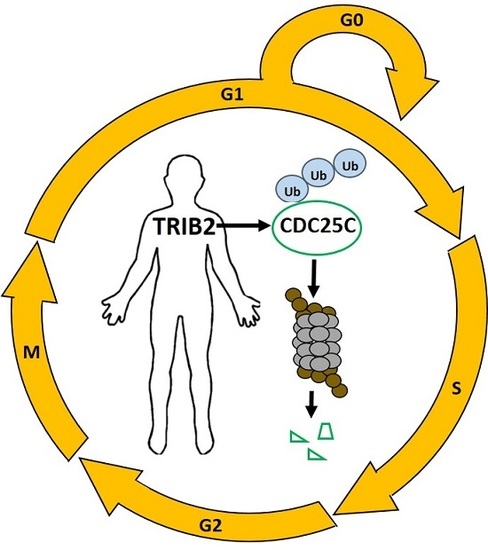
Human TRIB2 Oscillates during the Cell Cycle and Promotes Ubiquitination and Degradation of CDC25C
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. TRIB2 Interacts with CDC25B/C But Not CDC25A
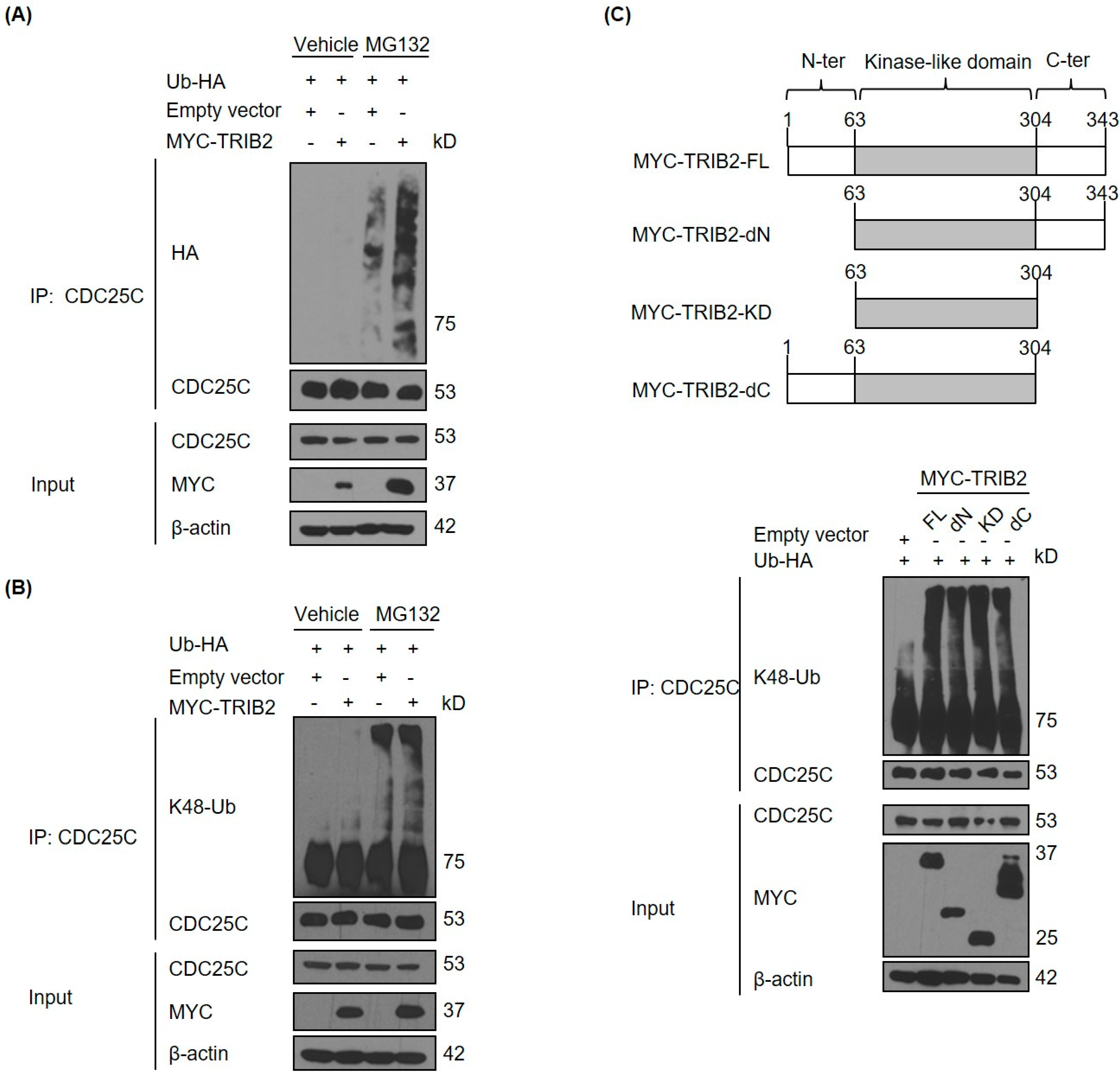
2.2. TRIB2 Promotes Ubiquitination and Proteasomal Degradation of CDC25C
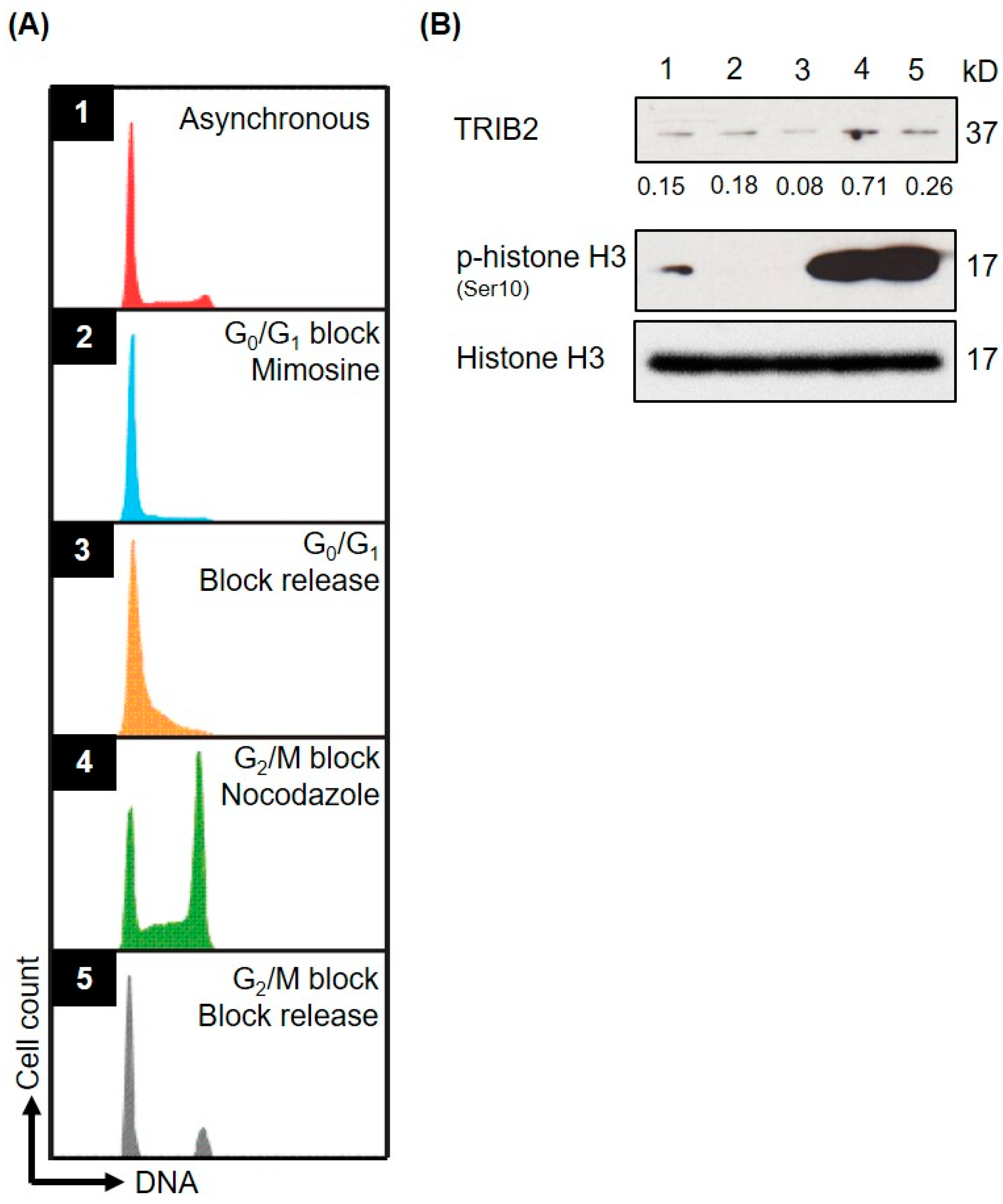
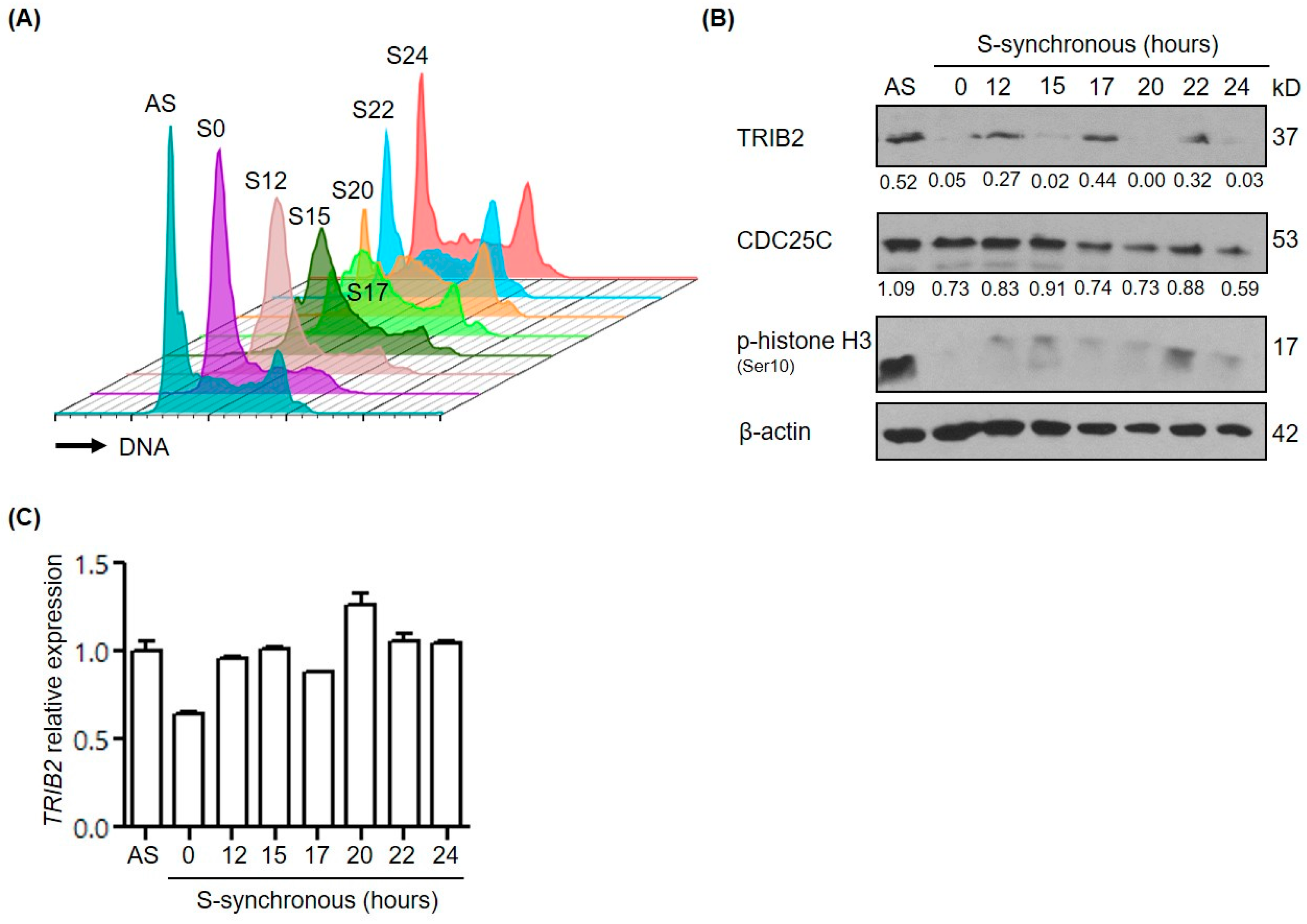
2.3. TRIB2 Protein Levels Are Regulated in a Cell Cycle Dependent Manner
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines
4.2. Plasmids and Transfection
4.3. Antibodies and Western Blotting
4.4. Co-Immunoprecipitation
4.5. Subcellular Fractionation
4.6. Ubiquitination Assay
4.7. Cell Cycle Synchronization
4.8. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.9. Quantitative RT-PCR
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AML | Acute myeloid leukemia |
| CDC25 | Cell division cycle 25 |
| C/EBP | CCAAT/enhancer binding protein |
| DMSO | Dimethylsulfoxide |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| KD | kinase-like domain |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| PBS | Phosphate buffered saline |
| RT-PCR | Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction |
| T-ALL | T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
| Trbl | Drosophila Tribbles |
| TRIB2 | Tribbles homolog 2 |
| Ub-HA | Ub-tagged ubiquitin |
References
- Seher, T.C.; Leptin, M. Tribbles, a cell-cycle brake that coordinates proliferation and morphogenesis during drosophila gastrulation. Curr. Biol. 2000, 10, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosshans, J.; Wieschaus, E. A genetic link between morphogenesis and cell division during formation of the ventral furrow in drosophila. Cell 2000, 101, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, J.; Curado, S.; Ephrussi, A.; Rorth, P. Tribbles coordinates mitosis and morphogenesis in drosophila by regulating string/CDC25 proteolysis. Cell 2000, 101, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, J.A.; O’Farrell, P.H. Mechanism and regulation of CDC25/twine protein destruction in embryonic cell-cycle remodeling. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rorth, P.; Szabo, K.; Texido, G. The level of C/EBP protein is critical for cell migration during drosophila oogenesis and is tightly controlled by regulated degradation. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Sebo, Z.; Pence, L.; Dobens, L.L. Drosophila tribbles antagonizes insulin signaling-mediated growth and metabolism via interactions with AKT kinase. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, F.P.; Byrne, D.P.; Oruganty, K.; Eyers, C.E.; Novotny, C.J.; Shokat, K.M.; Kannan, N.; Eyers, P.A. The Tribbles 2 (TRB2) pseudokinase binds to ATP and autophosphorylates in a metal-independent manner. Biochem. J. 2015, 467, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, J.M.; Zhang, Q.; Young, S.N.; Reese, M.L.; Bailey, F.P.; Eyers, P.A.; Ungureanu, D.; Hammaren, H.; Silvennoinen, O.; Varghese, L.N.; et al. A robust methodology to subclassify pseudokinases based on their nucleotide-binding properties. Biochem. J. 2014, 457, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, J.M.; Nakatani, Y.; Jamieson, S.A.; Dai, W.; Lucet, I.S.; Mace, P.D. Molecular mechanism of CCAAT-enhancer binding protein recruitment by the TRIB1 pseudokinase. Structure 2015, 23, 2111–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyers, P.A. Tribbles: A twist in the pseudokinase tail. Structure 2015, 23, 1974–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, T.; Nakamura, T. Tribbles in disease: Signaling pathways important for cellular function and neoplastic transformation. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeshan, K.; He, Y.; Wouters, B.J.; Shestova, O.; Xu, L.; Sai, H.; Rodriguez, C.G.; Maillard, I.; Tobias, J.W.; Valk, P.; et al. Tribbles homolog 2 inactivates C/EBPALPHA and causes acute myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, C.; Lohan, F.; Campos, J.; Ohlsson, E.; Salome, M.; Forde, C.; Artschwager, R.; Liskamp, R.M.; Cahill, M.R.; Kiely, P.A.; et al. The presence of C/EBPα and its degradation are both required for TRIB2-mediated leukaemia. Oncogene 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandinetti, K.B.; Stevens, T.A.; Ha, S.; Salamone, R.J.; Walker, J.R.; Zhang, J.; Agarwalla, S.; Tenen, D.G.; Peters, E.C.; Reddy, V.A. Overexpression of TRIB2 in human lung cancers contributes to tumorigenesis through downregulation of C/EBPALPHA. Oncogene 2011, 30, 3328–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Park, J.S.; Wei, Y.; Rajurkar, M.; Cotton, J.L.; Fan, Q.; Lewis, B.C.; Ji, H.; Mao, J. TRIB2 acts downstream of WNT/TCF in liver cancer cells to regulate yap and C/EBPALPHA function. Mol. Cell 2013, 51, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Ubiquitin E3 ligase SCF(β-TRCP) regulates TRIB2 stability in liver cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 441, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naiki, T.; Saijou, E.; Miyaoka, Y.; Sekine, K.; Miyajima, A. TRB2, a mouse tribbles ortholog, suppresses adipocyte differentiation by inhibiting AKT and C/EBPBETA. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 24075–24082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rishi, L.; Hannon, M.; Salome, M.; Hasemann, M.; Frank, A.K.; Campos, J.; Timoney, J.; O’Connor, C.; Cahill, M.R.; Porse, B.; et al. Regulation of TRIB2 by an E2F1-C/EBPALPHA feedback loop in AML cell proliferation. Blood 2014, 123, 2389–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, K.L.; O’Connor, C.; Veiga, J.P.; McCarthy, T.V.; Keeshan, K. TRIB2 regulates normal and stress-induced thymocyte proliferation. Cell Discov. 2016, 2, 15050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, A.K.; Reikvam, H.; Lavecchia, A.; Bruserud, O. Therapeutic targeting the cell division cycle 25 (CDC25) phosphatases in human acute myeloid leukemia—The possibility to target several kinases through inhibition of the various CDC25 isoforms. Molecules 2014, 19, 18414–18447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, B.A.; O’Farrell, P.H. The three postblastoderm cell cycles of drosophila embryogenesis are regulated in G2 by string. Cell 1990, 62, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutros, R.; Lobjois, V.; Ducommun, B. CDC25 phosphatases in cancer cells: Key players? Good targets? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomberg, I.; Hoffmann, I. Ectopic expression of CDC25A accelerates the G1/S transition and leads to premature activation of cyclin E- and cyclin A-dependent kinases. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 6183–6194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, I.; Draetta, G.; Karsenti, E. Activation of the phosphatase activity of human CDC25A by a CDK2-cyclin E dependent phosphorylation at the G1/S transition. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 4302–4310. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Millar, J.B.; Blevitt, J.; Gerace, L.; Sadhu, K.; Featherstone, C.; Russell, P. P55CDC25 is a nuclear protein required for the initiation of mitosis in human cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 10500–10504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielli, B.G.; de Souza, C.P.; Tonks, I.D.; Clark, J.M.; Hayward, N.K.; Ellem, K.A. Cytoplasmic