Influence of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors on Hypertension and Nephrotoxicity in Metastatic Renal Cell Cancer Patients
Abstract
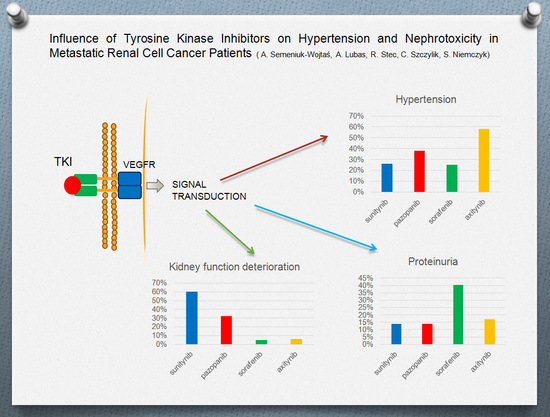
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
3.1. Hypertension
3.2. Proteinuria
3.3. Renal Function
4. Methods
4.1. Search Strategy
4.2. Selection Criteria
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GLOBOCAN 2012: Estimated Cancer Incidence, Mortality and Prevalence Worldwide in 2012. Available online: http://globocan.iarc.fr/Pages/fact_sheets_population.aspx (accessed on 11 July 2016).
- Kappers, M.H.; van Esch, J.H.; Sleijfer, S.; Danser, A.H.; van den Meiracker, A.H. Cardiovascular and renal toxicity during angiogenesis inhibition: Clinical and mechanistic aspects. J. Hypertens. 2009, 27, 2297–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, A.; Ye, D.W.; Pal, S. Overview and management of toxicities associated with systemic therapies for advanced renal cell carcinoma. Urol. Oncol. 2015, 33, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) V 3.0. Available online: http://ctep.cancer.gov/protocolDevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/ctcaev3.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2016).
- Motzer, R.J.; Hutson, T.E.; Tomczak, P.; Michaelson, M.D.; Bukowski, R.M.; Oudard, S.; Negrier, S.; Szczylik, C.; Pili, R.; Bjarnason, G.A.; et al. Overall survival and updated results for sunitinib compared with interferon alfa in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3584–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gore, M.E.; Szczylik, C.; Porta, C.; Bracarda, S.; Bjarnason, G.A.; Oudard, S.; Lee, S.H.; Haanen, J.; Castellano, D.; Vrdoljak, E.; et al. Final results from the large sunitinib global expanded-access trial in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akaza, H.; Naito, S.; Ueno, N.; Aoki, K.; Houzawa, H.; Pitman Lowenthal, S.; Lee, S.Y. Real-world use of sunitinib in Japanese patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: Efficacy, safety and biomarker analyses in 1689 consecutive patients. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 45, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sternberg, C.N.; Calabrò, F.; Bracarda, S.; Cartenì, G.; Lo Re, G.; Ruggeri, E.M.; Basso, U.; Gasparini, G.; Ciuffreda, L.; Ferrari, V.; et al. Safety and efficacy of sunitinib in patients from Italy with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Final results from an expanded-access trial. Oncology 2015, 88, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrdoljak, E.; Géczi, L.; Mardiak, J.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Leyman, S.; Zhang, K.; Sajben, P.; Torday, L. Central and eastern European experience with sunitinib in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A sub-analysis of the global expanded-access trial. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2015, 21, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sternberg, C.N.; Hawkins, R.E.; Wagstaff, J.; Salman, P.; Mardiak, J.; Barrios, C.H.; Zarba, J.J.; Gladkov, O.A.; Lee, E.; Szczylik, C.; et al. A randomised, double-blind phase III study of pazopanib in patients with advanced and/or metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Final overall survival results and safety update. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escudier, B.; Eisen, T.; Stadler, W.M.; Szczylik, C.; Oudard, S.; Siebels, M.; Negrier, S.; Chevreau, C.; Solska, E.; Desai, A.A.; et al. Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Procopio, G.; Verzoni, E.; Gevorgyan, A.; Mancin, M.; Pusceddu, S.; Catena, L.; Platania, M.; Guadalupi, V.; Martinetti, A.; Bajetta, E. Safety and activity of sorafenib in different histotypes of advanced renal cell carcinoma. Oncology 2007, 73, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, J.; Procopio, G.; Bajetta, E.; Keilholz, U.; Negrier, S.; Szczylik, C.; Bokemeyer, C.; Bracarda, S.; Richel, D.J.; Staehler, M.; et al. Final results of the European Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma Sorafenib (EU-ARCCS) expanded-access study: A large open-label study in diverse community settings. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 1812–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Nosov, D.; Eisen, T.; Bondarenko, I.; Lesovoy, V.; Lipatov, O.; Tomczak, P.; Lyulko, O.; Alyasova, A.; Harza, M.; et al. Tivozanib versus sorafenib as initial targeted therapy for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Results from a phase III trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3791–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Porta, C.