Exercise Therapy Downregulates the Overexpression of TLR4, TLR2, MyD88 and NF-?B after Cerebral Ischemia in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
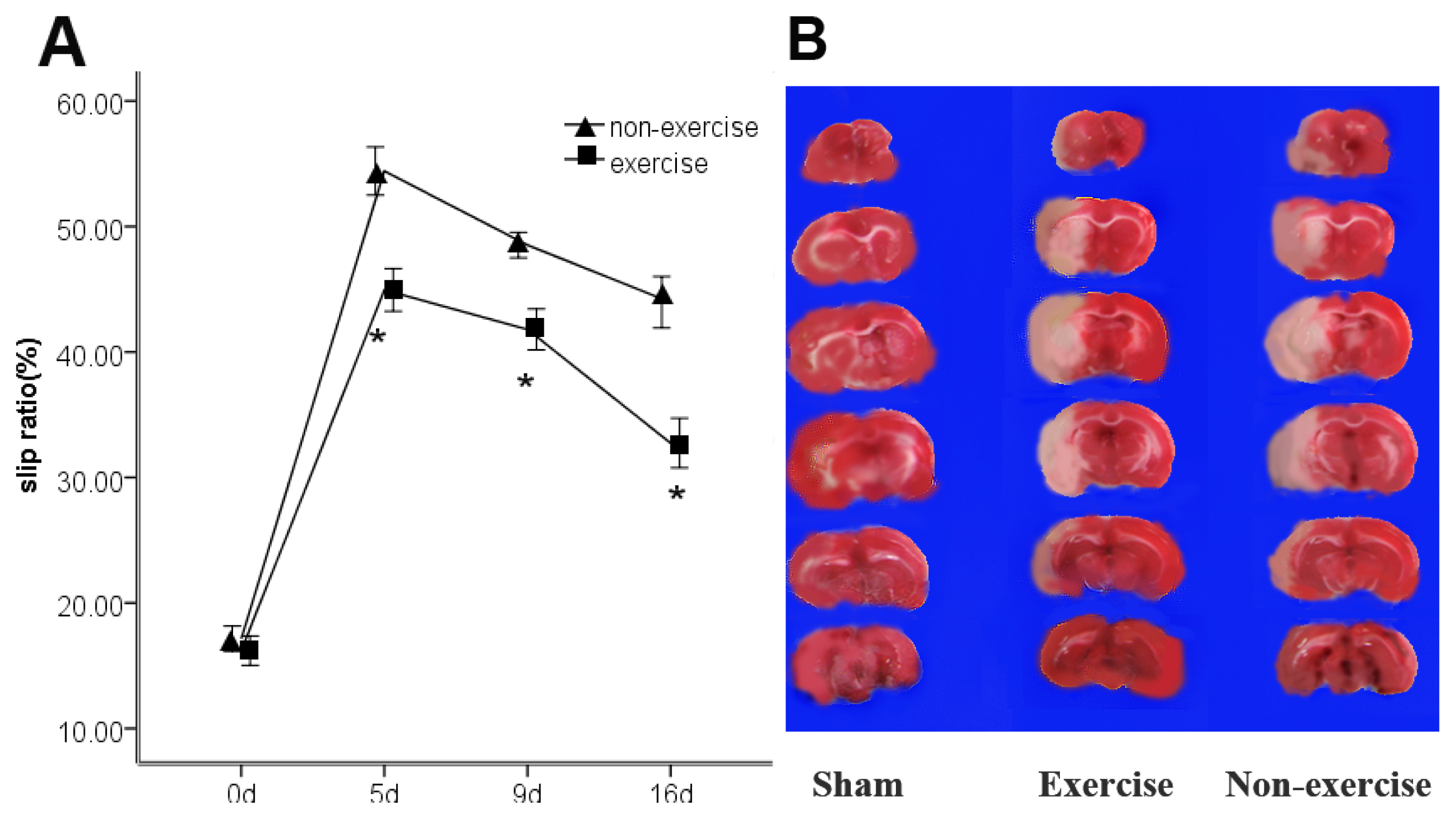
2.1. Exercise Promotes Neurological Function Recovery after MCAo/R
2.2. Exercise Has No Obvious Effect on the Infarct Volume
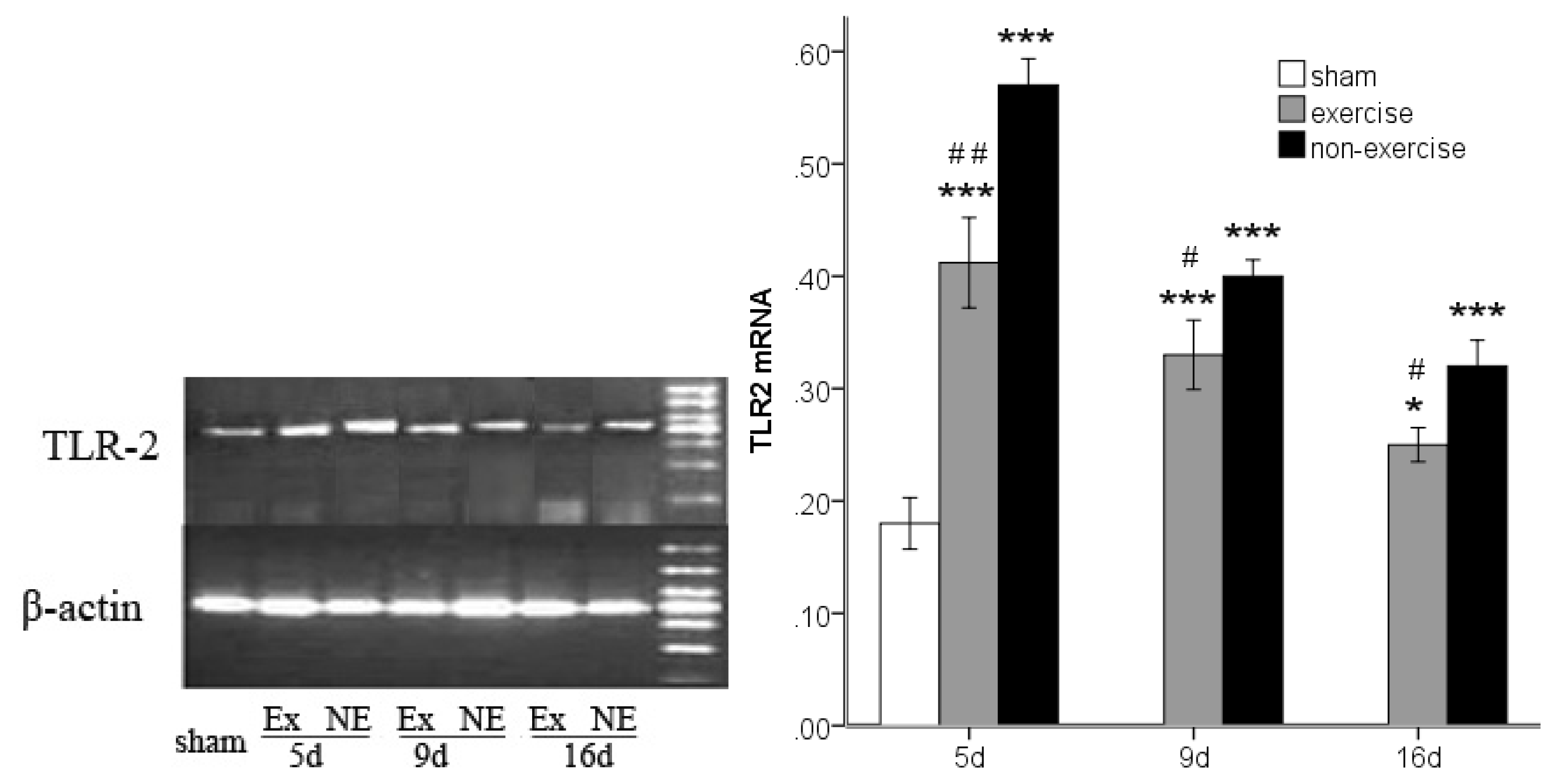
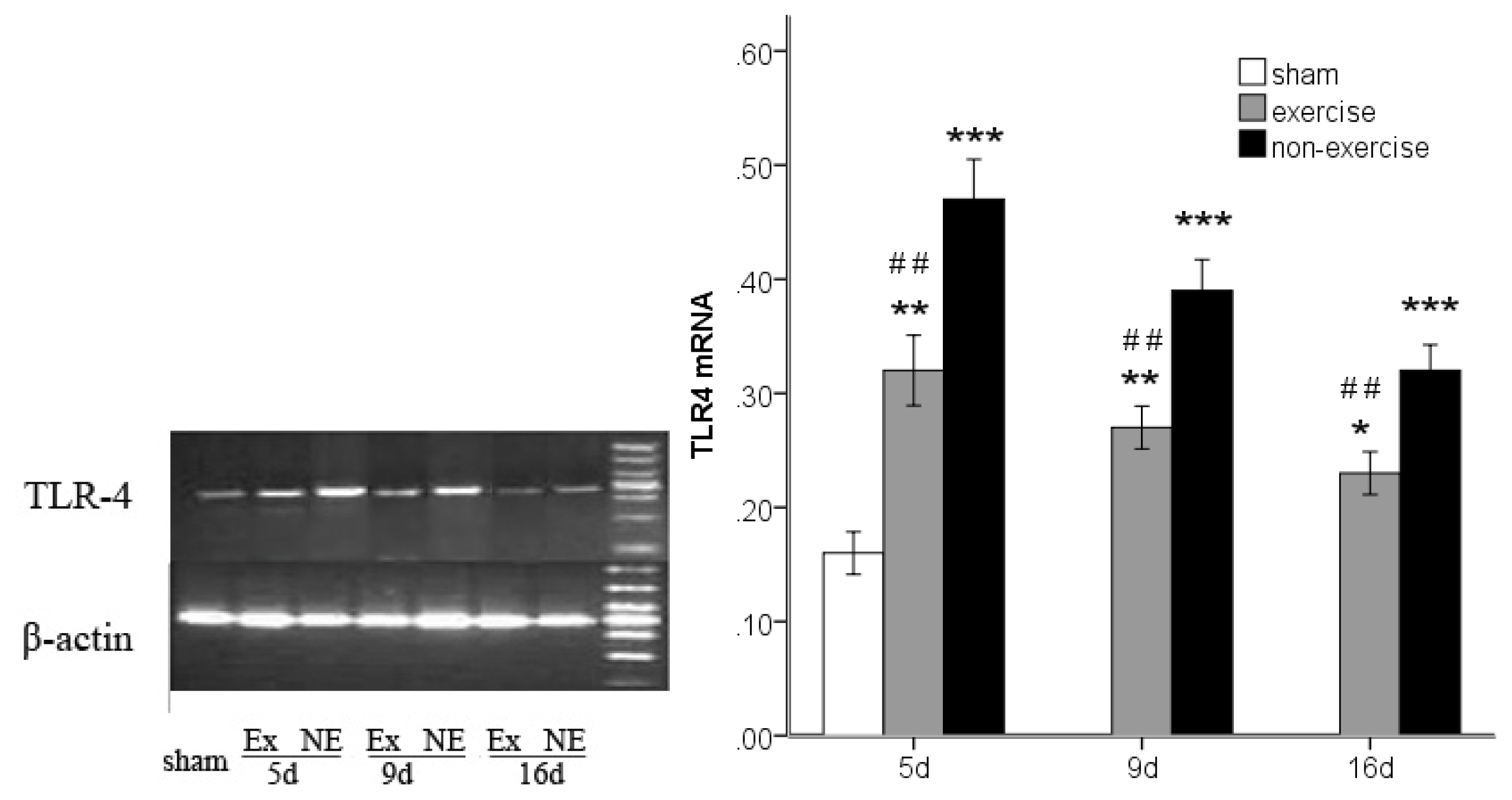
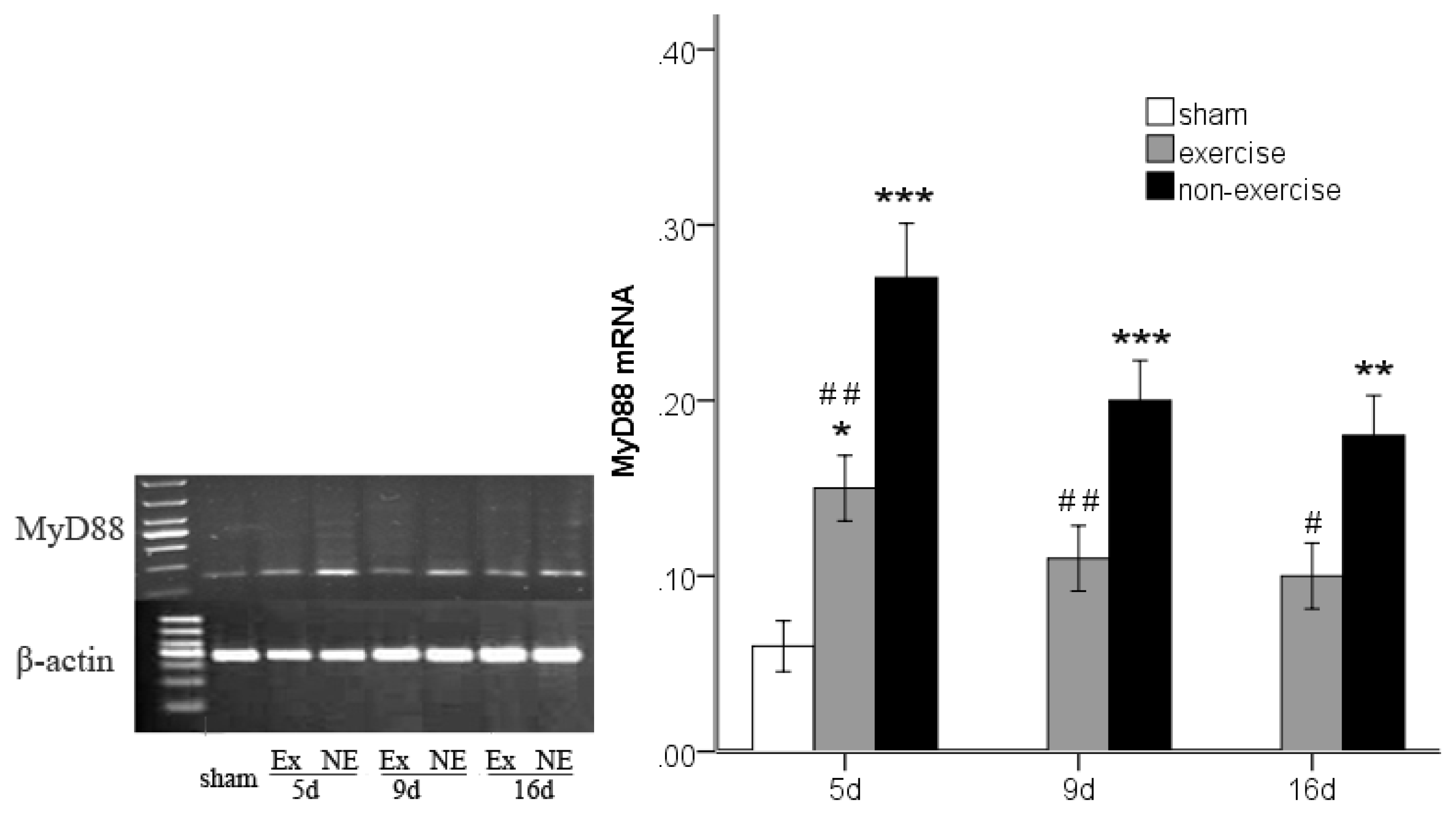
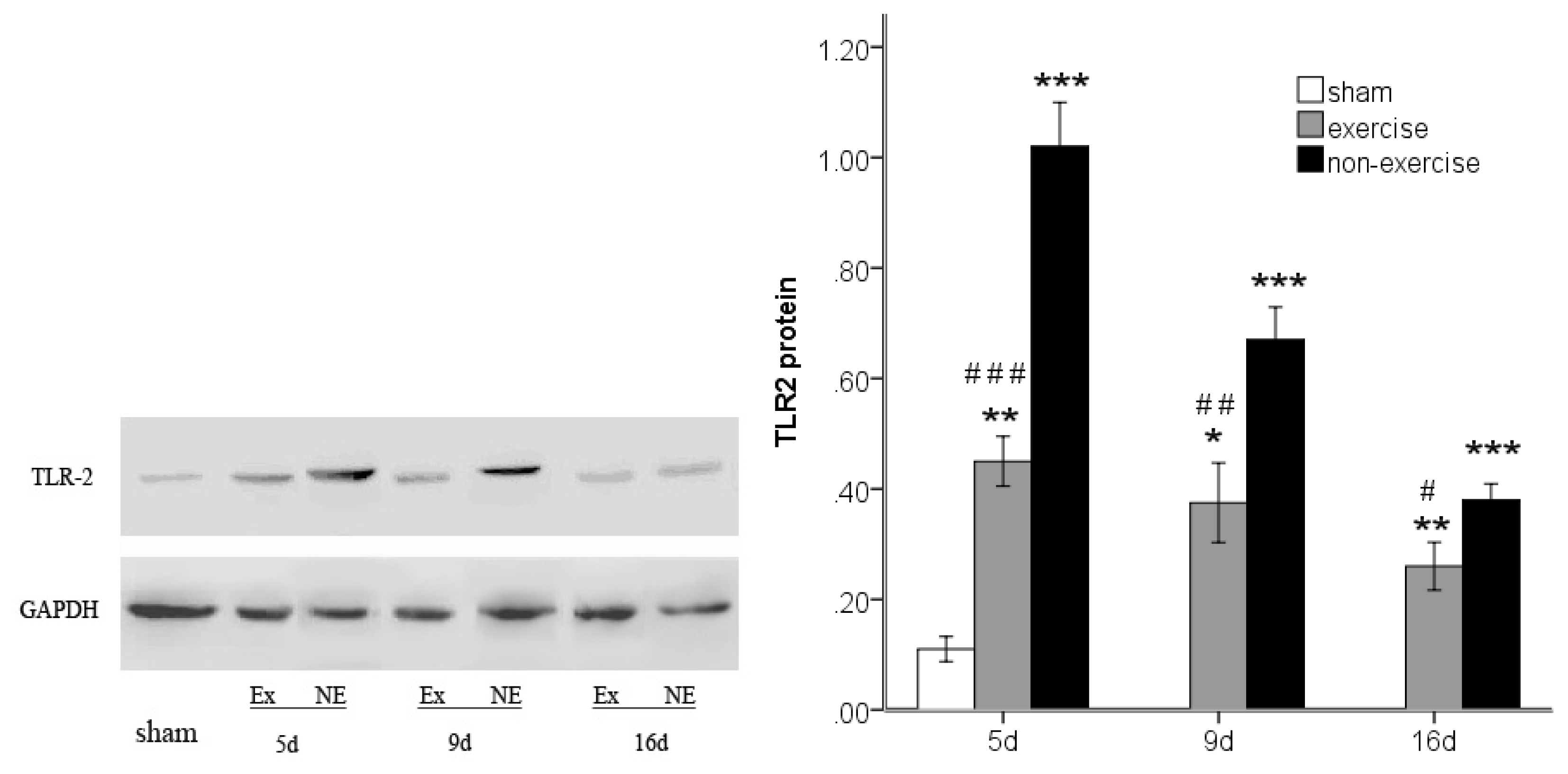
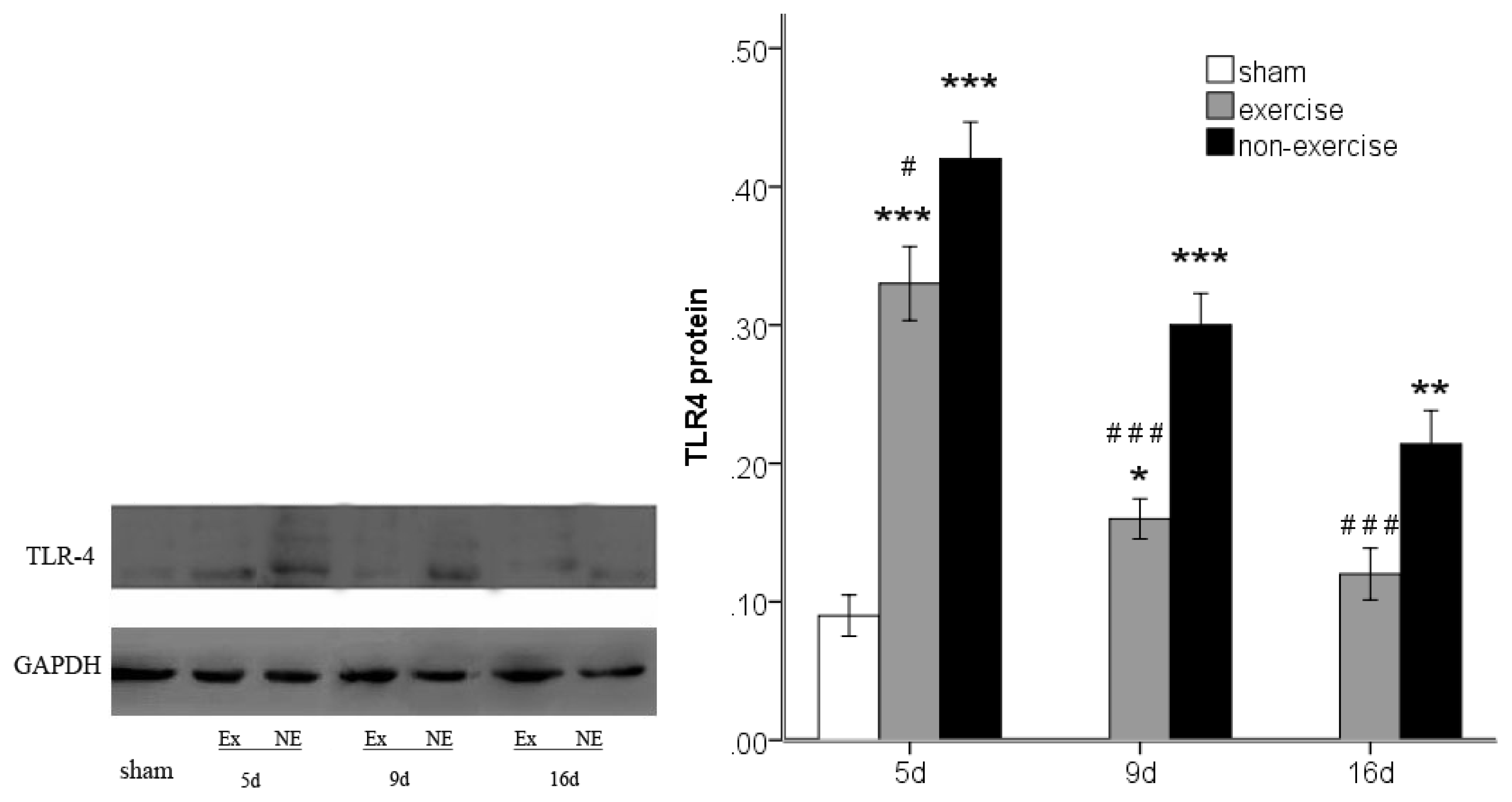
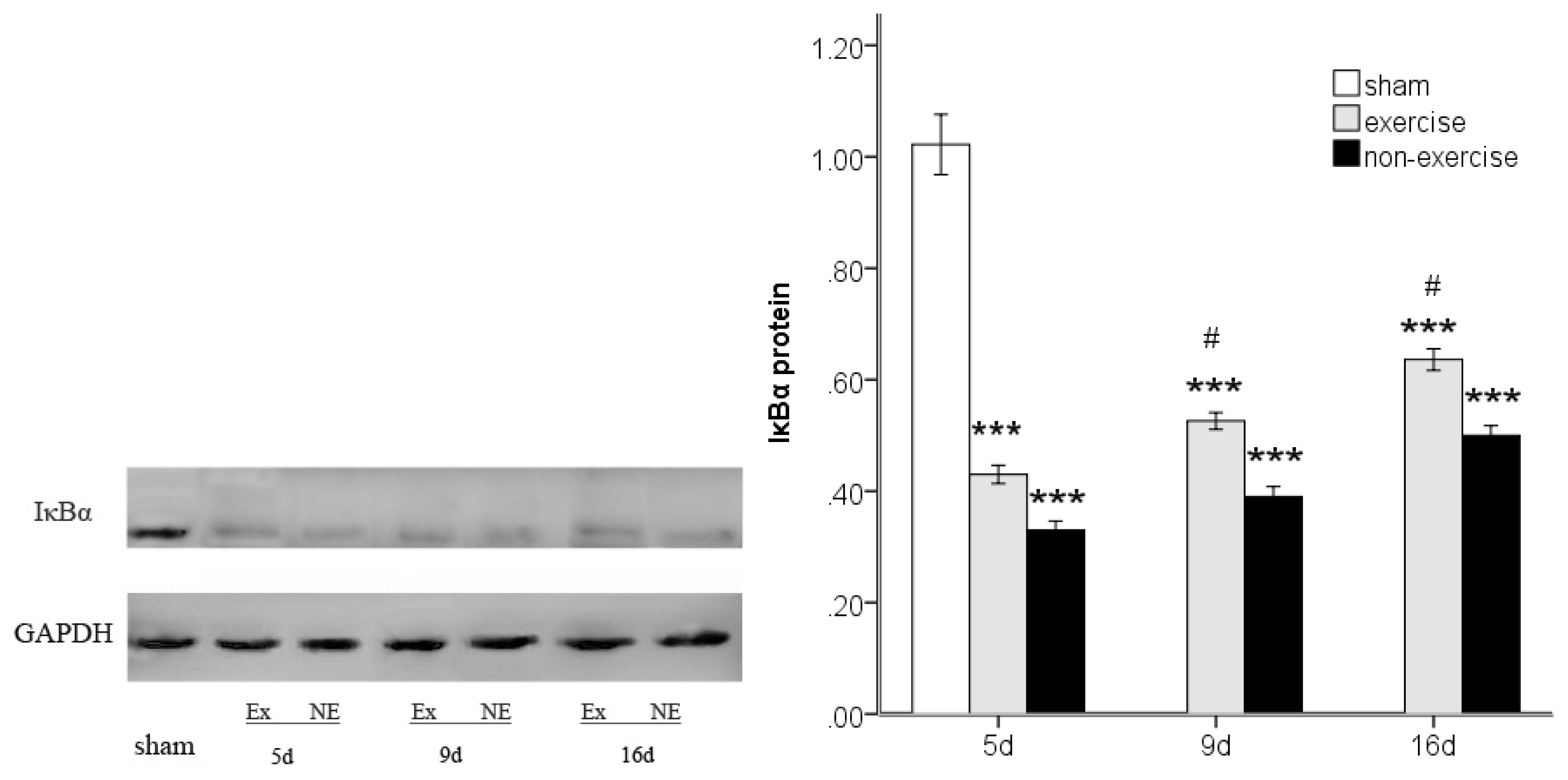
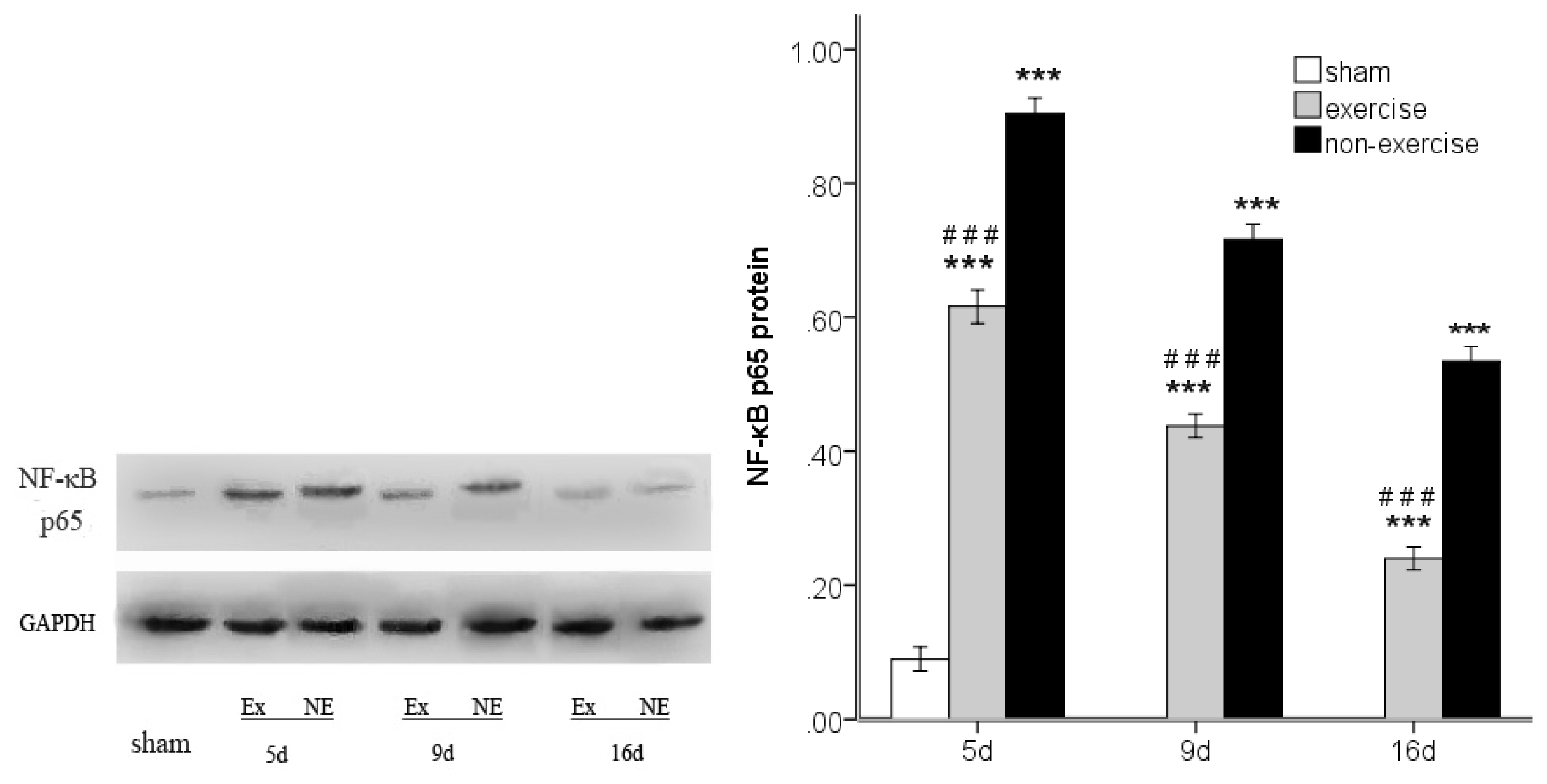
2.3. Decreased TLR2, TLR4, MyD88 and NF-κB Gene Expression after Exercise
2.4. Exercise Inhibits MCAo/R-Induced TLR2, TLR4 and NF-κB p65 Activation
2.5. Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Animal Preparation
3.2. Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion-Reperfusion (MCAo/R) Model
3.3. Behavioral Outcome Measures in Rats after Focal Cerebral Ischemia
3.4. Physical Exercise
3.5. Measurement of Cerebral Infarction Volume
3.6. TLR2, TLR4, MyD88 and NF-κB p65 Messenger RNA Expression
3.7. Western Blot Analysis
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Cao, C.X.; Yang, Q.W.; Lv, F.L.; Cui, J.; Fu, H.B.; Wang, J.Z. Reduced cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in Toll-like receptor 4 deficient mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2007, 353, 509–514. [Google Scholar]
