Chebulagic Acid, a Hydrolyzable Tannin, Exhibited Antiviral Activity in Vitro and in Vivo against Human Enterovirus 71
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
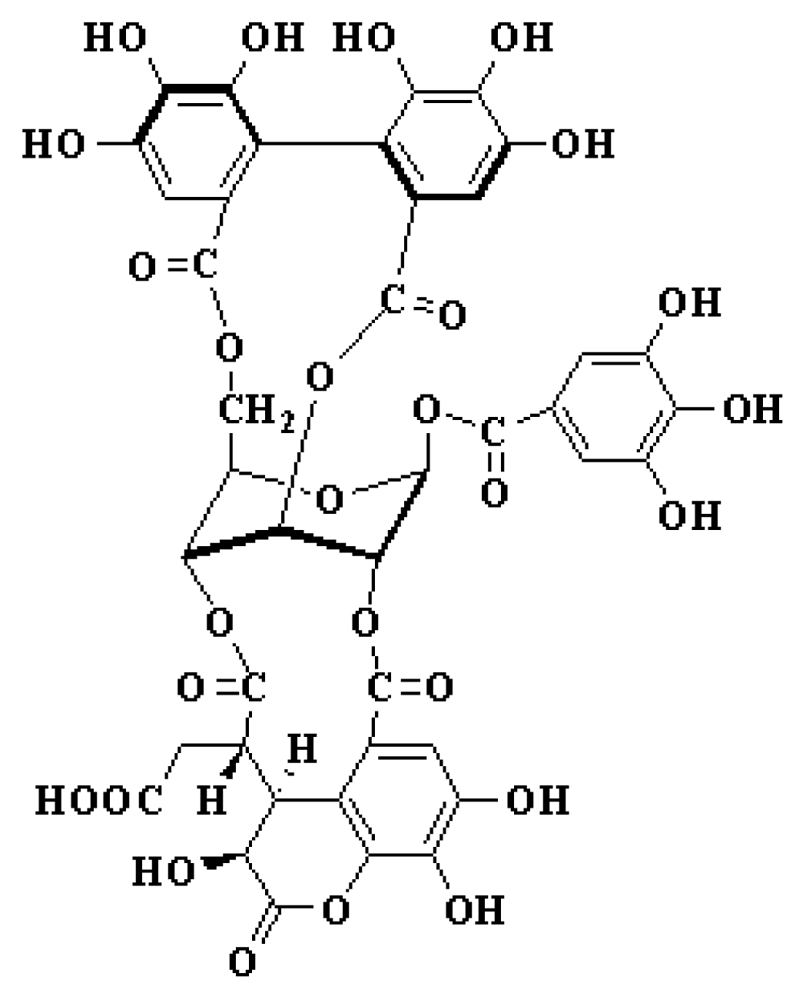
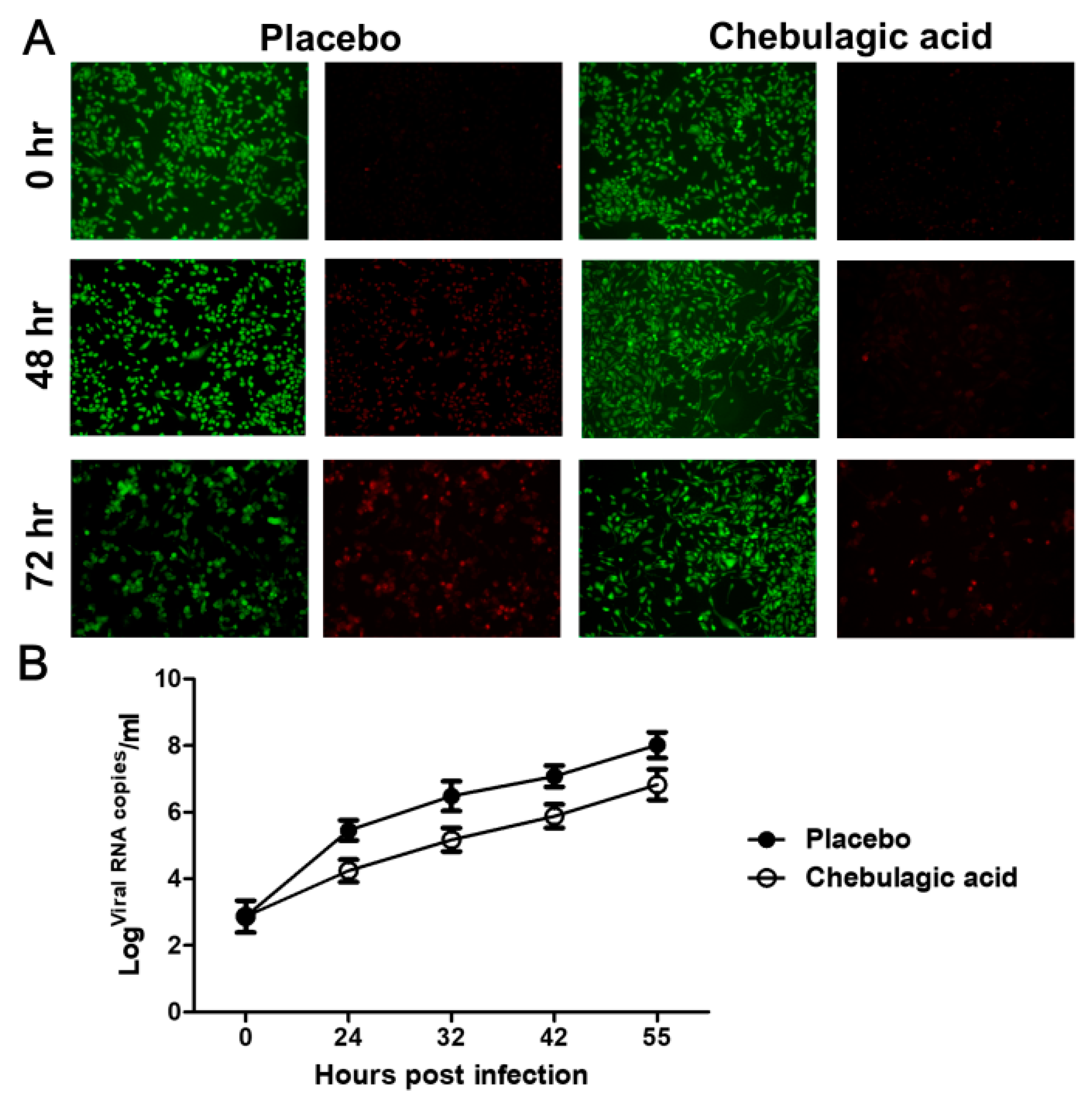
2.1. Chebulagic Acid Inhibited EV71 Infection in Vitro
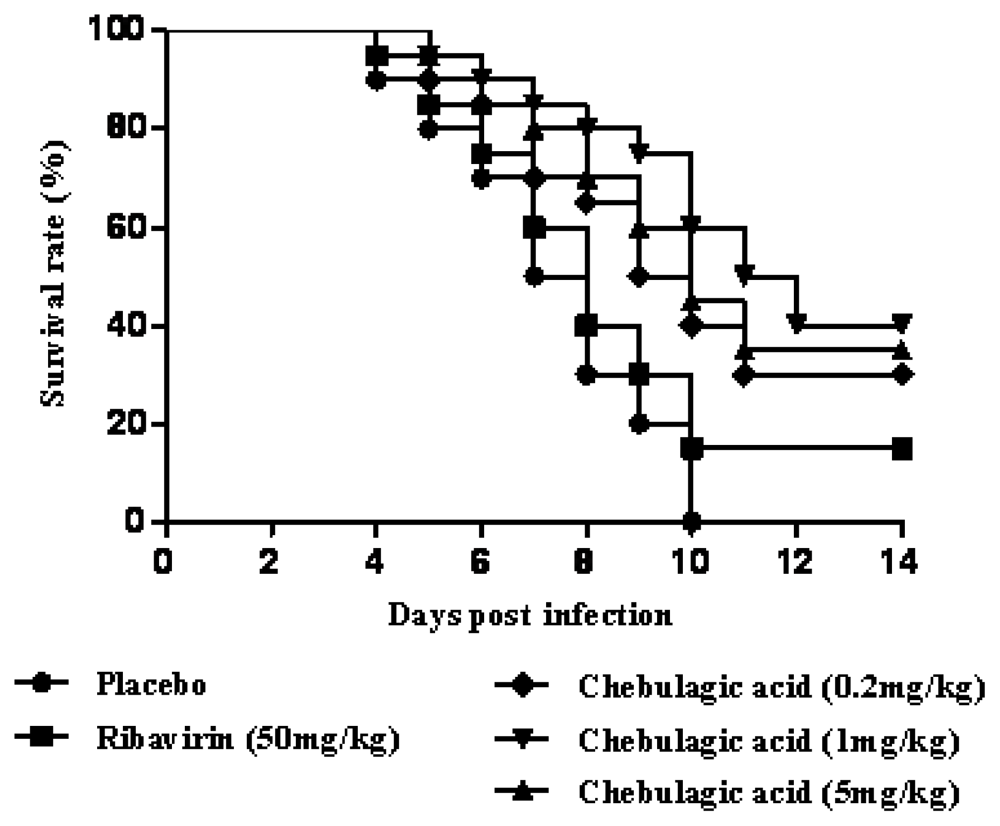
2.2. Chebulagic Acid Reduced the Mortality of Mice upon Lethal EV71 Challenge
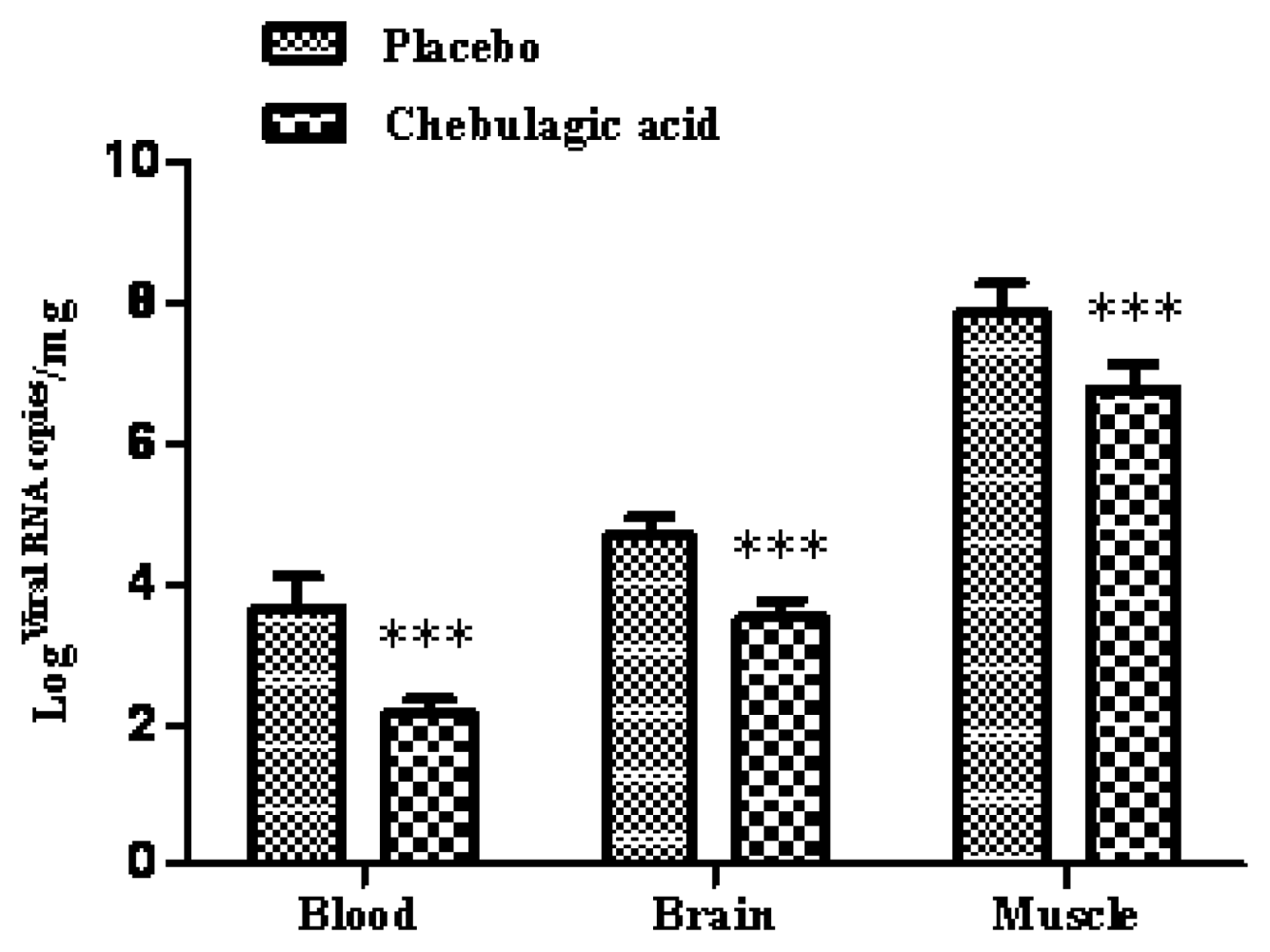
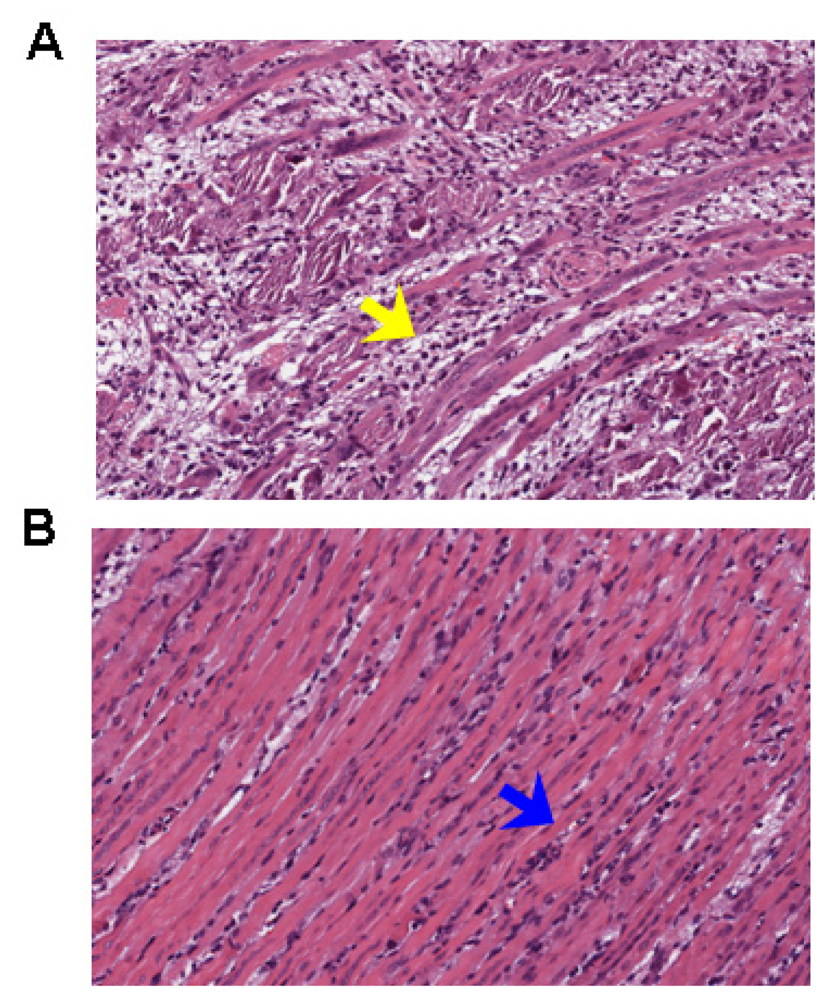
2.3. Chebulagic Acid Improved Symptoms of Infected-Mice by Inhibiting Viral Replication
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Cells, Viruses and Reagents
3.3. Mouse Protection Assay
3.4. Determination of the Viral Load
3.5. Pathology
3.6. Statistics
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Wu, K.X.; Ng, M.M.; Chu, J.J. Developments towards antiviral therapies against enterovirus 71. Drug Discov. Today 2010, 15, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, L.; Lu, J.; Kung, H.; He, M.L. The virology and developments toward control of human enterovirus 71. Crit. Rev. Microbiol 2011, 37, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.N.; Li, X.Y.; Fan, X.X.; Ma, C.M.; Qin, C.; Zhang, L.F. Adoptive transfer of macrophages from adult mice reduces mortality in mice infected with human enterovirus 71. Arch. Virol 2013, 158, 387–397. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, T.; Hu, Y.F.; Wang, X.F.; Du, J.; Li, Y.F.; Sun, S.X.; Sun, X.H.; Li, Z.F.; Jin, Q. Survey of enterovirus infections from hand, foot and mouth disease outbreak in China, 2009. Virol. J. 2011, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.N.; Zhao, D.D.; Gao, B.; Zhong, K.; Zhu, R.X.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, W.J.; Jia, L.R.; Gao, H. Anti-hyperglycemic effect of chebulagic acid from the fruits of Terminalia chebula. Retz. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2012, 13, 6320–6333. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.X.; Yu, S.J.; Liu, D.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W.H. Inhibitory effects of polyphenols toward HCV from the mangrove plant Excoecaria agallocha L. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 2012, 22, 1099–1102. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.T.; Chen, T.Y.; Chung, C.Y.; Noyce, R.S.; Grindley, T.B.; McCormick, C.; Lin, T.C.; Wang, G.H.; Lin, C.C.; Richardson, C.D. Hydrolyzable tannins (chebulagic acid and punicalagin) target viral glycoprotein-glycosaminoglycan interactions to inhibit herpes simplex virus 1 entry and cell-to-cell spread. J. Virol 2011, 85, 4386–4398. [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka, G.; Nishioka, I.; Nishizawa, M.; Yamagishi, T.; Kashiwada, Y.; Dutschman, G.E.; Bodner, A.J.; Kilkuskie, R.E.; Cheng, Y.C.; Lee, K.H. Anti-AIDS agents, 2: Inhibitory effects of tannins on HIV reverse transcriptase and HIV replication in H9 lymphocyte cells. J. Nat. Prod 1990, 53, 587–595. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.N.; Yang, Y.J.; Xu, Y.F.; Ma, C.M.; Qin, C.; Zhang, L.F. Lycorine reduces mortality of human enterovirus 71-infected mice by inhibiting virus replication. Viol. J 2011, 8, 483. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.J.; Xiu, J.H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.F.; Yan, K.; Qin, C.; Liu, J.N. Antiviral effect of matrine against human enterovirus 71. Molecules 2012, 17, 10370–10376. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, L.C.; Ng, L.T.; Cheng, P.W.; Chiang, W.; Lin, C.C. Antiviral activities of extracts and selected pure constituents of Ocimum basilicum. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol 2005, 32, 811–816. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.J.; Lim, C.H.; Song, J.H.; Baek, S.H.; Kwon, D.H. Antiviral activity of raoulic acid from Raoulia australis against Picornaviruses. Phytomedicine 2009, 16, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, H.Y.; Cheng, M.L.; Weng, S.F.; Leu, Y.L.; Chiu, D.T. Antiviral effect of epigallocatechin gallate on enterovirus 71. J. Agric. Food. Chem 2009, 57, 6140–6147. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.W.; Wu, C.F.; Hsiao, N.W.; Chang, C.Y.; Li, S.W.; Wan, L.; Lin, Y.J.; Lin, W.Y. Aloe-emodin is an interferon-inducing agent with antiviral activity against Japanese encephalitis virus and enterovirus 71. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2008, 32, 355–359. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.P.; Zhang, R.Q.; Li, X.; Su, W.H.; Long, F.; Luo, X.D.; Peng, T. Inhibition of enterovirus 71 replication by chrysosplenetin and penduletin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci 2011, 44, 392–398. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.J.; Zhang, L.F.; Fan, X.X.; Qin, C.; Liu, J.N. Antiviral effect of geraniin on human enterovirus 71 in vitro and in vivo. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 2012, 22, 2209–2211. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.J.; Xiu, J.H.; Zhang, L.F.; Qin, C.; Liu, J.N. Antiviral activity of punicalagin toward human enterovirus 71 in vitro and in vivo. Phytomedicine 2012, 20, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Buzzini, P.; Arapitsas, P.; Goretti, M.; Branda, E.; Turchetti, B.; Pinelli, P.; Ieri, F.; Romani, A. Antimicrobial and antiviral activity of hydrolysable tannins. Mini. Rev. Med. Chem 2008, 8, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar]
- Hamada, S.; Kataoka, T.; Woo, J.T.; Yamada, A.; Yoshida, T.; Nishimura, T.; Otake, N.; Nagai, K. Immunosuppressive effects of gallic acid and chebulagic acid on CTL-mediated cytotoxicity. Biol. Pharm. Bull 1997, 20, 1017–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.I.; Hyun, P.M.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, B.S.; Maeng, P.J.; Lim, J.S. Suppression of the onset and progression of collagen-induced arthritis by chebulagic acid screened from a natural product library. Arthritis Rheum 2005, 52, 345–353. [Google Scholar]

© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Xiu, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Qin, C.; Zhang, L. Chebulagic Acid, a Hydrolyzable Tannin, Exhibited Antiviral Activity in Vitro and in Vivo against Human Enterovirus 71. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 9618-9627. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14059618
Yang Y, Xiu J, Liu J, Zhang L, Li X, Xu Y, Qin C, Zhang L. Chebulagic Acid, a Hydrolyzable Tannin, Exhibited Antiviral Activity in Vitro and in Vivo against Human Enterovirus 71. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(5):9618-9627. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14059618
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yajun, Jinghui Xiu, Jiangning Liu, Li Zhang, Xiaoying Li, Yanfeng Xu, Chuan Qin, and Lianfeng Zhang. 2013. "Chebulagic Acid, a Hydrolyzable Tannin, Exhibited Antiviral Activity in Vitro and in Vivo against Human Enterovirus 71" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 5: 9618-9627. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14059618
APA StyleYang, Y., Xiu, J., Liu, J., Zhang, L., Li, X., Xu, Y., Qin, C., & Zhang, L. (2013). Chebulagic Acid, a Hydrolyzable Tannin, Exhibited Antiviral Activity in Vitro and in Vivo against Human Enterovirus 71. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(5), 9618-9627. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14059618



