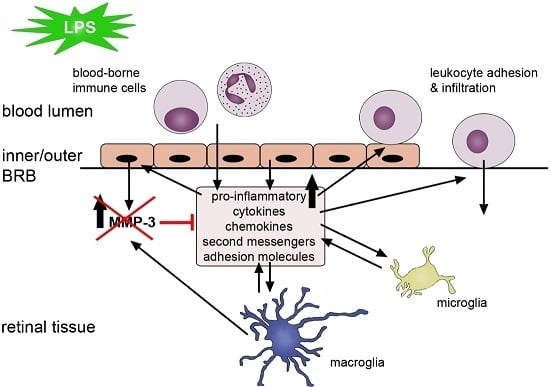
MMP-3 Deficiency Alleviates Endotoxin-Induced Acute Inflammation in the Posterior Eye Segment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
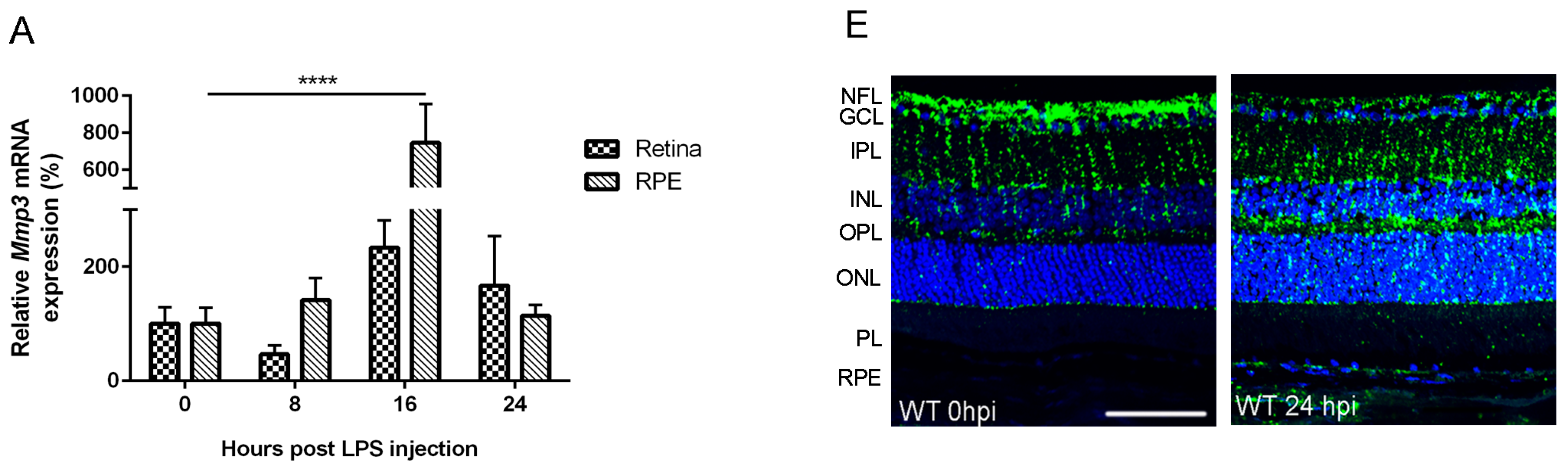
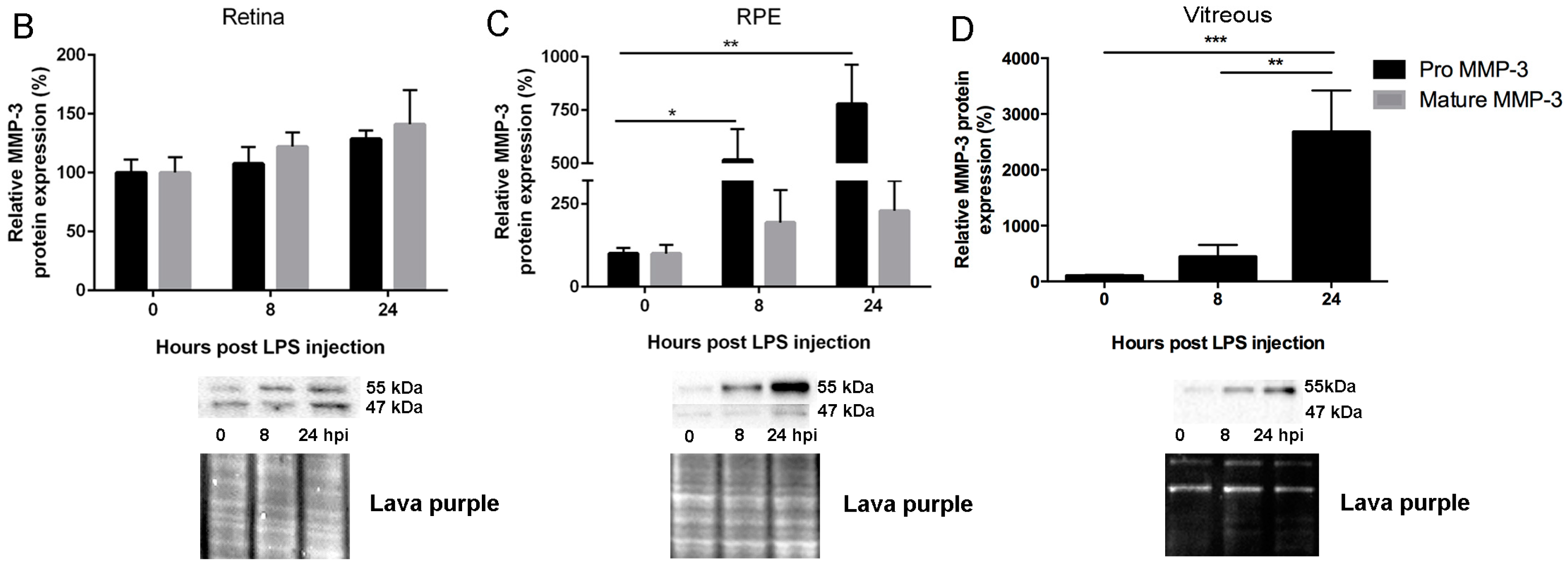
2.1. Endotoxemia Induces Upregulation of Matrix Metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3) mRNA and Protein Levels in the Posterior Part of the Eye
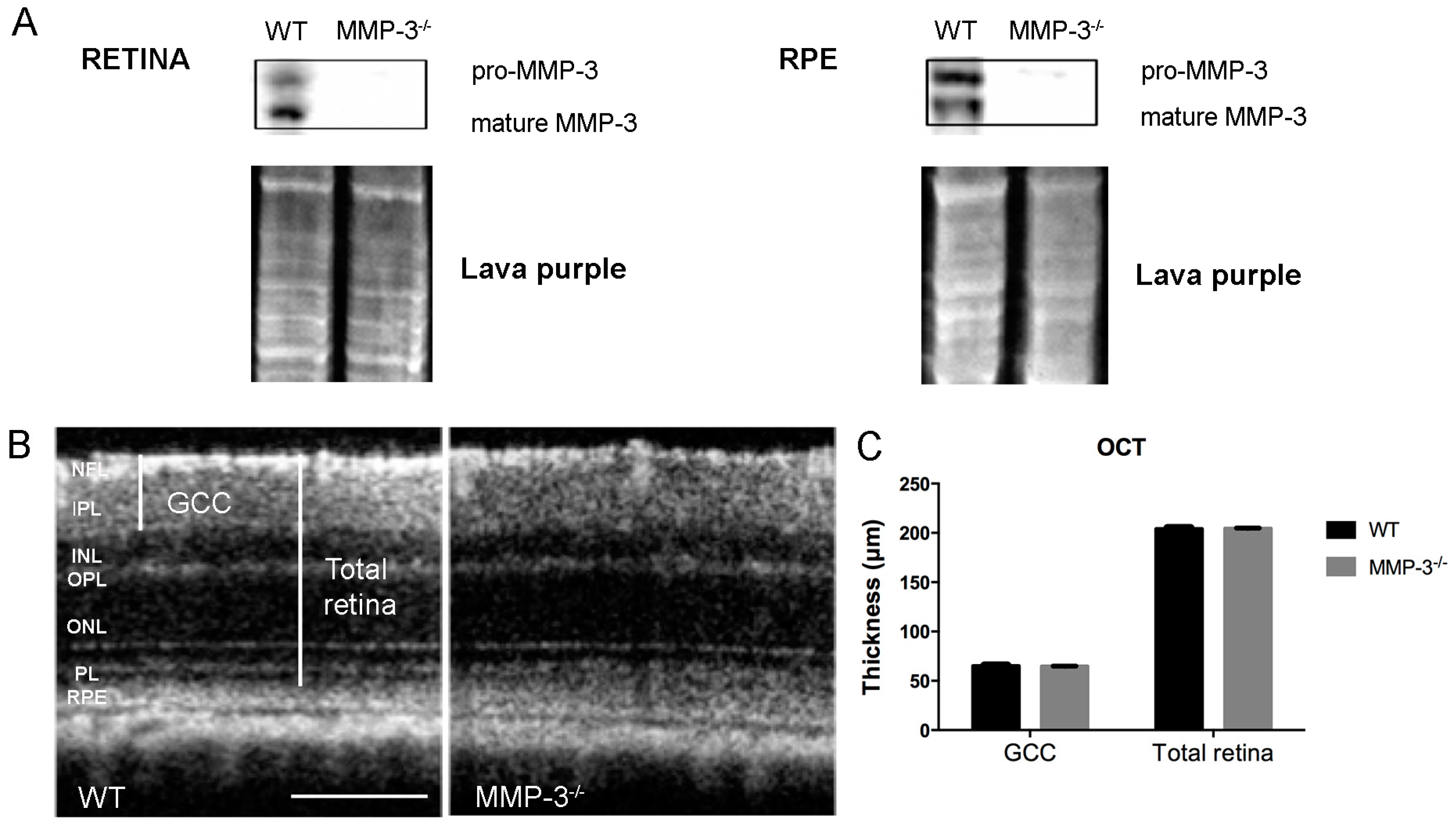
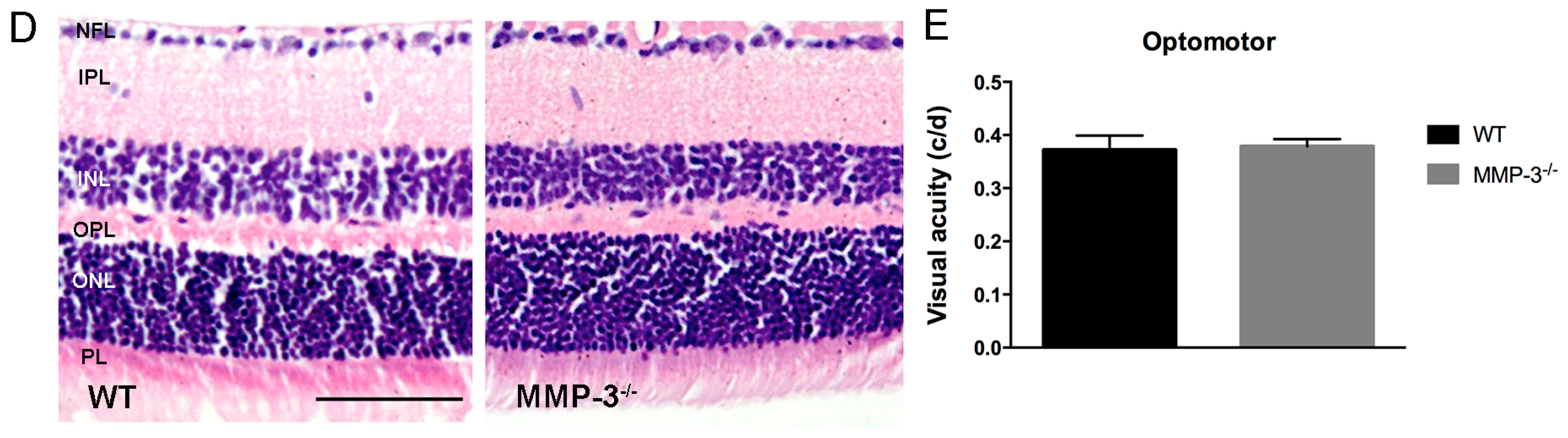
2.2. MMP-3 Deficient Mice Do Not Show an Aberrant Retinal Morphology or Visual Acuity
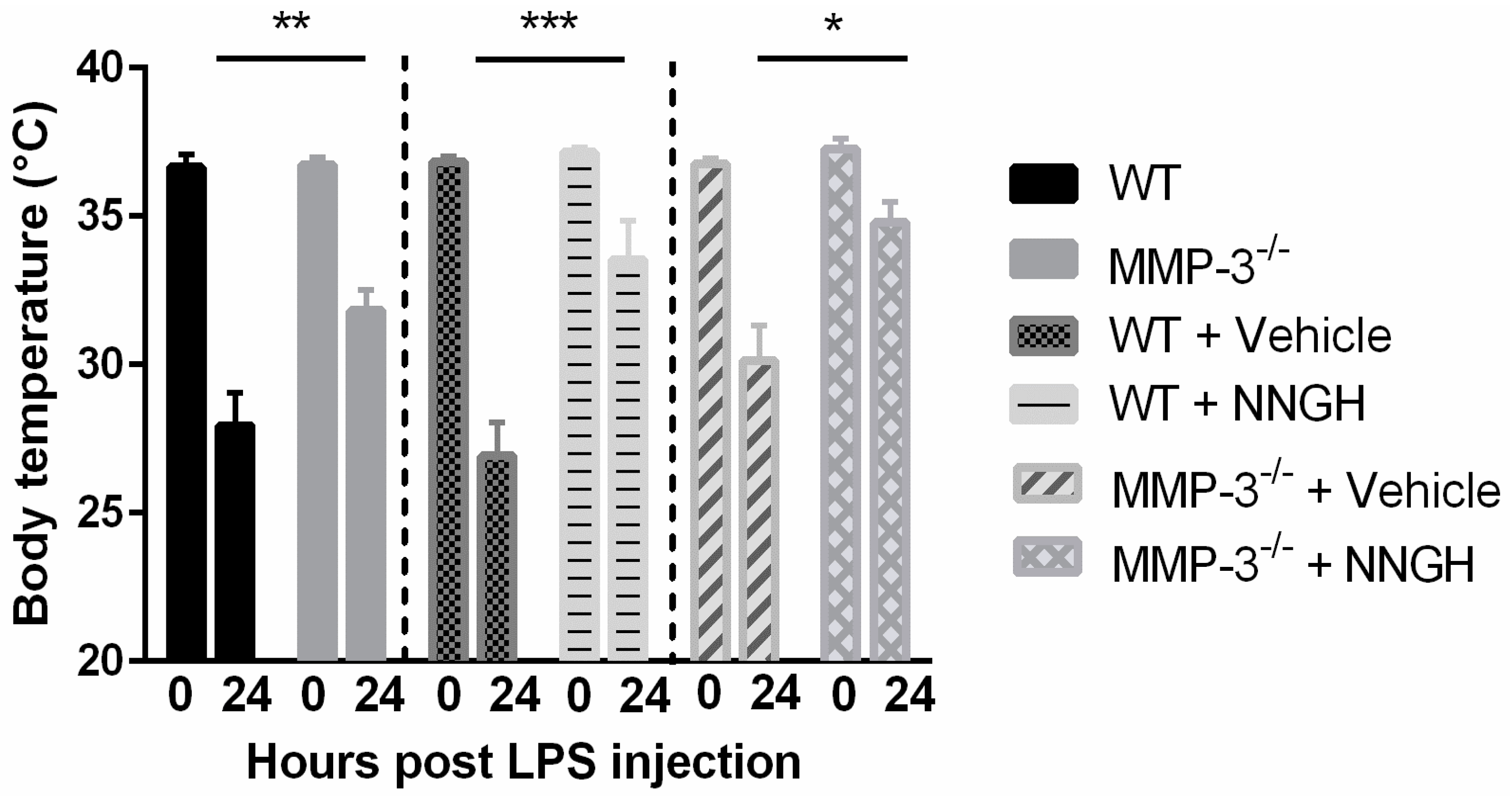
2.3. MMP-3 Deficiency and Knockdown Attenuates the Hypothermic Response after Endotoxemia
2.4. MMP-3 Deficiency or Knockdown Reduces Retinal Leukocyte Adhesion and Vitreous Infiltrating Leukocytes in the Endotoxin-Induced Uveitis (EIU) Model
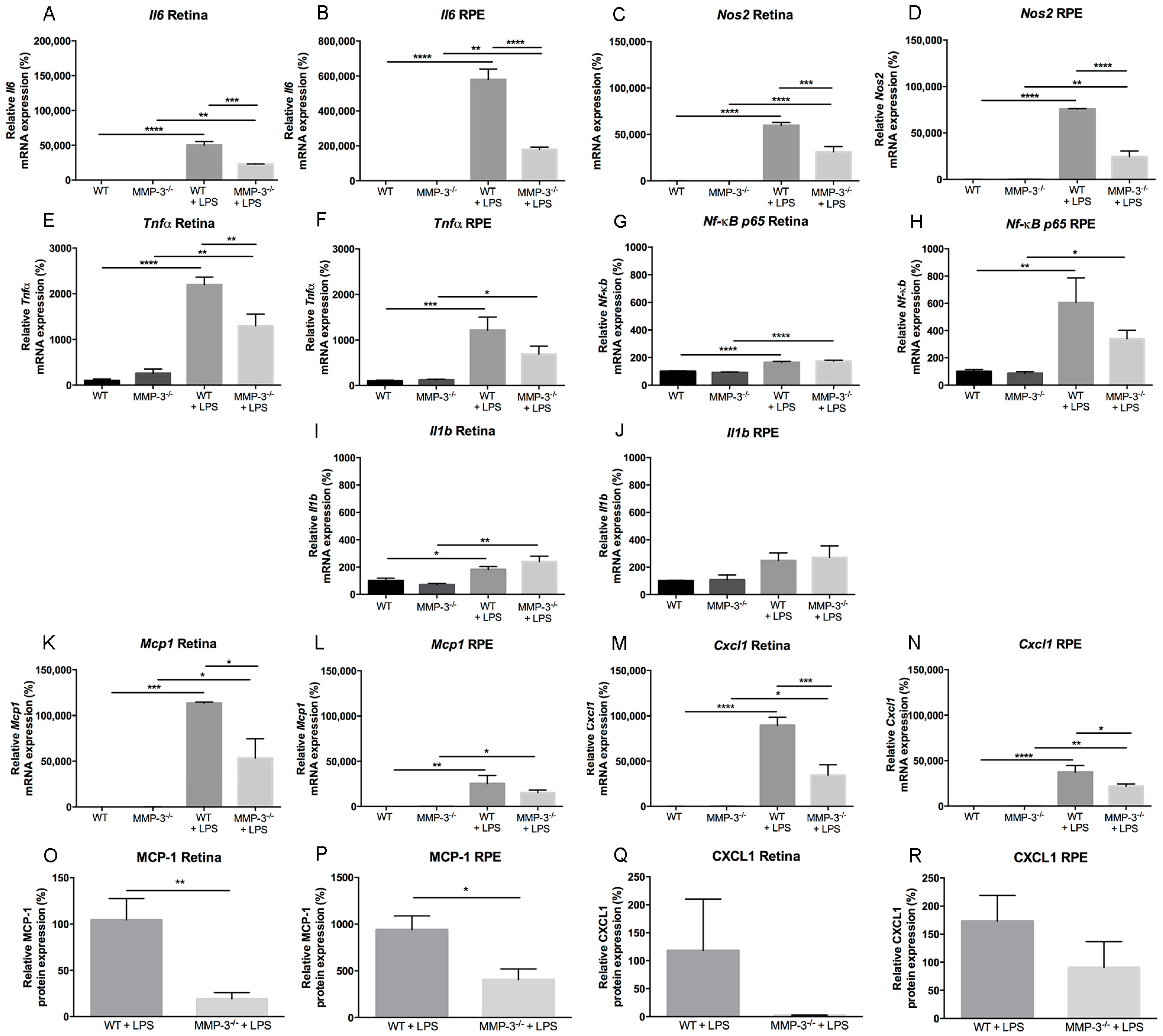
2.5. Inflammation-Associated Molecules Are Declined in the Retina and Retinal Pigment Epithelial (RPE) of MMP-3 Deficient Mice Subjected to EIU
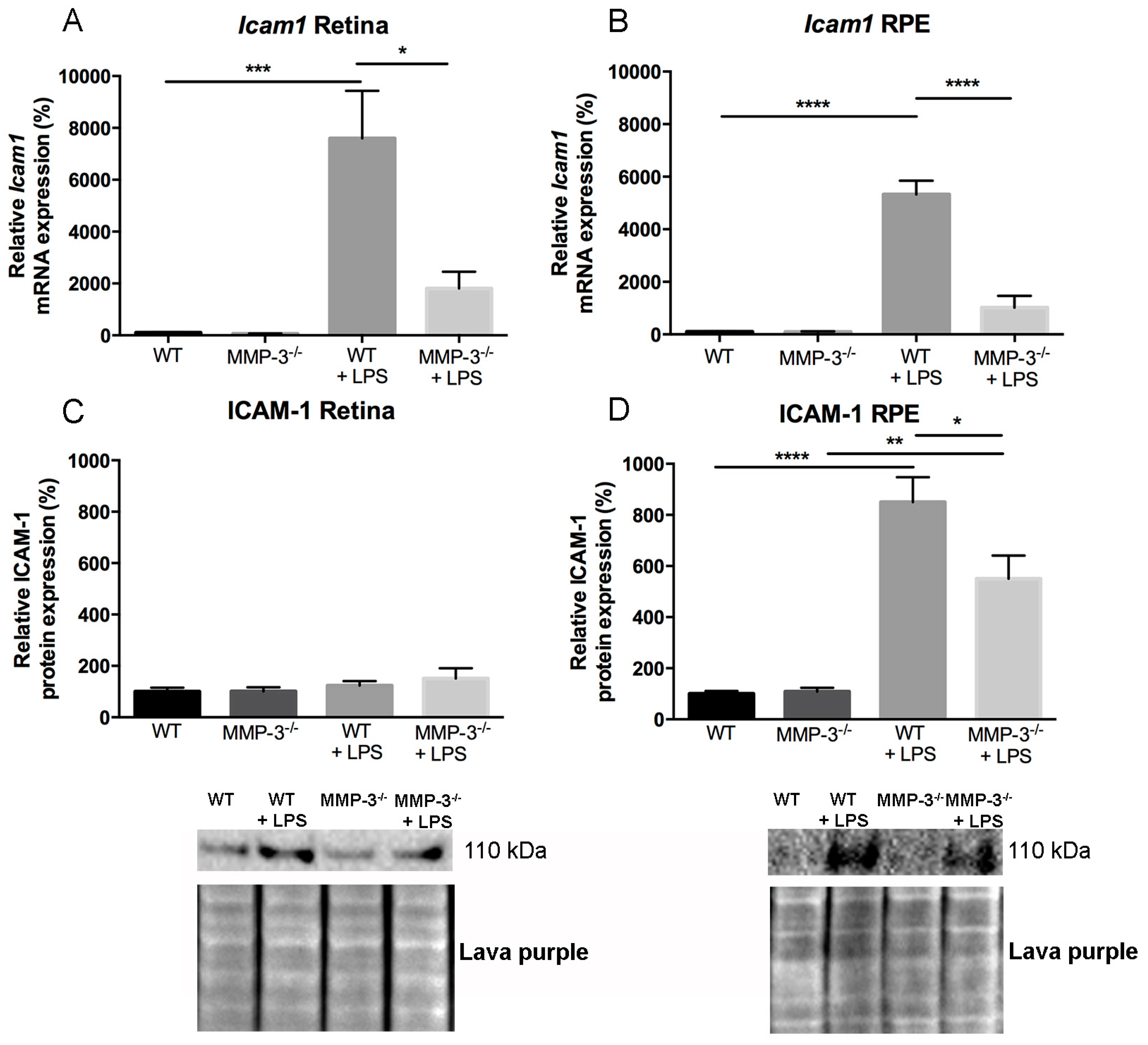
2.6. Impact of MMP-3 on the Adhesion Molecule Intercellular Adhesion Molecules (ICAM)-1 after EIU in the Retina and RPE
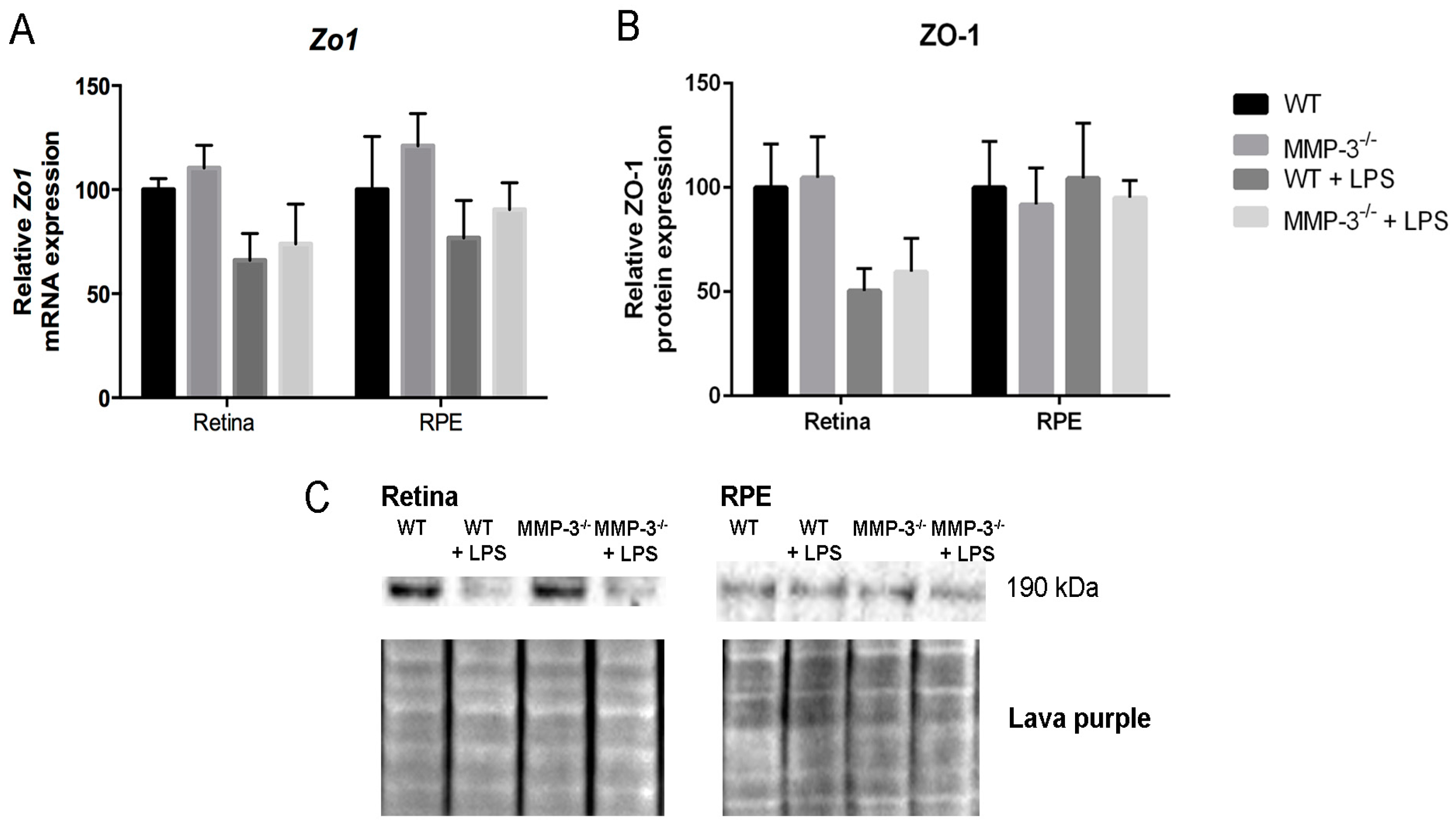
2.7. MMP-3 Deficiency Does Not Influence Zona Occludens 1 (ZO-1) Levels at the Inner or Outer Blood–Retinal Barrier (BRB) during EIU
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Endotoxemia Model
4.3. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.4. Western Blotting
4.5. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
4.6. Multiplex Cytokine Assay
4.7. Retinal Leukocyte Adhesion Quantification
4.8. Optical Coherence Tomography
4.9. Optokinetic Tracking Response
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNS | central nervous system |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| MMP-3 | matrix metalloproteinase 3 |
| WT | wild-type |
| RPE | retinal pigment epithelium |
| ip | intraperitoneal |
| EIU | endotoxin-induced uveitis |
| BRB | blood–retinal barrier |
| BBB | blood–brain barrier |
| BCSFB | blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier |
| BSCB | blood–spinal cord barrier |
| ICAM-1 | intercellular adhesion molecule 1 |
| IL/Il | interleukin |
| NOS2 | nitric oxide synthase 2 |
| MCP-1 | monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 |
| CXCL1 | (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor α |
| NF-κB p65 | nuclear factor kappa B p65 subunit |
| NNGH | N-Isobutyl-N-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-glycyl Hydroxamic Acid |
References
- Caspi, R.R. A look at autoimmunity and inflammation in the eye. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 3073–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crane, I.J.; Liversidge, J. Mechanisms of leukocyte migration across the blood-retina barrier. Semin. Immunopathol. 2008, 30, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, U.C.; Ramana, K.V. Endotoxin-induced uveitis in rodents. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1031, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kanda, A.; Noda, K.; Oike, Y.; Ishida, S. Angiopoietin-like protein 2 mediates endotoxin-induced acute inflammation in the eye. Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2012, 92, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Noda, K.; Kubota, S.; Hirasawa, M.; Ozawa, Y.; Tsubota, K.; Mizuki, N.; Ishida, S. Eicosapentaenoic acid suppresses ocular inflammation in endotoxin-induced uveitis. Mol. Vis. 2010, 16, 1382–1388. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tuaillon, N.; Shen, D.F.; Berger, R.B.; Lu, B.; Rollins, B.J.; Chan, C.C. Mcp-1 expression in endotoxin-induced uveitis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 1493–1498. [Google Scholar]