- Caso, J.R.; Pradillo, J.M.; Hurtado, O.; Leza, J.C.; Moro, M.A.; Lizasoain, I. Toll-like receptor 4 is involved in subacute stress-induced neuroinflammation and in the worsening of experimental stroke. Stroke 2008, 39, 1314–1320. [Google Scholar]
- Kilic, U.; Kilic, E.; Matter, C.M.; Bassetti, C.L.; Hermann, D.M. TLR-4 deficiency protects against focal cerebral ischemia and axotomy-induced neurodegeneration. Neurobiol. Dis 2008, 31, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Marsh, B.J.; Williams-Karnesky, R.L.; Stenzel-Poore, M.P. Toll-like receptor signaling in endogenous neuroprotection and stroke. Neuroscience 2009, 158, 1007–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, S.; Arumugam, T.; Xu, X.; Cheng, A.; Mughal, M.R.; Jo, D.G.; Lathia, J.D.; Siler, D.A.; Chigurupati, S.; Ouyang, X.; et al. Pivotal role for neuronal Toll-like receptors in ischemic brain injury and functional deficits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13798–13803. [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler, G.; Harhausen, D.; Schepers, C.; Hoffmann, O.; Rohr, C.; Prinz, V.; Konig, J.; Lehrach, H.; Nietfeld, W.; Trendelenburg, G. TLR2 has a detrimental role in mouse transient focal cerebral ischemia. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2007, 359, 574–579. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, F.; Ma, J.; Ha, T.; Kelley, J.L.; Kao, R.L.; Schweitzer, J.B.; Kalbfleisch, J.H.; Williams, D.L.; Li, C. Differential roles of TLR2 and TLR4 in acute focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Brain Res 2009, 1262, 100–108. [Google Scholar]
