Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Tryptophan Hydroxylase-1: Binding Modes and Free Energy Analysis to Phenylalanine Derivative Inhibitors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
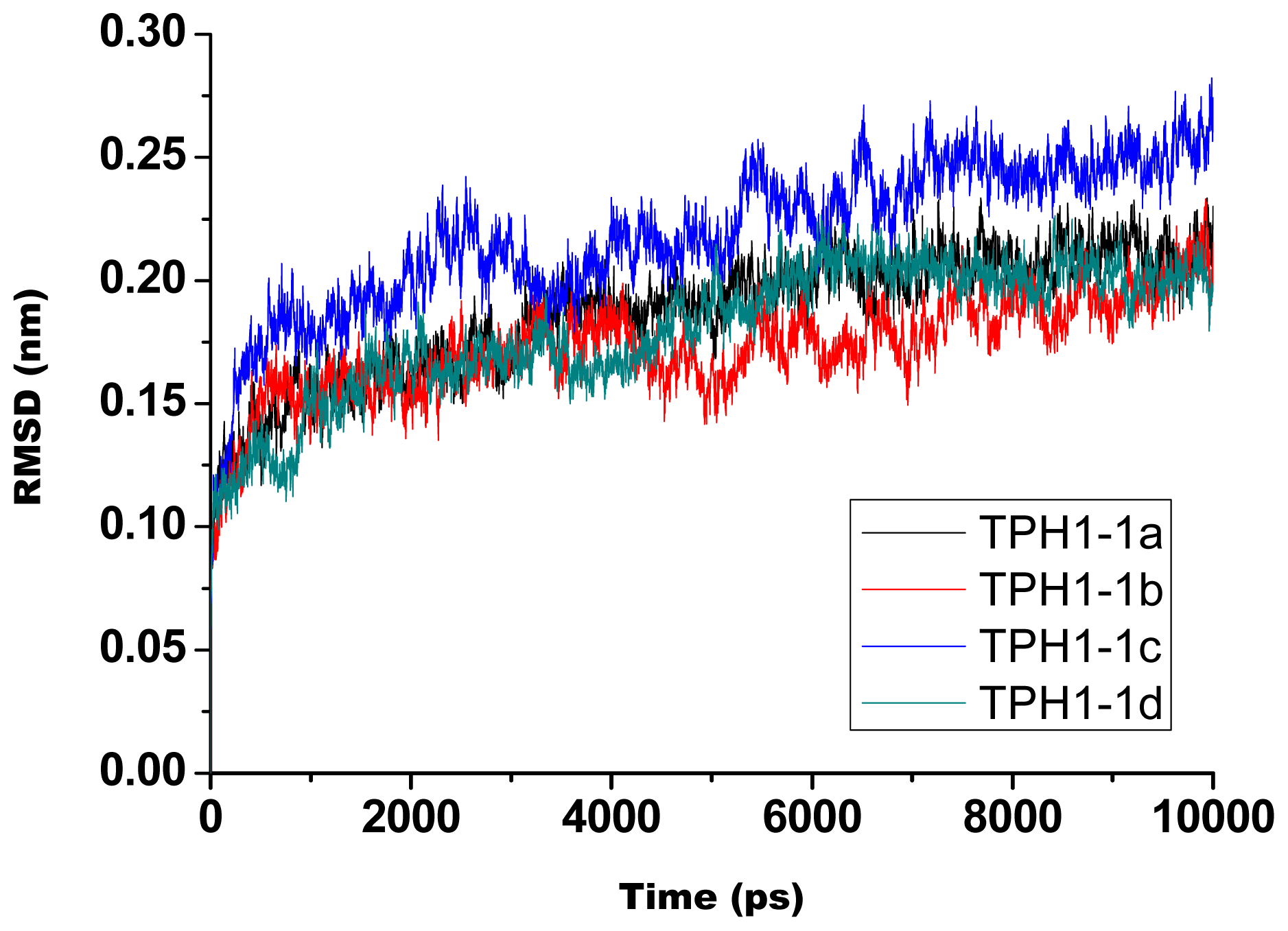
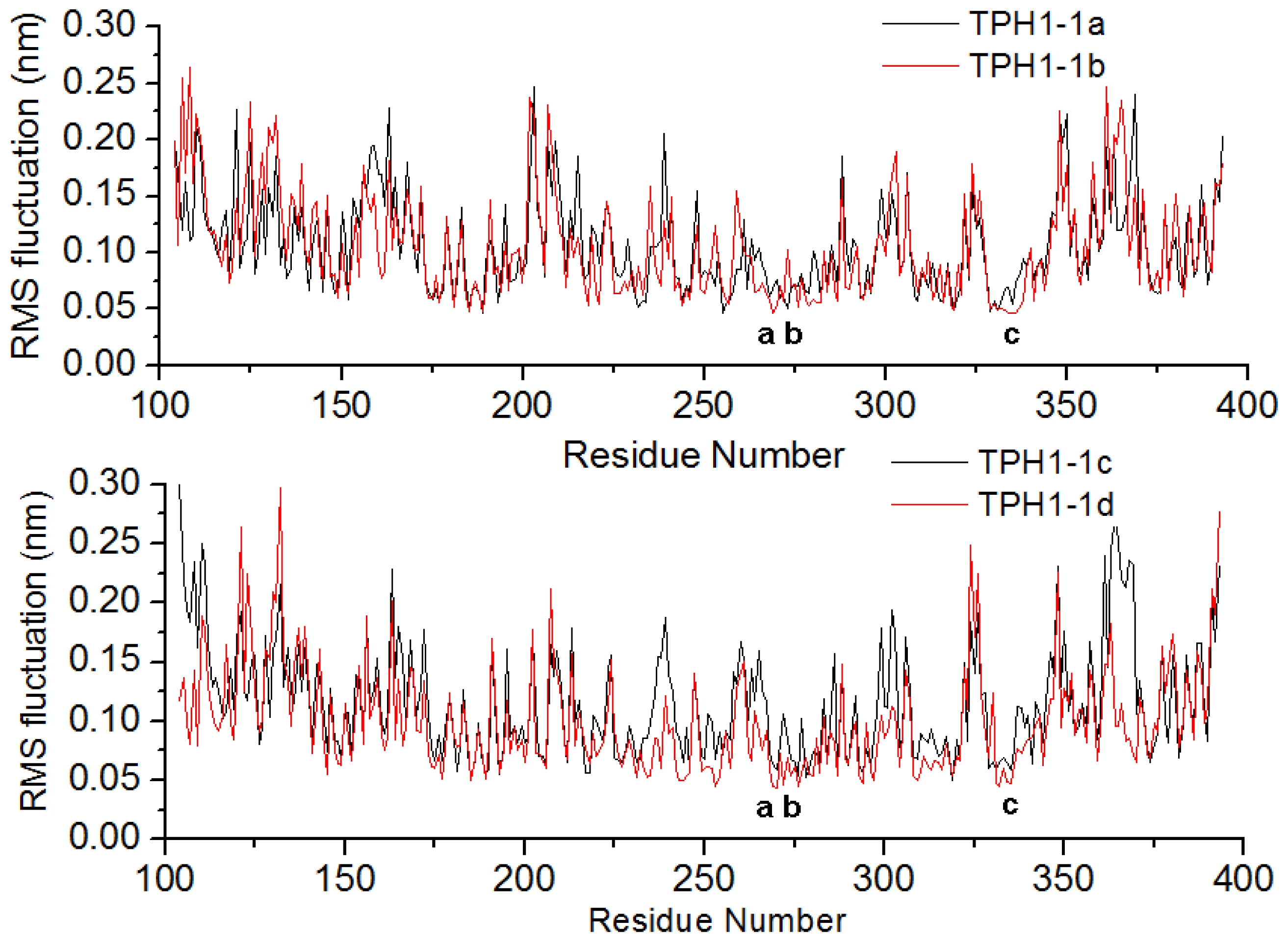
2.1. The Dynamics Stability MD Simulation
2.2. Calculation of Binding Free Energies by MM/GBSA
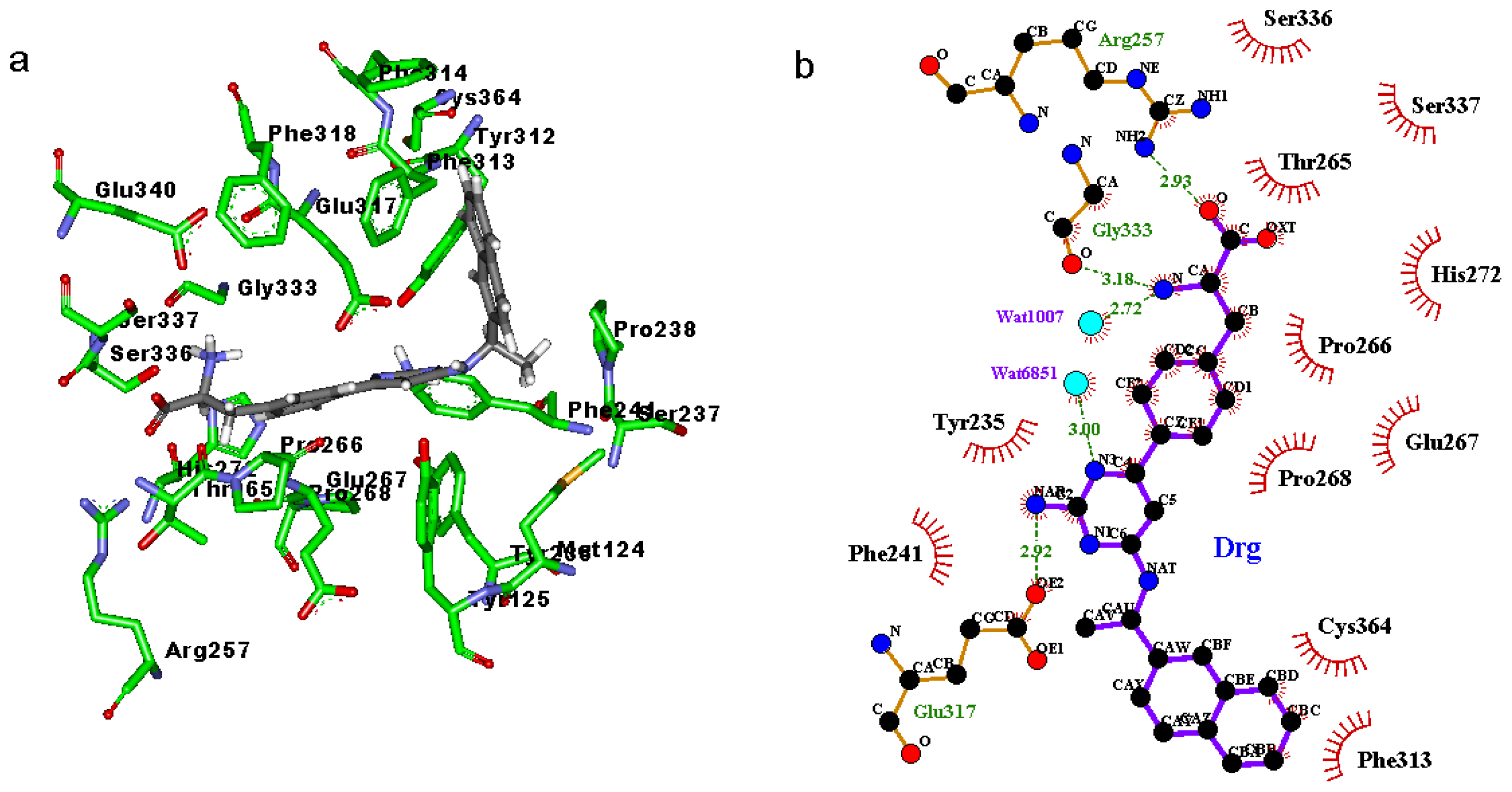
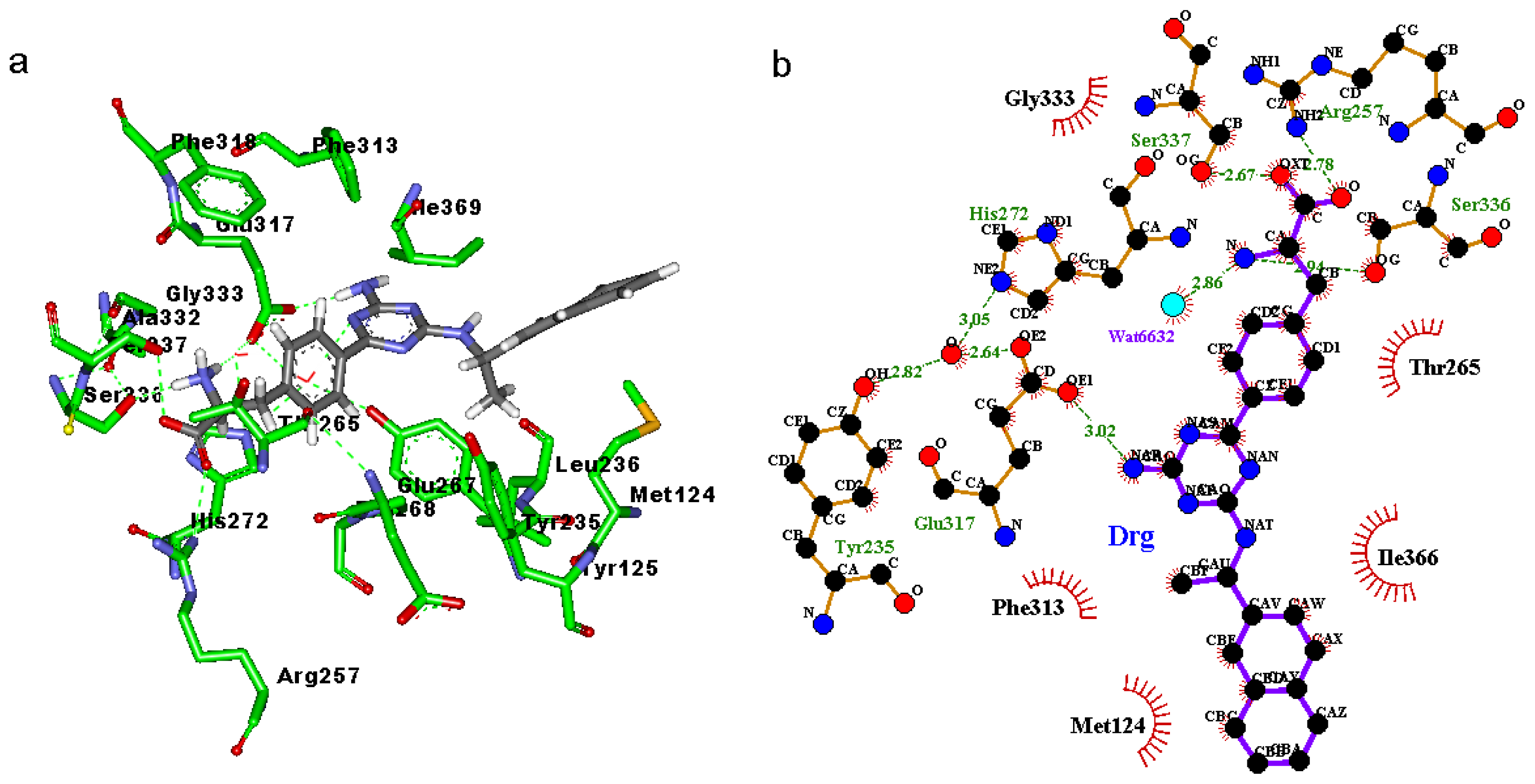
2.3. Binding Mode of the TPH1–Inhibitor Complex
2.4. Decomposition Analysis of the Binding Free Energies
2.5. Computational Mutagenesis of the Binding-Site Residues
3. Experimental Section
3.1. System Preparation
3.2. Molecular Dymanics Simulation
3.3. MM/GBSA Calculation
3.4. Free Energy Decomposition Analysis
3.5. Computational Alanine Scanning
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Information
ijms-14-09947-s001.pdfAcknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Gaspar, P.; Cases, O.; Maroteaux, L. The developmental role of serotonin: News from mouse molecular genetics. Nat. Rev. Neurosci 2003, 4, 1002–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Boyer, E.W.; Shannon, M. The serotonin syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med 2005, 352, 1112–1120. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, A.; Knappskog, P.M.; Haavik, J. A structural approach into human tryptophan hydroxylase and its implications for the regulation of serotonin biosynthesis. Curr. Med. Chem 2001, 8, 1077–1091. [Google Scholar]
- Walther, D.J.; Peter, J.U.; Bashammakh, S.; Hortnagl, H.; Voits, M.; Fink, H.; Bader, M. Synthesis of serotonin by a second tryptophan hydroxylase isoform. Science 2003, 299, 76–76. [Google Scholar]