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Sternberg, C.N.; Szczylik, C.; Zolnierek, J.; Kollmannsberger, C.; Rha, S.Y.; Bjarnason, G.A.; Melichar, B.; et al. Dovitinib versus sorafenib for third-line targeted treatment of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: An open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaza, H.; Oya, M.; Iijima, M.; Hyodo, I.; Gemma, A.; Itoh, H.; Adachi, M.; Okayama, Y.; Sunaya, T.; Inuyama, L. A large-scale prospective registration study of the safety and efficacy of sorafenib tosylate in unresectable or metastatic renal cell carcinoma in Japan: Results of over 3200 consecutive cases in post-marketing all-patient surveillance. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 45, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rini, B.I.; Escudier, B.; Tomczak, P.; Kaprin, A.; Szczylik, C.; Hutson, T.E.; Michaelson, M.D.; Gorbunova, V.A.; Gore, M.E.; Rusakov, I.G.; et al. Comparative effectiveness of axitinib versus sorafenib in advanced renal cell carcinoma (AXIS): A randomized phase 3 trial. Lancet 2011, 378, 1931–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutson, T.E.; Lesovoy, V.; Al-Shukri, S.; Stus, V.P.; Lipatov, O.N.; Bair, A.H.; Rosbrook, B.; Chen, C.; Kim, S.; Vogelzang, N.J. Axitinib versus sorafenib as first-line therapy in patients with metastatic renal-cell carcinoma: A randomized open-label phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Escudier, B.; Tomczak, P.; Hutson, T.E.; Michaelson, M.D.; Negrier, S.; Oudard, S.; Gore, M.E.; Tarazi, J.; Hariharan, S.; et al. Axitinib versus sorafenib as second-line treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma: Overall survival analysis and updated results from a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Bi, F.; Jin, J.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, J.; Ren, X.; Huang, Y.; Tarazi, J.; Tang, J.; Chen, C.; et al. Axitinib versus sorafenib as a second-line therapy in Asian patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Results from a randomized registrational study. OncoTargets Ther. 2015, 8, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar]
- Motzer, R.J.; Hutson, T.E.; Cella, D.; Reeves, J.; Hawkins, R.; Guo, J.; Nathan, P.; Staehler, M.; de Souza, P.; Merchan, J.R.; et al. Pazopanib versus sunitinib in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäger, D.; Ma, J.H.; Mardiak, J.; Ye, D.W.; Korbenfeld, E.; Zemanova, M.; Ahn, H.; Guo, J.; Leonhartsberger, N.; Stauch, K. Sorafenib treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma patients in daily practice: The large international PREDICT study. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2015, 13, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Stergiopoulos, K.; Wu, S. Risk of hypertension and renal dysfunction with an angiogenesis inhibitor sunitinib: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Oncol. 2009, 48, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, W.X.; Lin, F.; Sun, Y.J.; Tang, L.N.; He, A.N.; Yao, Y.; Shen, Z. Incidence and risk of hypertension with pazopanib in patients with cancer: A meta-analysis. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2013, 71, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, S.; Liang, X.; Meng, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Guo, H.; Shi, B. Incidence and risk of sorafenib-induced hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2014, 16, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei-Xiang, Q.; Ai-Na, H.; Shen, Z.; Yao, Y. Incidence and risk of hypertension with a novel multi-targeted kinase inhibitor axitinib in cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 76, 348–357. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, P.S.; Harshman, L.C.; Srinivas, S.; Witteles, R.M. The frequency and severity of cardiovascular toxicity from targeted therapy in advanced renal cell carcinoma patients. JACC Heart Fail. 2013, 1, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escudier, B.; Gore, M. Axitinib for the management of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Drugs R&D 2011, 11, 113–126. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo, D.G.; Autorino, R.; Bruni, G.; Cartenì, G.; Ricevuto, E.; Tudini, M.; Ficorella, C.; Romano, C.; Aieta, M.; Giordano, A.; et al. Cardiovascular toxicity following sunitinib therapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A multicenter analysis. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matrana, M.R.; Bathala, T.; Campbell, M.T.; Duran, C.; Shetty, A.; Teegavarapu, P.; Kalra, S.; Xiao, L.; Atkinson, B.; Corn, P.; et al. Outcomes of unselected patients with metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma treated with first line pazopanib therapy followed by vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors or mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors: A single institution experience. BJU Int. 2015, 118, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hamnvik, O.P.; Choueiri, T.K.; Turchin, A.; McKay, R.R.; Goyal, L.; Davis, M.; Kaymakcalan, M.D.; Williams, J.S. Clinical risk factors for the development of hypertension in patients treated with inhibitors of the VEGF signaling pathway. Cancer 2015, 15, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maitland, M.L.; Kasza, K.E.; Karrison, T.; Moshier, K.; Sit, L.; Black, H.R.; Undevia, S.D.; Stadler, W.M.; Elliott, W.J.; Ratain, M.J. Ambulatory monitoring detects sorafenib-induced blood pressure elevations on the first day of treatment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 6250–6257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.J.; Vaziri, S.A.J.; Rini, B.I.; Elson, P.; Garcia, J.A.; Wirka, R.; Dreicer, R.; Ganapathi, M.K.; Ganapathi, R. Association of VEGF and VEGFR-2 Single nucleotide polymorphisms with hypertension and clinical outcome in metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients treated with sunitinib. Cancer 2012, 118, 1946–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eechoute, K.; van der Veldt, A.A.M.; Oosting, S.; Kappers, M.H.; Wessels, J.A.; Gelderblom, H.; Guchelaar, H.J.; Reyners, A.K.; van Herpen, C.M.; Haanen, J.B.; et al. Polymorphisms in Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase (eNOS) and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) predict sunitinib-induced hypertension. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 92, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diekstra, M.H.M.; Liu, X.; Swen, J.J.; Boven, E.; Castellano, D.; Gelderblom, H.; Mathijssen, R.H.; Rodríguez-Antona, C.; García-Donas, J.; Rini, B.I.; et al. Association of single nucleotide polymorphisms in IL8 and IL13 with sunitinib-induced toxicity in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 71, 1477–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Erp, N.P.; Eechoute, K.; van der Veldt, A.A.; Haanen, J.B.; Reyners, A.K.; Mathijssen, R.H.; Boven, E.; van der Straaten, T.; Baak-Pablo, R.F.; Wessels, J.A.; et al. Pharmacogenetic pathway analysis for determination of sunitinib-induced toxicity. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4406–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.; Cao, Q.; Li, P.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Chu, H.; Zhou, L.; Li, X.; Ye, D.; et al. The influence of genetic variants of sorafenib on clinical outcomes and toxic effects in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20089–20103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noda, S.; Otsuji, T.; Baba, M.; Yoshida, T.; Kageyama, S.; Okamoto, K.; Okada, Y.; Kawauchi, A.; Onishi, H.; Hira, D. Assessment of sunitinib-induced toxicities and clinical outcomes based on therapeutic drug monitoring of sunitinib for patients with renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2015, 13, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diekstra, M.H.; Belaustegui, A.; Swen, J.J.; Boven, E.; Castellano, D.; Gelderblom, H.; Mathijssen, R.H.; García-Donas, J.; Rodríguez-Antona, C.; Rini, B.I. Sunitinib-induced hypertension in CYP3A4 rs4646437 A-allele carriers with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Pharmacogenom. J. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escudier, B.; Rini, B.I.; Motzer, R.J.; Tarazi, J.; Kim, S.; Huang, X.; Rosbrook, B.; English, P.A.; Loomis, A.K.; Williams, J.A. Genotype correlations with blood pressure and efficacy from a randomized phase III trial of second-line axitinib versus sorafenib in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2015, 13, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rini, B.I.; Escudier, B.; Hariharan, S.; Roberts, W.G.; Tarazi, J.; Rosbrook, B.; Askerova, Z.; DeAnnuntis, L.L.; Motzer, R.J. Long-term safety with axitinib in previously treated patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2015, 13, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, C.; Gore, M.E.; Rini, B.I.; Escudier, B.; Hariharan, S.; Charles, L.P.; Yang, L.; DeAnnuntis, L.; Motzer, R.J. Long-term safety of sunitinib in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaymakcalan, M.D.; Xie, W.; Albiges, L.; North, S.A.; Kollmannsberger, C.K.; Smoragiewicz, M.; Kroeger, N.; Wells, J.C.; Rha, S.Y.; Lee, J.L.; et al. Risk factors and model for predicting toxicity-related treatment discontinuation in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy: Results from the international metastatic renal cell carcinoma database consortium. Cancer 2016, 122, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA), Version 15.0 Terminology. Available online: http://www.meddra.org/how-to-use/support-documentation (accessed on 10 July 2016).
- Ich Harmonised Tripartite Guideline Clinical Safety Data Management: Definitions and Standards for Expedited Reporting E2a. Available online: https://www.imim.es/media/upload/arxius/MEDIA436.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2016).
- Hood, J.D.; Meininger, C.J.; Ziche, M.; Granger, H.J. VEGF upregulates ecNOS message, protein, and NO production in human endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 274, 1054–1058. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Venema, V.J.; Gu, X.; Venema, R.C.; Marrero, M.B.; Caldwell, R.B. Vascular endothelial growth factor signals endothelial cell production of nitric oxide and prostacyclin through flk-1/KDR activation of c-Src. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 25130–25135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kappers, M.H.W.; van Esch, J.H.M.; Sluiter, W.; Sleijfer, S.; Danser, A.H.; van den Meiracker, A.H. Hypertension induced by the tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinib is associated with increased circulating endothelin-1 levels. Hypertension 2010, 56, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Veldt, A.A.M.; de Boer, M.P.; Boven, E.; Eringa, E.C.; van den Eertwegh, A.J.; van Hinsbergh, V.W.; Smulders, Y.M.; Serné, E.H. Reduction in skin microvascular density and changes in vessel morphology in patients treated with sunitinib. Anti Cancer Drugs 2010, 21, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thijs, A.M.J.; van Herpen, C.M.L.; Verweij, V.; Pertijs, J.; van den Broek, P.H.; van der Graaf, W.T.; Rongen, G.A. Impaired endothelium-dependent vasodilation does not initiate the development of sunitinib-associated hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2015, 33, 2075–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamba, T.; Tam, B.Y.Y.; Hashizume, H.; Haskell, A.; Sennino, B.; Mancuso, M.R.; Norberg, S.M.; O’Brien, S.M.; Davis, R.B.; Gowen, L.C.; et al. VEGF-dependent plasticity of fenestrated capillaries in the normal adult microvasculature. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 290, 560–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baffert, F.; Le, T.; Sennino, B.; Thurston, G.; Kuo, C.J.; Hu-Lowe, D.; McDonald, D.M. Cellular changes in normal blood capillaries undergoing regression after inhibition of VEGF signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 290, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Pacheco, F.R.; Deudero, J.J.; Castellanos, M.C.; Castilla, M.A.; Alvarez-Arroyo, M.V.; Yagüe, S.; Caramelo, C. Mechanisms of endothelial response to oxidative aggression: Protective role of autologous VEGF and induction of VEGFR-2 by H2O2. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 291, 1395–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayman, S.R.; Leung, N.; Grande, J.P.; Garovic, V.D. VEGF Inhibition, hypertension, and renal toxicity. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 14, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, S.H.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.K.; Oh, K.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Han, J.S.; Kim, T.M.; Lee, S.H.; Joo, K.W. Renal adverse effects of sunitinib and its clinical significance: A single-center experience in Korea. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2014, 29, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axitinib (AG-013736) for the Treatment of Metastatic Renal Cell Cancer. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/results/NCT00920816 (accessed on 30 June 2016).