- Lehnardt, S.; Lehmann, S.; Kaul, D.; Tschimmel, K.; Hoffmann, O.; Cho, S.; Krueger, C.; Nitsch, R.; Meisel, A.; Weber, J.R. Toll-like receptor 2 mediates CNS injury in focal cerebral ischemia. J. Neuroimmunol 2007, 190, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Brea, D.; Blanco, M.; Ramos-Cabrer, P.; Moldes, O.; Arias, S.; Perez-Mato, M.; Leira, R.; Sobrino, T.; Castillo, J. Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in ischemic stroke: Outcome and therapeutic values. J. Cereb. Blood Flow & Metab 2011, 31, 1424–1431. [Google Scholar]
- Akira, S. TLR signaling. Curr. Top. Microboil. Immunol 2006, 311, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin, A.S., Jr. The NF-κB and IκB proteins: New discoveries and insights. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1996, 14, 649–681. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, A.; Martin-Villalba, A.; Weih, F.; Vogel, J.; Wirth, T.; Schwaninger, M. NF-κB is activated and promotes cell death in focal cerebral ischemia. Nat. Med 1999, 5, 554–559. [Google Scholar]
- Nurmi, A.; Lindsberg, P.J.; Koistinaho, M.; Zhang, W.; Juettler, E.; Karjalainen-L, M.L.; Weih, F.; Frank, N.; Schwaninger, M.; Koistinaho, J. Nuclear factor-κB contributes to infarction after permanent focal ischemia. Stroke 2004, 35, 987–991. [Google Scholar]
- Nurmi, A.; Vartiainen, N.; Pihlaja, R. Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate inhibits translocation of nuclear factor kappa-B in neurons and protects against brain ischemia with a wide therapeutic time window. J. Neurochem 2004, 91, 755–765. [Google Scholar]