- Matthes, S.; Mosienko, V.; Bashammakh, S.; Alenina, N.; Bader, M. Tryptophan hydroxylase as novel target for the treatment of depressive disorders. Pharmacology 2010, 85, 95–109. [Google Scholar]
- Sikander, A.; Rana, S.V.; Prasad, K.K. Role of serotonin in gastrointestinal motility and irritable bowel syndrome. Clin. Chim. Acta 2009, 403, 47–55. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H.H.; Cianchetta, G.; Devasagayaraj, A.; Gu, K.J.; Marinelli, B.; Samal, L.; Scott, S.; Stouch, T.; Tunoori, A.; Wang, Y.; et al. Substituted 3-(4-(1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-phenyl)-2-aminopropanoic acids as novel tryptophan hydroxylase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 2009, 19, 5229–5232. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.C.; Devasagayaraj, A.; Gu, K.J.; Jin, H.; Marinelli, B.; Samala, L.; Scott, S.; Stouch, T.; Tunoori, A.; Wang, Y.; et al. Modulation of peripheral serotonin levels by novel tryptophan hydroxylase inhibitors for the potential treatment of functional gastrointestinal disorders. J. Med. Chem 2008, 51, 3684–3687. [Google Scholar]
- Ducy, P.; Karsenty, G. The two faces of serotonin in bone biology. J. Cell Biol 2010, 191, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ducy, P. 5-HT and bone biology. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol 2011, 11, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Goltzman, D. LRP5, serotonin, and bone: Complexity, contradictions, and conundrums. J. Bone Miner. Res 2011, 26, 1997–2001. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, V.K.; Balaji, S.; Suresh, P.S.; Liu, X.S.; Lu, X.; Li, Z.S.; Guo, X.E.; Mann, J.J.; Balapure, A.K.; Gershon, M.D.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of gut-derived serotonin synthesis is a potential bone anabolic treatment for osteoporosis. Nat. Med 2010, 16, 308–312. [Google Scholar]
