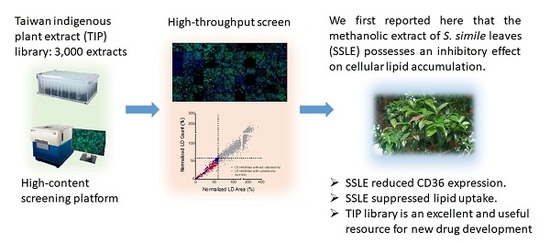
High-Content Screening of a Taiwanese Indigenous Plant Extract Library Identifies Syzygium simile leaf Extract as an Inhibitor of Fatty Acid Uptake
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
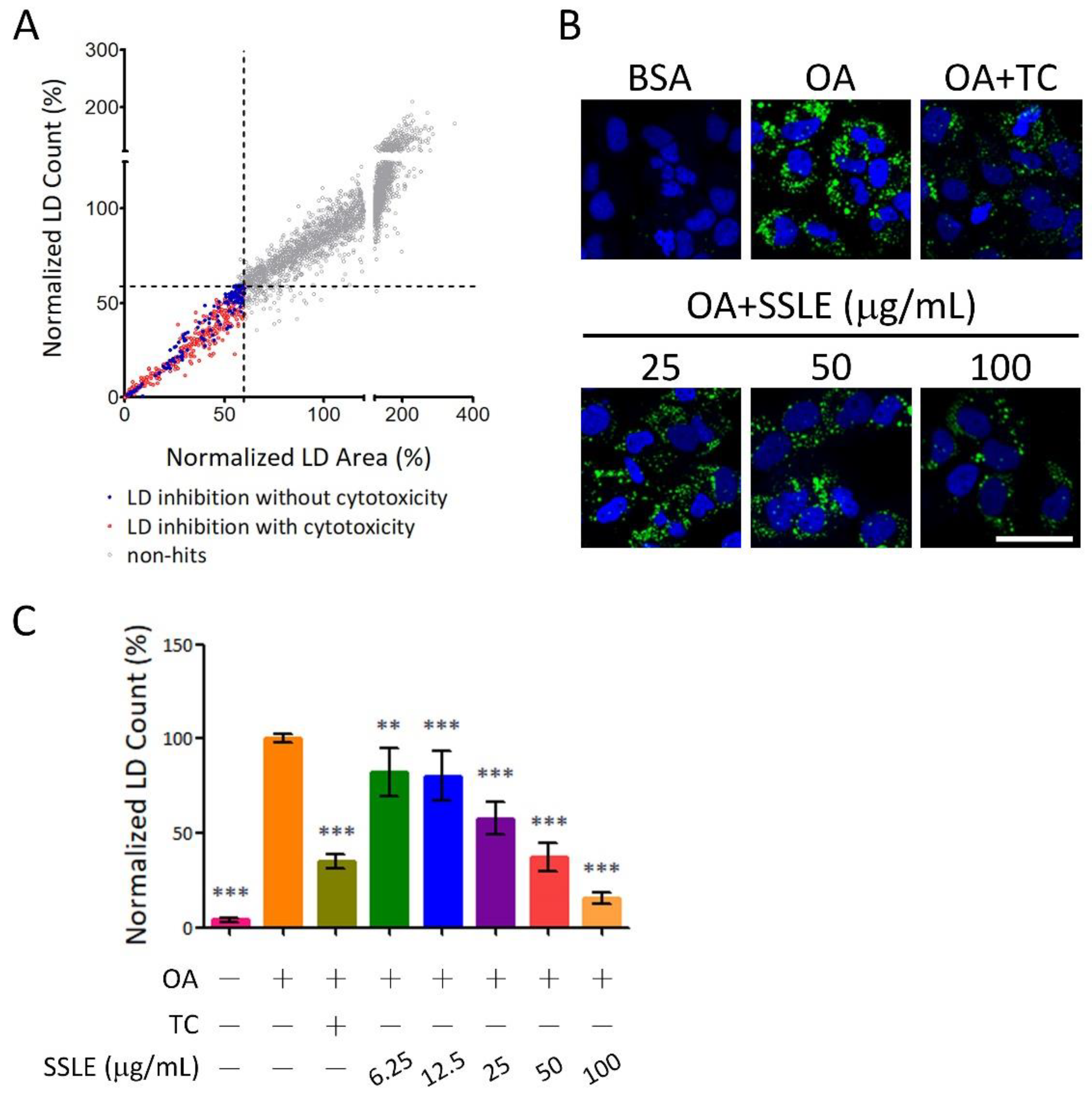
2.1. High-Throughput Image-Based Screening Identifies Syzygium simile leaf Extract (SSLE) as a Suppressor of Lipid Accumulation
2.2. SSLE Exerts Anti-LD (Lipid Droplet) Formation Activity in Other Liver Cell Lines
2.3. SSLE Reduces mRNA and Protein Expression of CD36
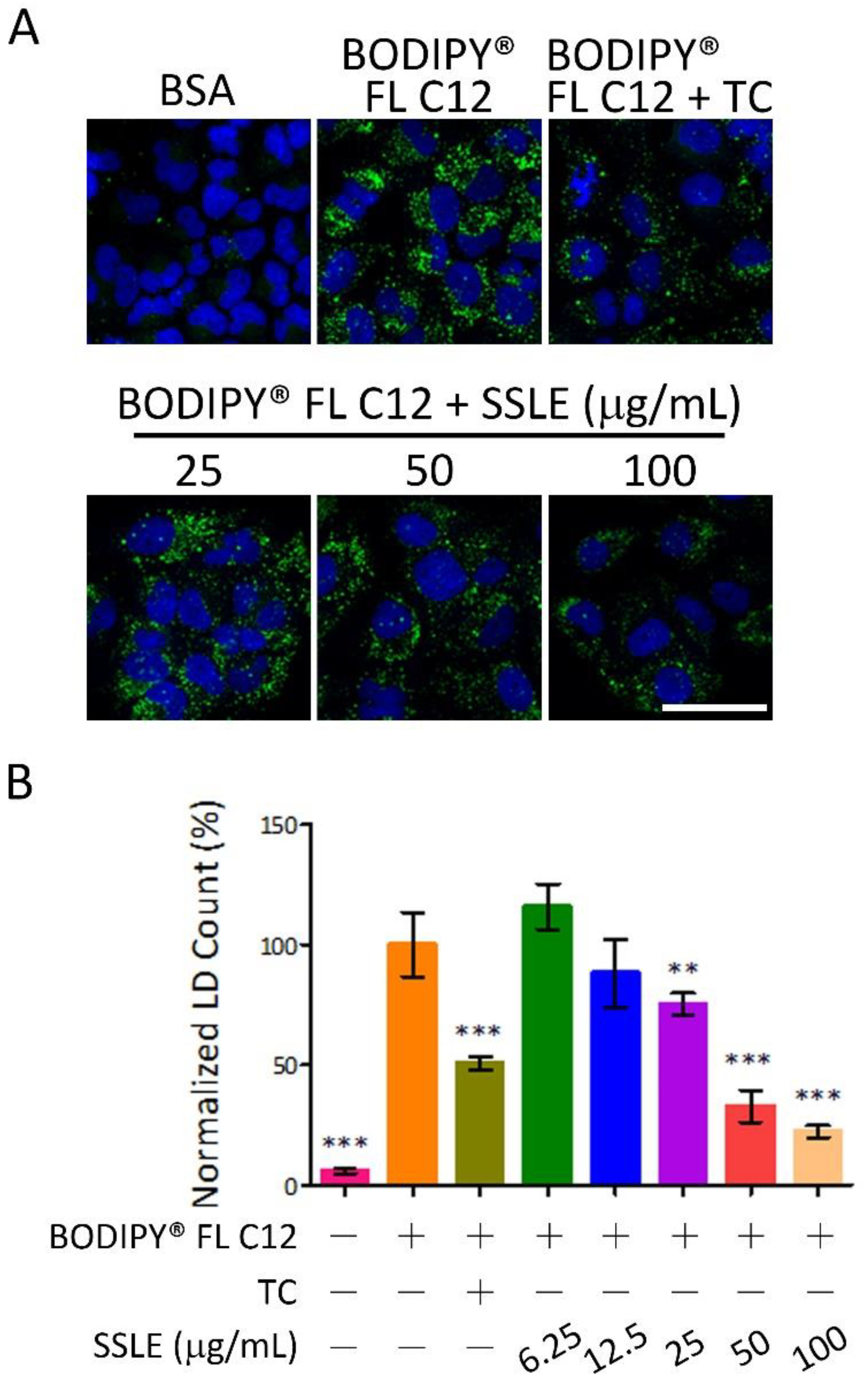
2.4. SSLE Reduced Fatty Acid Uptake
2.5. SSLE Showed Limited Reducing Effects on Pre-Formed LDs
2.6. SSLE Exerted an LD-Reducing Effect in Other Cell Types
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Construction of the Taiwanese Indigenous Plant Extract Library (TIP Library)
4.2. Cell Lines
4.3. LD Assay and Fatty Acid Uptake Assay
4.4. RNA Isolation, Reverse Transcription (RT), and Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
4.5. Immunoblotting
4.6. Statistical Analyses and Target Selection
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NAFLD | non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| LD | lipid droplet |
| HTS | high-throughput screening |
| NASH | nonalcoholic steatohepatitis |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| CVD | cardiovascular disease |
| CKD | chronic kidney disease |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| TG | triglyceride |
| TIP | Taiwanese Indigenous Plant |
| HCS | high content screening |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| OA | oleic acid |
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| RT | reverse transcription |
| qPCR | real-time PCR |
| S/N | signal-to-noise ratio |
| S/B | signal-to-background ratio |
| TC | triacsin C |
| SD | standard deviation |
| ACSL | long-chain fatty acyl-CoA synthetase |
| VLDL | very-low-density lipoprotein |
| DGAT1 | diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1 |
| CPT1 | carnitine palmitoyltransferase I |
| APOB | apolipoprotein B |
| MTTP | microsomal triglyceride transfer protein |
| SIRT1 | sirtuin 1 |
| PGC1a | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha |
| NAFLD | non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| LD | lipid droplet |
References
- Anstee, Q.M.; McPherson, S.; Day, C.P. How big a problem is non-alcoholic fatty liver disease? BMJ 2011, 343, d3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minervini, M.I.; Ruppert, K.; Fontes, P.; Volpes, R.; Vizzini, G.; de Vera, M.E.; Gruttadauria, S.; Miraglia, R.; Pipitone, L.; Marsh, J.W.; et al. Liver biopsy findings from healthy potential living liver donors: Reasons for disqualification, silent diseases and correlation with liver injury tests. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.T.; Changsri, C.; Shackleton, C.R.; Poordad, F.F.; Nissen, N.N.; Colquhoun, S.; Geller, S.A.; Vierling, J.M.; Martin, P. Living donor liver transplantation: Histological abnormalities found on liver biopsies of apparently healthy potential donors. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 21, 381–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadalin, S.; Malago, M.; Valentin-Gamazo, C.; Testa, G.; Baba, H.A.; Liu, C.; Fruhauf, N.R.; Schaffer, R.; Gerken, G.; Frilling, A.; et al. Preoperative donor liver biopsy for adult living donor liver transplantation: Risks and benefits. Liver Transplant. 2005, 11, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chiu, W.H.; Chen, R.C.; Chen, F.L.; Tung, T.H. The clinical investigation of disparity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a Chinese occupational population in Taipei, Taiwan: Experience at a teaching hospital. Asia Pac. J. Public Health 2015, 27, NP1793–NP1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.; Anstee, Q.M.; Marietti, M.; Hardy, T.; Henry, L.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Bugianesi, E. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Day, C.P. Progression of NAFLD to diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease or cirrhosis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarapurkar, D.N.; Hashimoto, E.; Lesmana, L.A.; Sollano, J.D.; Chen, P.J.; Goh, K.L. How common is non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in the Asia-Pacific region and are there local differences? J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 22, 788–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. NAFLD: A multisystem disease. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, S47–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuppan, D.; Schattenberg, J.M. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Pathogenesis and novel therapeutic approaches. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, A.; Williams, J.R.; Muckett, P.J.; Mayer, F.V.; Liljevald, M.; Bohlooly, Y.M.; Carling, D. Liver-Specific Activation of AMPK Prevents Steatosis on a High-Fructose Diet. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 3043–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welte, M.A. Expanding roles for lipid droplets. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, R470–R481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walther, T.C.; Farese, R.V., Jr. Lipid droplets and cellular lipid metabolism. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 687–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gluchowski, N.L.; Becuwe, M.; Walther, T.C.; Farese, R.V., Jr. Lipid droplets and liver disease: From basic biology to clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the 30 years from 1981 to 2010. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 311–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogbourne, S.M.; Parsons, P.G. The value of nature’s natural product library for the discovery of New Chemical Entities: The discovery of ingenol mebutate. Fitoterapia 2014, 98, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cragg, G.M.; Newman, D.J. Natural products: A continuing source of novel drug leads. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 3670–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.H.; Chung, T.D.; Oldenburg, K.R. A Simple Statistical Parameter for Use in Evaluation and Validation of High Throughput Screening Assays. J. Biomol. Screen. 1999, 4, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, Y.; Onoduka, J.; Homma, K.J.; Yamaguchi, S.; Mori, M.; Higashi, Y.; Makita, M.; Kinoshita, T.; Noda, J.; Itabe, H.; et al. Long-chain fatty acids induce lipid droplet formation in a cultured human hepatocyte in a manner dependent of Acyl-CoA synthetase. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 2174–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, K.L.; Smith, C.I.; Schwarzenberg, S.J.; Jessurun, J.; Boldt, M.D.; Parks, E.J. Sources of fatty acids stored in liver and secreted via lipoproteins in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collot-Teixeira, S.; Martin, J.; McDermott-Roe, C.; Poston, R.; McGregor, J.L. CD36 and macrophages in atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 75, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.T.; Dyck, J.R. The role of CD36 in the regulation of myocardial lipid metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1861, 1450–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ofosu, A.; Ramai, D.; Reddy, M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Controlling an emerging epidemic, challenges, and future directions. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2018, 31, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumida, Y.; Yoneda, M. Current and future pharmacological therapies for NAFLD/NASH. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 362–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascaes, M.M.; Guilhon, G.M.; Andrade, E.H.; Zoghbi, M.; Santos Lda, S. Constituents and Pharmacological Activities of Myrcia (Myrtaceae): A Review of an Aromatic and Medicinal Group of Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 23881–23904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.E. Myrtaceae. In Flora of Taiwan, 2nd ed.; Editorial Committee of the Flora of Taiwan: Taipei, Taiwan, 1993; Volume 3, pp. 886–900. [Google Scholar]
- Govaerts, R.; Sobral, M.; Ashton, P.; Barrie, F.; Holst, B.K.; Landrum, L.L.; Matsumoto, K.; Mazine, F.F.; Nic Lughadha, E.; Proença, C. Word Checklist of Myrtaceae; Kew Publishing, Royal Botanic Gardens: Kew, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Aqil, F.; Gupta, A.; Munagala, R.; Jeyabalan, J.; Kausar, H.; Sharma, R.J.; Singh, I.P.; Gupta, R.C. Antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of anthocyanin/ellagitannin-enriched extracts from Syzygium cumini L. (Jamun, the Indian Blackberry). Nutr. Cancer 2012, 64, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobeh, M.; Mahmoud, M.F.; Petruk, G.; Rezq, S.; Ashour, M.L.; Youssef, F.S.; El-Shazly, A.M.; Monti, D.M.; Abdel-Naim, A.B.; Wink, M. Syzygium aqueum: A Polyphenol- Rich Leaf Extract Exhibits Antioxidant, Hepatoprotective, Pain-Killing and Anti-inflammatory Activities in Animal Models. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.H.; Jiang, C.B.; Juan, S.H.; Lin, R.D.; Hou, W.C. Antioxidant and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1)-induced effects of selected Taiwanese plants. Fitoterapia 2006, 77, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.W.; Wu, T.S.; Hsieh, Y.S.; Kuo, S.C.; Chao, P.D. Terpenoids of Syzygium formosanum. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 327–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miquilena-Colina, M.E.; Lima-Cabello, E.; Sanchez-Campos, S.; Garcia-Mediavilla, M.V.; Fernandez-Bermejo, M.; Lozano-Rodriguez, T.; Vargas-Castrillon, J.; Buque, X.; Ochoa, B.; Aspichueta, P.; et al. Hepatic fatty acid translocase CD36 upregulation is associated with insulin resistance, hyperinsulinaemia and increased steatosis in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and chronic hepatitis C. Gut 2011, 60, 1394–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, C.G.; Tran, J.L.; Erion, D.M.; Vera, N.B.; Febbraio, M.; Weiss, E.J. Hepatocyte-Specific Disruption of CD36 Attenuates Fatty Liver and Improves Insulin Sensitivity in HFD-Fed Mice. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 570–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Wu, C.; Shih, N.; Li, Q.; Chan, C.; Pan, H.; Yao, D.; Pan, Y.; Liang, W.; Shen, L.; et al. Discovery of dimethyl pent-4-ynoic acid derivatives, as potent and orally bioavailable DGAT1 inhibitors that suppress body weight in diet-induced mouse obesity model. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 1686–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Liang, K.; Zhao, S.; Jia, W.; Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Lv, J.; Cao, C.; Chen, T.; Zhuang, S.; et al. Chemoproteomics reveals baicalin activates hepatic CPT1 to ameliorate diet-induced obesity and hepatic steatosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Filippo, M.; Moulin, P.; Roy, P.; Samson-Bouma, M.E.; Collardeau-Frachon, S.; Chebel-Dumont, S.; Peretti, N.; Dumortier, J.; Zoulim, F.; Fontanges, T.; et al. Homozygous MTTP and APOB mutations may lead to hepatic steatosis and fibrosis despite metabolic differences in congenital hypocholesterolemia. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, R.A.; Singh, B.K.; Yen, P.M. Direct effects of thyroid hormones on hepatic lipid metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldridge, G.R.; Vervoort, H.C.; Lee, C.M.; Cremin, P.A.; Williams, C.T.; Hart, S.M.; Goering, M.G.; O’Neil-Johnson, M.; Zeng, L. High-throughput method for the production and analysis of large natural product libraries for drug discovery. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 3963–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, C.H.; Lai, C.C.; Shia, T.H.; Chen, M.; Yu, H.C.; Liu, Y.P.; Chang, F.R. Gynura divaricata attenuates tumor growth and tumor relapse after cisplatin therapy in HCC xenograft model through suppression of cancer stem cell growth and Wnt/beta-catenin signalling. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 213, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| S/N a | 37.8 |
