FM1 | Δ | FM2 | Δ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transport proteins | |||||||||||||
| 1 | Serotransferrin | TRFE_HUMAN | 1053 | 47 | 87.3411 | Iron transport | 1 | 1.171 | 1.61 | + | 1.16 | ||
| 2 | Apolipoprotein E | APOE_HUMAN | 560 | 26 | 38.2412 | Lipid transport | 1 | 1.462 | 1.86 | + | 1.24 | ||
| 3 | Apolipoprotein A-IV | APOA4_HUMAN | 37 | 6 | 49.5504 | Lipid metabolism | 1 | 1.52 | + | 1.31 | 1.98 | + | |
| 4 | Phospholipid transfer protein | PLTP_HUMAN | 46 | 3 | 57.4823 | Lipid transport | 1 | 1.611 | + | 1.75 | + | 1.28 | |
| Immunoglobulins | |||||||||||||
| 5 | Ig gamma-3 chain C region | IGHG3_HUMAN | 51 | 6 | 36.36 | Immune response | 1 | 1.544 | + | 1.47 | 1.61 | + | |
| 6 | Ig kappa chain C region | KAC_HUMAN | 464 | 8 | 13.0366 | Immune response | 1 | 1.38 | 1.63 | + | 2.56 | +++ | |
| 7 | Ig kappa chain V-I region | KV108_HUMAN | 74 | 4 | 12.3321 | Immune response | 1 | 0.992 | 1.27 | 1.54 | + | ||
| 8 | Ig lambda chain C regions | LAC_HUMAN | 170 | 5 | 12.6644 | Immune response | 1 | 1.572 | + | 1.31 | 2.02 | ++ | |
| 9 | Ig gamma-1 chain C region | IGHG1_HUMAN | 210 | 9 | 40.676 | Immune response | 1 | 1.426 | 1.55 | + | 1.64 | + | |
| 10 | Ig mu chain C region | MUC_HUMAN | 233 | 11 | 53.3918 | Immune response | 1 | 1.848 | + | 1.65 | + | 1.83 | + |
| 11 | Ig heavy chain V-III region TUR | HV318_HUMAN | 54 | 3 | 13.0917 | Immune response | 1 | 2.114 | ++ | 1.52 | + | 1.58 | + |
| Glycoproteins | |||||||||||||
| 12 | Osteopontin | OSTP_HUMAN | 462 | 7 | 38.4212 | Cell communication | 1 | 1.644 | + | 1.49 | 3.39 | +++ | |
| 13 | Vitronectin | VTNC_HUMAN | 28 | 4 | 57.9411 | Cell communication | 1 | 1.574 | + | 1.78 | + | 1.38 | |
| 14 | Zinc-alpha-2-glycoprotein precursor | ZA2G_HUMAN | 47 | 2 | 37.061 | Cell adhesion. lipid degradation | 1 | 2.024 | ++ | 1.51 | + | 1.53 | + |
| 15 | Beta-2-glycoprotein 1 | APOH_HUMAN | 47 | 2 | 43.7975 | Regulation of blood coagulation | 1 | 1.341 | 1.53 | + | 1.64 | + | |
| 16 | SPARC-like protein 1 precursor | SPRL1_HUMAN | 85 | 3 | 82.6318 | Calcium ion binding | 1 | 1.677 | + | 1.82 | + | 1.44 | |
| 17 | Chitinase-3-like protein 1 | CH3L1_HUMAN | 78 | 5 | 46.0906 | Tissue remodeling | 1 | 1.334 | 1.62 | + | 1.38 | ||
| Coagulation factors | |||||||||||||
| 18 | Fibrinogen beta chain | FIBB_HUMAN | 165 | 8 | 61.7759 | Cell proliferation | 1 | 1.416 | 1.83 | + | 1.89 | + | |
| 19 | Fibrinogen alpha chain | FIBA_HUMAN | 156 | 8 | 101.853 | Cell proliferation | 1 | 1.073 | 0.97 | 1.88 | + | ||
| Complement factors | |||||||||||||
| 20 | Complement factor B | CFAB_HUMAN | 28 | 4 | 94.3637 | Immune response | 1 | 1.725 | + | 1.97 | + | 1.26 | |
| 21 | Complement C4-A | CO4A_HUMAN | 339 | 27 | 205.178 | Immune response | 1 | 1.474 | 1.68 | + | 1.63 | + | |
| Enzymes | |||||||||||||
| 22 | Elongation factor 2 kinase | EF2K_HUMAN | 29 | 4 | 88.2004 | Translational elongation | 1 | 1.642 | + | 2.35 | ++ | 1.16 | |
