Genes and Gene Networks Involved in Sodium Fluoride-Elicited Cell Death Accompanying Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Oral Epithelial Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Effects of Sodium Fluoride (NaF) on Cell Number and Cell Viability in Oral Epithelial ROE2 Cells
2.2. The Effects of NaF on Protein Content, Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP) and Cell Death in ROE2 Cells
2.3. Global Gene Expression and Cluster Analyses
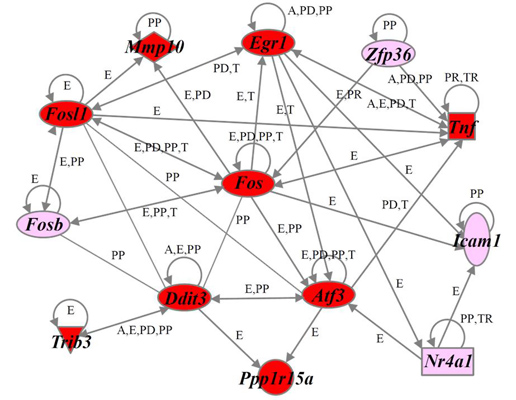
2.4. Identification of Gene Functions and Gene Networks
2.5. Verification of Differentially Expressed Genes
2.6. Effects of Knockdown of Hspa5 and Ddit3 on Cell Viability
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Incubation of Cells with the Compound
4.3. Measurements of Cell Number, Cell Viability and Cell Death
4.4. Measurements of Protein Content and MMP
4.5. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and Western Blotting
4.6. RNA Isolation
4.7. Microarray and Pathway Analyses
4.8. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
4.9. siRNA Transfection
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
- Author ContributionsY.T. and N.H. designed the experiments. Y.T. and T.Y. performed the experiments. Y.T. and T.Y. analyzed the data. N.H., N.S. and T.K. contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools. Y.T. wrote the paper.
References
- Barbier, O.; Arreola-Mendoza, L.; del Razo, L.M. Molecular mechanisms of fluoride toxicity. Chem. Biol. Interact 2010, 188, 319–333. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, A.L.; Sun, G.; Zhang, Y.; Grandjean, P. Developmental fluoride neurotoxicity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Health Perspect 2012, 120, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Denbesten, P.; Li, W. Chronic fluoride toxicity: Dental fluorosis. Monogr. Oral Sci 2012, 22, 81–96. [Google Scholar]
- Whitford, G.M. The physiological and toxicological characteristics of fluoride. J. Dent. Res 1990, 69, 539–549. [Google Scholar]
- Gabler, W.L. Absorption of fluoride through the oral mucosa of rats. Arch. Oral Biol 1968, 13, 619–623. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.F.; Chen, J.G. DNA damage, apoptosis and cell cycle changes induced by fluoride in rat oral mucosal cells and hepatocytes. World J. Gastroenterol 2006, 12, 1144–1148. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, C.L.; Lin, J.W.; Kuo, H.K.; Tai, M.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Shyr, C.R.; Wu, P.C. Induction of apoptosis in rabbit oral mucosa by 1.23% acidulated phosphate fluoride gel. Arch. Toxicol 2008, 82, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Jeng, J.H.; Hsieh, C.C.; Lan, W.H.; Chang, M.C.; Lin, S.K.; Hahn, L.J.; Kuo, M.Y. Cytotoxicity of sodium fluoride on human oral mucosal fibroblasts and its mechanisms. Cell Biol. Toxicol 1998, 14, 383–389. [Google Scholar]
- Kubota, K.; Lee, D.H.; Tsuchiya, M.; Young, C.S.; Everett, E.T.; Martinez-Mier, E.A.; Snead, M.L.; Nguyen, L.; Urano, F.; Bartlett, J.D. Fluoride induces endoplasmic reticulum stress in ameloblasts responsible for dental enamel formation. J. Biol. Chem 2005, 280, 23194–23202. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.; Tsuchiya, M.; Bartlett, J.D. Fluoride induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and inhibits protein synthesis and secretion. Environ. Health Perspect 2008, 116, 1142–1146. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Wang, Z.; Farquharson, C.; Alkasir, R.; Zahra, M.; Ren, G.; Han, B. Sodium fluoride induces apoptosis and alters bcl-2 family protein expression in MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2011, 410, 910–915. [Google Scholar]
- Hirano, S.; Ando, M. Fluoride mediates apoptosis in osteosarcoma UMR 106 and its cytotoxicity depends on the pH. Arch. Toxicol 1997, 72, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen Ngoc, T.D.; Son, Y.O.; Lim, S.S.; Shi, X.; Kim, J.G.; Heo, J.S.; Choe, Y.; Jeon, Y.M.; Lee, J.C. Sodium fluoride induces apoptosis in mouse embryonic stem cells through ROS-dependent and caspase- and JNK-mediated pathways. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol 2012, 259, 329–337. [Google Scholar]
- Sano, R.; Reed, J.C. ER stress-induced cell death mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Kaufman, R.J. From acute ER stress to physiological roles of the unfolded protein response. Cell Death Differ 2006, 13, 374–384. [Google Scholar]
