miR-143 Inhibits NSCLC Cell Growth and Metastasis by Targeting Limk1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. miR-143 Is Downregulated in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Tissues and Cell Lines

| Variable | N | Low | High | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 0.161 a | |||
| ≥60 | 14 | 8 | 6 | |
| <60 | 10 | 6 | 4 | |
| Gender | 0.542 a | |||
| Male | 11 | 6 | 5 | |
| Female | 13 | 7 | 6 | |
| Size | 0.231 a | |||
| >3 cm | 14 | 8 | 6 | |
| ≤3 cm | 10 | 4 | 6 | |
| Histology type | 0.416 a | |||
| Adenocarcinoma | 13 | 6 | 7 | |
| Squamous cancer | 11 | 6 | 5 | |
| Histological grade | 0.214 b | |||
| I | 11 | 5 | 7 | |
| II | 6 | 4 | 2 | |
| III | 7 | 4 | 3 | |
| Lymph node status | 0.024 a | |||
| Metastasis | 13 | 9 | 4 | |
| No Metastasis | 11 | 3 | 8 |
2.2. miR-143 Suppresses the Proliferation of NSCLC Cells
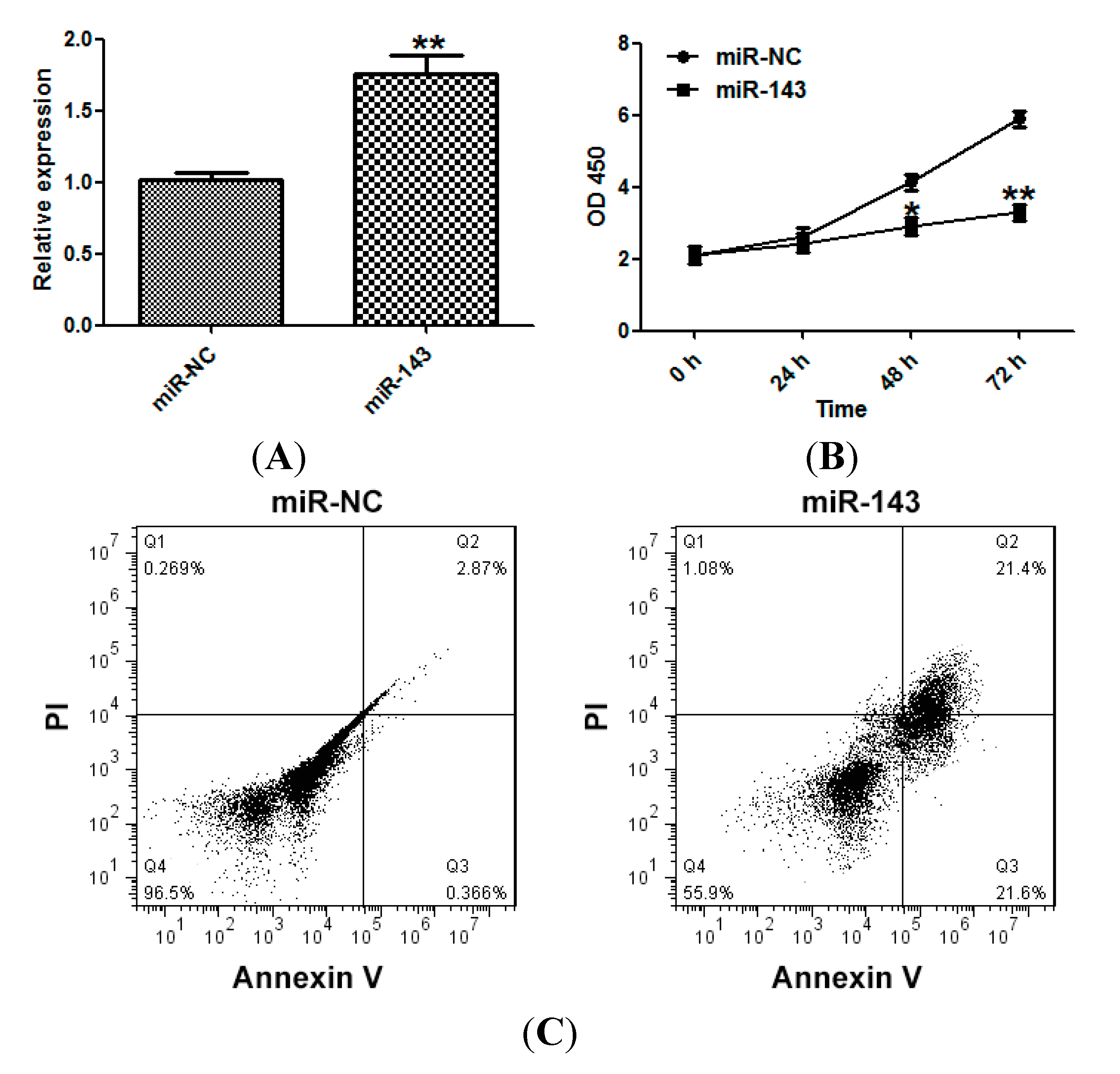
2.3. miR-143 Suppresses Migration and Invasion of NSCLC Cells

2.4. LIM Domain Kinase 1 (Limk1) Is a Direct Target of miR-143 in NSCLC Cells

2.5. miR-143 Suppresses NSCLC Development by Targeting Limk1

3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Clinical Samples and Cell Lines
4.2. RNA Preparation and Quantitative Real Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.3. Plasmid Construction
4.4. Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis Assays
4.5. Cell Migration and Invasion Assays
4.6. Western Blot
4.7. Luciferase Reporter Assays
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.; Xu, J.; Ward, E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2010, 60, 277–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdecchia, A.; Francisci, S.; Brenner, H.; Gatta, G.; Micheli, A.; Mangone, L.; Kunkler, I.; Group, E.-W. Recent cancer survival in Europe: A 2000-02 period analysis of EUROCARE-4 data. Lancet Oncol. 2007, 8, 784–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Nie, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, G.; Huang, Q.; Cao, J.; Du, Y.; Li, J.; Deng, R.; Huang, D. MicroRNA-181a functions as an oncomir in gastric cancer by targeting the tumour suppressor gene ATM. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2014, 20, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongchun, Z.; Linwei, T.; Xicai, W.; Lianhua, Y.; Guangqiang, Z.; Ming, Y.; Guangjian, L.; Yujie, L.; Yunchao, H. MicroRNA-195 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting MYB. Cancer Lett. 2014, 347, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, H.; Wu, J.; Zhu, X.; Yuan, J.; Li, M. miR-503 targets PI3K p85 and IKK-β and suppresses progression of non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Cancer. 2014. Available online: onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ijc.28799/abstract (accessed on 3 March 2014). [CrossRef]
- Fiori, M.E.; Barbini, C.; Haas, T.L.; Marroncelli, N.; Patrizii, M.; Biffoni, M.; de Maria, R. Antitumor effect of miR-197 targeting in p53 wild-type lung cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Zhang, L.; Fan, K.; Wang, J. miR-27b targets Limk1 to inhibit growth and invasion of NSCLC cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 390, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Zheng, T.