- Sironi, L.; Banfi, C.; Brioschi, M.; Gelosa, P.; Guerrini, U.; Nobili, E.; Gianella, A.; Paoletti, R.; Tremoli, E.; Cimino, M. Activation of NF-κB and ERK1/2 after permanent focal ischemia is abolished by simvastatin treatment. Neurobiol. Dis 2006, 22, 445–451. [Google Scholar]
- Moseley, A.M.; Stark, A.; Cameron, I.D.; Pollock, A. Treadmill training and body weight support for walking after stroke. Cochrane Data-Base Syst. Rev. 2005, 3, CD002840. [Google Scholar]
- Ploughman, M.; Attwood, Z.; White, N.; Doré, J.J.; Corbett, D. Endurance exercise facilitates relearning of forelimbmotor skill after focal ischemia. Eur. J. Neurosci 2007, 25, 3453–3460. [Google Scholar]
- Langhammer, B.; Lindmark, B. Functional exercise and physical fitness post stroke: The importance of exercise maintenance for motor control and physical fitness after stroke. Stroke Res. Treat. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimyan, M.A.; Cohen, L.G. Neuroplasticity in the context of motor rehabilitation after stroke. Nat. Rev. Neurol 2011, 7, 76–85. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Pu, H.; Wu, Y.; Bai, Y.; Vosler, P.S.; Chen, J.; Shi, H.; Gao, Y.; Hu, Y. Very early-initiated physical rehabilitation protects against ischemic brain injury. Front. Biosci 2012, 4, 2476–2489. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, A.G.; Carvalho, B.M.; Tobar, N. Physical exercise reduces circulating lipopolysaccharide and TLR4 activation and improves insulin signaling in tissues of DIO rats. Diabetes 2011, 60, 784–796. [Google Scholar]
