Biocompatible PEGylated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles as Photothermal Agents for Near-Infrared Light Modulated Cancer Therapy
Abstract
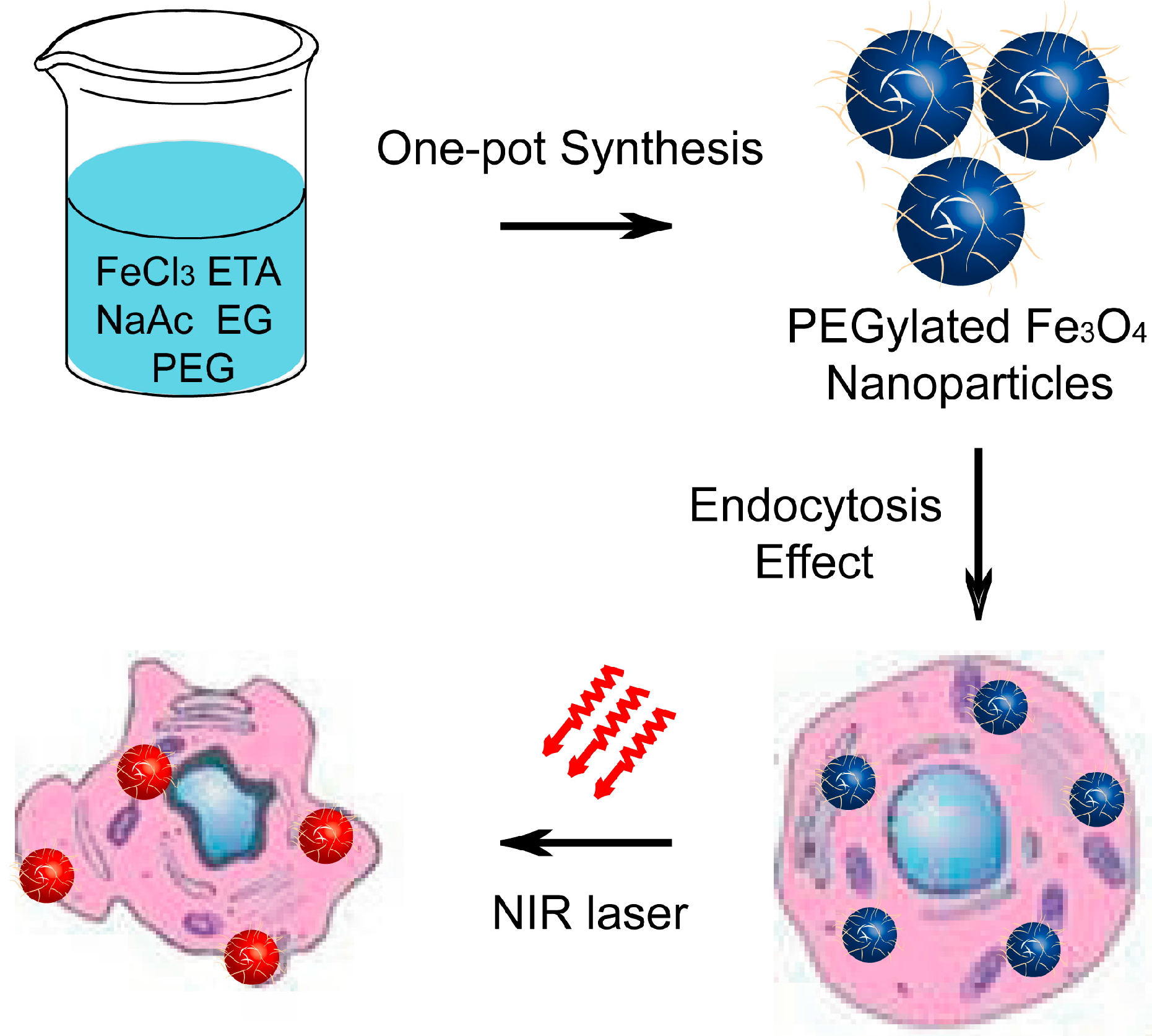
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion





3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Preparation of PEGylated Magnetic Nanoparticles
3.3. Measurements and Characterizations
3.4. Cell Cultures
3.5. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Studies
3.6. Enhanced Temperature Measure
3.7. In Vitro Photothermal Toxicity of PEG–Fe3O4
3.8. Fluorescence Microscopy Analysis
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, J.; Piao, Y.; Hyeon, T. Multifunctional nanostructured materials for multimodal imaging, and simultaneous imaging and therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 372–390. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, Y.; Seo, J.; Cheon, J. Nanoscaling laws for magnetic nanoparticles and their applications in biomedical sciences. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 179–189. [Google Scholar]
- Bardhan, R.; Lal, S.; Joshi, A.; Halas, N. Theranostic nanoshells: Form probe design to imaging and treatment of cancer. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 936–946. [Google Scholar]
- Idris, N.; Gnanasammandhan, M.; Zhang, J.; Ho, P.; Mahenndran, R.; Zhang, Y. In vivo photodynamic therapy using upconversion nanoparticles as remote-controlled nanostransducers. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1580–1585. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Q.; Zheng, X.; Bu, W.; Ge, W.; Zhang, S.; Chen, F.; Xing, H.; Ren, Q.; Fan, W.; Zhao, K.; et al. A core/satellite multifunctional nanotheranostic for in vivo imaging and tumor eeadication by radiation/photothermal synergistic therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 13041–13048. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, K.; Huang, C.; Hwu, J.; Su, W.; Shieh, D.; Yeh, C. A new photothermal therapeutic agent: core-free nanostructured AuxAg1–x dendrites. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 2956–2964. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Tsai, P.; Chen, Y. Multifunctional Fe3O4@Au nanoeggs as photothermal agents for selective killing of nosocomial and antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Small 2009, 5, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, S.; Kim, B.; Joe, A.; Han, H.; Chen, X.; Cheng, Z.; Jang, E. NIR-light-induced surface-enhanced raman scattering for detection and photothermal/photodynamic therapy of cancer cells using methylene blue-embedded gold nanorod@SiO2 nanocomposites. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 3309–3318. [Google Scholar]
- Loo, C.; Lowery, A.; Halas, N.; West, J.; Drezek, R. Immunotargeted nanoshells for integrated cancer imaging and therapy. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 709–711. [Google Scholar]
- Sherlock, S.; Dai, H. Multifunctional FeCo-graphitic carbon nanocrystals for combined imaging, drug delivery and tumor-specific photothermal therapy in mice. Nano Res. 2011, 4, 1248–1260. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Jiang, X.; Li, X.; Hu, Z.; Ji, Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, C. Mesoporous silica-coated gold nanorods as a light-mediated multifunctional theranostic platform for ancer treatment. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1418–1423. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Wan, J.; Zhang, S.; Tian, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. The influence of surface chemistry and size of nanoscale graphene oxide on photothermal therapy of cancer using ultra-low laser power. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 2206–2214. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Zhang, R.; Huang, M.; Lu, W.; Song, S.; Melancon, M.; Tian, M.; Liang, D.; Li, C. A chelator-free multifunctional [64Cu]CuS nanoparticl platform for simultaneous micro-PET/CT imaging and photothermal ablation therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 15351–15358. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, J.; Hong, G.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yaghi, O.; Dai, H. In vivo fluorescence imaging in the second near-infrared window with long circulating carbon nanotubes capable of ultrahigh tumor uptake. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 10664–10669. [Google Scholar]
