Cloning and Functional Characterisation of the Duplicated RDL Subunits from the Pea Aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
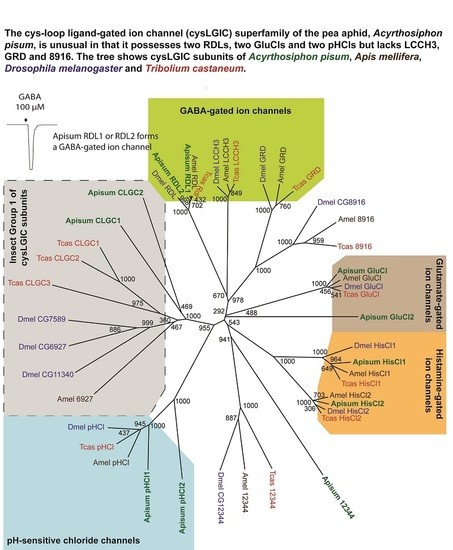
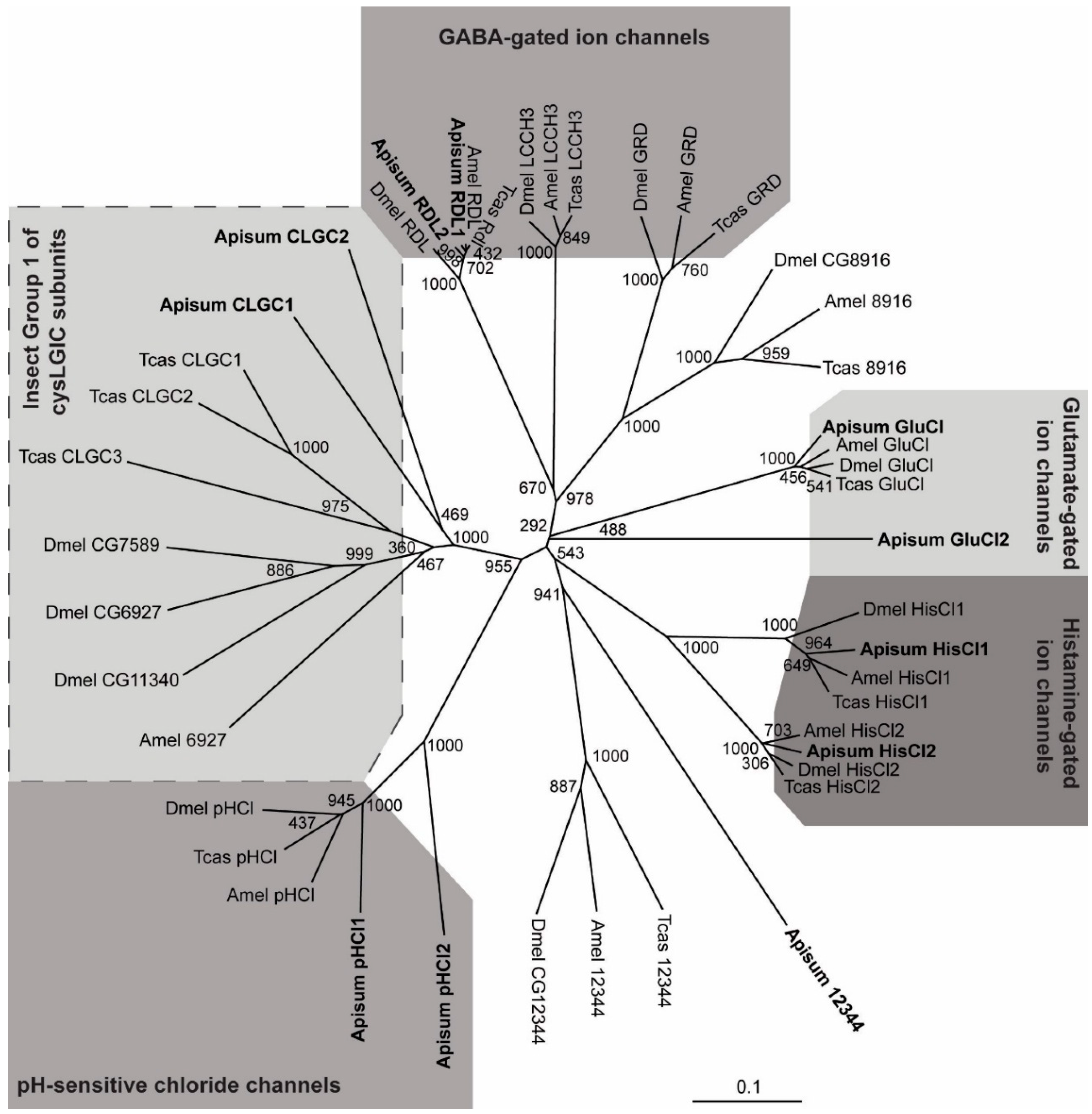
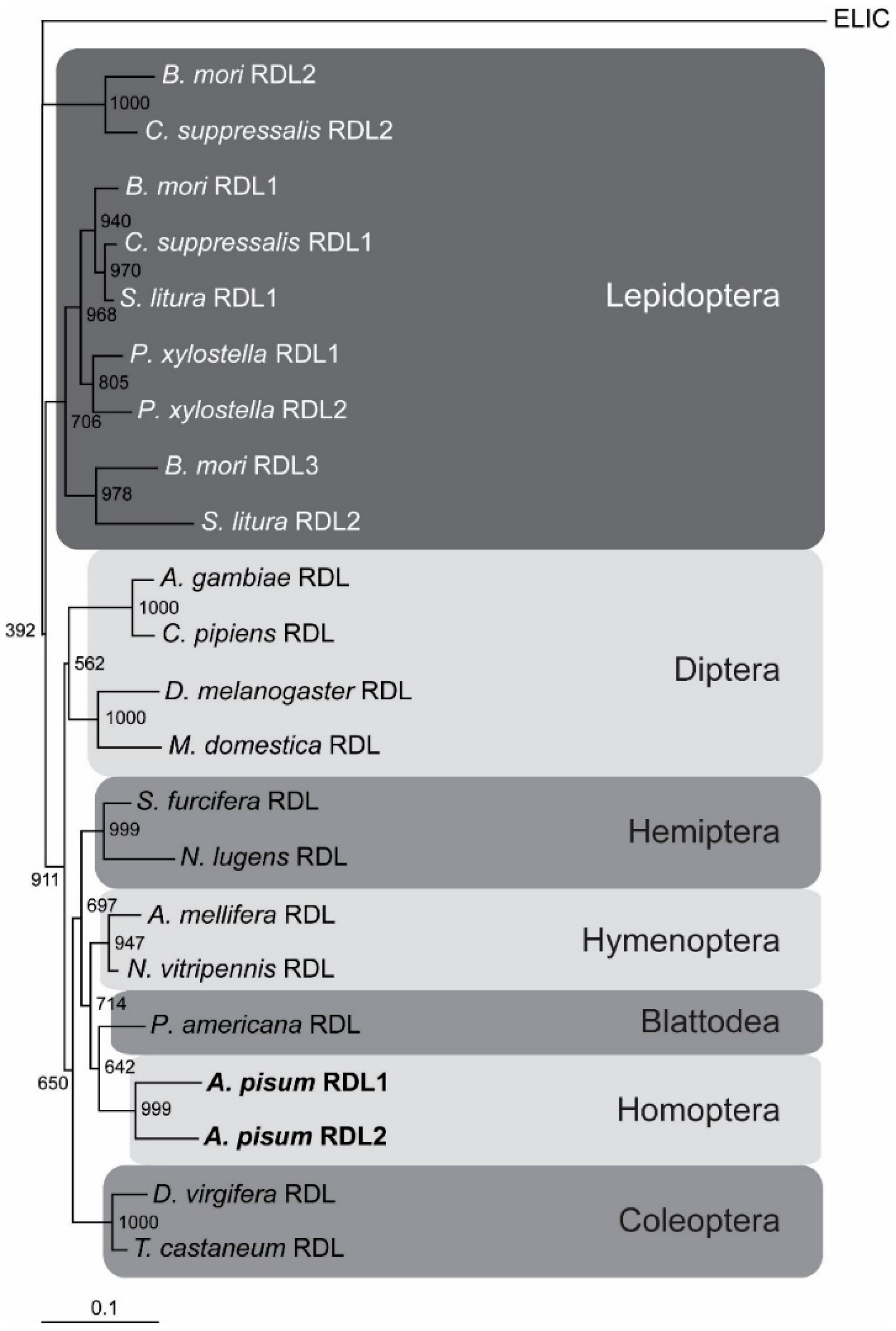
2.1. The A. pisum cysLGIC Superfamily Possesses Two Rdl Genes
2.2. Cloning and Functional Expression of Apisum Rdl1 and Apisum Rdl2
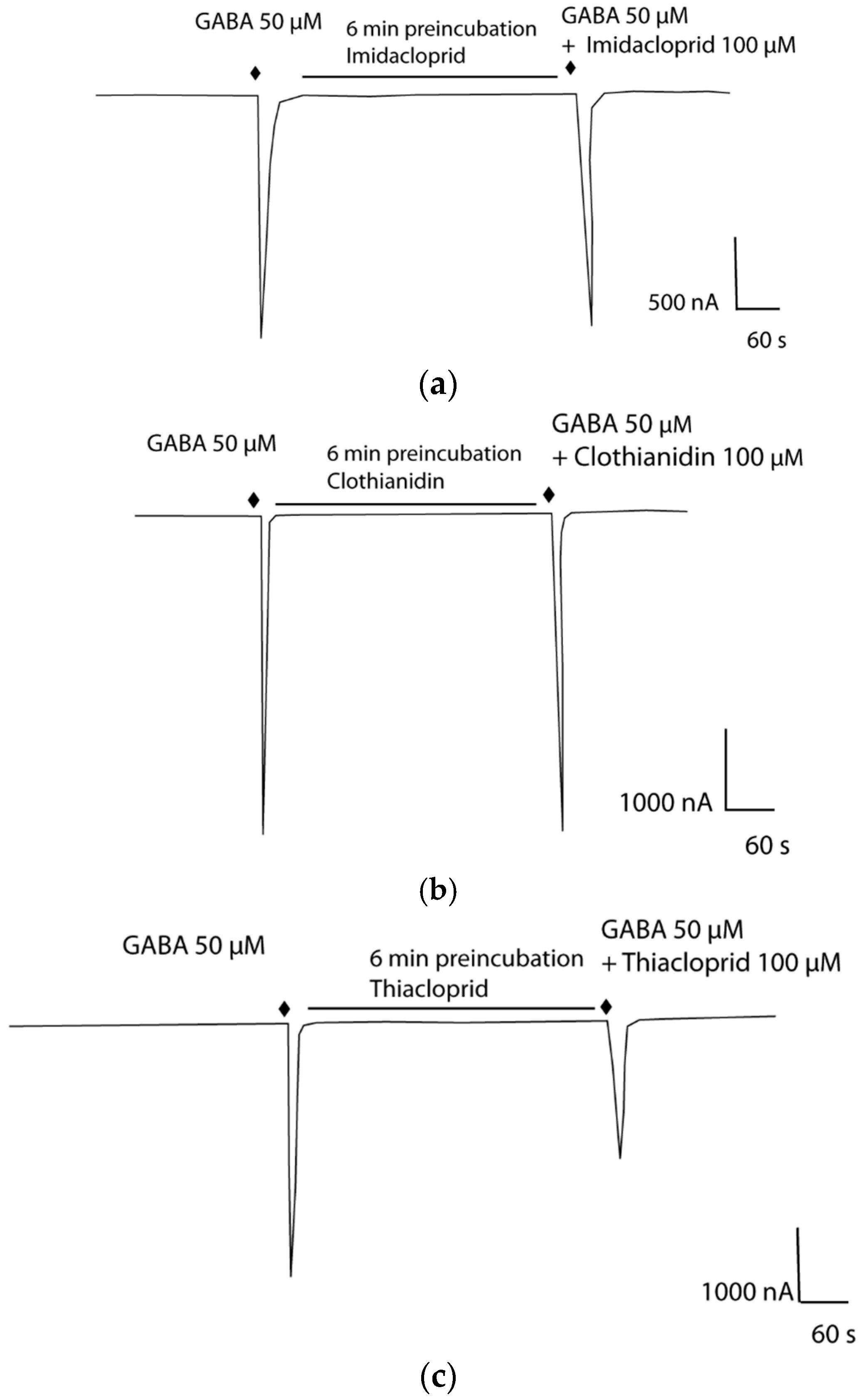
2.3. Antagonistic Actions of Fipronil and Neonicotinoids on Apisum RDL1 and Apisum RDL2
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation of Rdl1 and Rdl2 from A. pisum
4.2. Sequence Analysis
4.3. Preparation and Expression of Apisum RDL1 and Apisum RDL2 in X. laevis Oocytes and Two-Electrode Voltage-Clamp Electrophysiology
4.4. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| cysLGIC | cys-loop ligand-gated ion channel |
| RDL | resistant to dieldrin |
| nAChR | nicotinic acetylcholine receptor |
References
- Liu, S.; Lamaze, A.; Liu, Q.; Tabuchi, M.; Yang, Y.; Fowler, M.; Bharadwaj, R.; Zhang, J.; Bedont, J.; Blackshaw, S.; et al. Wide awake mediates the circadian timing of sleep onset. Neuron 2014, 82, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Q.; Song, Y.; Yang, C.H.; Jan, L.Y.; Jan, Y.N. Female contact modulates male aggression via a sexually dimorphic GABAergic circuit in Drosophila. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Buchanan, M.E.; Han, K.A.; Davis, R.L. The GABAA receptor RDL suppresses the conditioned stimulus pathway for olfactory learning. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 1573–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Q.; Li, H.; Wu, Y.; Ren, J.; Guo, A. A GABAergic inhibitory neural circuit regulates visual reversal learning in Drosophila. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 11524–11538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.K.; Bera, A.N.; Lees, K.; Sattelle, D.B. The cys-loop ligand-gated ion channel gene superfamily of the parasitoid wasp, Nasonia Vitripennis. Heredity 2010, 104, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nys, M.; Kesters, D.; Ulens, C. Structural insights into Cys-loop receptor function and ligand recognition. