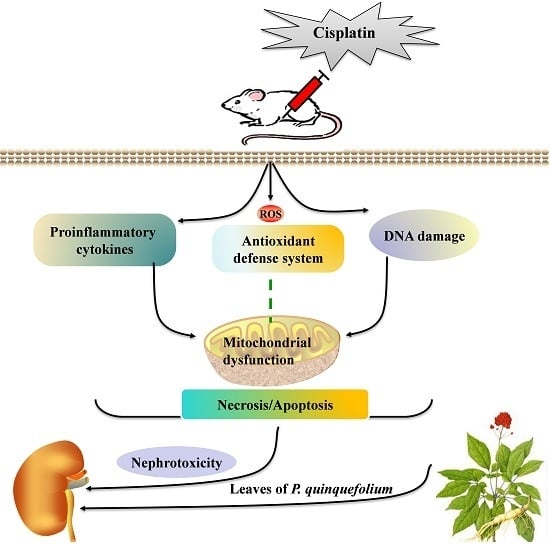
Nephroprotective Effects of Saponins from Leaves of Panax quinquefolius against Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
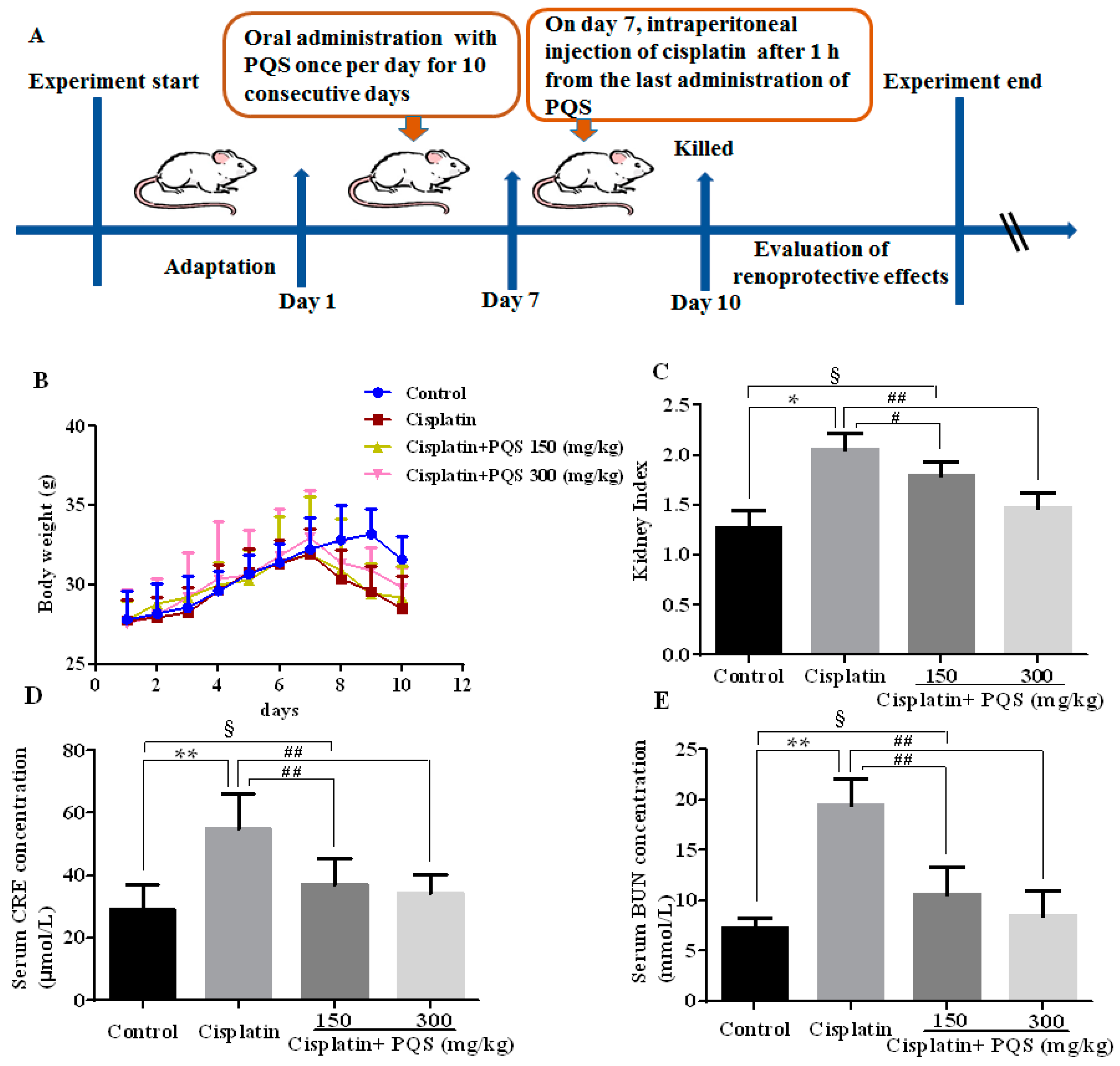
2.1. Effects of P. quinquefolius (PQS) on Renal Dysfunction in Cisplatin-Treated Mice
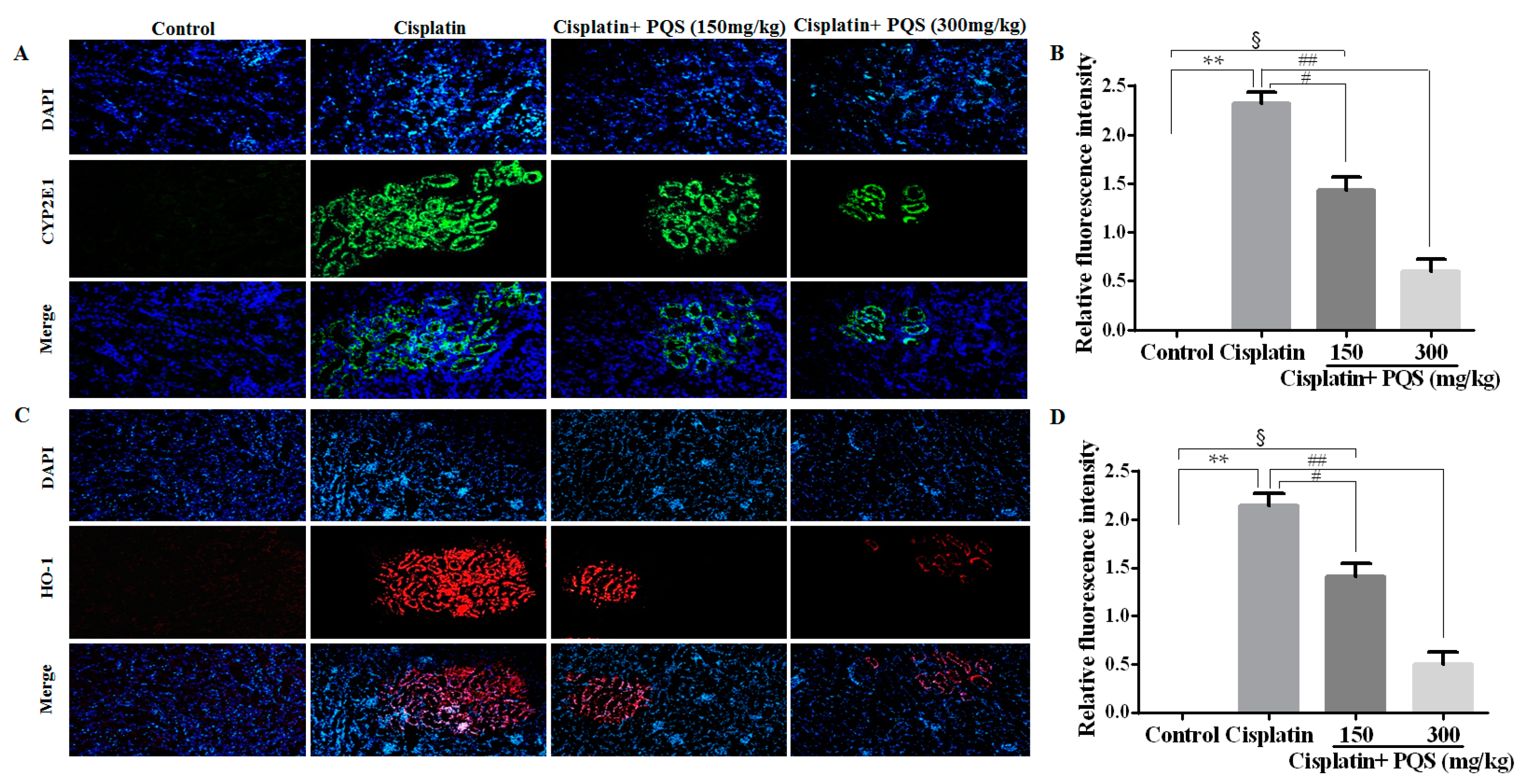
2.2. Effects of PQS on Oxidative Stress of Kidney in Cisplatin-Treated Mice
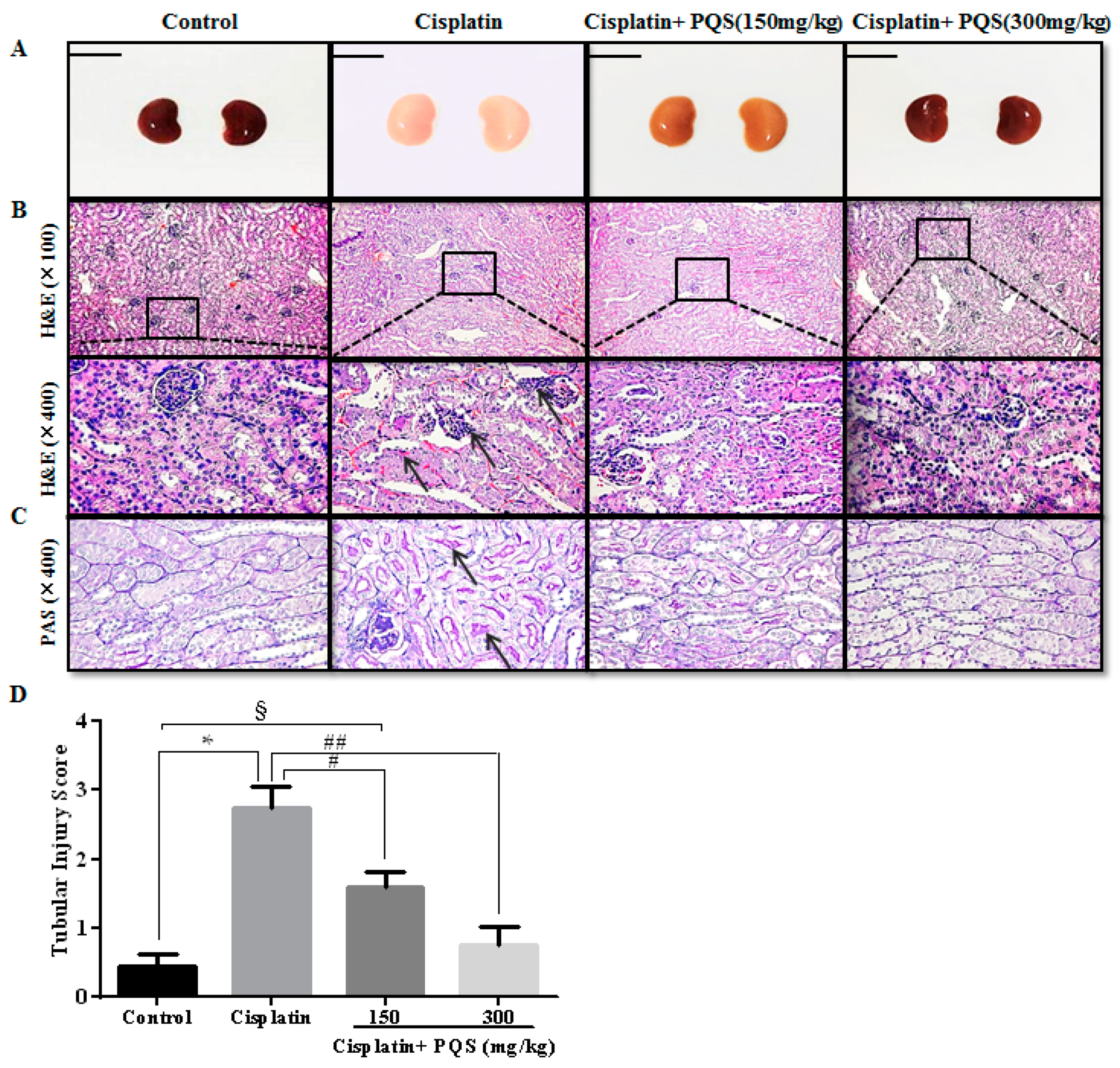
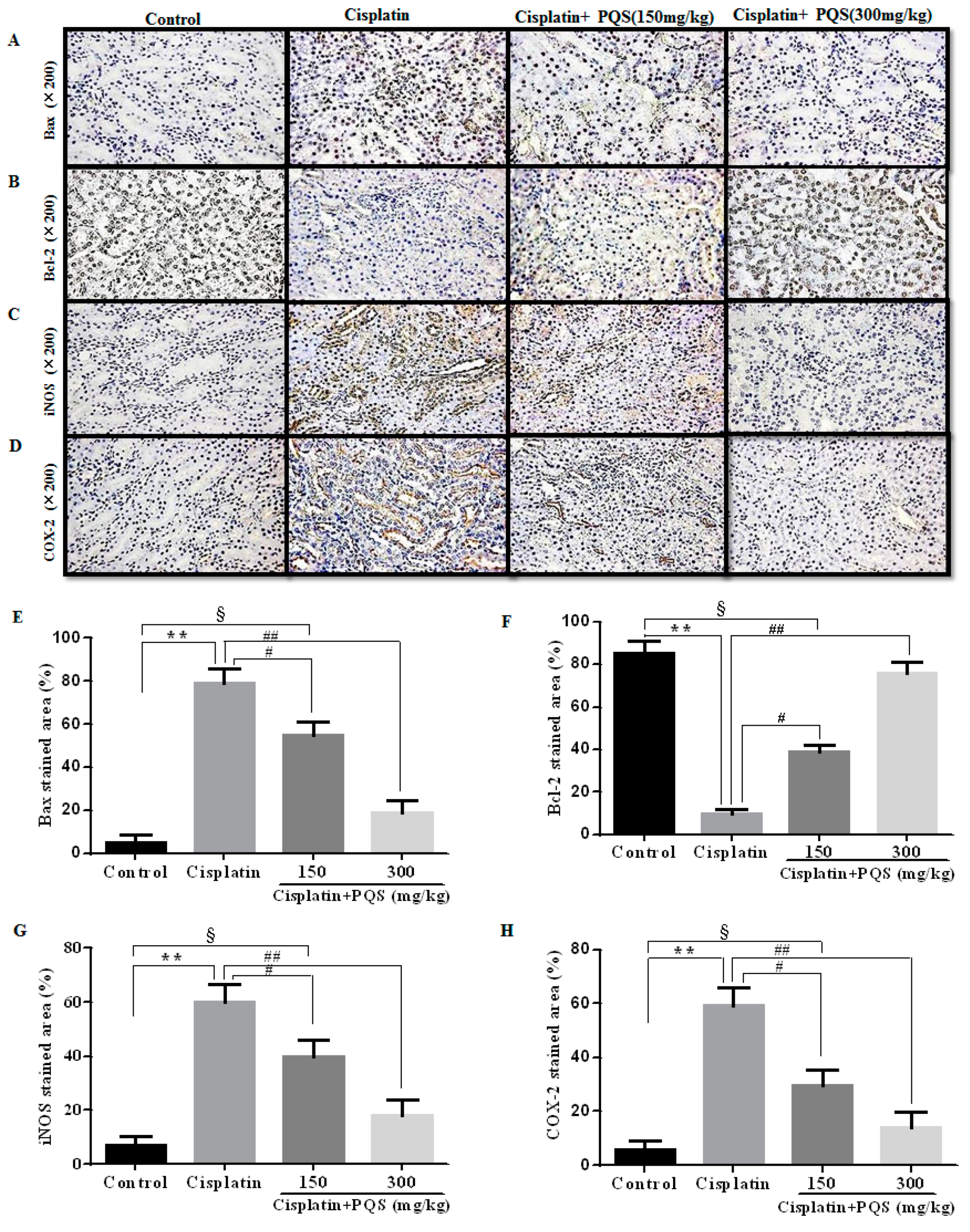
2.3. Effects of PQS on Histopathological Changes of Kidney in Cisplatin-Treated Mice
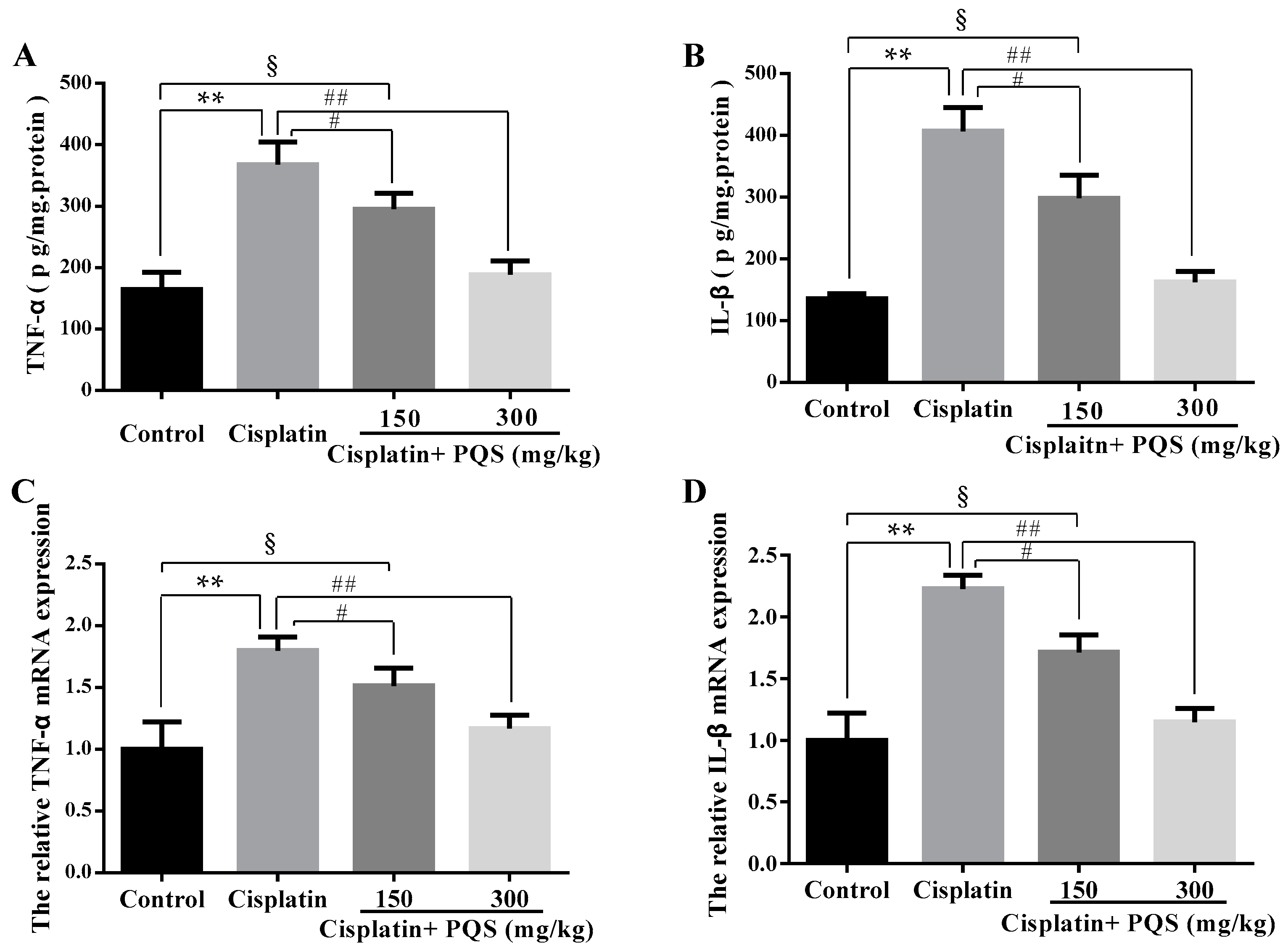
2.4. Effects of PQS on Inflammation of Kidney in Cisplatin-Treated Mice
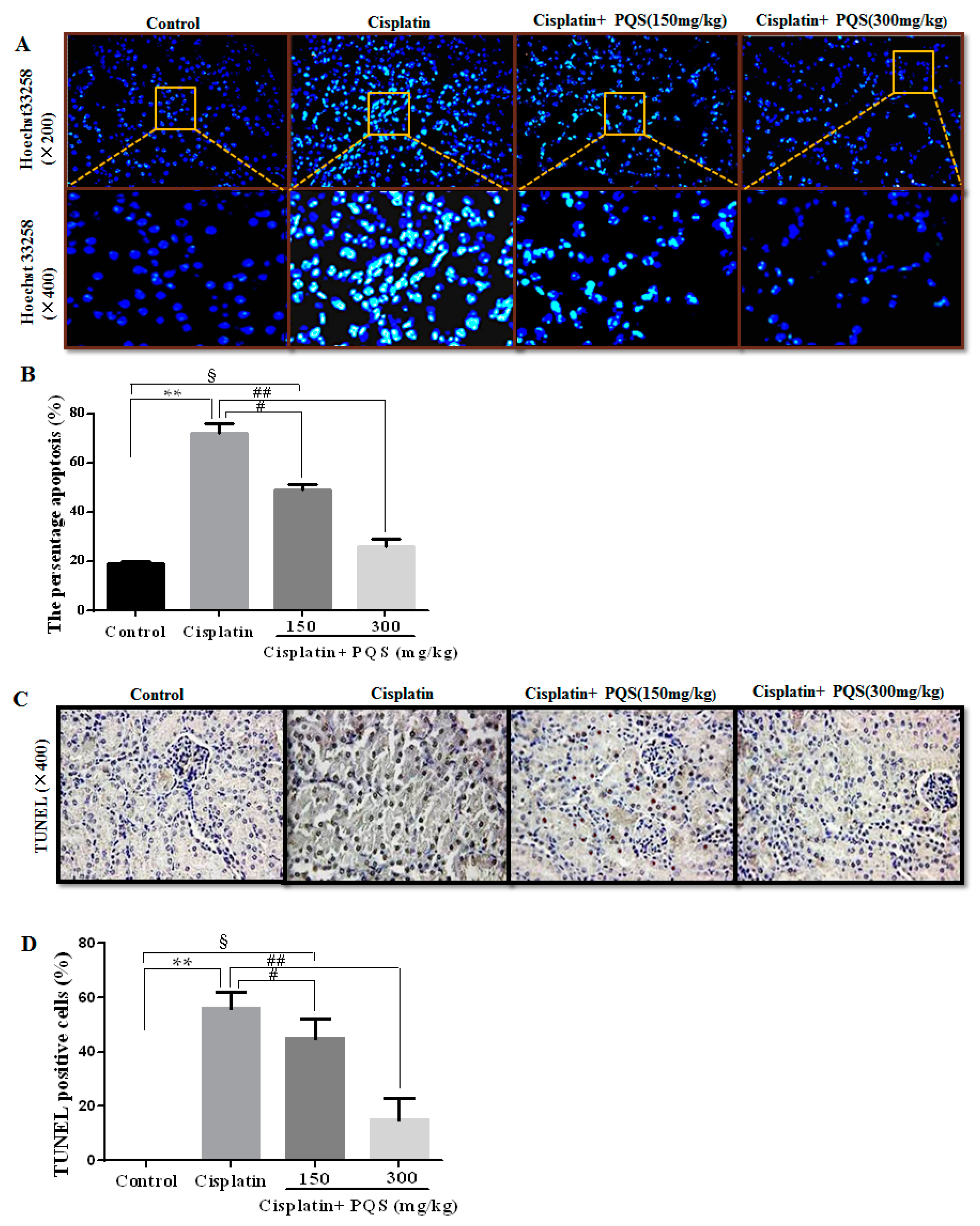
2.5. Effects of PQS on Apoptosis of Kidney in Cisplatin-Treated Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Kits
4.2. Animals and Experimental Protocol
4.3. Assessment of Biochemical Parameters
4.4. Determination of Inflammatory Cytokines
4.5. Histopathological Examination
4.6. Hoechst 33258 Staining Analysis
4.7. TUNEL Staining Analysis
4.8. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Immunofluorescence Analysis
4.9. Real-Time PCR Analysis
4.10. Western Blotting Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PQ | Panax quinquefolius |
| AKI | Acute kidney injury |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| BUN | Blood urea nitrogen |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| CRE | Creatinine |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| iNOS | Inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| CYP2E1 | Cytochrome P450 E1 |
| HO-1 | Heme oxygenase-1 |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor-κB |
| qRT-PCR | quantitative real-time PCR |
| Nox4 | NADPH oxidase type 4 |
References
- Arany, I.; Safirstein, R.L. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Semin. Nephrol. 2003, 23, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuertes, M.A.; Castilla, J.; Alonso, C.; Perez, J.M. Cisplatin biochemical mechanism of action: From cytotoxicity to induction of cell death through interconnections between apoptotic and necrotic pathways. Curr. Med. Chem. 2003, 10, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Lee, M.Y.; Son, H.Y.; Park, B.K.; Ryu, S.Y.; Jung, J.Y. Red ginseng ameliorates acute cisplatin-induced nephropathy. Planta Med. 2014, 80, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabla, N.; Dong, Z. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: Mechanisms and renoprotectivestrategies. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 994–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosohata, K.; Ando, H.; Fujimura, A. Urinary vanin-1 as a novel biomarker for early detection of drug-induced acute kidney injury. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 341, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, V.S.; Ramirez, V.; Ichimura, T.; Bobadilla, N.A.; Bonventre, J.V. Urinary kidney injury molecule-1: A sensitive quantitative biomarker for early detection of kidney tubular injury. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2006, 290, F517–F529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, J.; Ma, Q.; Prada, A.; Mitsnefes, M.; Zahedi, K.; Yang, J.; Barasch, J.; Devarajan, P. Identification of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a novel early urinary biomarker for ischemic renal injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 2534–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, E.M.; Xu, L.Y.; Xiong, H.Q.; Cai, W.J.; Wu, B.L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.F.; Lin, Y.; Shen, Z.Y. Cloning and identification of 5′-untranslated region (UTR) and 3′-untranslated region of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) gene from esophageal carcinoma cell line sheec. Ai Zheng 2003, 22, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Metnitz, P.G.; Krenn, C.G.; Steltzer, H.; Lang, T.; Ploder, J.; Lenz, K.; Le Gall, J.R.; Druml, W. Effect of acute renal failure requiring renal replacement therapy on outcome in critically ill patients. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 30, 2051–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lameire, N.H.; de Vriese, A.S.; Vanholder, R. Prevention and nondialytic treatment of acute renal failure. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2003, 9, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosohata, K. Role of oxidative stress in drug-induced kidney injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ognjanovic, B.I.; Djordjevic, N.Z.; Matic, M.M.; Obradovic, J.M.; Mladenovic, J.M.; Stajn, A.S.; Saicic, Z.S. Lipid peroxidative damage on cisplatin exposure and alterations in antioxidant defense system in rat kidneys: A possible protective effect of selenium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 1790–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, X.; Miao, G.; Sun, C.; Zhang, H. NADPH oxidase activation contributes to heavy ion irradiation-induced cell death. Dose Response 2017, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nlandu-Khodo, S.; Dissard, R.; Hasler, U.; Schafer, M.; Pircher, H.; Jansen-Durr, P.; Krause, K.H.; Martin, P.Y.; de Seigneux, S. NADPH oxidase 4 deficiency increases tubular cell death during acute ischemic reperfusion injury. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, B.D.; Kalvala, A.K.; Koneru, M.; Mahesh Kumar, J.; Kuncha, M.; Rachamalla, S.S.; Sistla, R. Ameliorative effect of fisetin on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats via modulation of NF-κB activation and antioxidant defence. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushal, G.P.; Kaushal, V.; Hong, X.; Shah, S.V. Role and regulation of activation of caspases in cisplatin-induced injury to renal tubular epithelial cells. Kidney Int. 2001, 60, 1726–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Yan, M.H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.S. Ginsenoside Rg5 ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice through inhibition of inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. Nutrients 2016, 8, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, R.M.; Gomez, Y.G.; Ramirez, E.B. Nephroprotective activity of Prosthechea michuacana against cisplatin-induced acute renal failure in rats. J. Med. Food 2010, 13, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayir, K.; Karadeniz, A.; Simsek, N.; Yildirim, S.; Karakus, E.; Kara, A.; Akkoyun, H.T.; Sengul, E. Pomegranate seed extract attenuates chemotherapy-induced acute nephrotoxicity and hepatotoxicity in rats. J. Med. Food 2011, 14, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana, S.; Verma, K.; Khan, R. Nephroprotective efficacy of chrysin against cisplatin-induced toxicity via attenuation of oxidative stress. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2012, 64, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.Z.; Hu, Y.; Wu, W.Y.; Ye, M.; Guo, D.A. Saponins in the genus Panax L. (Araliaceae): A systematic review of their chemical diversity. Phytochemistry 2014, 106, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szeto, Y.T.; Sin, Y.S.; Pak, S.C.; Kalle, W. American ginseng tea protects cellular DNA within 2 h from consumption: Results of a pilot study in healthy human volunteers. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 66, 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.T.; Wang, C.Z.; Ni, M.; Wu, J.A.; Mehendale, S.R.; Aung, H.H.; Foo, A.; Yuan, C.S. American ginseng berry juice intake reduces blood glucose and body weight in ob/ob mice. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, S590–S594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yu, X.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Yao, Y.; Lui, E.M.; Ren, G. Structural and anti-inflammatory characterization of a novel neutral polysaccharide from north american ginseng (Panax quinquefolius). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 74, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, S.; Chen, S.; Feng, B.; Wu, Y.; Lui, E.; Chakrabarti, S. American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius) prevents glucose-induced oxidative stress and associated endothelial abnormalities. Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, K.M.; Lee, C.; Lo, Y.M.; Moon, B. The hypoglycemic effects of american red ginseng (Panax quinquefolius L.) on a diabetic mouse model. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, H147–H152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Z.; Zhang, B.; Song, W.X.; Wang, A.; Ni, M.; Luo, X.; Aung, H.H.; Xie, J.T.; Tong, R.; He, T.C.; et al. Steamed american ginseng berry: Ginsenoside analyses and anticancer activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 9936–9942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.L.; Shi, D.Z.; Yin, H.J. Effect of Panax quinquefolius saponin on angiogenesis and expressions of VEGF and BFGF in myocardium of rats with acute myocardial infarction. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2007, 27, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Shang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Shi, D. Interaction of Panax quinquefolius saponin and dual antiplatelets on vascular endothelial function in rats with acute myocardial infarction. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 932751. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yin, H.; Huang, Y.; Guo, C.; Xia, C.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, L. Panax quinquefolius saponin of stem and leaf attenuates intermittent high glucose-induced oxidative stress injury in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells via PI3K/Akt/GSK-3 β pathway. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Shi, D.; Wang, W.; Zhang, C.; Fu, M.; Ge, J. Panax quinquefolium saponins inhibited immune maturation of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells via blocking nuclear factor-κB pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 141, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Rojas, B.; Rodriguez-Rangel, D.S.; Granados-Castro, L.F.; Negrette-Guzman, M.; Leon-Contreras, J.C.; Hernandez-Pando, R.; Molina-Jijon, E.; Reyes, J.L.; Zazueta, C.