- Lal, S.; Clare, S.; Halas, N. Nanoshell-enabled photothermal cancer therapy: Impending clinical impact. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1842–1851. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ai, K.; Liu, J.; Deng, M.; He, Y.; Lu, L. Dopamine-melanin colloidal nanospheres: An efficient near-infrared photothermal therapeutic agent for in vivo cancer therapy. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Xu, H.; Cheng, L.; Sun, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z. In vitro and in vivo near-infrared photothermal therapy of cancer using polypyrrole organic nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 5586–5592. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Chen, D.; Li, L.; Liu, T.; Tan, L.; Wu, X.; Tang, F. Multifunctional gold nanoshells on silica nanorattles: A platform for the combination of photothermal therapy and chemotherapy with low systemic toxicity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 891–895. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Su, C.; Li, W.; Liu, T.; Chen, J.; Yeh, C. Bifunctional Gd2O3/C nanoshells for MR imaging and NIR therapeutic applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 249–258. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Song, G.; Song, L.; Hu, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Zhu, M.; et al. Ultrathin PEGylated W18O49 nanowires as a new 980 nm-laser-driven photothermal agent for efficient ablation of cancer cells in vivo. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2095–2100. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, J.; Yu, M.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, K.; Jia, Y.; Gao, X.; Chen, C.; Wei, T. The inhibition of migration and invasion of cancer cells by graphene via the impairment of mitochondrial respiration. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 1597–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, A.; Salabas, E.; Schüth, F. Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1222–1244. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, N.; Cho, H.; Oh, M.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.; Kim, B.; Shin, K.; Ahn, T.; Choi, J.; Kim, Y.; et al. Multifunctional Fe3O4/TaOx core/shell nanoparticles for simultaneous magnetic resonance imaging and X-ray computed tomography. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 10309–10312. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Li, M.; Li, Z.; Pu, F.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Easy access to selective binding and recyclable separation of histidine-tagged proteins using Ni2+-decorated superparamagnetic nanoparticles. Nano Res. 2012, 5, 450–459. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Chen, K.; Noh, S.; Garcia, M.; Wang, H.; Lin, W.; Jeong, H.; Kong, B.; Stout, D.; Cheon, J.; et al. On-demand drug release system for in vivo cancer treatment through self-assembled magnetic nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4384–4388. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Quan, Z.; Hou, Z.; Li, C.; Kang, X.; Cheng, Z.; Lin, J. A magnetic, luminescent and mesoporous core-shell structured composite materials as drug carrier. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 4786–4795. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Liu, G.; Eden, H.; Ai, H.; Chen, X. Surface-engineered magnetic nanoparticle platforms for cancer imaging and therapy. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 883–892. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.; Lee, N.; Kim, H.; An, K.; Prak, Y.; Choi, Y.; Shin, K.; Lee, Y.; Kwon, S.; Na, H.; et al. Large-scale synthesis of uniform and extremely small-sized iron oxide nanoparticles for high-resolution T1 magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 12624–12631. [Google Scholar]