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 86, 1042–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckingham, S.; Ihara, M.; Sattelle, D.B.; Matsuda, K. Mechanisms of action, resistance and toxicity of insecticides targeting GABA receptors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 2935–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ffrench-Constant, R.H.; Rocheleau, T.A.; Steichen, J.C.; Chalmers, A.E. A point mutation in a Drosophila GABA receptor confers insecticide resistance. Nature 1993, 363, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosie, A.M.; Baylis, H.A.; Buckingham, S.D.; Sattelle, D.B. Actions of the insecticide fipronil, on dieldrin-sensitive and resistant GABA receptors of Drosophila melanogaster. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 115, 909–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor-Wells, J.; Jones, A.K. Variations in the insect GABA ieceptor, RDL, and their impact on receptor pharmacology. In Advances in Agrochemicals: Ion Channels and G Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCRs) as Targets for Pest Control; Gross, A.D., Ozoe, Y., Coats, J.R., Eds.; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; Volume 2, pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Du, W.; Awolola, T.S.; Howell, P.; Koekemoer, L.L.; Brooke, B.D.; Benedict, M.Q.; Coetzee, M.; Zheng, L. Independent mutations in the Rdl locus confer dieldrin resistance to Anopheles gambiae and An. arabiensis. Insect. Mol. Biol. 2005, 14, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor-Wells, J.; Brooke, B.D.; Bermudez, I.; Jones, A.K. The neonicotinoid imidacloprid, and the pyrethroid deltamethrin, are antagonists of the insect Rdl GABA receptor. J. Neurochem. 2015, 135, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Domingues, L.N.; Guerrero, F.D.; Becker, M.E.; Alison, M.W.; Foil, L.D. Discovery of the Rdl mutation in association with a cyclodiene resistant population of horn flies, Haematobia irritans (Diptera: Muscidae). Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 198, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bass, C.; Schroeder, I.; Turberg, A.; Field, L.M.; Williamson, M.S. Identification of the Rdl mutation in laboratory and field strains of the cat flea, Ctenocephalides felis (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae). Pest. Manag. Sci. 2004, 60, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakao, T. Mechanisms of resistance to insecticides targeting RDL GABA receptors in planthoppers. Neurotoxicology 2017, 60, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casida, J.E.; Durkin, K.A. Novel GABA receptor pesticide targets. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 121, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jones, A.K.; Sattelle, D.B. The cys-loop ligand-gated ion channel superfamily of the honeybee, Apis mellifera. Invert. Neurosci. 2006, 6, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.K.; Sattelle, D.B. The cys-loop ligand-gated ion channel gene superfamily of the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.G.; Warren, W.C.; Beukeboom, L.W.; Bopp, D.; Clark, A.G.; Giers, S.D.; Hediger, M.; Jones, A.K.; Kasai, S.; Leichter, C.A.; et al. Genome of the house fly, Musca domestica L., a global vector of diseases with adaptations to a septic environment. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheng, C.W.; Jia, Z.Q.; Ozoe, Y.; Huang, Q.T.; Han, Z.J.; Zhao, C.Q. Molecular cloning, spatiotemporal and functional expression of GABA receptor subunits RDL1 and RDL2 of the rice stem borer Chilo suppressalis. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 94, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.; Gao, W.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y. Molecular cloning, genomic structure, and genetic mapping of two Rdl-orthologous genes of GABA receptors in the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2010, 74, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.L.; Cui, Y.J.; Lang, G.J.; Zhang, M.Y.; Zhang, C.X. The ionotropic γ-aminobutyric acid receptor gene family of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Genome 2010, 53, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, N.; Unruh, T.; Ganser, D.; ffrench-Constant, R. Duplication of the Rdl GABA receptor subunit gene in an insecticide-resistant aphid, Myzus persicae. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1998, 260, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, R.P.; Jones, A.K.; Tamborindeguy, C.; Davies, T.G.; Amey, J.S.; Williamson, S.; Wolstenholme, A.; Field, L.M.; Williamson, M.S.; Walsh, T.K.; et al. Identification of ion channel genes in the Acyrthosiphon pisum genome. Insect Mol. Biol. 2010, 19 (Suppl. 2), 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Aphid Genomics Consortium. Genome sequence of the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corringer, P.J.; Le Novere, N.; Changeux, J.P. Nicotinic receptors at the amino acid level. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2000, 40, 431–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ffrench-Constant, R.H.; Rocheleau, T.A. Drosophila gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor gene Rdl shows extensive alternative splicing. J. Neurochem. 1993, 60, 2323–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnizler, K.; Saeger, B.; Pfeffer, C.; Gerbaulet, A.; Ebbinghaus-Kintscher, U.; Methfessel, C.; Franken, E.M.; Raming, K.; Wetzel, C.H.; Saras, A.; et al. A novel chloride channel in Drosophila melanogaster is inhibited by protons. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 16254–16262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilf, R.J.; Dutzler, R. X-ray structure of a prokaryotic pentameric ligand-gated ion channel. Nature 2008, 452, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.K.; Buckingham, S.D.; Papadaki, M.; Yokota, M.; Sattelle, B.M.; Matsuda, K.; Sattelle, D.B. Splice-variant- and stage-specific RNA editing of the Drosophila GABA receptor modulates agonist potency. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 4287–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor-Wells, J.; Hawkins, J.; Colombo, C.; Bermudez, I.; Jones, A.K. Cloning and functional expression of intracellular loop variants of the honey bee (Apis mellifera) RDL GABA receptor. Neurotoxicology 2017, 60, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misof, B.; Liu, S.; Meusemann, K.; Peters, R.S.; Donath, A.; Mayer, C.; Frandsen, P.B.; Ware, J.; Flouri, T.; Beutel, R.G.; et al. Phylogenomics resolves the timing and pattern of insect evolution. Science 2014, 346, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Meng, X.; Bao, H.; Fang, J.; Liu, Z. Identification of polymorphisms in Cyrtorhinus lividipennis RDL subunit contributing to fipronil sensitivity. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 117, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor-Wells, J.; Senan, A.; Bermudez, I.; Jones, A.K. Species specific RNA A-to-I editing of mosquito RDL modulates GABA potency and influences agonistic, potentiating and antagonistic actions of ivermectin. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 93, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrood, W.T.; Zimmer, C.T.; Gutbrod, O.; Luke, B.; Williamson, M.S.; Bass, C.; Nauen, R.; Emyr Davies, T.G. Influence of the RDL A301S mutation in the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens on the activity of phenylpyrazole insecticides. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 142, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deglise, P.; Grunewald, B.; Gauthier, M. The insecticide imidacloprid is a partial agonist of the nicotinic receptor of honeybee Kenyon cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 321, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihara, M.; Buckingham, S.D.; Matsuda, K.; Sattelle, D.B. Modes of Action, Resistance and Toxicity of Insecticides Targeting Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 2925–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Plewniak, F.; Jeanmougin, F.; Higgins, D.G. The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, H. Predicting Secretory Proteins with SignalP. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1611, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigrist, C.J.; de Castro, E.; Cerutti, L.; Cuche, B.A.; Hulo, N.; Bridge, A.; Bougueleret, L.; Xenarios, I. New and continuing developments at PROSITE. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D344–D347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, R.D. TreeView: An application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 1996, 12, 357–358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]