- Hoekzema, R.; Verhagen, C.; van Haren, M.; Kijlstra, A. Endotoxin-induced uveitis in the rat. The significance of intraocular interleukin-6. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1992, 33, 532–539. [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi, K.; Poulaki, V.; Doehmen, S.; Welsandt, G.; Radetzky, S.; Lappas, A.; Kociok, N.; Kirchhof, B.; Joussen, A.M. Contribution of TNF-α to leukocyte adhesion, vascular leakage, and apoptotic cell death in endotoxin-induced uveitis in vivo. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 2184–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satofuka, S.; Ichihara, A.; Nagai, N.; Yamashiro, K.; Koto, T.; Shinoda, H.; Noda, K.; Ozawa, Y.; Inoue, M.; Tsubota, K.; et al. Suppression of ocular inflammation in endotoxin-induced uveitis by inhibiting nonproteolytic activation of prorenin. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 2686–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Baban, B.; Rojas, M.; Tofigh, S.; Virmani, S.K.; Patel, C.; Behzadian, M.A.; Romero, M.J.; Caldwell, R.W.; Caldwell, R.B. Arginase activity mediates retinal inflammation in endotoxin-induced uveitis. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurney, K.J.; Estrada, E.Y.; Rosenberg, G.A. Blood-brain barrier disruption by stromelysin-1 facilitates neutrophil infiltration in neuroinflammation. Neurobiol. Dis. 2006, 23, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Rosenberg, G.A. Blood-brain barrier breakdown in acute and chronic cerebrovascular disease. Stroke J. Cereb. Circ. 2011, 42, 3323–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenbroucke, R.E.; Dejonckheere, E.; van Lint, P.; Demeestere, D.; van Wonterghem, E.; Vanlaere, I.; Puimege, L.; van Hauwermeiren, F.; de Rycke, R.; Mc Guire, C.; et al. Matrix metalloprotease 8-dependent extracellular matrix cleavage at the blood-CSF barrier contributes to lethality during systemic inflammatory diseases. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 9805–9816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brkic, M.; Balusu, S.; van Wonterghem, E.; Gorle, N.; Benilova, I.; Kremer, A.; van Hove, I.; Moons, L.; de Strooper, B.; Kanazir, S.; et al. Amyloid β oligomers disrupt blood-CSF barrier integrity by activating matrix metalloproteinases. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 12766–12778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiggins-Dohlvik, K.; Merriman, M.; Shaji, C.A.; Alluri, H.; Grimsley, M.; Davis, M.L.; Smith, R.W.; Tharakan, B. Tumor necrosis factor-α disruption of brain endothelial cell barrier is mediated through matrix metalloproteinase-9. Am. J. Surg. 2014, 208, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Choi, H.Y.; Ahn, H.J.; Ju, B.G.; Yune, T.Y. Matrix metalloproteinase-3 promotes early blood-spinal cord barrier disruption and hemorrhage and impairs long-term neurological recovery after spinal cord injury. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 2985–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, L.J.; Donovan, F.; Igarashi, T.; Goussev, S.; Werb, Z. Matrix metalloproteinases limit functional recovery after spinal cord injury by modulation of early vascular events. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 7526–7535. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lakhan, S.E.; Kirchgessner, A.; Tepper, D.; Leonard, A. Matrix metalloproteinases and blood-brain barrier disruption in acute ischemic stroke. Front. Neurol. 2013, 4, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Estrada, E.Y.; Thompson, J.F.; Liu, W.; Rosenberg, G.A. Matrix metalloproteinase-mediated disruption of tight junction proteins in cerebral vessels is reversed by synthetic matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor in focal ischemia in rat. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2007, 27, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuwelt, E.; Abbott, N.J.; Abrey, L.; Banks, W.A.; Blakley, B.; Davis, T.; Engelhardt, B.; Grammas, P.; Nedergaard, M.; Nutt, J.; et al. Strategies to advance translational research into brain barriers. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun-Bryce, S.; Lukes, A.; Wallace, J.; Lukes-Marx, M.; Rosenberg, G.A. Stromelysin-1 and gelatinase a are upregulated before TNF-α in LPS-stimulated neuroinflammation. Brain Res. 2002, 933, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.C.; Kim, Y.S.; Bok, E.; Yune, T.Y.; Maeng, S.; Jin, B.K. MMP-3 contributes to nigrostriatal dopaminergic neuronal loss, BBB damage, and neuroinflammation in an MPTP mouse model of parkinson’s disease. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 370526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljubisavljevic, S.; Stojanovic, I.; Basic, J.; Vojinovic, S.; Stojanov, D.; Djordjevic, G.; Pavlovic, D. The role of matrix metalloproteinase 3 and 9 in the pathogenesis of acute neuroinflammation. Implications for disease modifying therapy. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 56, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalal, F.Y.; Yang, Y.; Thompson, J.; Lopez, A.C.; Rosenberg, G.A. Myelin loss associated with neuroinflammation in hypertensive rats. Stroke 2012, 43, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brkic, M.; Balusu, S.; Libert, C.; Vandenbroucke, R.E. Friends or foes: Matrix metalloproteinases and their multifaceted roles in neurodegenerative diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 620581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossetete, M.; Phelps, J.; Arko, L.; Yonas, H.; Rosenberg, G.A. Elevation of matrix metalloproteinases 3 and 9 in cerebrospinal fluid and blood in patients with severe traumatic brain injury. Neurosurgery 2009, 65, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakis, J.M. Activation of the AP-1 transcription factor by inflammatory cytokines of the TNF family. Gene Expr. 1999, 7, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Overall, C.M.; Lopez-Otin, C. Strategies for MMP inhibition in cancer: Innovations for the post-trial era. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 657–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, G.A. Matrix metalloproteinases and their multiple roles in neurodegenerative diseases. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candelario-Jalil, E.; Taheri, S.; Yang, Y.; Sood, R.; Grossetete, M.; Estrada, E.Y.; Fiebich, B.L.; Rosenberg, G.A. Cyclooxygenase inhibition limits blood-brain barrier disruption following intracerebral injection of tumor necrosis factor-α in the rat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 323, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.M.; Hwang, O. Role of matrix metalloproteinase-3 in neurodegeneration. J. Neurochem. 2011, 116, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, M.S.; Park, J.S.; Choi, I.Y.; Kim, W.K.; Kim, H.S. Inhibition of MMP-3 or -9 suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of proinflammatory cytokines and inos in microglia. J. Neurochem. 2008, 106, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankowski, J.C.; DeMars, K.M.; Ahmad, A.S.; Hawkins, K.E.; Yang, C.; Leclerc, J.L.; Dore, S.; Candelario-Jalil, E. Detrimental role of the EP1 prostanoid receptor in blood-brain barrier damage following experimental ischemic stroke. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichler, W.; Friedrichs, U.; Thies, A.; Tratz, C.; Wiedemann, P. Modulation of matrix metalloproteinase and TIMP-1 expression by cytokines in human RPE cells. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 2767–2773. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Yoneda, M.; Takeyama, M.; Sugita, I.; Tsunekawa, H.; Yamada, H.; Watanabe, D.; Mukai, T.; Yamamura, M.; Iwaki, M.; et al. Effect of infliximab on tumor necrosis factor-α-induced alterations in retinal microvascular endothelial cells and retinal pigment epithelial cells. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 26, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leu, S.T.; Batni, S.; Radeke, M.J.; Johnson, L.V.; Anderson, D.H.; Clegg, D.O. Drusen are cold spots for proteolysis: Expression of matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitor proteins in age-related macular degeneration. Exp. Eye Res. 2002, 74, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemzek, J.A.; Hugunin, K.M.; Opp, M.R. Modeling sepsis in the laboratory: Merging sound science with animal well-being. Comp. Med. 2008, 58, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.H.; Kim, J.H.; Seo, J.H.; Lee, J.; Choi, W.S.; Kim, Y.S. Matrix metalloproteinase-3 causes dopaminergic neuronal death through Nox1-regenerated oxidative stress. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christianson, C.A.; Fitzsimmons, B.L.; Shim, J.H.; Agrawal, A.; Cohen, S.M.; Hua, X.Y.; Yaksh, T.L. Spinal matrix metalloproteinase 3 mediates inflammatory hyperalgesia via a tumor necrosis factor-dependent mechanism. Neuroscience 2012, 200, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauly, T.; Ratliff, M.; Pietrowski, E.; Neugebauer, R.; Schlicksupp, A.; Kirsch, J.; Kuhse, J. Activity-dependent shedding of the nmda receptor glycine binding site by matrix metalloproteinase 3: A putative mechanism of postsynaptic plasticity. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.J.; Gardner, P.J.; Copland, D.A.; Liyanage, S.E.; Gonzalez-Cordero, A.; Kleine Holthaus, S.M.; Luhmann, U.F.; Smith, A.J.; Ali, R.R.; Dick, A.D. Multimodal analysis of ocular inflammation using the endotoxin-induced uveitis mouse model. Dis. Models Mech. 2016, 9, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadjanski, I.; Williams, S.K.; Hein, K.; Sattler, M.B.; Bahr, M.; Diem, R. Correlation of optical coherence tomography with clinical and histopathological findings in experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis. Exp. Eye Res. 2011, 93, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.J.; Herrmann, P.; Carvalho, L.S.; Liyanage, S.E.; Bainbridge, J.W.; Ali, R.R.; Dick, A.D.; Luhmann, U.F. Assessment and in vivo scoring of murine experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis using optical coherence tomography. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes, M.E.; Durham, S.K.; Swerdel, M.R.; Lewin, A.C.; Barton, D.S.; Megill, J.R.; Bravo, R.; Lira, S.A. Controlled recruitment of monocytes and macrophages to specific organs through transgenic expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1. J. Immunol. 1995, 155, 5769–5776. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Becker, M.D.; Garman, K.; Whitcup, S.M.; Planck, S.R.; Rosenbaum, J.T. Inhibition of leukocyte sticking and infiltration, but not rolling, by antibodies to ICAM-1 and LFA-1 in murine endotoxin-induced uveitis. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2001, 42, 2563–2566. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, D.H.; Kim, E.M.; Son, H.J.; Joh, T.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, D.; Flint Beal, M.; Hwang, O. A novel intracellular role of matrix metalloproteinase-3 during apoptosis of dopaminergic cells. J. Neurochem. 2008, 106, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasche, Y.; Copin, J.C.; Sugawara, T.; Fujimura, M.; Chan, P.H. Matrix metalloproteinase inhibition prevents oxidative stress-associated blood-brain barrier disruption after transient focal cerebral ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2001, 21, 1393–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeni, P.; Doepker, E.; Schulze-Topphoff, U.; Huewel, S.; Tenenbaum, T.; Galla, H.J. MMPs contribute to TNF-α-induced alteration of the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier in vitro. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 293, C855–C864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudharshan, S.; Ganesh, S.K.; Biswas, J. Current approach in the diagnosis and management of posterior uveitis. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 58, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kubota, S.; Kurihara, T.; Mochimaru, H.; Satofuka, S.; Noda, K.; Ozawa, Y.; Oike, Y.; Ishida, S.; Tsubota, K. Prevention of ocular inflammation in endotoxin-induced uveitis with resveratrol by inhibiting oxidative damage and nuclear factor-kappab activation. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 3512–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page-McCaw, A.; Ewald, A.J.; Werb, Z. Matrix metalloproteinases and the regulation of tissue remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Groef, L.; Andries, L.; Lemmens, K.; van Hove, I.; Moons, L. Matrix metalloproteinases in the mouse retina: A comparative study of expression patterns and mmp antibodies. BMC Ophthalmol. 