- Frost, M.; Andersen, T.; Gossiel, F.; Hansen, S.; Bollerslev, J.; van Hul, W.; Eastell, R.; Kassem, M.; Brixen, K. Levels of serotonin, sclerostin, bone turnover markers as well as bone density and microarchitecture in patients with high-bone-mass phenotype due to a mutation in Lrp5. J. Bone Miner. Res 2011, 26, 1721–1728. [Google Scholar]
- Inose, H.; Zhou, B.; Yadav, V.K.; Guo, X.E.; Karsenty, G.; Ducy, P. Efficacy of serotonin inhibition in mouse models of bone loss. J. Bone Miner. Res 2011, 26, 2002–2011. [Google Scholar]
- Camilleri, M. LX-1031, a tryptophan 5-hydroxylase inhibitor, and its potential in chronic diarrhea associated with increased serotonin. Neurogastroenterol. Motil 2011, 23, 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, L.; He, G.; Huang, W.; Song, X.; Wu, F.; Xiang, M. Combined structure-based pharmacophore and 3D-QSAR studies on phenylalanine series compounds as TPH1 inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2012, 13, 5348–5363. [Google Scholar]
- Case, D.A.; Cheatham, T.E.; Darden, T.; Gohlke, H.; Luo, R.; Merz, K.M.; Onufriev, A.; Simmerling, C.; Wang, B.; Woods, R.J. The Amber biomolecular simulation programs. J. Comput. Chem 2005, 26, 1668–1688. [Google Scholar]