| S/B a | 14.6 |
| Z’-factor a | 0.66 |
| Cell Line | IC50 (μg/mL) a | CC50 (μg/mL) a |
|---|---|---|
| Huh7 | 30.7 ± 1.9 | 168.8 ± 6.6 |
| HepG2 | 76.7 ± 1.6 | >200 |
| AML12 | 54.3 ± 1.7 | 81.9 ± 0.6 |
| Clone9 | 7.6 ± 0.02 | 174.9 ± 3.6 |
| Gene | Species | Forward (5′>3′) | Reverse (5′>3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD36 | Homo sapiens | TCCTGCAGAATACCATTTGATCC | GGTTTCTACAAGCTCTGGTTCTTA |
| CPT1 | Homo sapiens | TCCAGTTGGCTTATCGTGGTG | CTAACGAGGGGTCGATCTTGG |
| SIRT1 | Homo sapiens | GCGGTTCCTACTGCGCGA | TCACTAGAGCTTGCATGTGAGG |
| DGAT1 | Homo sapiens | CAACAAGGACGGAGACGCCGG | GATGCCACGGTAGTTGCTGAAGCC |
| APOB | Homo sapiens | ACCTCCAGAACATGGGATTGC | GGGCTGGTGTCCTAACAGTC |
| MTTP | Homo sapiens | TGAGGCAGTGGCCATAGAAAAT | CTTTGTCTTGATGAGCCTGGTA |
| PGC1a | Homo sapiens | GTCACCACCCAAATCCTTAT | ATCTACTGCCTGGAGACCTT |
| TBP | Homo sapiens | CAGAAGTTGGGTTTTCCAGCTAA | ACATCACAGCTCCCCACCAT |
| Cd36 | Mus musculus | CCTTAAAGGAATCCCCGTGT | TGCATTTGCCAATGTCTAGC |
| Gapdh | Mus musculus | CTGCACCACCAACTGCTTAGC | GGTCATGAGCCCTTCCACAAT |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yen, C.-H.; Chang, H.-S.; Yang, T.-H.; Wang, S.-F.; Wu, H.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Lin, K.-J.; Wang, S. High-Content Screening of a Taiwanese Indigenous Plant Extract Library Identifies Syzygium simile leaf Extract as an Inhibitor of Fatty Acid Uptake. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072130
Yen C-H, Chang H-S, Yang T-H, Wang S-F, Wu H-C, Chen Y-C, Lin K-J, Wang S. High-Content Screening of a Taiwanese Indigenous Plant Extract Library Identifies Syzygium simile leaf Extract as an Inhibitor of Fatty Acid Uptake. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(7):2130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072130
Chicago/Turabian StyleYen, Chia-Hung, Hsun-Shuo Chang, Tsai-Hsun Yang, Sheng-Fan Wang, Ho-Cheng Wu, Yu-Chang Chen, Kai-Jay Lin, and Sheena Wang. 2018. "High-Content Screening of a Taiwanese Indigenous Plant Extract Library Identifies Syzygium simile leaf Extract as an Inhibitor of Fatty Acid Uptake" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 7: 2130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072130
APA StyleYen, C.-H., Chang, H.-S., Yang, T.-H., Wang, S.-F., Wu, H.-C., Chen, Y.-C., Lin, K.-J., & Wang, S. (2018). High-Content Screening of a Taiwanese Indigenous Plant Extract Library Identifies Syzygium simile leaf Extract as an Inhibitor of Fatty Acid Uptake. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(7), 2130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072130