2015, 15, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sternlicht, M.D.; Werb, Z. How matrix metalloproteinases regulate cell behavior. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2001, 17, 463–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopalan, S.; Meng, X.P.; Ramasamy, S.; Harrison, D.G.; Galis, Z.S. Reactive oxygen species produced by macrophage-derived foam cells regulate the activity of vascular matrix metalloproteinases in vitro. Implications for atherosclerotic plaque stability. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 2572–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.Y.; Wen, M.H. Lipopolysaccharide-mediated reactive oxygen species and signal transduction in the regulation of interleukin-1 gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 22131–22139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, M.; Ozawa, Y.; Kurihara, T.; Noda, K.; Imamura, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Ishida, S.; Tsubota, K. Neuroprotective effect of an antioxidant, lutein, during retinal inflammation. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 1433–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowluru, R.A.; Chan, P.S. Oxidative stress and diabetic retinopathy. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2007, 2007, 43603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neria, F.; del Carmen Serrano-Perez, M.; Velasco, P.; Urso, K.; Tranque, P.; Cano, E. Nfatc3 promotes Ca2+ -dependent Mmp3 expression in astroglial cells. Glia 2013, 61, 1052–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwmeester, T.; Bauch, A.; Ruffner, H.; Angrand, P.O.; Bergamini, G.; Croughton, K.; Cruciat, C.; Eberhard, D.; Gagneur, J.; Ghidelli, S.; et al. A physical and functional map of the human TNF-α/NF-κB signal transduction pathway. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skipor, J.; Szczepkowska, A.; Kowalewska, M.; Herman, A.P.; Lisiewski, P. Profile of toll-like receptor mRNA expression in the choroid plexus in adult ewes. Acta Vet. Hung. 2015, 63, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.C.; Yeh, W.C.; Ohashi, P.S. LPS/TLR4 signal transduction pathway. Cytokine 2008, 42, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Akashi, S.; Miyake, K.; Petty, H.R. Lipopolysaccharide induces physical proximity between CD14 and toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) prior to nuclear translocation of NF-κB. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 3541–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallard, C. Innate immune regulation by toll-like receptors in the brain. ISRN Neurol. 2012, 2012, 701950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elner, S.G.; Petty, H.R.; Elner, V.M.; Yoshida, A.; Bian, Z.M.; Yang, D.; Kindezelskii, A.L. TLR4 mediates human retinal pigment epithelial endotoxin binding and cytokine expression. Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 2005, 103, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alge-Priglinger, C.S.; Kreutzer, T.; Obholzer, K.; Wolf, A.; Mempel, M.; Kernt, M.; Kampik, A.; Priglinger, S.G. Oxidative stress-mediated induction of MMP-1 and MMP-3 in human RPE cells. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 5495–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Liu, B.; Lukas, T.J.; Neufeld, A.H. The aged retinal pigment epithelium/choroid: A potential substratum for the pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenenbaum, T.; Matalon, D.; Adam, R.; Seibt, A.; Wewer, C.; Schwerk, C.; Galla, H.J.; Schroten, H. Dexamethasone prevents alteration of tight junction-associated proteins and barrier function in porcine choroid plexus epithelial cells after infection with streptococcus suis in vitro. Brain Res. 2008, 1229, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Saffar, H.; Lewis, K.; Liu, E.; Schober, A.; Corrigan, J.J.; Shibata, K.; Steiner, A.A. Lipopolysaccharide-induced hypothermia and hypotension are associated with inflammatory signaling that is triggered outside the brain. Brain Behav. Immun. 