- Miyake, H.; Harada, K.; Imai, S.; Miyazaki, A.; Fujisawa, M. Non‑significant impact of proteinuria on renal function in Japanese patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with axitinib. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 20, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorich, M.J.; Rowland, A.; Kichenadasse, G.; Woodman, R.J.; Mangoni, A.A. Risk factors of proteinuria in renal cell carcinoma patients treated with VEGF inhibitors: A secondary analysis of pooled clinical trial data. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 1313–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Land, J.D.; Chen, J.H.; Atkinson, B.J.; Cauley, D.H.; Tannir, N.M. Proteinuria with first-line therapy of metastatic renal cell cancer. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2016, 22, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nozawa, M.; Sugimoto, K.; Ohzeki, T.; Minami, T.; Shimizu, N.; Adomi, S.; Saito, Y.; Nose, K.; Yoshimura, K.; Uemura, H. Axitinib-induced proteinuria and efficacy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 21, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usui, J.; Glezerman, I.G.; Salvatore, S.P.; Salvatore, S.P.; Chandran, C.B.; Flombaum, C.D.; Seshan, S.V. Clinicopathological spectrum of kidney diseases in cancer patients treated with vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitors: A report of 5 cases and review of literature. Hum. Pathol. 2014, 45, 1918–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stylianou, K.; Lioudaki, E.; Papadimitraki, E.; Papadimitraki, E.; Kokologiannakis, G.; Kroustalakis, N.; Liotsi, C.; Giannakakis, K.; Georgoulias, V.; Daphnis, E. Crescentic glomerulonephritis associated with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitor and bisphosphonate administration. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 1742–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolleman, E.J.; Weening, J.; Betjes, M.G. Acute nephritic syndrome after anti-VEGF therapy for renal cell carcinoma. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 2002–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costero, O.; Picazo, M.L.; Zamora, P.; Zamora, P.; Romero, S.; Martinez-Ara, J.; Selgas, R. Inhibition of tyrosine kinases by sunitinib associated with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis lesion in addition to thrombotic microangiopathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 1001–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.S.; Chen, C.L.; Wang, J.S. Nephrotic syndrome and acute renal failure apparently induced by sunitinib. Case Rep. Oncol. 2009, 2, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winn, S.K.; Ellis, S.; Savage, P.; Sampson, S.; Marsh, J.E. Biopsy-proven acute interstitial nephritis associated with the tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinib: A class effect? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 673–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eremina, V.; Jefferson, J.A.; Kowalewska, J.; Kowalewska, J.; Hochster, H.; Haas, M.; Weisstuch, J.; Richardson, C.; Kopp, J.B.; Kabir, M.G.; et al. VEGF inhibition and renal thrombotic microangiopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eremina, V.; Sood, M.; Haigh, J.; Nagy, A.; Lajoie, G.; Ferrara, N.; Gerber, H.P.; Kikkawa, Y.; Miner, J.H.; Quaggin, S.E. Glomerular-specific alterations of VEGF-A expression lead to distinct congenital and acquired renal diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertuccio, C.; Veron, D.; Aggarwal, P.K.; Holzman, L.; Tufro, A. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 direct interaction with nephrin links VEGF-A signals to actin in kidney podocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 39933–39944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Lin, Q.; Feng, J.; Dong, X.; Chen, W.; Liu, Q.; Ye, J. Inhibition of nephrin activation by c-mip through Csk-Cbp-Fyn axis plays a critical role in angiotensin II-induced podocyte damage. Cell Signal. 2013, 25, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzedine, H.; Mangier, M.; Ory, V.; Zhang, S.Y.; Sendeyo, K.; Bouachi, K.; Audard, V.; Péchoux, C.; Soria, J.C.; Massard, C.; et al. Expression patterns of RelA and c-mip are associated with different glomerular diseases following anti-VEGF therapy. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echeverria, V.; Burgess, S.; Gamble-George, J.; Zeitlin, R.; Lin, X.; Cao, C.; Arendash, G.W. Sorafenib inhibits nuclear factor κB, decreases inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 expression, and restores working memory in APPswe mice. Neuroscience 2009, 162, 1220–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magyarlaki, T.; Kiss, B.; Buzogany, I.; Fazekas, A.; Sükösd, F.; Nagy, J. Renal cell carcinoma and paraneoplastic IgA nephropathy. Nephron 1999, 82, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, Y.; Kashiwagi, T.; Takei, H.; Takada, D.; Kitamura, H.; Iino, Y.; Katayama, Y. Membranous nephropathy complicated by renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2004, 8, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, H.; Kondo, T.; Iida, S.; Takagi, T.; Tanabe, K. Treatment-related deterioration of renal function is associated with the antitumor efficacy of sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, G.; Golshayan, A.; Elson, P.; Wood, L.; Garcia, J.; Bukowski, R.; Rini, B. Sunitinib and sorafenib in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients with renal insufficiency. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 1618–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, H.; Muramaki, M.; Imai, S.; Harada, K.; Fujisawa, M. Changes in renal function of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma during treatment with molecular-targeted agents. Target. Oncol. 2016, 11, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.S.; Son, N.H.; Byun, S.S.; Lee, S.E.; Hong, S.K.; Jeong, C.W.; Lee, S.C.; Chae, D.W.; Choi, W.S.; Park, Y.H.; et al. Trends in renal function after radical nephrectomy: A multicentre analysis. BJU Int. 2014, 113, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scosyrev, E.; Messing, E.M.; Sylvester, R.; Campbell, S.; van Poppel, H. Renal function after nephron-sparing surgery versus radical nephrectomy: Results from EORTC Randomized Trial 30904. Eur. Urol. 2014, 65, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, R.K.; Andreoni, C.; Ortiz, V. Impact of radical and partial nephrectomy on renal function in patients with renal cancer. Urol. Int. 2014, 92, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toshio, T.; Tsunenori, K.; Kenji, O.; Junpei, I.; Hirohito, K.; Kazuhiko, Y.; Yasunobu, H.; Kazunari, T. Comparison of progression to end‑stage renal disease requiring dialysis after partial or radical nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma in patients with severe chronic kidney disease. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2016, 48, 1421–1427. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, R.; Kapoor, A.; Liu, Z.; Saarela, O.; Tanguay, S.; Jewett, M.; Finelli, A.; Lacombe, L.; Kawakami, J.; Moore, R.; et al. The natural history of renal function after surgical management of renal cell carcinoma: Results from the Canadian Kidney Cancer Information System. Urol. Oncol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Launay-Vacher, V.; Ayllon, J.; Janus, N.; Medioni, J.; Deray, G.; Isnard-Bagnis, C.; Oudard, S. Evolution of renal function in patients treated with antiangiogenics after nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma. Urol. Oncol. 