Functional Analysis of the Promoter Region of Japanese Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) β-actin Gene: A Useful Tool for Gene Research in Marine Fish
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation and Sequence Analysis of β-actin 5′-Flanking Region
2.2. Analysis of the Proximal Promoter Regions
2.3. Functional Analysis of Japanese Flounder β-Actin Promoter Regulatory Regions
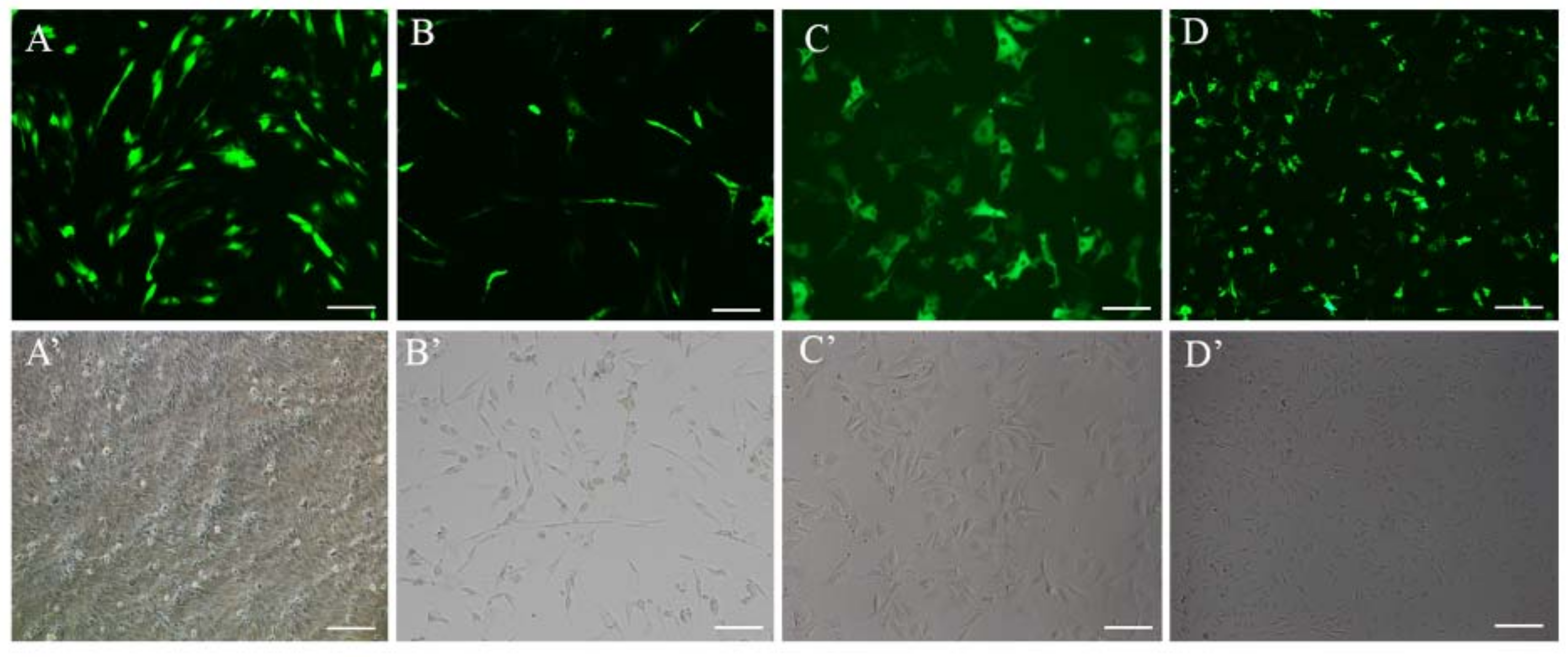
2.4. Expression of eGFP Using Japanese Flounder β-actin Promoter in FBC and FEC Cells
2.5. Screening of eGFP Overexpression in Stable Cell Line
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Fish
4.2. Cell Line Culture
4.3. Cloning of Poβ-actin Promoter Sequence
4.4. Sequence Analysis
4.5. Construction of Promoter-Luciferase Cassette
4.6. Construction of EGFP Plasmid
4.7. Transient Transfection
4.8. Screening of Poβ-actin-EGFP Overexpression Cells
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CMV | CytoMegalo Virus |
| GFP | Green Fluorescent Protein |
| IDT | Integrated DNA Technologies |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| FEC | Flounder Embryo Cell line |
| FBC | Flounder Brain Cell line |
| DMED/F12 | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Media: Nutrient Mixture F-12 |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| PBS | Phosphate Buffered Saline |
References
- Hightower, R.C.; Meagher, R.B. The molecular evolution of actin. Genetics 1986, 114, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bohnsack, M.T.; Stüven, T.; Kuhn, C.; Cordes, V.C.; Görlich, D. A selective block of nuclear actin export stabilizes the giant nuclei of Xenopus oocytes. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, R.; Holmes, K.C. Actin structure and function. Ann. Rev. Biophys. 2011, 40, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunger, M.K.; Moran, S.M.; Glover, E.; Thomae, T.L.; Lahvis, G.P.; Lin, B.C.; Bradfield, C.A. Resistance to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin toxicity and abnormal liver development in mice carrying a mutation in the nuclear localization sequence of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 17767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitade, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Uji, T.; Fukuda, S.; Endo, H.; Saga, N. Structural features and gene-expression profiles of actin homologs in Porphyra yezoensis (Rhodophyta). Gene 2008, 423, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Du, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X. Identification and expression of piwil2 in turbot Scophthalmus maximus, with implications of the involvement in embryonic and gonadal development. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 208, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Yang, D.; Zhou, C.; Cheng, K.; Liu, Z.; Chen, L.; Fang, L.; Xie, P. β-actin as a loading control for plasma-based Western blot analysis of major depressive disorder patients. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 427, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosuga, M.; Enosawa, S.; Li, X.K.; Suzuki, S.; Matsuo, N.; Yamada, M.; Roychowdhury, J.; Koiwai, O.; Okuyama, T. Strong, long-term transgene expression in rat liver using chicken β-actin promoter associated with cytomegalovirus immediate-early enhancer (CAG promoter). Cell Transp. 2000, 9, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Soderlund, M.; Xiang, J.; Lu, Y. Function and Regulation Domains of a Newly Isolated Putative β-Actin Promoter from Pacific White Shrimp. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, D.S.; Nam, Y.K. Functional ability of cytoskeletal β-actin regulator to drive constitutive and ubiquitous expression of a fluorescent reporter throughout the life cycle of transgenic marine medaka Oryzias dancena. Transgenic Res. 2011, 20, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.K.; Holland, N.D.; Holland, L.Z. Tissue-specific expression of FoxD reporter constructs in amphioxus embryos. Dev. Biol. 2004, 274, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, L.Z.; Onai, T. Analyses of gene function in amphioxus embryos by microinjection of mRNAs and morpholino oligonucleotides. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 770, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sternberg, S.H.; Redding, S.; Jinek, M.; Greene, E.C.; Doudna, J.A. DNA Interrogation by the CRISPR RNA-Guided Endonuclease Cas9. Nature 2014, 507, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, Y.; Duan, C. Microinjection of Antisense Morpholinos, CRISPR/Cas9 RNP, and RNA/DNA into Zebrafish Embryos. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1742, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martínez, R.; Estrada, M.P.; Berlanga, J.; Guillén, I.; Hernández, O.; Cabrera, E.; Pimentel, R.; Morales, R.; Herrera, F.; Morales, A. Growth enhancement in transgenic tilapia by ectopic expression of tilapia growth hormone. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1996, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shears, M.A.; Fletcher, G.; Hew, C.L.; Gauthier, S.; Davies, P.L. Transfer, Expression, and Stable Inheritance of Antifreeze Protein Genes in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1991, 1, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Halloran, M.C.; Satomaeda, M.; Warren, J.T.; Su, F.; Lele, Z.; Krone, P.H.; Kuwada, J.Y.; Shoji, W. Laser-induced gene expression in specific cells of transgenic zebrafish. Development 2000, 127, 1953–1960. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nickenig, G.; Laufs, U.; Schnabel, P.; Knorr, A.; Paul, M.; Bohm, M.P. Down-regulation of aortic and cardiac AT1 receptor gene expression in transgenic (mRen-2) 27 rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 121, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldosari, M.; Zhang, G.; Knapp, J.E.; Liu, D. Evaluation of viral and mammalian promoters for driving transgene expression in mouse liver. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 339, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashijima, S.; Okamoto, H.; Ueno, N.; Hotta, Y.; Eguchi, G. High-frequency generation of transgenic zebrafish which reliably express GFP in whole muscles or the whole body by using promoters of zebrafish origin. Dev. Biol. 1997, 192, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, S.; Sasado, T.; Tamiya, G.; Ozato, K.; Wakamatsu, Y.; Takeshita, A.; Kimura, M. An efficient expression vector for transgenic medaka construction. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hamada, K.; Tamaki, K.; Sasado, T.; Watai, Y.; Kani, S.; Wakamatsu, Y.; Ozato, K.; Kinoshita, M.; Kohno, R.; Takagi, S. Usefulness of the medaka β-actin promoter investigated using a mutant GFP reporter gene in transgenic medaka (Oryzias latipes). Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1998, 7, 173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.S.; Lavender, F.L.; Iyengar, A.; Rahman, M.A.; Ayad, H.H.; Lathe, R.; Morley, S.D.; Maclean, N. Comparison of the activity of carp and rat β-actin gene regulatory sequences in tilapia and rainbow trout embryos. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 1996, 45, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.W.; Müller, F.; Lavender, F.L.; Orbán, L.; Maclean, N. High transgene activity in the yolk syncytial layer affects quantitative transient expression assays in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Transgenic Res. 1996, 5, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley, S.; Smith, T.J.; Muller, F.; Maclean, N.; Uzbekova, S.; Prunet, P.; Breton, B. Isolation and functional analysis of the histone H3 promoter from atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1998, 7, 165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X. Locus Number Estimation of MHC Class II B in Stone Flounder and Japanese Flounder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 6000–6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanasaksiri, K.; Hirono, I.; Kondo, H. Identification and expression analysis of suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) of Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 58, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, M.; Xu, W.T.; Li, H.L.; Wang, L.; Xiu, Y.J.; Yang, Y.M.; Li, Y.Z.; Zhao, F.Z.; Chen, S.L. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of a novel r-spondin member (rspo2l) in Chinese tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 72, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Tan, X.; Jiao, S.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Zou, Y. A new pattern of primordial germ cell migration in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) identified using nanos3. Dev. Genes Evol. 2015, 225, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Xin, N.; Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Qi, J. Characterization of F-spondin in Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) and its role in the nervous system development of teleosts. Gene 2015, 575, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.L.; Mizuguchi, H.; Ishii-Watabe, A.; Uchida, E.; Mayumi, T.; Hayakawa, T. Optimization of transcriptional regulatory elements for constructing plasmid vectors. Gene 2001, 272, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breathnach, R.; Chambon, P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 1981, 50, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatyol, K.; Illes, K.; Szalay, A.A. An alternative intronic promoter of the Bombyx A3 cytoplasmic actin gene exhibits a high level of transcriptional activity in mammalian cells. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1999, 261, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Y.; Qi, J.; Zhang, Q. GATA4 is a transcriptional regulator of R-spondin1 in Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Gene 2018, 648, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q. Evolutionary Conservation ofpou5f3Genomic Organization and Its Dynamic Distribution during Embryogenesis and in Adult Gonads in Japanese FlounderParalichthys olivaceus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, G.L.; Azizur, R.M.; Abdul, R.S.; Sohm, F.; Farahmand, H.; Smith, A.; Brooks, C.; Maclean, N. Isolation and characterisation of tilapia β-actin promoter and comparison of its activity with carp β-actin promoter. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1625, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.J.; Moav, B.; Faras, A.J.; Guise, K.S.; Kapuscinski, A.R.; Hackett, P. Importance of the CArG box in regulation of β-actin-encoding genes. Gene 1991, 108, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Moav, B.; Faras, A.J.; Guise, K.S.; Kapuscinski, A.R.; Hackett, P.B. Functional analysis of elements affecting expression of the β-actin gene of carp. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1990, 10, 3432–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamoto, T.; Makino, K.; Niwa, H.; Sugiyama, H.; Kimura, S.; Amemura, M.; Nakata, A.; Kakunaga, T. Identification of the human β-actin enhancer and its binding factor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1988, 8, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falahzadeh, K.; Shahhoseini, M.; Afsharian, P. Differential Incorporation of β-actin as A Component of RNA Polymerase II into Regulatory Regions of Stemness/Differentiation Genes in Retinoic Acid-Induced Differentiated Human Embryonic Carcinoma Cells. Cell J. 2016, 18, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Noh, J.K.; Cho, K.N.; Han, E.H.; Kim, A.R.; Lee, J.S.; Dong, S.K.; Kim, C.G. Genomic Cloning of Mud Loach Misgurnus mizolepis (Cypriniformes, Cobitidae) β-Actin Gene and Usefulness of Its Promoter Region for Fish Transgenesis. Mar. Biotechnol. 2003, 5, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D Canaani, P.B. Regulated expression of human interferon β 1 gene after transduction into cultured mouse and rabbit cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 5166–5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.L.; Li, H.; Miao, H.Z. The establishment and partial characterization of a continuous fish cell line FG-9307 from the gill of flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Aquaculture 1997, 156, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, N.; Guo, H.R.; Zhang, S.C.; Li, Z.J.; Yin, L.C. In vitro and in vivo acute toxicity of fenpyroximate to flounder Paralichthys olivaceus and its gill cell line FG. Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 92, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1982; pp. 895–909. [Google Scholar]






© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Wang, H.; Gao, C.; Liu, Y.; Jin, C.; Sun, M.; Zhang, Q.; Qi, J. Functional Analysis of the Promoter Region of Japanese Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) β-actin Gene: A Useful Tool for Gene Research in Marine Fish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051401
Wang B, Wang H, Gao C, Liu Y, Jin C, Sun M, Zhang Q, Qi J. Functional Analysis of the Promoter Region of Japanese Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) β-actin Gene: A Useful Tool for Gene Research in Marine Fish. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(5):1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051401
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Bo, Huizhen Wang, Chen Gao, Yuxiang Liu, Chaofan Jin, Minmin Sun, Quanqi Zhang, and Jie Qi. 2018. "Functional Analysis of the Promoter Region of Japanese Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) β-actin Gene: A Useful Tool for Gene Research in Marine Fish" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 5: 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051401
APA StyleWang, B., Wang, H., Gao, C., Liu, Y., Jin, C., Sun, M., Zhang, Q., & Qi, J. (2018). Functional Analysis of the Promoter Region of Japanese Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) β-actin Gene: A Useful Tool for Gene Research in Marine Fish. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(5), 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051401