2013, 28, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon, L.R. Hypothermia in systemic inflammation: Role of cytokines. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 1877–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplanski, J.; Nassar, A.; Sharon-Granit, Y.; Jabareen, A.; Kobal, S.L.; Azab, A.N. Lithium attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced hypothermia in rats. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 18, 1829–1837. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vanlaere, I.; Libert, C. Matrix metalloproteinases as drug targets in infections caused by gram-negative bacteria and in septic shock. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 224–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipowsky, H.H.; Sah, R.; Lescanic, A. Relative roles of doxycycline and cation chelation in endothelial glycan shedding and adhesion of leukocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 300, H415–H422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenbroucke, R.E.; Vanlaere, I.; van Hauwermeiren, F.; van Wonterghem, E.; Wilson, C.; Libert, C. Pro-inflammatory effects of matrix metalloproteinase 7 in acute inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. 2014, 7, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, J.; Vandenbroucke, R.E.; Dera, R.; Balusu, S.; van Wonterghem, E.; Moons, L.; Libert, C.; Dehaen, W.; Arckens, L. Synthesis and validation of a hydroxypyrone-based, potent, and specific matrix metalloproteinase-12 inhibitor with anti-inflammatory activity in vitro and in vivo. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 510679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenbroucke, R.E.; Dejonckheere, E.; van Hauwermeiren, F.; Lodens, S.; de Rycke, R.; van Wonterghem, E.; Staes, A.; Gevaert, K.; Lopez-Otin, C.; Libert, C. Matrix metalloproteinase 13 modulates intestinal epithelial barrier integrity in inflammatory diseases by activating TNF. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 1000–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, D.F.; Buggage, R.R.; Eng, H.C.; Chan, C.C. Cytokine gene expression in different strains of mice with endotoxin-induced uveitis (EIU). Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2000, 8, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planck, S.R.; Huang, X.N.; Robertson, J.E.; Rosenbaum, J.T. Cytokine mRNA levels in rat ocular tissues after systemic endotoxin treatment. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1994, 35, 924–930. [Google Scholar]
- Hoekzema, R.; Murray, P.I.; van Haren, M.A.; Helle, M.; Kijlstra, A. Analysis of interleukin-6 in endotoxin-induced uveitis. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1991, 32, 88–95. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, K.W.; Barnstable, C.J.; Tombran-Tink, J. Bacterial endotoxin activates retinal pigment epithelial cells and induces their degeneration through IL-6 and IL-8 autocrine signaling. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 1374–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vos, A.F.; Klaren, V.N.; Kijlstra, A. Expression of multiple cytokines and IL-1RA in the uvea and retina during endotoxin-induced uveitis in the rat. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1994, 35, 3873–3883. [Google Scholar]
- Ley, K.; Laudanna, C.; Cybulsky, M.I.; Nourshargh, S. Getting to the site of inflammation: The leukocyte adhesion cascade updated. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Gu, X.; Boyce, T.M.; Zheng, M.; Reagan, A.M.; Qi, H.; Mandal, N.; Cohen, A.W.; Callegan, M.C.; Carr, D.J.; et al. Caveolin-1 increases proinflammatory chemoattractants and blood-retinal barrier breakdown but decreases leukocyte recruitment in inflammation. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 6224–6234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benhar, I.; Reemst, K.; Kalchenko, V.; Schwartz, M. The retinal pigment epithelium as a gateway for monocyte trafficking into the eye. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 1219–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goureau, O.; Bellot, J.; Thillaye, B.; Courtois, Y.; de Kozak, Y. Increased nitric oxide production in endotoxin-induced uveitis. Reduction of uveitis by an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase. J. Immunol. 1995, 154, 6518–6523. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, F.; Duan, S.; Cui, J.; Yan, X.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Xie, X. Induction of matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3) expression in the microglia by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) via upregulation of glycoprotein nonmetastatic melanoma B (GPNMB) expression. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2014, 54, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinfield, J.K.; Das, A.; O’Regan, D.J.; Ball, S.G.; Porter, K.E.; Turner, N.A. P38 MAPK alpha mediates cytokine-induced IL-6 and MMP-3 expression in human cardiac fibroblasts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 430, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuder, L.E.; Keener, J.M.; Eckert, R.E.; Trujillo, J.C.; Jones, S.L. Role of p38 MAPK in LPS induced pro-inflammatory cytokine and chemokine gene expression in equine leukocytes. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2009, 129, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guha, M.; O’Connell, M.A.; Pawlinski, R.; Hollis, A.; McGovern, P.; Yan, S.F.; Stern, D.; Mackman, N. Lipopolysaccharide activation of the MEK-ERK1/2 pathway in human monocytic cells mediates tissue factor and tumor necrosis factor alpha expression by inducing Elk-1 phosphorylation and EGR-1 expression. Blood 2001, 98, 1429–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenport, M.; Khan, K.M.; Du, B.; Barnhard, S.E.; Dannenberg, A.J.; Falcone, D.J. Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-1 and MMP-3 induce macrophage MMP-9: Evidence for the role of TNF-α and cyclooxygenase-2. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 8119–8127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gearing, A.J.; Beckett, P.; Christodoulou, M.; Churchill, M.; Clements, J.M.; Crimmin, M.; Davidson, A.H.; Drummond, A.H.; Galloway, W.A.; Gilbert, R.; et al. Matrix metalloproteinases and processing of pro-TNF-α. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1995, 57, 774–777. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Konari, K.; Sawada, N.; Zhong, Y.; Isomura, H.; Nakagawa, T.; Mori, M. Development of the blood-retinal barrier in vitro: Formation of tight junctions as revealed by occludin and ZO-1 correlates with the barrier function of chick retinal pigment epithelial cells. Exp. Eye Res. 1995, 61, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russ, P.K.; Davidson, M.K.; Hoffman, L.H.; Haselton, F.R. Partial characterization of the human retinal endothelial cell tight and adherens junction complexes. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1998, 39, 2479–2485. [Google Scholar]
- Poulaki, V.; Iliaki, E.; Mitsiades, N.; Mitsiades, C.S.; Paulus, Y.N.; Bula, D.V.; Gragoudas, E.S.; Miller, J.W. Inhibition of Hsp90 attenuates inflammation in endotoxin-induced uveitis. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 2113–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zech, J.C.; Pouvreau, I.; Cotinet, A.; Goureau, O.; Le Varlet, B.; de Kozak, Y. Effect of cytokines and nitric oxide on tight junctions in cultured rat retinal pigment epithelium. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1998, 39, 1600–1608. [Google Scholar]