| Subunit | Apisum RDL1 | Apisum RDL2 | Apisum GluCl1 | Apisum GluCl2 | Apisum HisCl1 | Apisum HisCl2 | Apisum pHCl1 | Apisum pHCl2 | Apisum CLGC1 | Apisum CLGC2 | Apisum 12344 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apisum RDL1 | - | 83/87 | 25/38 | 23/38 | 20/34 | 20/34 | 15/28 | 15/29 | 16/31 | 17/29 | 15/30 |
| Tcas RDL | 70/73 | 69/72 | 28/43 | 27/44 | 23/40 | 24/40 | 19/34 | 18/36 | 20/36 | 19/34 | 19/36 |
| Apsium RDL2 | 83/87 | - | 25/37 | 23/38 | 20/35 | 20/34 | 16/28 | 15/29 | 17/31 | 17/28 | 15/31 |
| Apisum GluCl1 | 25/38 | 25/38 | - | 29/44 | 26/42 | 25/42 | 20/38 | 19/38 | 23/37 | 18/36 | 17/34 |
| Tcas GluCl | 25/38 | 25/38 | 74/80 | 29/44 | 26/42 | 26/42 | 21/38 | 20/39 | 22/36 | 19/37 | 18/34 |
| Apisum GluCl2 | 23/38 | 23/38 | 29/44 | - | 26/46 | 28/47 | 18/37 | 20/38 | 24/39 | 20/35 | 18/35 |
| Apisum HisCl1 | 20/34 | 20/34 | 26/42 | 26/46 | - | 49/63 | 18/34 | 18/34 | 18/33 | 18/32 | 19/34 |
| Tcas HisCl1 | 20/35 | 21/36 | 27/43 | 27/47 | 72/78 | 55/69 | 18/35 | 19/35 | 19/34 | 18/33 | 20/35 |
| Apisum HisCl2 | 20/34 | 20/34 | 25/42 | 28/47 | 49/63 | - | 18/34 | 19/36 | 20/35 | 17/32 | 20/35 |
| Tcas HisCl2 | 22/34 | 22/34 | 26/43 | 29/48 | 48/63 | 79/84 | 18/35 | 19/38 | 19/36 | 19/34 | 20/35 |
| Apisum pHCl1 | 15/28 | 16/28 | 20/38 | 18/37 | 18/34 | 18/34 | - | 49/64 | 21/36 | 19/34 | 13/30 |
| Tcas pHCl | 16/30 | 17/31 | 22/40 | 20/39 | 19/36 | 19/37 | 66/74 | 51/66 | 21/35 | 19/33 | 15/32 |
| Apisum pHCl2 | 15/29 | 15/29 | 19/38 | 20/38 | 18/34 | 19/36 | 49/64 | - | 20/37 | 19/34 | 15/32 |
| Apisum CLGC1 | 16/31 | 17/31 | 23/37 | 24/39 | 18/33 | 20/35 | 21/36 | 20/37 | - | 36/53 | 15/30 |
| Tcas CLGC1 | 18/31 | 18/31 | 20/37 | 21/37 | 17/33 | 19/36 | 18/31 | 19/33 | 35/49 | 27/44 | 13/29 |
| Apisum CLGC2 | 17/29 | 17/28 | 18/36 | 20/35 | 18/32 | 17/32 | 19/34 | 19/34 | 36/53 | - | 13/31 |