- Gleeson, M.; McFarlin, B.; Flynn, M. Exercise and Toll-like receptors. Exerc. Immunol. Rev 2006, 12, 34–53. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, M.G.; McFarlin, B.K. Toll-like receptor 4: Link to the anti-inflammatory effects of exercise? Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev 2006, 34, 176–181. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, C.P.; Wright, N.R.; Finck, B.N.; Villareal, D.T. Exercise but not diet-induced weight loss decreases skeletal muscle inflammatory gene expression in frail obese elderly persons. J. Appl. Physiol 2008, 105, 473–478. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Kou, J.P.; Yu, B.Y. Ginsenoside Rg1 protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death in PC12 cells via inhibiting NF-kappaB activation. Neuro. Chem Int 2011, 58, 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- Huntley, G.W. Synaptic circuit remodelling by matrix metalloproteinases in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci 2012, 13, 743–757. [Google Scholar]
- Pyoria, O.; Talvitie, U.; Nyrkko, H.; Kautiainen, H.; Pohjolainen, T.; Kasper, V. The effect of two physiotherapy approaches on physicaland cognitive functions and independent coping at home in stroke rehabilitation. A preliminary follow-up study. Disabil. Rehabil 2007, 29, 503–511. [Google Scholar]
- Langhammer, B.; Lindmark, B.; Stanghelle, J.K. Stroke patients and long-term training: Is it worthwhile? A randomized comparison of two different training strategiesafter rehabilitation. Clin. Rehabil 2007, 21, 495–510. [Google Scholar]
- Gertz, K.; Priller, J.; Kronenberg, G.; Fink, K.B.; Winter, B.; Schröck, H.; Ji, S.; Milosevic, M.; Harms, C.; Böhm, M.; et al. Physical activity improves long-term stroke outcome via endothelial nitric oxide synthase-dependent augmentation of neovascularization and cerebral blood flow. Circ. Res. 2006, 99, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.R.; Chang, H.C.; Wang, P.S.; Wang, R.Y. Motor performance improved by exercises in cerebral ischemic rats. J. Mot. Behav 2012, 44, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Yang, Y.; Yin, J. Oxymatrine downregulates TLR4, TLR2, MyD88, and NF-kappaB and protects rat brains against focal ischemia. Mediat. Inflamm. 2009, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shichita, T.; Sakaguchi, R.; Suzuki, M.; Yoshimura, A. Post-Ischemic Inflammation in the Brain. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro, A.; Meisel, A.; Planas, A.M.; Urra, X.; Beek, D.V.D.; Veltkamp, R. The immunology of acute stroke. Nat. Rev. Neurol 2012, 8, 401–410. [Google Scholar]
- Iadecola, C.; Anrather, J. The immunology of stroke: From mechanisms to translation. Nat. Med 2011, 7, 796–808. [Google Scholar]
- Zwagerman, N.; Plumlee, C.; Guthikonda, M.; Ding, Y. Toll-like receptor-4 and cytokine cascade in stroke after exercise. Rev. Neurol 2010, 32, 123–126. [Google Scholar]
