Parts Per Trillion Detection of 7-Aminonitrazepam by Nano-Enhanced ELISA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
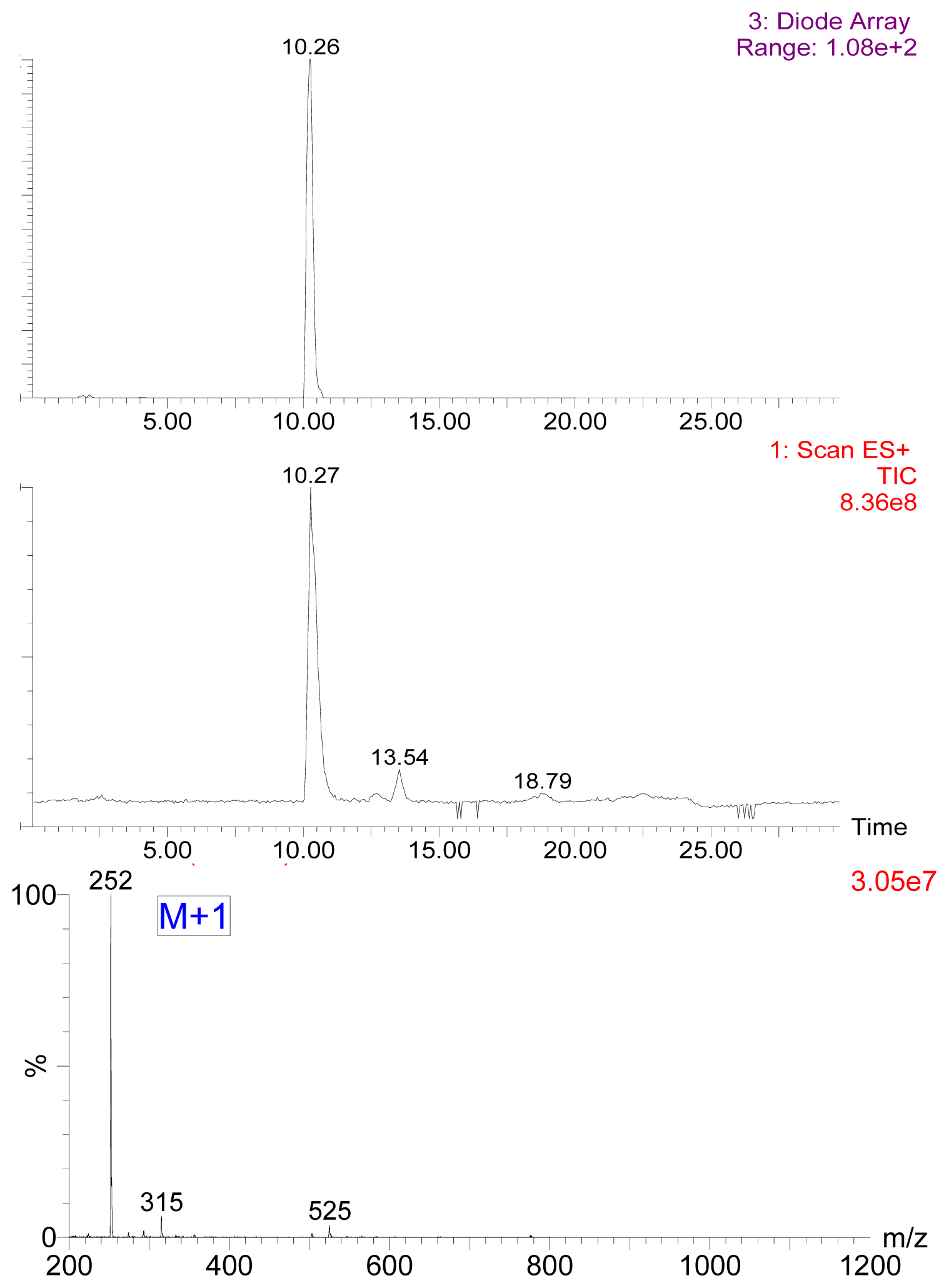
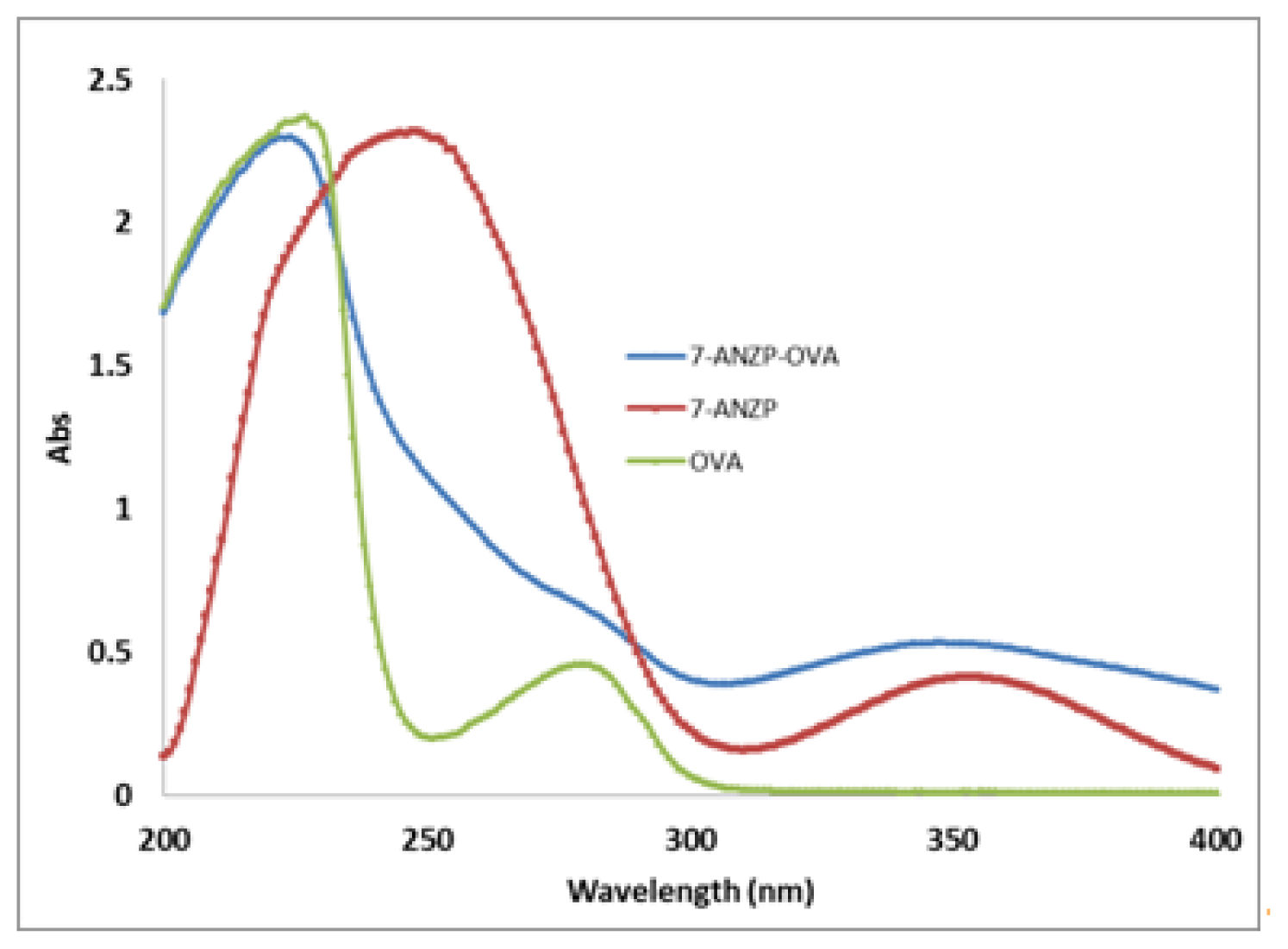
2.1. Preparation of 7-Aminonitrazepam -Protein Conjugate
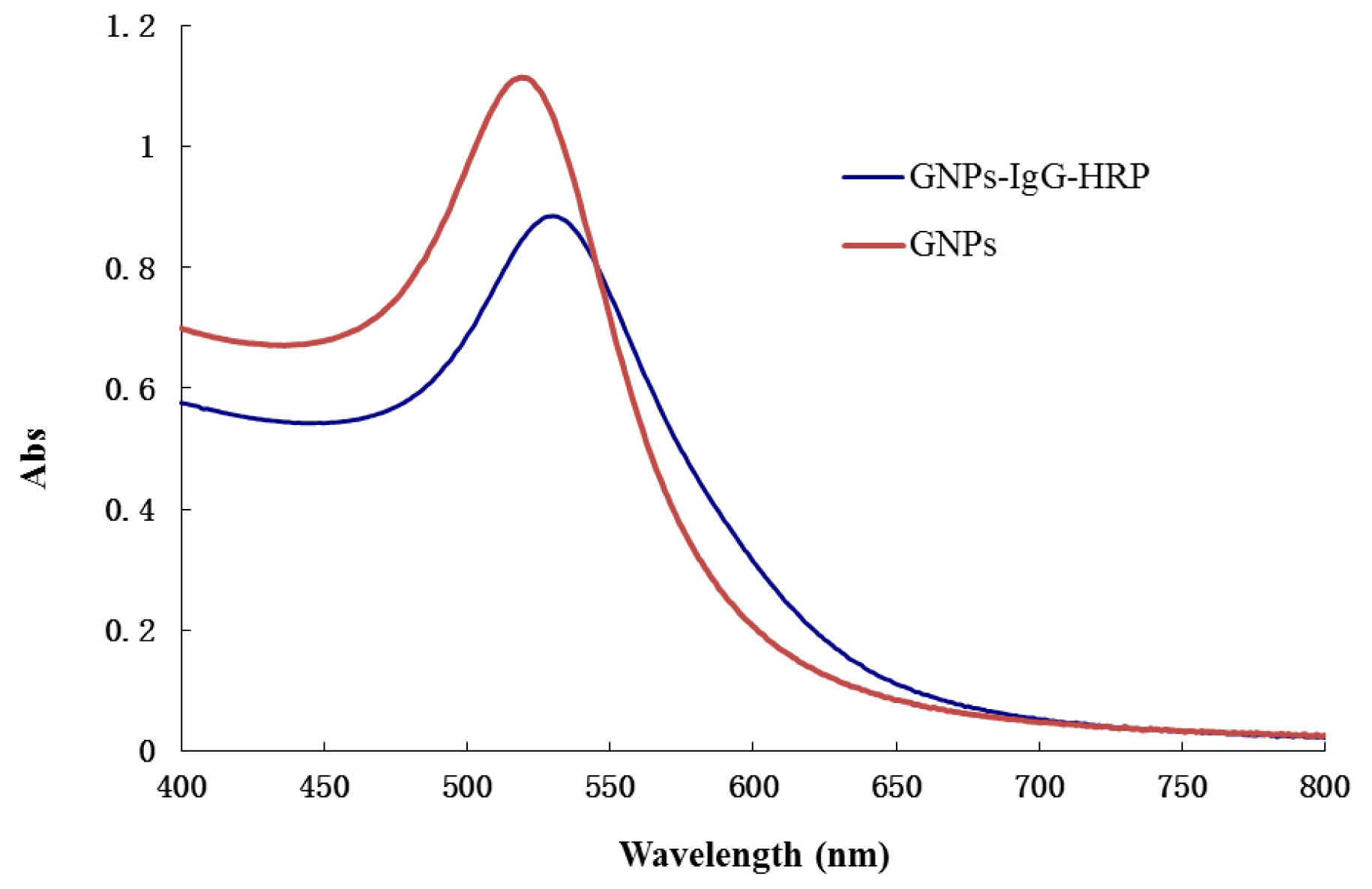
2.2. Characterization of GNPs and GNPs-IgG-HRP Bioconjugate
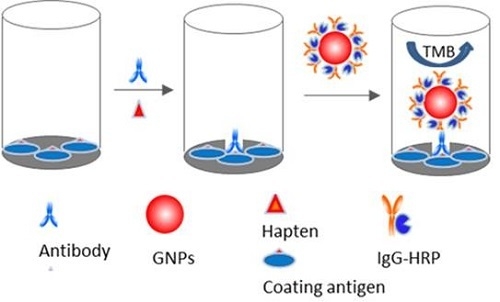
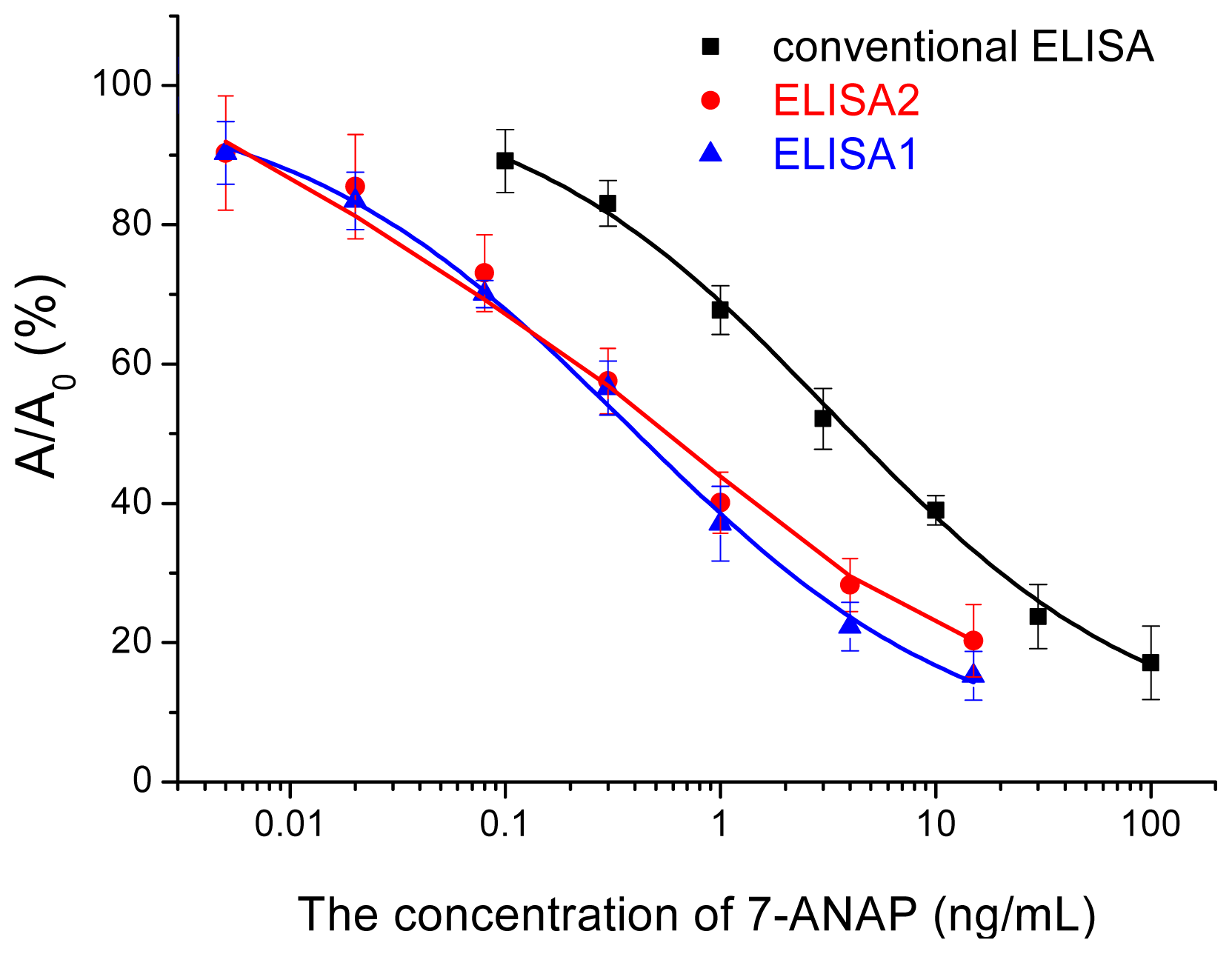
2.3. Nano-Enhanced ELISA
2.4. Validation of the Nano-Enhanced ELISA
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Solutions and Buffers
3.3. Preparation of Hapten and Hapten-Protein Conjugate
3.4. Synthesis and Characterization of Gold Nanoparticles and GNPs-IgG-HRP Conjugate
3.5. Nano-Enhanced ELISA
2.6. Sample Pretreatment and Validation of the Nano-ELISA
4. Conclusions

| 7-ANZP(ng/mL) | CV (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Intra-assay | Inter-assay | |
| 0.005 | 4.8 | 5.2 |
| 0.02 | 4.2 | 4.7 |
| 0.08 | 1.9 | 4.8 |
| 0.3 | 3.8 | 5.5 |
| 1 | 4.3 | 3.6 |
| 4 | 3.5 | 4.4 |
| 15 | 5.5 | 3.9 |
| Spiked concentration (ng/mL) | Results measured (ng/mL) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 0.417 ± 0.039 | 83.4 | 7.8 |
| 1.5 | 1.352 ± 0.141 | 90.1 | 9.3 |
| 4.0 | 3.823 ± 0.405 | 95.5 | 10.1 |