- Gass, J.N.; Gifford, N.M.; Brewer, J.W. Activation of an unfolded protein response during differentiation of antibody-secreting B cells. J. Biol. Chem 2002, 277, 49047–49054. [Google Scholar]
- Zinszner, H.; Kuroda, M.; Wang, X.; Batchvarova, N.; Lightfoot, R.T.; Remotti, H.; Stevens, J.L.; Ron, D. CHOP is implicated in programmed cell death in response to impaired function of the endoplasmic reticulum. Genes Dev 1998, 12, 982–995. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Gao, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhao, L.; Sun, D. Excessive fluoride induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and interferes enamel proteinases secretion. Environ. Toxicol 2013, 28, 332–341. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.L.; Shi, H.Y.; Li, X.N.; Lv, P.; Li, G.S.; Liu, Q.Y.; Xu, H. Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in aberrant activation of fluoride-treated osteoblasts. Biol. Trace Elem. Res 2013, 154, 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Wurtz, T.; Houari, S.; Mauro, N.; MacDougall, M.; Peters, H.; Berdal, A. Fluoride at non-toxic dose affects odontoblast gene expression in vitro. Toxicology 2008, 249, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Hao, Y.Q.; Li, J.Y.; Zhou, X.D. Gene expression profiles of the incisor pulp tissue during fluorosis. Int. Endod. J 2010, 43, 629–636. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Niu, R.; Wang, B.; Jiao, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, J. Fluoride-induced apoptosis and gene expression profiling in mice sperm in vivo. Arch. Toxicol. 2011, 85, 1441–1452. [Google Scholar]
- Tabuchi, Y.; Furusawa, Y.; Kariya, A.; Wada, S.; Ohtsuka, K.; Kondo, T. Common gene expression patterns responsive to mild temperature hyperthermia in normal human fibroblastic cells. Int. J. Hyperth 2013, 29, 38–50. [Google Scholar]
- Tabuchi, Y.; Sugahara, Y.; Ikegame, M.; Suzuki, N.; Kitamura, K.; Kondo, T. Genes responsive to low-intensity pulsed ultrasound in MC3T3-E1 preosteoblast cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2013, 14, 22721–22740. [Google Scholar]
- Tabuchi, Y.; Wada, S.; Ikegame, M.; Kariya, A.; Furusawa, Y.; Hoshi, N.; Yunoki, T.; Suzuki, N.; Takasaki, I.; Kondo, T.; et al. Development of an oral epithelial cell line ROE2 with differentiation potential from transgenic rats harboring temperature-sensitive simian virus 40 large T-antigen. Exp. Anim 2014, 63, 31–44. [Google Scholar]
- Smiley, S.T.; Reers, M.; Mottola-Hartshorn, C.; Lin, M.; Chen, A.; Smith, T.W.; Steele, G.D., Jr.; Chen, L.B. Intracellular heterogeneity in mitochondrial membrane potentials revealed by a J-aggregate-forming lipophilic cation JC-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 3671–3675. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes-Alnemri, T.; Litwack, G.; Alnemri, E.S. CPP32, a novel human apoptotic protein with homology to Caenorhabditis elegans cell death protein Ced-3 and mammalian interleukin-1 β-converting enzyme. J. Biol. Chem 1994, 269, 30761–30764. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, S.L.; Fu, W.; Zhang, P.; Cheng, A.; Lee, J.; Kokame, K.; Mattson, M.P. Herp stabilizes neuronal Ca2+ homeostasis and mitochondrial function during endoplasmic reticulum stress. J. Biol. Chem 2004, 279, 28733–28743. [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak, S.J.; Yun, C.Y.; Oyadomari, S.; Novoa, I.; Zhang, Y.; Jungreis, R.; Nagata, K.; Harding, H.P.; Ron, D. CHOP induces death by promoting protein synthesis and oxidation in the stressed endoplasmic reticulum. Genes Dev 2004, 18, 3066–3077. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, X.; Piao, J.H.; Nakajima, A.; Sakon-Komazawa, S.; Kojima, Y.; Mori, K.; Yagita, H.; Okumura, K.; Harding, H.; Nakano, H. Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) induces the unfolded protein response (UPR) in a reactive oxygen species (ROS)-dependent fashion, and the UPR counteracts ROS accumulation by TNFα. J. Biol. Chem 2005, 280, 33917–33925. [Google Scholar]