- Case, D.A.; Darden, T.A.; Cheatham, T.E., III; Simmerling, C.L.; Wang, J.; Duke, R.E.; Luo, R.; Walker, R.C.; Zhang, W.; Merz, K.M.; et al. AMBER 12; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, C.; Xiu, Z.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Hao, C.; Teng, H. Comparative molecular dynamics simulations of histone deacetylase-like protein: Binding modes and free energy analysis to hydroxamic acid inhibitors. Proteins-Struct. Funct. Bioinforma 2008, 73, 134–149. [Google Scholar]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Swindells, M.B. LigPlot+: Multiple ligand-protein interaction diagrams for drug discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model 2011, 51, 2778–2786. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, A.C.; Laskowski, R.A.; Thornton, J.M. LIGPLOT—A program to generate schematic diagrams of protein ligand interactions. Protein Eng 1995, 8, 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- Sybyl-X Molecular Modeling Software Packages, Version 2.0; TRIPOS Associates, Inc: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2012.
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Montgomery, J.A., Jr.; Raghavachari, K.; Vreven, T.; Kudin, K.N.; et al. Gaussian 09, Revision C.01; Gaussian, Inc: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Cui, W.; Chen, Q.A.; Tung, C.H.; Ji, M.J.; Zhang, F.S. The molecular mechanism studies of chirality effect of PHA-739358 on Aurora kinase A by molecular dynamics simulation and free energy calculations. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des 2011, 25, 171–180. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Yao, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, Y. Identification of novel potential beta-N-Acetyl-d-hexosaminidase inhibitors by virtual screening, molecular dynamics simulation and MM-PBSA calculations. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2012, 13, 4545–4563. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, G. Exploring the proton conductance and drug resistance of BM2 channel through molecular dynamics simulations and free energy calculations at different pH conditions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 982–988. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G. Computational studies of difference in binding modes of peptide and non-peptide inhibitors to MDM2/MDMX based on molecular dynamics simulations. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2012, 13, 2176–2195. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, T.G.; Mesick, H.C.; Darby, R.L. Numerical integration. Ann. Biomed. Eng 1977, 5, 322–328. [Google Scholar]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N log (N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar]
- Campanera, J.M.; Pouplana, R. MMPBSA decomposition of the binding energy throughout a molecular dynamics simulation of amyloid-beta (Aβ10–35) aggregation. Molecules 2010, 15, 2730–2748. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zan, J.; Yu, G.; Jiang, M.; Liu, P. A combination of 3D-QSAR, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation studies of benzimidazole-quinolinone derivatives as iNOS inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2012, 13, 11210–11227. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.-J.; Chong, F.-C. Combining Molecular docking and molecular dynamics to predict the binding modes of flavonoid derivatives with the neuraminidase of the 2009 H1N1 influenza a virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2012, 13, 4496–4507. [Google Scholar]
- Mongan, J.; Simmerling, C.; McCammon, J.A.; David, A.; Onufriev, A. Generalized Born model with a simple, robust molecular volume correction. J. Chem. Theory. Comput 2007, 3, 156–169. [Google Scholar]
- Connolly, M.L. Analytical molecular surface calculation. J. Appl. Cryst 1983, 16, 548–558. [Google Scholar]
- Gohlke, H.; Kiel, C. Case DA Insights into protein-protein binding by binding free energy calculation and free energy decomposition for the Ras-Raf and Ras-Ral GDS complexes. J. Mol. Biol 2003, 330, 891–913. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, M.; Ren, H.; Luo, F.; Zhang, S.; Qiu, J.; Ji, M.; Si, H.; Li, G. A computational study on thiourea analogs as potent MK-2 inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2012, 13, 7057–7079. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Che, T.; Xu, X. A descriptor of amino acids SVWG and its applications in peptide QSAR. J. Chemom 2012, 26, 549–555. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, J.; Liu, S. Three-dimensional holographic vector of atomic interaction field applied in QSAR of anti-HIV HEPT analogues. Qsar Comb. Sci 2008, 27, 330–337. [Google Scholar]



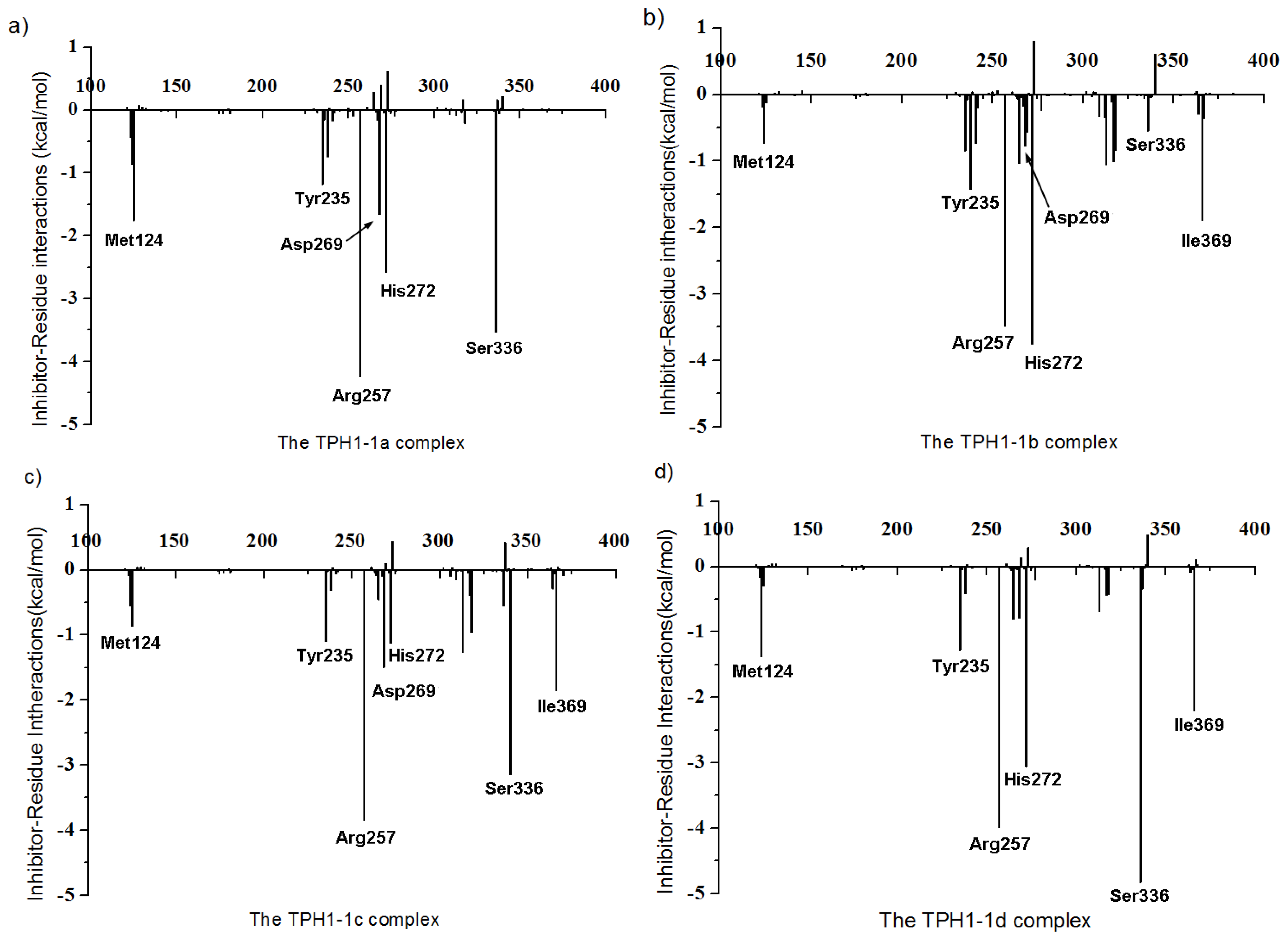
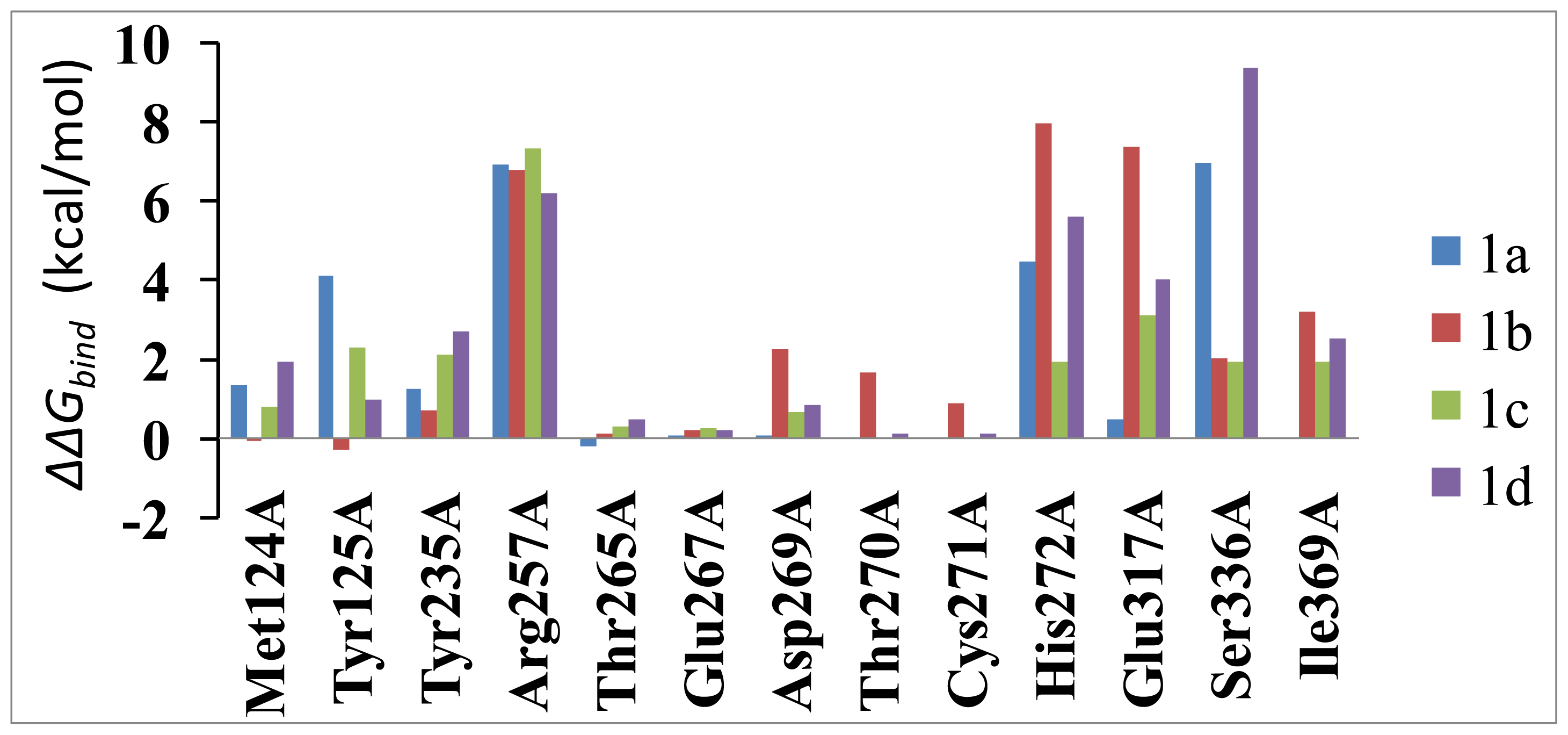
| Contribution | 1a | 1b | 1c | 1d |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −49.8 (0.82) | −45.7 (0.82) | −47.3 (0.85) | −52.5 (0.55) | |
| −42.8 (0.25) | −41.7 (0.45) | −49.3 (0.39) | −41.0 (0.37) | |
| −6.0 (0.02) | −7.677 (0.02) | −6.9 (0.03) | −6.6 (0.04) | |
| 66.9 (0.59) | 68.837 (0.52) | 69.2 (0.86) | 66.7 (0.67) | |
| ΔGsola | 60.9(0.58) | 61.2 (0.51) | 62.3 (0.84) | 60.1 (0.59) |
| ΔGeleb | 17.1 (0.38) | 23.1 (0.53) | 21.9 (0.58) | 14.2 (0.43) |
| −TΔS | −12.6 | −11.8 | −13.3 | −13.0 |