- Kievit, F.; Zhang, M. Surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 853–862. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, Y.; Lee, J.; Cheon, J. Chemical design of nanoparticle probes for high-performance magnetic resonance imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 5122–5135. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C.; Ting, C.; Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Yen, T.; Yeh, C. SPIO-conjugated, doxorubicin-loaded microbubbles for concurrent MRI and focused-ultrasound enhanced brain-tumor drug delivery. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 3706–3715. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, T.; Li, P.; Tseng, T.; Chen, Y. Multifunctional Fe3O4/alumina core/shell MNPs as photothermal agents for targeted hyperthermia of nosocomial and antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, M.; Lai, P.; Yu, H.; Lin, H.; Huang, C. Innovative ligand-assisted synthesis of NIR-activated iron oxide for cancer theranostics. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 5319–5321. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, M.; Shao, Y.; Peng, J.; Dai, X.; Li, H.; Wu, Q.; Shi, D. Near-infrared laser light mediated cancer therapy by photothermal effect of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 4078–4088. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.; Li, X.; Peng, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Li, Y. Monodisperse magnetic single-crystal ferrite microshperes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 2782–2785. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Li, M.; Yang, X.; Yin, M.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. The use of multifunctional magnetic mesoporous core/shell heteronanostructures in a biomolecule separation system. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 4683–4690. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Lei, J.; Tian, Y. Uniform iron oxide hollow spheres for high-performance delivery of insoluble anticancer drugs. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 7275. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Sun, Z.; Deng, Y.; Zou, Y.; Li, C.; Guo, X.; Xiong, L.; Gao, Y.; Li, F.; Zhao, D. Highly water-dispersible biocompatible magnetite particles with low cytotoxicity stabilized by citrate groups. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 5875–5879. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Z.; Wei, W.; You, Z.; Yang, Q.; Yue, H.; Su, Z.; Ma, G. Iron oxide nanotubes for magneticall guided delivery and pH-activated release of insoluble anticancer drugs. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 3446–3453. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Yang, X.; Ren, J.; Qu, K.; Qu, X. Using graphene oxide high near-infrared absorbance for photothermal treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1722–1728. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Kuo, L.; Chang, C.; Hwu, Y.; Huang, C.; Lee, S.; Chen, K.; Lin, S.; Huang, J.; Chen, Y. In situ real-time investigation of cancer cell photothermolysis mediated by excited gold nanorod surface plasmons. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4104–4112. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Kuo, L.; Lee, S.; Hwu, Y.; Chou, S.; Chen, C.; Chang, F.; Lin, K.; Tsai, D.; Chen, Y. Photothermal cancer therapy via femtosecond-laser-excited FePt nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 1128–1134. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, G.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, K.; Luo, Q. Biocompatible PEGylated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles as Photothermal Agents for Near-Infrared Light Modulated Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 18776-18788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151018776
Yuan G, Yuan Y, Xu K, Luo Q. Biocompatible PEGylated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles as Photothermal Agents for Near-Infrared Light Modulated Cancer Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(10):18776-18788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151018776
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Gang, Yongjie Yuan, Kan Xu, and Qi Luo. 2014. "Biocompatible PEGylated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles as Photothermal Agents for Near-Infrared Light Modulated Cancer Therapy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 10: 18776-18788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151018776
APA StyleYuan, G., Yuan, Y., Xu, K., & Luo, Q. (2014). Biocompatible PEGylated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles as Photothermal Agents for Near-Infrared Light Modulated Cancer Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(10), 18776-18788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151018776