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J. C-phycocyanin prevents cisplatin-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2015, 406, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yuan, F.; Cao, X.; Zhai, Z.; Gang, H.; Du, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, J.; et al. P2X7 receptor blockade protects against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice by decreasing the activities of inflammasome components, oxidative stress and caspase-3. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2014, 281, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C.A.; Nick, H.S.; Agarwal, A. Manganese superoxide dismutase attenuates cisplatin-induced renal injury: Importance of superoxide. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2001, 12, 2683–2690. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, H.M.; Cho, J.M.; Lee, H.R.; Shim, G.S.; Kwak, M.K. Renal protection by 3H-1,2-dithiole-3-thione against cisplatin through the NRF2-antioxidant pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 76, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shino, Y.; Itoh, Y.; Kubota, T.; Yano, T.; Sendo, T.; Oishi, R. Role of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase in cisplatin-induced injury in LLC-PK1 cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 35, 966–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Rojas, B.; Medina-Campos, O.N.; Hernandez-Pando, R.; Negrette-Guzman, M.; Huerta-Yepez, S.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J. C-phycocyanin prevents cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity through inhibition of oxidative stress. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedard, K.; Krause, K.H. The nox family of ROS-generating nadph oxidases: Physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 245–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thallas-Bonke, V.; Jha, J.C.; Gray, S.P.; Barit, D.; Haller, H.; Schmidt, H.H.; Coughlan, M.T.; Cooper, M.E.; Forbes, J.M.; Jandeleit-Dahm, K.A. Nox-4 deletion reduces oxidative stress and injury by PKC-α-associated mechanisms in diabetic nephropathy. Physiol. Rep. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Wu, W.F.; Dong, L.; Ren, G.L.; Li, H.D.; Yang, Q.; Li, X.F.; Xu, T.; Li, Z.; Wu, B.M.; et al. Protocatechuic aldehyde attenuates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by suppressing Nox-mediated oxidative stress and renal inflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Baliga, M.; Baliga, R. Effect of cytochrome p450 2E1 inhibitors on cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity to renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. Anticancer Res. 2002, 22, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Valko, M.; Leibfritz, D.; Moncol, J.; Cronin, M.T.; Mazur, M.; Telser, J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 44–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Baliga, R. Cytochrome p450 2E1 null mice provide novel protection against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and apoptosis. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 1687–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domitrovic, R.; Cvijanovic, O.; Susnic, V.; Katalinic, N. Renoprotective mechanisms of chlorogenic acid in cisplatin-induced kidney injury. Toxicology 2014, 324, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nojiri, T.; Hosoda, H.; Kimura, T.; Tokudome, T.; Miura, K.; Takabatake, H.; Miyazato, M.; Okumura, M.; Kangawa, K. Protective effects of ghrelin on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice. Peptides 2016, 82, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Li, C.; Wei, Z.; Wang, J.; Kou, J.; Liu, W.; Shi, M.; Yang, Z.; Fu, Y. Protective role of apigenin in cisplatin-induced renal injury. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 789, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, G.; Reeves, W.B. TNF-α mediates chemokine and cytokine expression and renal injury in cisplatin nephrotoxicity. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktan, F. Inos-mediated nitric oxide production and its regulation. Life Sci. 2004, 75, 639–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itzkowitz, S.H. Molecular biology of dysplasia and cancer in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2006, 35, 553–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honma, S.; Takahashi, N.; Shinohara, M.; Nakamura, K.; Mitazaki, S.; Abe, S.; Yoshida, M. Amelioration of cisplatin-induced mouse renal lesions by a cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 selective inhibitor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 715, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Dong, Z. Regulation and pathological role of p53 in cisplatin nephrotoxicity. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 327, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.W.; Jeong, J.Y.; Lim, B.J.; Chang, Y.K.; Lee, S.J.; Na, K.R.; Shin, Y.T.; Choi, D.E. Sildenafil attenuates renal injury in an experimental model of rat cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Toxicology 2009, 257, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousef, M.I.; Hussien, H.M. Cisplatin-induced renal toxicity via tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin 6, tumor suppressor p53, DNA damage, xanthine oxidase, histological changes, oxidative stress and nitric oxide in rats: Protective effect of ginseng. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 78, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Checinska, A.; Hoogeland, B.S.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Giaccone, G.; Kruyt, F.A. Role of XIAP in inhibiting cisplatin-induced caspase activation in non-small cell lung cancer cells: A small molecule Smac mimic sensitizes for chemotherapy-induced apoptosis by enhancing caspase-3 activation. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, G. ARL6IP1 mediates cisplatin-induced apoptosis in caski cervical cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2010, 23, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zheng, Y.; Han, L.; Wang, H.; Saito, M.; Ling, M.; Kimura, Y.; Feng, Y. Saponins (ginsenosides) from stems and leaves of Panax quinquefolium prevented high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice. Phytomedicine 2008, 15, 1140–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Qu, X.N.; Han, Y.; Zheng, S.W.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.P. Ameliorative effects of 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furfural (5-HMF) from schisandra chinensis on alcoholic liver oxidative injury in mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 2446–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, G.; Reeves, W.B. Salicylate reduces cisplatin nephrotoxicity by inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-α. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Han, Y.; Tian, Y.H.; Zhang, G.S.; Sun, Y.S.; Wang, Y.P. Platycodin D isolated from the aerial parts of platycodon grandiflorum protects alcohol-induced liver injury in mice. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 1418–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Xu, Q.; He, Y.F.