accumulation of CDC25B phosphatase in mitosis triggers centrosomal microtubule nucleation in hela cells. J. Cell Sci. 1996, 109, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mailand, N.; Podtelejnikov, A.V.; Groth, A.; Mann, M.; Bartek, J.; Lukas, J. Regulation of G2/M events by CDC25A through phosphorylation-dependent modulation of its stability. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 5911–5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lincoln, A.J.; Wickramasinghe, D.; Stein, P.; Schultz, R.M.; Palko, M.E.; de Miguel, M.P.; Tessarollo, L.; Donovan, P.J. CDC25B phosphatase is required for resumption of meiosis during oocyte maturation. Nat. Genet. 2002, 30, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.S.; Hurov, J.; White, L.S.; Woodford-Thomas, T.; Piwnica-Worms, H. Absence of apparent phenotype in mice lacking CDC25C protein phosphatase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 3853–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, A.M.; White, L.S.; Donovan, P.J.; Piwnica-Worms, H. Normal cell cycle and checkpoint responses in mice and cells lacking CDC25B and CDC25C protein phosphatases. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 2853–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavecchia, A.; Di Giovanni, C.; Pesapane, A.; Montuori, N.; Ragno, P.; Martucci, N.M.; Masullo, M.; de Vendittis, E.; Novellino, E. Discovery of new inhibitors of CDC25B dual specificity phosphatases by structure-based virtual screening. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 4142–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusuf, I.; Fruman, D.A. Regulation of quiescence in lymphocytes. Trends Immunol. 2003, 24, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Rollins, B.J. Cyclin C/CDK3 promotes RB-dependent G0 exit. Cell 2004, 117, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, F.P.; Byrne, D.P.; McSkimming, D.; Kannan, N.; Eyers, P.A. Going for broke: Targeting the human cancer pseudokinome. Biochem. J. 2015, 465, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, S.; Ohoka, N.; Onozaki, K.; Kitagawa, M.; Nakanishi, M.; Hayashi, H. Dual mode of regulation of cell division cycle 25 a protein by TRB3. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 33, 1112–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabbeer, S.; Omer, D.; Berneman, D.; Weitzman, O.; Alpaugh, A.; Pietraszkiewicz, A.; Metsuyanim, S.; Shainskaya, A.; Papa, M.Z.; Yarden, R.I. BRCA1 targets G2/M cell cycle proteins for ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Oncogene 2013, 32, 5005–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salome, M.; Campos, J.; Keeshan, K. TRIB2 and the ubiquitin proteasome system in cancer. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2015, 43, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komander, D. The emerging complexity of protein ubiquitination. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2009, 37, 937–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeshan, K.; Bailis, W.; Dedhia, P.H.; Vega, M.E.; Shestova, O.; Xu, L.W.; Toscano, K.; Uljon, S.N.; Blacklow, S.C.; Pear, W.S. Transformation by tribbles homolog 2 (TRIB2) requires both the TRIB2 kinase domain and COP1 binding. Blood 2010, 116, 4948–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, Z.; Bower, J.; Lu, Y.; Leonard, S.S.; Ding, M.; Castranova, V.; Piwnica-Worms, H.; Shi, X. Arsenite-induced CDC25C degradation is through the KEN-box and ubiquitin–proteasome pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 1990–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfleger, C.M.; Kirschner, M.W. The KEN box: An APC recognition signal distinct from the D box targeted by CDH1. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; He, G.; Nelman-Gonzalez, M.; Ashorn, C.L.; Gallick, G.E.; Stukenberg, P.T.; Kirschner, M.W.; Kuang, J. Regulation of CDC25C by ERK-map kinases during the G2/M transition. Cell 2007, 128, 1119–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eymin, B.; Claverie, P.; Salon, C.; Brambilla, C.; Brambilla, E.; Gazzeri, S. P14ARF triggers G2 arrest through ERK-mediated CDC25C phosphorylation, ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Cell Cycle 2006, 5, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, G.J.; Tsuji, T.; Cross, J.V.; Davis, R.J.; Templeton, D.J.; Jiang, W.; Ronai, Z.A. JNK-mediated phosphorylation of CDC25C regulates cell cycle entry and G2/M DNA damage checkpoint. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 14217–14228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manke, I.A.; Nguyen, A.; Lim, D.; Stewart, M.Q.; Elia, A.E.; Yaffe, M.B. MAPKAP kinase-2 is a cell cycle checkpoint kinase that regulates the G2/M transition and S phase progression in response to UV irradiation. Mol. Cell 2005, 17, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, T.; Kanno, Y.; Yamazaki, Y.; Takahara, T.; Miyata, S.; Nakamura, T. TRIB1 links the MEK1/ERK pathway in myeloid leukemogenesis. Blood 2010, 116, 2768–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soubeyrand, S.; Martinuk, A.; Lau, P.; McPherson, R. TRIB1 is regulated post-transcriptionally by proteasomal and non-proteasomal pathways. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, M.; Lorente, M.; Orea-Soufi, A.; Davila, D.; Erazo, T.; Lizcano, J.; Carracedo, A.; Kiss-Toth, E.; Velasco, G. Oncosuppressive functions of tribbles pseudokinase 3. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2015, 43, 1122–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, S.; Fergusson, W.D.; Oostra, A.B.; Medhurst, A.L.; Waisfisz, Q.; de Winter, J.P.; Chen, F.; Carr, T.F.; Clayton-Smith, J.; Clancy, T.; et al. A cross-linker-sensitive myeloid leukemia cell line from a 2-year-old boy with severe Fanconi anemia and biallelic FANCD1/BRCA2 mutations. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2005, 42, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savitsky, P.A.; Finkel, T. Redox regulation of CDC25C. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 20535–20540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, K.L.; Paredes, R.; Carmody, R.; Eyers, P.A.; Meyer, S.; McCarthy, T.V.; Keeshan, K. Human TRIB2 Oscillates during the Cell Cycle and Promotes Ubiquitination and Degradation of CDC25C. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091378
Liang KL, Paredes R, Carmody R, Eyers PA, Meyer S, McCarthy TV, Keeshan K. Human TRIB2 Oscillates during the Cell Cycle and Promotes Ubiquitination and Degradation of CDC25C. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(9):1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091378
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Kai Ling, Roberto Paredes, Ruaidhri Carmody, Patrick A. Eyers, Stefan Meyer, Tommie V. McCarthy, and Karen Keeshan. 2016. "Human TRIB2 Oscillates during the Cell Cycle and Promotes Ubiquitination and Degradation of CDC25C" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 9: 1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091378
APA StyleLiang, K. L., Paredes, R., Carmody, R., Eyers, P. A., Meyer, S., McCarthy, T. V., & Keeshan, K. (2016). Human TRIB2 Oscillates during the Cell Cycle and Promotes Ubiquitination and Degradation of CDC25C. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(9), 1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091378