| Tcas CLGC2 | 16/29 | 17/30 | 19/35 | 21/37 | 16/32 | 17/33 | 16/30 | 17/31 | 31/48 | 25/43 | 13/28 |
| Apisum 12344 | 15/30 | 15/31 | 17/34 | 18/35 | 19/34 | 20/35 | 13/30 | 15/32 | 15/30 | 13/31 | - |
| Tcas 12344 | 19/33 | 20/34 | 21/38 | 23/41 | 23/42 | 26/46 | 18/34 | 20/37 | 19/37 | 16/32 | 20/37 |
| Tcas CLGC3 | 16/30 | 16/30 | 19/36 | 20/38 | 18/36 | 19/38 | 19/35 | 19/37 | 29/49 | 22/44 | 13/31 |
| Tcas GRD | 27/41 | 27/41 | 24/40 | 22/38 | 21/36 | 21/38 | 16/31 | 18/33 | 19/34 | 18/31 | 13/31 |
| Tcas LCCH3 | 28/44 | 28/43 | 26/44 | 27/44 | 23/38 | 25/41 | 16/32 | 16/32 | 19/37 | 20/37 | 17/33 |
| Tcas 8916 | 24/40 | 24/39 | 23/38 | 22/36 | 19/33 | 21/35 | 15/30 | 15/31 | 19/33 | 17/32 | 14/27 |
| Subunit | Imax (μA) | GABA | Fipronil IC50 (μM) | % of GABA Response with 100 μM: | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC50 (μM) | nH | IMI | CLO | THI | |||
| Apisum RDL1ad | 1.6 ± 0.6 | 23 ± 1.7 1 | 1.6 ± 0.1 | 0.64 ± 0.15 | 100 | 100 | – |
| Apisum RDL1bd | 1.4 ± 1.3 | 51 ± 9.2 1 | 2.0 ± 0.3 | 0.18 ± 0.06 2 | 100 | 100 | 55 ± 7 |
| Apisum RDL2b var 1 | 1.4 ± 1.5 | 28 ± 5.4 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 0.72 ± 0.19 2 | – | – | 62 ± 2 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Del Villar, S.G.; Jones, A.K. Cloning and Functional Characterisation of the Duplicated RDL Subunits from the Pea Aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082235
Del Villar SG, Jones AK. Cloning and Functional Characterisation of the Duplicated RDL Subunits from the Pea Aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(8):2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082235
Chicago/Turabian StyleDel Villar, Silvia G., and Andrew K. Jones. 2018. "Cloning and Functional Characterisation of the Duplicated RDL Subunits from the Pea Aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 8: 2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082235
APA StyleDel Villar, S. G., & Jones, A. K. (2018). Cloning and Functional Characterisation of the Duplicated RDL Subunits from the Pea Aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(8), 2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082235