2011, 29, 492–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, J.S.; McDonald, R.J.; Carter, R.E.; Katzberg, R.W.; Kallmes, D.F.; Williamson, E.E. Risk of intravenous contrast material-mediated acute kidney injury: A propensity score matched study stratified by baseline-estimated glomerular filtration rate. Radiology 2014, 271, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.M.; Cha, R.; Lee, J.P.; Kim, D.K.; Oh, K.H.; Joo, K.W.; Lim, C.S.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.S. Incidence and outcomes of contrast-induced nephropathy after computed tomography in patients with CKD: A quality improvement report. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2010, 55, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bono, P.; Rautiola, J.; Utriainen, T.; Joensuu, H. Hypertension as predictor of sunitinib treatment outcome in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Acta Oncol. 2011, 50, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, M.; Kuwada, M.; Hori, S.; Morizawa, Y.; Tatsumi, Y.; Anai, S.; Hosokawa, Y.; Hayashi, Y.; Tomioka, A.; Otani, T.; et al. The best objective response of target lesions and the incidence of treatment-related hypertension are associated with the survival of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with sunitinib: A Japanese retrospective study. BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rini, B.I.; Schiller, J.H.; Fruehauf, J.P.; Cohen, E.E.; Tarazi, J.C.; Rosbrook, B.; Bair, A.H.; Ricart, A.D.; Olszanski, A.J.; Letrent, K.J.; et al. Diastolic blood pressure as a biomarker of axitinib efficacy in solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 3841–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rini, B.I.; Cohen, D.P.; Lu, D.R.; Chen, I.; Hariharan, S.; Gore, M.E.; Figlin, R.A.; Baum, M.S.; Motzer, R.J. Hypertension as a biomarker of efficacy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with sunitinib. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, D.; Rosenberg, J.E.; Figlin, R.A.; Townsend, R.R.; McCann, L.; Carpenter, C.; Pandite, L. Is change in blood pressure a biomarker of pazopanib and sunitinib efficacy in advanced/metastatic renal cell carcinoma? Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 53, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Adverse Event | Grade | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Hypertension | Asymptomatic, transient (<24 h) increase by >20 mmHg (diastolic) or to >150/100 if previously WNL; intervention not indicated | Recurrent or persistent (≥24 h) or symptomatic increase by >20 mmHg (diastolic) or to >150/100 if previously WNL; monotherapy may be indicated | Requiring more than one drug or more intensive therapy than previously | Life-threatening consequences (e.g., hypertensive crisis) | Death |
| Proteinuria | 1+ or 0.15–1.0 g/24 h | 2+ to 3+ or >1.0–3.5 g/24 h | 4+ or >3.5 g/24 h | Nephrotic syndrome | Death |
| Creatinine increased | >ULN–1.5 × ULN | >1.5–3.0 × ULN | >3.0–6.0 × ULN | >6.0 × ULN | Death |
| Reference | Author | Treatment | Number of Patients | Hypertension | Proteinuria | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grade (%) | ≥3 (%) | All Grade (%) | ≥3 Grade (%) | ||||
| [5] | Motzer et al., 2009 | sunitinib | 375 | 112 (30) | 45 (12) | - | - |
| [6] | Gore et al., 2015 | sunitinib | 4543 | 1104 (24) | 267 (6) | - | - |
| [7] | Akaza et al., 2015 | sunitinib | 1671 | 584 (35) | 168 (10) | - | - |
| [8] | Sternberg et al., 2014 | sunitynib | 521 | 135(26) | 27 (5) | - | - |
| [9] | Vrdoljak et al., 2015 | sunitynib | 401 | 93 (23) | 28 (7) | - | - |
| [10] | Sternberg et al., 2013 | pazopanib | 290 | 116 (40) | 13 (4) | 30 (10) | 7 (3) |
| [11] | Escudier et al. 2007 | sorafenib | 451 | 76 (17) | 16 (4) | - | - |