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Z. miR-96 downregulates RECK to promote growth and motility of non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 390, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Huang, Y.; Gong, W. Inhibition of miR-92b suppresses nonsmall cell lung cancer cells growth and motility by targeting RECK. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 387, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wei, X.; Xu, L. miR-150 promotes the proliferation of lung cancer cells by targeting p53. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 2346–2351. [Google Scholar]
- Kojima, S.; Enokida, H.; Yoshino, H.; Itesako, T.; Chiyomaru, T.; Kinoshita, T.; Fuse, M.; Nishikawa, R.; Goto, Y.; Naya, Y. The tumor-suppressive microRNA-143/145 cluster inhibits cell migration and invasion by targeting GOLM1 in prostate cancer. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 59, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Yu, J.; Yin, Y.; He, J.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.Q.; Li, C.Y.; Shi, Z.M.; Xu, Q. microRNA-143 inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis and sensitizes chemosensitivity to oxaliplatin in colorectal cancers. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, E.K.; Li, R.; Shin, V.Y.; Siu, J.M.; Ma, E.S.; Kwong, A. MicroRNA-143 is down-regulated in breast cancer and regulates DNA methyltransferases 3A in breast cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 2013, 35, 2591–2598. [Google Scholar]
- Mallick, R.; Patnaik, S.K.; Yendamuri, S. MicroRNAs and lung cancer: Biology and applications in diagnosis and prognosis. J. Carcinog. 2010, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanaihara, N.; Caplen, N.; Bowman, E.; Seike, M.; Kumamoto, K.; Yi, M.; Stephens, R.M.; Okamoto, A.; Yokota, J.; Tanaka, T. Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Su, Y.; Xu, L. Targeting PKCepsilon by miR-143 regulates cell apoptosis in lung cancer. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 3661–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Pu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Ye, S.; Wu, S.; Zhong, G.; Ren, J. microRNA-143 inhibits migration and invasion of human non-small-cell lung cancer and its relative mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 9, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Lian, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Gu, J.; He, X.; Xie, L. Application of microRNA and mRNA expression profiling on prognostic biomarker discovery for hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Gen. 2014, 15, S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicentini, C.; Fassan, M.; D’Angelo, E.; Corbo, V.; Silvestris, N.; Nuovo, G.J.; Scarpa, A. Clinical application of microrna testing in neuroendocrine tumors of the gastrointestinal tract. Molecules 2014, 19, 2458–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.L.; Zhang, S.Y.; Zheng, J.F.; Yuan, H.; Wang, Y. Altered miR-143 and miR-150 expressions in peripheral blood mononuclear cells for diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Chin. Med. J. 2013, 126, 4510–4516. [Google Scholar]