- Outinen, P.A.; Sood, S.K.; Pfeifer, S.I.; Pamidi, S.; Podor, T.J.; Li, J.; Weitz, J.I.; Austin, R.C. Homocysteine-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and growth arrest leads to specific changes in gene expression in human vascular endothelial cells. Blood 1999, 94, 959–967. [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa, T.; Zhu, H.; Morishima, N.; Li, E.; Xu, J.; Yankner, B.A.; Yuan, J. Caspase-12 mediates endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptosis and cytotoxicity by amyloid-β. Nature 2000, 403, 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Sorli, S.C.; Colié, S.; Albinet, V.; Dubrac, A.; Touriol, C.; Guilbaud, N.; Bedia, C.; Fabriàs, G.; Casas, J.; Ségui, B.; et al. The nonlysosomal β-glucosidase GBA2 promotes endoplasmic reticulum stress and impairs tumorigenicity of human melanoma cells. FASEB J 2013, 27, 489–498. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumori, M.; Itoh, H.; Toyoshima, I.; Komatsuda, A.; Sawada, K.; Fukuda, J.; Tanaka, T.; Okubo, A.; Kinouchi, H.; Mizoi, K.; et al. Characterization of the 105-kDa molecular chaperone. Identification, biochemical properties, and localization. Eur. J. Biochem 2002, 269, 5632–5641. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.; Wolfgang, C.D.; Hai, T. Activating transcription factor 3, a stress-inducible gene, suppresses Ras-stimulated tumorigenesis. J. Biol. Chem 2006, 281, 10473–10481. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.H.; Chiu, W.T.; Wang, Y.K.; Wu, C.C.; Chen, T.L.; Teng, C.F.; Chang, W.T.; Chang, H.C.; Tang, M.J. Deregulation of AP-1 proteins in collagen gel-induced epithelial cell apoptosis mediated by low substratum rigidity. J. Biol. Chem 2007, 282, 752–763. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, T.; Tsujimura, T.; Takeda, K.; Sugihara, A.; Maekawa, A.; Terada, N.; Yoshida, N.; Akira, S. Targeted disruption of ATF4 discloses its essential role in the formation of eye lens fibres. Genes Cells 1998, 3, 801–810. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Chan, L.; Lee, A.S. Novel mechanism of anti-apoptotic function of 78-kDa glucose-regulated protein (GRP78): Endocrine resistance factor in breast cancer, through release of B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) from BCL-2-interacting killer (BIK). J. Biol. Chem 2011, 286, 25687–25696. [Google Scholar]
- Bjørkøy, G.; Lamark, T.; Brech, A.; Outzen, H.; Perander, M.; Overvatn, A.; Stenmark, H.; Johansen, T. p62/SQSTM1 forms protein aggregates degraded by autophagy and has a protective effect on huntingtin-induced cell death. J. Cell Biol 2005, 171, 603–614. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura, Y.; Hua, X.; Bergelson, S.; Lodish, H.F. Critical role of Smads and AP-1 complex in transforming growth factor-β-dependent apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem 2000, 275, 36295–36302. [Google Scholar]
- Shirsat, N.V.; Shaikh, S.A. Overexpression of the immediate early gene fra-1 inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis, and reduces tumourigenicity of c6 glioma cells. Exp. Cell Res 2003, 291, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, J.R.; Keating, A.E. Comprehensive identification of human bZIP interactions with coiled-coil arrays. Science 2003, 300, 2097–2101. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.P.; Wolfgang, C.D.; Hai, T. Analysis of ATF3, a transcription factor induced by physiological stresses and modulated by gadd153/Chop10. Mol. Cell Biol 1996, 16, 1157–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Ohoka, N.; Yoshii, S.; Hattori, T.; Onozaki, K.; Hayashi, H. TRB3, a novel ER stress-inducible gene, is induced via ATF4–CHOP pathway and is involved in cell death. EMBO J 2005, 24, 1243–1255. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, D.; Su, Z.Z.; Lebedeva, I.V.; Sauane, M.; Gopalkrishnan, R.V.; Valerie, K.; Dent, P.; Fisher, P.B. mda-7 (IL-24) Mediates selective apoptosis in human melanoma cells by inducing the coordinated overexpression of the GADD family of genes by means of p38 MAPK. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 10054–10059. [Google Scholar]
- Szczepański, M.; Kamianowska, M.; Kamianowski, G. Effects of fluorides on apoptosis and activation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Oral Dis 2012, 18, 280–284. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, E.; Vollmer, J.Y.; Bovey, R.; Stamenkovic, I. Matrix metalloproteinases 9 and 10 inhibit protein kinase C-potentiated, p53-mediated apoptosis. Cancer Res 2005, 65, 4261–4272. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.W.; Ma, L.; Yan, X.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X.K.; Cohen, P. Rapid apoptosis induction by IGFBP-3 involves an insulin-like growth factor-independent nucleomitochondrial translocation of RXRalpha/Nur77. J. Biol. Chem 2005, 280, 16942–16948. [Google Scholar]