- Vanden Berghe, T.; Hulpiau, P.; Martens, L.; Vandenbroucke, R.E.; van Wonterghem, E.; Perry, S.W.; Bruggeman, I.; Divert, T.; Choi, S.M.; Vuylsteke, M.; et al. Passenger mutations confound interpretation of all genetically modified congenic mice. Immunity 2015, 43, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verslegers, M.; van Hove, I.; Dekeyster, E.; Gantois, I.; Hu, T.T.; D’Hooge, R.; Arckens, L.; Moons, L. MMP-2 mediates purkinje cell morphogenesis and spine development in the mouse cerebellum. Brain Struct. Funct. 2015, 220, 1601–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hove, I.; Verslegers, M.; Buyens, T.; Delorme, N.; Lemmens, K.; Stroobants, S.; Gantois, I.; D’Hooge, R.; Moons, L. An aberrant cerebellar development in mice lacking matrix metalloproteinase-3. Mol. Neurobiol. 2012, 45, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, M.; Barbazetto, I.A.; Spaide, R.F. Intravitreal cellular infiltrate imaged as punctate spots by spectral-domain optical coherence tomography in eyes with posterior segment inflammatory disease. Retina 2013, 33, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prusky, G.T.; Alam, N.M.; Beekman, S.; Douglas, R.M. Rapid quantification of adult and developing mouse spatial vision using a virtual optomotor system. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 4611–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, R.M.; Alam, N.M.; Silver, B.D.; McGill, T.J.; Tschetter, W.W.; Prusky, G.T. Independent visual threshold measurements in the two eyes of freely moving rats and mice using a virtual-reality optokinetic system. Vis. Neurosci. 2005, 22, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Groef, L.; Dekeyster, E.; Geeraerts, E.; Lefevere, E.; Stalmans, I.; Salinas-Navarro, M.; Moons, L. Differential visual system organization and susceptibility to experimental models of optic neuropathies in three commonly used mouse strains. Exp. Eye Res. 2016, 145, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer | Probe |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ywhaz | cgtacctacaatgcctccatc | catcctgctgtccattgctta | tccttgattttgcctcagctccca |
| Rn18s1 | cgtacctacaatgcctccatc | agaattgcaacagctcgattg | cagcccctgatgagaatgtaccagc |
| Gusb | gacccaagataccgacatgag | cagcttgctaatgtcagcct | aatcccattcacccacacaactgc |
| Mmp3 | gatgaacgatggacagaggatg | tgtggaggacttgtagactgg | tggttgctgctcatgaacttggc |
| Il6 | tccttagccactccttctgt | agccagagtccttcagaga | cctaccccaatttccaatgctctcct |
| Il1b | ctcttgttgatgtgctgctg | gacctgttctttgaagttgacg | ttccaaacctttgacctgggctgt |
| Tnfα | tctttagatccatgccgttg | agaccctcacactcagatca | ccacgtcgtagcaaaccaccaagt |
| Nf-κBp65 | ccctctgttttggttgctcta | tgaacactgctttgactcact | atgggccatctgttgacagtggt |
| Mcp1 | aactacagcttctttgggaca | catccacgtgttggctca | actcacctgctgctactcattcacc |
| Cxcl1 | gtgccatcagagcagtct | ccaaaccgaagtcatagcca | aggtgtccccaagtaacggagaaag |
| Icam1 | ggtccttgcctacttgctg | ctgtgctttgagaactgtgg | ccgctaccatcaccgtgtattcgtt |
| Nos2 | cacttctgctccaaatccaac | gactgagctgttagagacactt | tgaacaagacccaagcgtgaggag |
| Zo1 | gcaactacagtatgaccatcc | aatgaataatatcagcaccatgcc | ctgtccctgtgagtccttcagctg |
| Rplp2 | gtcatcgctcagggtgttg | gactcctccttcttctcatctttc | ctgtggctgtttctgctgccc |
| Hprt | cgtgattagcgatgatgaacc | catgacatctcgagcaagtct | cctcatggactgattatggacaggactga |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Van Hove, I.; Lefevere, E.; De Groef, L.; Sergeys, J.; Salinas-Navarro, M.; Libert, C.; Vandenbroucke, R.; Moons, L. MMP-3 Deficiency Alleviates Endotoxin-Induced Acute Inflammation in the Posterior Eye Segment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111825
Van Hove I, Lefevere E, De Groef L, Sergeys J, Salinas-Navarro M, Libert C, Vandenbroucke R, Moons L. MMP-3 Deficiency Alleviates Endotoxin-Induced Acute Inflammation in the Posterior Eye Segment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(11):1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111825
Chicago/Turabian StyleVan Hove, Inge, Evy Lefevere, Lies De Groef, Jurgen Sergeys, Manuel Salinas-Navarro, Claude Libert, Roosmarijn Vandenbroucke, and Lieve Moons. 2016. "MMP-3 Deficiency Alleviates Endotoxin-Induced Acute Inflammation in the Posterior Eye Segment" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 11: 1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111825
APA StyleVan Hove, I., Lefevere, E., De Groef, L., Sergeys, J., Salinas-Navarro, M., Libert, C., Vandenbroucke, R., & Moons, L. (2016). MMP-3 Deficiency Alleviates Endotoxin-Induced Acute Inflammation in the Posterior Eye Segment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(11), 1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111825