| ΔG bind | −46.2 (0.41) | −38.0 (0.39) | −47.6 (0.56) | −46.4 (0.33) |
| IC50(nM) | 32 | 380 | 26 | 44 |
| ΔGexpc | −42.7 | −36.6 | −43.3 | −42.0 |
| Inhibitor | Donor | AcceptorH | Acceptor | % Occupied | Distance (Ǻ) | Angle (Degree) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | DRG:O | 257:HH22 | 257:NH2 | 98.3 | 2.832 | 21.92 |
| 336:OG | DRG:H1 | DRG:N | 86.0 | 3.094 | 39.82 | |
| 333:O | DRG:H1 | DRG:N | 71.7 | 3.016 | 41.57 | |
| 317:OE2 | DRG:HAR | DRG:NAR | 17.3 | 3.046 | 18.62 | |
| 317:OE1 | DRG:HAR | DRG:NAR | 15.0 | 3.113 | 22.19 | |
| DRG:O | 265:HG1 | 265:OG1 | 11.7 | 3.003 | 31.25 | |
| 1b | 267:O | DRG:H1 | DRG:N | 80.7 | 2.899 | 30.02 |
| 317:OE1 | DRG:HAR | DRG:NAR | 74.7 | 2.834 | 31.52 | |
| DRG:OXT | 257:HH22 | 257:NH2 | 66.0 | 2.847 | 19.37 | |
| DRG:OXT | 257:HH12 | 257:NH1 | 37.3 | 3.161 | 42.36 | |
| DRG:O | 257:HH22 | 257:NH2 | 27.0 | 2.823 | 22.22 | |
| DRG:O | 257:HH12 | 257:NH1 | 17.7 | 3.243 | 43.09 | |
| 267:O | DRG:H2 | DRG:N | 10.0 | 2.990 | 33.24 | |
| 1c | DRG:O | 257:HH22 | 257:NH2 | 87.0 | 2.844 | 18.14 |
| DRG:O | 336:HG | 336:OG | 72.7 | 2.746 | 16.02 | |
| 333:O | DRG:H2 | DRG:N | 53.3 | 2.952 | 16.27 | |
| 340:OE2 | DRG:H1 | DRG:N | 52.3 | 2.731 | 37.99 | |
| 340:OE2 | DRG:H2 | DRG:N | 26.7 | 2.813 | 38.05 | |
| 333:O | DRG:H1 | DRG:N | 26.0 | 2.943 | 17.35 | |
| DRG:O | 257:HH12 | 257:NH1 | 20.0 | 3.224 | 43.44 | |
| 317:OE1 | DRG:HAR | DRG:NAR | 13.3 | 2.860 | 25.73 | |
| DRG:OXT | 257:HH12 | 257:NH1 | 10.0 | 3.227 | 24.00 | |
| DRG:OXT | 257:HH22 | 257:NH2 | 9.7 | 3.265 | 35.96 | |
| 235:OH | DRG:HAR | DRG:NAR | 8.0 | 3.165 | 40.77 | |
| 1d | DRG:O | 257:HH22 | 257:NH2 | 99.3 | 2.800 | 18.60 |
| 336:OG | DRG:H1 | DRG:N | 97.7 | 2.917 | 22.46 | |