- Sidoti-de Fraisse, C.; Rincheval, V.; Risler, Y.; Mignotte, B.; Vayssière, J.L. TNF-α activates at least two apoptotic signaling cascades. Oncogene 1998, 17, 1639–1651. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, B.A.; Blackwell, T.K. Multiple tristetraprolin sequence domains required to induce apoptosis and modulate responses to TNFα through distinct pathways. Oncogene 2002, 21, 4237–4246. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Zhou, Y.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Lu, P.; Li, G.S. Activation of PERK signaling through fluoride-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress in OS732 cells. Toxicology 2010, 277, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Q.; Liu, H.; Guan, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Guo, S.; He, P.; Guo, L.; Gao, P.; Xu, B.; Xu, Z.; et al. The effect of c-Fos demethylation on sodium fluoride-induced apoptosis in L-02 cells. Biol. Trace Elem. Res 2012, 149, 102–109. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Jiang, C.; Liu, H.; Guan, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Zhang, C.; Lei, R.; Xia, T.; Gao, H.; Yang, L.; et al. Fluoride-elicited developmental testicular toxicity in rats: Roles of endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammatory response. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol 2013, 271, 206–215. [Google Scholar]
- Ishiyama, M.; Miyazono, Y.; Sasamoto, K.; Ohkura, Y.; Ueno, K. A highly water-soluble disulfonated tetrazolium salt as a chromogenic indicator for NADH as well as cell viability. Talanta 1997, 44, 1299–1305. [Google Scholar]
- Yunoki, T.; Kariya, A.; Kondo, T.; Hayashi, A.; Tabuchi, Y. The combination of silencing BAG3 and inhibition of the JNK pathway enhances hyperthermia sensitivity in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett 2013, 335, 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar]
- Towbin, H.; Staehelin, T.; Gordon, J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: Procedure and some applications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 4350–4354. [Google Scholar]










| Clusters Functions | Genes |
|---|---|
| Up-I | |
| Pro-cell death 1 | Atf3, Ddit3, Egr1, Fos, Fosb, Fosl1, Gch1, Hbegf, Icam1, Mmp10, Nedd9, Nr4a1, Ppp1r15a, Rassf1, Tnf, Trib3, Zfp36, VGF |
| Anti-cell death 2 | Abcb4, Areg, Bdkrb2, Clcf1, Dusp1, Egr2, Gdf15, Herpud1, Il6, Itsn1, Nr4a2, Nr4a3, Plaur, Procr, Sema6a, Tslp, Vegfa, Zmynd15 |
| Up-II | |
| Pro-cell death | Abcb1, Atf2, Casp4, Casp12, Cxcl12, Fem1b, Il23a, Mllt11, Nrg1, Per1, Slscr1, Ppif, S100a8, Smox, Surf1, Tfrc, Zc3h8 |
| Anti-cell death | Alkbh1, Atf4, Atp2b1, Bcl2a1, Cd55, Cdhr1, Cflar, Csf3, Dnajb9, Ehd4, Hspa5, Hyou1, Itgav, Lin7c, Lonp1, Mafk, Manf, Naa30, Nabp1, Odc1, Plaur, Rbbp6, Rbpj, Slc1a1, Slc25a19, Slc29a2, Sqstm1, Thbd |
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Tabuchi, Y.; Yunoki, T.; Hoshi, N.; Suzuki, N.; Kondo, T. Genes and Gene Networks Involved in Sodium Fluoride-Elicited Cell Death Accompanying Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Oral Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 8959-8978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15058959
Tabuchi Y, Yunoki T, Hoshi N, Suzuki N, Kondo T. Genes and Gene Networks Involved in Sodium Fluoride-Elicited Cell Death Accompanying Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Oral Epithelial Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(5):8959-8978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15058959
Chicago/Turabian StyleTabuchi, Yoshiaki, Tatsuya Yunoki, Nobuhiko Hoshi, Nobuo Suzuki, and Takashi Kondo. 2014. "Genes and Gene Networks Involved in Sodium Fluoride-Elicited Cell Death Accompanying Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Oral Epithelial Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 5: 8959-8978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15058959
APA StyleTabuchi, Y., Yunoki, T., Hoshi, N., Suzuki, N., & Kondo, T. (2014). Genes and Gene Networks Involved in Sodium Fluoride-Elicited Cell Death Accompanying Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Oral Epithelial Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(5), 8959-8978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15058959