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laurie, D.; Mason, A.J.; Piggott, N.H.; Rowell, F.J.; Seviour, J.; Strachan, D.; Tyson, J.D. Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay for detecting benzodiazepines in urine. Analyst 1996, 121, 951–954. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, H.; Li, Q.; Shen, C.; Xu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, C.; Wang, W. A highly sensitive method for the determination of 7-aminonitrazepam, a metabolite of nitrazepam, in human urine using high-performance electrospray liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr 2009, 23, 740–744. [Google Scholar]
- Moriya, F.; Hashimoto, Y. Tissue distribution of nitrazepam and 7-aminonitrazepam in a case of nitrazepam intoxication. Forensic Sci. Int 2003, 131, 108–112. [Google Scholar]
- Elian, A.A. ELISA detection of clonazepam and 7-aminoclonazepam in whole blood and urine. Forensic Sci. Int 2003, 134, 54–56. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Tan, J.Y.; Sun, Y.Q. Determination of 7-aminonitrazepam, metabolite of nitrazepam, in urine by tert-butyldimethylsilyl derivatization-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Chin. J. Anal. Chem 2003, 31, 850–852. [Google Scholar]
- Smink, B.E.; Brandsma, J.E.; Dijkhuizen, A.; Lusthof, K.J.; de Gier, J.J.; Egberts, A.C.G.; Uges, D.R.A. Quantitative analysis of 33 benzodiazepines, metabolites and benzodiazepine-like substances in whole blood by liquid chromatography-(tandem) mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B-Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci 2004, 811, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, E.I.; Wylie, F.M.; Oliver, J.S. Detection of benzodiazepines in hair using ELISA and LC-ESI-MS-MS. J. Anal. Toxicol 2006, 30, 441–448. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, M. Analyses of benzodiazepines and their metabolites in various biological matrices by LC-MS(/MS). Biomed. Chromatogr 2011, 25, 1283–1307. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, N.; Wu, L.; Li, L.; Xu, C. Multi-residue detection of benzodiazepines by ELISA based on class selective antibodies. Food Agric. Immunol 2009, 20, 281–293. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Peng, C.; Jin, Z.; Qiao, R.; Wang, W.; Zhu, S.; Wang, L.; Jing, Q.; Xu, C. Ultrasensitive immunoassay of 7-aminoclonazepam in human urine based on CdTe nanoparticle bioconjugations by fabricated microfluidic chip. Biosens. Bioelectron 2009, 24, 2051–2056. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, S. Monoclonal antibody-based ELISA and colloidal gold immunoassay for detecting 19-nortestosterone residue in animal tissues. J. Agric. Food Chem 2011, 59, 9763–9769. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Han, Z.; Lu, L.; Wang, L.; Ni, G.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, A.; Zheng, X. Development of a new rabbit monoclonal antibody and its based competitive indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for rapid detection of sulfonamides. J. Sci. Food Agric 2013, 93, 667–673. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, C.-H.; Hung, C.-Y.; Chang, T.; Lin, H.-P.; Lin, Y.-C. An immunoassay using antibody-gold nanoparticle conjugate, silver enhancement and flatbed scanner. Microfluid. Nanofluid 2009, 6, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, T.; Fang, G.; Ma, D.; Wang, S. Development of a solid-phase extraction-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the determination of 17beta-19-nortestosterone levels in antifatigue functional foods. J. Food Sci 2009, 74, T67–T74. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.-F.; Chen, Y.-W.; Chen, W.; Xu, C.-L.; Kim, J.-M.; Jin, Z.-Y. Development of a sensitive heterologous ELISA method for analysis of acetylgestagen residues in animal fat. Food Chem 2008, 109, 647–653. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrosi, A.; Airò, F.; Merkoçi, A. Enhanced gold nanoparticle based ELISA for a breast cancer biomarker. Anal. Chem 2009, 82, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, G.; Chu, H.; Hu, Y.; Xu, C. Ultrasensitive signal amplified immunoassay of medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) using the atomic absorption of silver deposited on the surface of gold nanoparticles. Food Agric. Immunol 2010, 21, 165–173. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, Z.; Chu, H.; Chen, W.; Xue, F.; Liu, J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, L. Ultrasensitive one-step rapid visual detection of bisphenol A in water samples by label-free aptasensor. Biosens. Bioelectron 2013, 39, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Tian, X.L.; Li, Y.S.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.H.; Wang, X.R.; Lu, S.Y.; Ren, H.L.; Liu, Z.S. A versatile and highly sensitive probe for Hg(II), Pb(II) and Cd(II) detection individually and totally in water samples. Biosens. Bioelectron 2011, 30, 310–314. [Google Scholar]
- Borrey, D.; Meyer, E.; Lambert, W.; van Peteghem, C.; de Leenheer, A.P. Simultaneous determination of fifteen low-dosed benzodiazepines in human urine by solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography—mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2001, 765, 187–197. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, C.; Duan, X.; Song, S.; Xue, F. Parts Per Trillion Detection of 7-Aminonitrazepam by Nano-Enhanced ELISA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 19474-19483. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141019474
Peng C, Duan X, Song S, Xue F. Parts Per Trillion Detection of 7-Aminonitrazepam by Nano-Enhanced ELISA. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(10):19474-19483. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141019474
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Chifang, Xiaohui Duan, Shanshan Song, and Feng Xue. 2013. "Parts Per Trillion Detection of 7-Aminonitrazepam by Nano-Enhanced ELISA" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 10: 19474-19483. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141019474