- Vartanian, K.B.; Stevens, S.L.; Marsh, B.J.; Williams-Karnesky, R.; Lessov, N.S.; Stenzel-Poore, M.P. LPS preconditioning redirects TLR signaling following stroke: TRIF-IRF3 plays a seminal role in mediating tolerance to ischemic injury. J. Neuroinflamm 2011, 8, 140. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, S.L.; Leung, P.Y.; Vartanian, K.B.; Gopalan, B.; Yang, T.; Simon, R.P.; Stenzel-Poore, M.P. Multiple preconditioning paradigms converge on interferon regulatory factor-dependent signaling to promote tolerance to ischemic brain injury. J. Neurosci 2011, 31, 8456–8463. [Google Scholar]
- Pradillo, J.M.; Fernández-López, D.; García-Yébenes, I.; Sobrado, M.; Hurtado, O.; Moro, M.A.; Lizasoain, I. Toll-like receptor 4 is involved in neuroprotection afforded by ischemic preconditioning. J. Neurochem 2009, 109, 287–294. [Google Scholar]
- Clemens, J.A.; Stephenson, D.T.; Smalstig, E.B.; Dixon, E.P.; Little, S.P. Global ischemia activates nuclear factor-κB in forebrain neurons of rats. Stroke 1997, 28, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson, D.; Yin, T.; Smalstig, E.B.; Hsu, M.A.; Panetta, J.; Little, S.; Clemens, J. Transcription factor nuclear factor-κB is activated in neurons after focal cerebral ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab 2000, 20, 592–603. [Google Scholar]
- Longa, E.Z.; Weinstein, P.R.; Carlson, S.; Cummins, R. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 1989, 20, 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- NIH Image Analyzer Software. Available online: http://rsbweb.nih.gov/ij/index.html accessed on 6 January 2013.