| [12] | Procopio et al. 2007 | sorafenib | 136 | 36 (26) | 2 (1.4) | - | - |
| [13] | Beck et al., 2011 | sorafenib | 1145 | 223 (19.5) | 70 (6.1) | - | - |
| [14] | Motzer et al., 2013 | sorafenib | 257 | 88 (34) | 46 (18) | 187 (73) | 7 (3) |
| [15] | Motzer et al., 2014 | sorafenib | 286 | 79 (28) | 47 (17) | - | - |
| [16] | Akaza et al., 2015 * | sorafenib | 3255 | 1171 (36) | 65 (2) | - | - |
| [17] | Rini et al., 2011 | axitynib | 359 | 145 (40) | 56 (16) | - | - |
| sorafenib | 355 | 103 (29) | 39 (11) | - | - | ||
| [18] | Hutson et al., 2013 | axitynib | 189 | 92 (49) | 26 (13) | - | - |
| [19] | Motzer et al., 2013 | sorafenib | 355 | 107 (30) | 43 (12) | 27 (8) | 4 (1) |
| axitynib | 359 | 149 (42) | 60 (17) | 45 (13) | 11 (3) | ||
| [20] | Qin et al., 2015 | axitynib | 135 | 67 (49.6) | 26 (19.3) | 28 (20.7) | 7 (5.2) |
| [21] | Motzer et al., 2013 | pazopanib | 554 | 257 (46) | 82 (15) | 98 (18) | 23 (4) |
| sunitynib | 548 | 223 (41) | 81(15) | 75 (14) | 22 (4) | ||
| [22] | Jäger et al., 2015 | sorafenib | 2599 | 114 (4.2) | - | - | - |
| Reference | Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms | Full Name of Gene | VEGF Inhibitor |
|---|---|---|---|
| [30] | VEGF rs2010963 (−634 G > C) | vascular endothelial growth factor | sunitinib |
| [31] | VEGFA rs699947(−2578 A > C) | vascular endothelial growth factor A | sunitinib |
| VEGFA rs833061 (−460 C > T) | |||
| VEGFA rs2010963 (405 C > G) | |||
| [33] | VEGFR-2 rs2305948 (1191 C > T) | vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | sunitinib |
| [37] | VEGFR-2 rs2305948 (1192 C > T) | vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | axitinib |
| [31] | IL-8 rs1126647 (A > T) | interleukin 8 | sunitinib |
| [31] | eNOS rs2070744 (−786 T > C) | nitric oxide synthase | sunitinib |
| [34] | ABCB1 rs1045642 (C > T) | ATP binding cassette subfamily B member 1 | sorafenib |
| [36] | CYP3A4 rs4646437 (G > A) | cytochrome P450 family 3 subfamily A member 4 | sunitinib |
| The Causes of Proteinuria in Patients Receiving Anti-VEGF Therapy | |
|---|---|
| The slit diaphragm dysfunction | loss of endothelial fenestrations in the glomeruli |
| endothelial cells cytoplasm swelling | |
| podocyte damage | |
| decreased expression of nephrin | |
| The narrowing or occlusion of capillary lumina by basement membrane | |
| Acute interstitial nephritis | |
| Acute tubular necrosis | |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Semeniuk-Wojtaś, A.; Lubas, A.; Stec, R.; Szczylik, C.; Niemczyk, S. Influence of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors on Hypertension and Nephrotoxicity in Metastatic Renal Cell Cancer Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2073. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122073
Semeniuk-Wojtaś A, Lubas A, Stec R, Szczylik C, Niemczyk S. Influence of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors on Hypertension and Nephrotoxicity in Metastatic Renal Cell Cancer Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(12):2073. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122073
Chicago/Turabian StyleSemeniuk-Wojtaś, Aleksandra, Arkadiusz Lubas, Rafał Stec, Cezary Szczylik, and Stanisław Niemczyk. 2016. "Influence of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors on Hypertension and Nephrotoxicity in Metastatic Renal Cell Cancer Patients" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 12: 2073. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122073
APA StyleSemeniuk-Wojtaś, A., Lubas, A., Stec, R., Szczylik, C., & Niemczyk, S. (2016). Influence of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors on Hypertension and Nephrotoxicity in Metastatic Renal Cell Cancer Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(12), 2073. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122073