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S.B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, L.C. Anti-tumor effect of steamed codonopsis lanceolata in H22 tumor-bearing mice and its possible mechanism. Nutrients 2015, 7, 8294–8307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.Y.; Hu, J.N.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, R.; He, Y.F.; Hou, W.; Wang, Z.Q.; Yang, G.; Li, W. Saponins (ginsenosides) from the leaves of panax quinquefolius ameliorated acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 3684–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhang, M.; Gu, J.; Meng, Z.J.; Zhao, L.C.; Zheng, Y.N.; Chen, L.; Yang, G.L. Hypoglycemic effect of protopanaxadiol-type ginsenosides and compound K on type 2 diabetes mice induced by high-fat diet combining with streptozotocin via suppression of hepatic gluconeogenesis. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Primer Name | Nucleotide Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| TNF-α forward | CTTCTCATTCCTGCTTGTG |
| TNF-α reverse | ACTTGGTGGTTTGCTACG |
| IL-1β forward | TTGTGGCTGTGGAGAAG |
| IL-1β reverse | CATCAGAGGCAAGGAGG |
| GAPDH forward | AGGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG |
| GAPDH reverse | GGGGTCGTTGATGGCAACA |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Z.-N.; Li, Y.-Z.; Li, W.; Yan, X.-T.; Yang, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, L.-C.; Yang, L.-M. Nephroprotective Effects of Saponins from Leaves of Panax quinquefolius against Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071407
Ma Z-N, Li Y-Z, Li W, Yan X-T, Yang G, Zhang J, Zhao L-C, Yang L-M. Nephroprotective Effects of Saponins from Leaves of Panax quinquefolius against Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(7):1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071407
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Zhi-Na, Yan-Zi Li, Wei Li, Xiao-Tong Yan, Ge Yang, Jing Zhang, Li-Chun Zhao, and Li-Min Yang. 2017. "Nephroprotective Effects of Saponins from Leaves of Panax quinquefolius against Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 7: 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071407
APA StyleMa, Z.-N., Li, Y.-Z., Li, W., Yan, X.-T., Yang, G., Zhang, J., Zhao, L.-C., & Yang, L.-M. (2017). Nephroprotective Effects of Saponins from Leaves of Panax quinquefolius against Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(7), 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071407