- Pereira, M.P.; Hurtado, O.; Cárdenas, A.; Alonso-Escolano, D.; Boscá, L.; Vivancos, J.; Nombela, F.; Leza, J.C.; Lorenzo, P.; Lizasoain, I.; et al. The nonthiazolidinedione PPAR-gamma agonist L-796,449 is neuroprotective in experimental stroke. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 64, 797–805. [Google Scholar]

© 2013 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; He, M.; Qiang, L. Exercise Therapy Downregulates the Overexpression of TLR4, TLR2, MyD88 and NF-?B after Cerebral Ischemia in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 3718-3733. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14023718
Ma Y, He M, Qiang L. Exercise Therapy Downregulates the Overexpression of TLR4, TLR2, MyD88 and NF-?B after Cerebral Ischemia in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(2):3718-3733. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14023718
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yuewen, Man He, and Lin Qiang. 2013. "Exercise Therapy Downregulates the Overexpression of TLR4, TLR2, MyD88 and NF-?B after Cerebral Ischemia in Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 2: 3718-3733. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14023718
APA StyleMa, Y., He, M., & Qiang, L. (2013). Exercise Therapy Downregulates the Overexpression of TLR4, TLR2, MyD88 and NF-?B after Cerebral Ischemia in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(2), 3718-3733. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14023718