| DRG:OXT | 337:HG | 337:OG | 32.3 | 2.655 | 19.75 | |
| 235:OH | DRG:HAR | DRG:NAR | 17.3 | 3.192 | 41.50 | |
| DRG:O | 257:HH12 | 257:NH1 | 12.7 | 3.363 | 49.29 | |
| 333:O | DRG:H1 | DRG:N | 6.0 | 3.234 | 56.37 | |
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, H.; Huang, W.; He, G.; Peng, C.; Wu, F.; Ouyang, L. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Tryptophan Hydroxylase-1: Binding Modes and Free Energy Analysis to Phenylalanine Derivative Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 9947-9962. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14059947
Zhong H, Huang W, He G, Peng C, Wu F, Ouyang L. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Tryptophan Hydroxylase-1: Binding Modes and Free Energy Analysis to Phenylalanine Derivative Inhibitors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(5):9947-9962. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14059947
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Hao, Wei Huang, Gu He, Cheng Peng, Fengbo Wu, and Liang Ouyang. 2013. "Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Tryptophan Hydroxylase-1: Binding Modes and Free Energy Analysis to Phenylalanine Derivative Inhibitors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 5: 9947-9962. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14059947
APA StyleZhong, H., Huang, W., He, G., Peng, C., Wu, F., & Ouyang, L. (2013). Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Tryptophan Hydroxylase-1: Binding Modes and Free Energy Analysis to Phenylalanine Derivative Inhibitors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(5), 9947-9962. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14059947