- Takagi, T.; Iio, A.; Nakagawa, Y.; Naoe, T.; Tanigawa, N.; Akao, Y. Decreased expression of microRNA-143 and -145 in human gastric cancers. Oncology 2009, 77, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, N.I.; Reis, S.T.; Dip, N.G.; Morais, D.R.; Moura, C.M.; Silva, I.A.; Katz, B.; Srougi, M.; Leite, K.R.; Antunes, A.A. MicroRNAs 143 and 145 may be involved in benign prostatic hyperplasia pathogenesis through regulation of target genes and proteins. Int. J Biol. Markers. [Online early access]. Available online: http://www.biological-markers.com/article/micrornas-143-and-145-may-be-involved-in-benign-prostatic-hyperplasia-pathogenesis-through-regulation-of-target-genes-and-proteins (accessed on 22 January 2014). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, Y.; Ti, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, B. Down-regulation of miR-145 and miR-143 might be associated with DNA methyltransferase 3B overexpression and worse prognosis in endometrioid carcinomas. Hum. Pathol. 2013, 44, 2571–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.C.; Chow, A.S.; Au, J.S. Restoration of tumour suppressor hsa-miR-145 inhibits cancer cell growth in lung adenocarcinoma patients with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 2197–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zeng, H.; Guo, Y.; Liu, P.; Pan, H.; Deng, A.; Hu, J. miRNA-145 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation by targeting c-Myc. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 29, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Doherty, J.; Antonipillai, J.; Chen, S.; Devlin, M.; Visser, K.; Baell, J.; Street, I.; Anderson, R.L.; Bernard, O. LIM kinase inhibition reduces breast cancer growth and invasiveness but systemic inhibition does not reduce metastasis in mice. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2013, 30, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Jiao, D.; Hu, H.; Song, J.; Yan, J.; Wu, L.; Xu, L.Q. Down-regulation of Limk1 level inhibits migration of lung cancer cells and enhances sensitivity to chemotherapy drugs. Oncol. Res. 2013, 20, 491–498. [Google Scholar]
- Davila, M.; Frost, A.R.; Grizzle, W.E.; Chakrabarti, R. LIM kinase 1 is essential for the invasive growth of prostate epithelial cells: Implications in prostate cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 36868–36875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, H.; Sun, S.; Wang, B.; Wang, T.; Liang, C.; Li, G.; Huang, C.; Qi, D.; Chu, X. miR-143 Inhibits NSCLC Cell Growth and Metastasis by Targeting Limk1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 11973-11983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150711973
Xia H, Sun S, Wang B, Wang T, Liang C, Li G, Huang C, Qi D, Chu X. miR-143 Inhibits NSCLC Cell Growth and Metastasis by Targeting Limk1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(7):11973-11983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150711973
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Hui, Shengjie Sun, Bo Wang, Tao Wang, Chaoyang Liang, Guo Li, Chongbiao Huang, Daliang Qi, and Xiangyang Chu. 2014. "miR-143 Inhibits NSCLC Cell Growth and Metastasis by Targeting Limk1" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 7: 11973-11983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150711973
APA StyleXia, H., Sun, S., Wang, B., Wang, T., Liang, C., Li, G., Huang, C., Qi, D., & Chu, X. (2014). miR-143 Inhibits NSCLC Cell Growth and Metastasis by Targeting Limk1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(7), 11973-11983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150711973