| 23 | Prostaglandin-H2 D-isomerase | PTGDS_HUMAN | 216 | 11 | 22.7844 | Enzyme activity | 1 | 1.178 | 1.59 | + | 1.03 | ||
| 24 | Cystatin-C | CYTC_HUMAN | 249 | 12 | 17.1259 | Enzyme regulator | 1 | 1.53 | + | 2.11 | ++ | 1.57 | + |
| Structural/membrane asssociated | |||||||||||||
| 25 | Calsyntenin-1 | CSTN1_HUMAN | 90 | 3 | 117.941 | Signal transduction | 1 | 1.596 | + | 2.21 | ++ | 1.62 | + |
| 26 | Limbic system-associated membrane protein precursor | LSAMP_HUMAN | 73 | 1 | 40.3779 | Cell adhesion. neuronal growth | 1 | 2.205 | ++ | 2.37 | ++ | 1.79 | + |
| 27 | Basement membrane-specific heparan sulfate proteoglycan core protein | PGBM_HUMAN | 39 | 5 | 487.116 | Protein binding | 1 | 2.014 | ++ | 2.8 | +++ | 2.06 | ++ |
| 28 | Neural cell adhesion molecule 1. | NCA11_HUMAN | 71 | 2 | 102.35 | Cell adhesion | 1 | 1.451 | 1.77 | + | 1.53 | + | |
| 29 | Monocyte differentiation antigen CD14 | CD14_HUMAN | 27 | 5 | 41.9976 | Immune response | 1 | 1.569 | + | 1.846 | + | 1.88 | + |
| Miscellaneous | |||||||||||||
| 30 | Serum amyloid A protein | SAA_HUMAN | 87 | 2 | 14.4341 | Acute phase response | 1 | 1.27 | 1.59 | + | 2.58 | +++ | |
| Age (years) | Gender | Duration of the disease | EDSS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fulminant MS t1 | 15 | M | 8 months | 5 |
| Fulminant MS t2 | 16 | M | 22 months | 8 |
| RR MS | 25 | F | 20 years | 2 |
| Control | 23 | M | NA | NA |
© 2012 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Füvesi, J.; Hanrieder, J.; Bencsik, K.; Rajda, C.; Kovács, S.K.; Kaizer, L.; Beniczky, S.; Vécsei, L.; Bergquist, J. Proteomic Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid in a Fulminant Case of Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 7676-7693. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13067676
Füvesi J, Hanrieder J, Bencsik K, Rajda C, Kovács SK, Kaizer L, Beniczky S, Vécsei L, Bergquist J. Proteomic Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid in a Fulminant Case of Multiple Sclerosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2012; 13(6):7676-7693. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13067676
Chicago/Turabian StyleFüvesi, Judit, Jörg Hanrieder, Krisztina Bencsik, Cecilia Rajda, S. Krisztián Kovács, László Kaizer, Sándor Beniczky, László Vécsei, and Jonas Bergquist. 2012. "Proteomic Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid in a Fulminant Case of Multiple Sclerosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 13, no. 6: 7676-7693. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13067676
APA StyleFüvesi, J., Hanrieder, J., Bencsik, K., Rajda, C., Kovács, S. K., Kaizer, L., Beniczky, S., Vécsei, L., & Bergquist, J. (2012). Proteomic Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid in a Fulminant Case of Multiple Sclerosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(6), 7676-7693. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13067676





