VGF Peptides in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Dementia with Lewy Bodies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
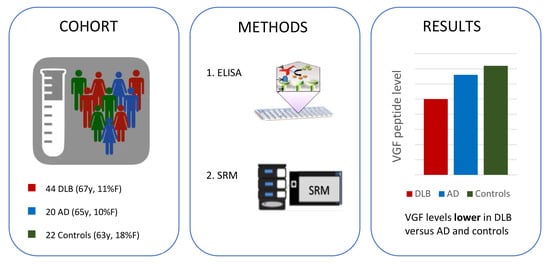
2.1. Patient Characteristics
2.2. CSF VGF Levels in DLB, AD, and Controls
2.3. Correlations Between VGF and Other CSF Biomarkers
2.4. VGF and Cognitive Decline in DLB Patients
2.5. VGF and Survival in DLB Patients
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Cogntive Assessment
4.3. Mortality
4.4. CSF Procedures
4.5. Alpha-Synuclein Analysis
4.6. VGF Analysis
4.6.1. ELISA Analysis
4.6.2. SRM Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Aβ1-42 | amyloid-β 1-42 |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| APOE | Apolipoprotein |
| CSF | cerebrospinal fluid |
| DAT-SPECT | 123I[FP-CIT] single photon emission computed tomography |
| DLB | dementia with Lewy bodies |
| EEG | electroencephalography |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays |
| MCI | mild cognitive impairment |
| MMSE | Mini-Mental State Examination |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| p-tau | tau phosphorylated at threonine 181 |
| RBD | REM (rapid eye movement) sleep behavior disorder |
| SCD | Subjective cognitive decline |
| SRM | selected reaction monitoring |
| t-tau | total tau |
| VGF | neurosecretory protein VGF |
References
- Walker, Z.; Possin, K.L.; Boeve, B.F.; Aarsland, D. Lewy body dementias. Lancet 2015, 386, 1683–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKeith, I.G.; Boeve, B.F.; Dickson, D.W.; Halliday, G.; Taylor, J.P.; Weintraub, D.; Aarsland, D.; Galvin, J.; Attems, J.; Ballard, C.G.; et al. Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: Fourth consensus report of the DLB Consortium. Neurology 2017, 89, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vekrellis, K.; Xilouri, M.; Emmanouilidou, E.; Rideout, H.J.; Stefanis, L. Pathological roles of alpha-synuclein in neurological disorders. Lancet. Neurol. 2011, 10, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colom-Cadena, M.; Pegueroles, J.; Herrmann, A.G.; Henstridge, C.M.; Munoz, L.; Querol-Vilaseca, M.; Martin-Paniello, C.S.; Luque-Cabecerans, J.; Clarimon, J.; Belbin, O.; et al. Synaptic phosphorylated alpha-synuclein in dementia with Lewy bodies. Brain 2017, 140, 3204–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J. The synaptic pathology of alpha-synuclein aggregation in dementia with Lewy bodies, Parkinson’s disease and Parkinson’s disease dementia. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 120, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calo, L.; Wegrzynowicz, M.; Santivanez-Perez, J.; Grazia Spillantini, M. Synaptic failure and alpha-synuclein. Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S.B.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomucci, A.; Possenti, R.; Mahata, S.K.; Fischer-Colbrie, R.; Loh, Y.P.; Salton, S.R. The extended granin family: Structure, function, and biomedical implications. Endocr. Rev. 2011, 32, 755–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, G.L.; Noli, B.; Brancia, C.; D’Amato, F.; Cocco, C. VGF: An inducible gene product, precursor of a diverse array of neuro-endocrine peptides and tissue-specific disease biomarkers. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2011, 42, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alder, J.; Thakker-Varia, S.; Bangasser, D.A.; Kuroiwa, M.; Plummer, M.R.; Shors, T.J.; Black, I.B. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor-induced gene expression reveals novel actions of VGF in hippocampal synaptic plasticity. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 10800–10808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozdagi, O.; Rich, E.; Tronel, S.; Sadahiro, M.; Patterson, K.; Shapiro, M.L.; Alberini, C.M.; Huntley, G.W.; Salton, S.R. The neurotrophin-inducible gene Vgf regulates hippocampal function and behavior through a brain-derived neurotrophic factor-dependent mechanism. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 9857–9869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fargali, S.; Garcia, A.L.; Sadahiro, M.; Jiang, C.; Janssen, W.G.; Lin, W.J.; Cogliani, V.; Elste, A.; Mortillo, S.; Cero, C.; et al. The granin VGF promotes genesis of secretory vesicles, and regulates circulating catecholamine levels and blood pressure. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 2120–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartolomucci, A.; Pasinetti, G.M.; Salton, S.R. Granins as disease-biomarkers: Translational potential for psychiatric and neurological disorders. Neuroscience 2010, 170, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrette, O.; Demalte, I.; Scherl, A.; Yalkinoglu, O.; Corthals, G.; Burkhard, P.; Hochstrasser, D.F.; Sanchez, J.C. A panel of cerebrospinal fluid potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Proteomics 2003, 3, 1486–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bereczki, E.; Branca, R.M.; Francis, P.T.; Pereira, J.B.; Baek, J.H.; Hortobagyi, T.; Winblad, B.; Ballard, C.; Lehtio, J.; Aarsland, D. Synaptic markers of cognitive decline in neurodegenerative diseases: A proteomic approach. Brain 2018, 141, 582–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottschall, P.E.; Ajmo, J.M.; Eakin, A.K.; Howell, M.D.; Mehta, H.; Bailey, L.A. Panel of synaptic protein ELISAs for evaluating neurological phenotype. Exp. Brain Res. 2010, 201, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pasinetti, G.M.; Ungar, L.H.; Lange, D.J.; Yemul, S.; Deng, H.; Yuan, X.; Brown, R.H.; Cudkowicz, M.E.; Newhall, K.; Peskind, E.; et al. Identification of potential CSF biomarkers in ALS. Neurology 2006, 66, 1218–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Lange, D.J.; Ho, L.; Bonini, S.; Shao, B.; Salton, S.R.; Thomas, S.; Pasinetti, G.M. Vgf is a novel biomarker associated with muscle weakness in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), with a potential role in disease pathogenesis. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2008, 5, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brancia, C.; Noli, B.; Boido, M.; Boi, A.; Puddu, R.; Borghero, G.; Marrosu, F.; Bongioanni, P.; Orru, S.; Manconi, B.; et al. VGF Protein and Its C-Terminal Derived Peptides in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Human and Animal Model Studies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancia, C.; Noli, B.; Boido, M.; Pilleri, R.; Boi, A.; Puddu, R.; Marrosu, F.; Vercelli, A.; Bongioanni, P.; Ferri, G.L.; et al. TLQP Peptides in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Possible Blood Biomarkers with a Neuroprotective Role. Neuroscience 2018, 380, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruetschi, U.; Zetterberg, H.; Podust, V.N.; Gottfries, J.; Li, S.; Hviid Simonsen, A.; McGuire, J.; Karlsson, M.; Rymo, L.; Davies, H.; et al. Identification of CSF biomarkers for frontotemporal dementia using SELDI-TOF. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 196, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocco, C.; D’Amato, F.; Noli, B.; Ledda, A.; Brancia, C.; Bongioanni, P.; Ferri, G.L. Distribution of VGF peptides in the human cortex and their selective changes in Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases. J. Anat. 2010, 217, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmalm, G.; Sjodin, S.; Simonsen, A.H.; Hasselbalch, S.G.; Zetterberg, H.; Brinkmalm, A.; Blennow, K. A Parallel Reaction Monitoring Mass Spectrometric Method for Analysis of Potential CSF Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrickson, R.C.; Lee, A.Y.; Song, Q.; Liaw, A.; Wiener, M.; Paweletz, C.P.; Seeburger, J.L.; Li, J.; Meng, F.; Deyanova, E.G.; et al. High Resolution Discovery Proteomics Reveals Candidate Disease Progression Markers of Alzheimer’s Disease in Human Cerebrospinal Fluid. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtta, M.; Minthon, L.; Hansson, O.; Holmen-Larsson, J.; Pike, I.; Ward, M.; Kuhn, K.; Ruetschi, U.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; et al. An integrated workflow for multiplex CSF proteomics and peptidomics-identification of candidate cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahn, H.; Wittke, S.; Zurbig, P.; Raedler, T.J.; Arlt, S.; Kellmann, M.; Mullen, W.; Eichenlaub, M.; Mischak, H.; Wiedemann, K. Peptide fingerprinting of Alzheimer’s disease in cerebrospinal fluid: Identification and prospective evaluation of new synaptic biomarkers. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llano, D.A.; Bundela, S.; Mudar, R.A.; Devanarayan, V.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging, I. A multivariate predictive modeling approach reveals a novel CSF peptide signature for both Alzheimer’s Disease state classification and for predicting future disease progression. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selle, H.; Lamerz, J.; Buerger, K.; Dessauer, A.; Hager, K.; Hampel, H.; Karl, J.; Kellmann, M.; Lannfelt, L.; Louhija, J.; et al. Identification of novel biomarker candidates by differential peptidomics analysis of cerebrospinal fluid in Alzheimer’s disease. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen 2005, 8, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonsen, A.H.; McGuire, J.; Podust, V.N.; Hagnelius, N.O.; Nilsson, T.K.; Kapaki, E.; Vassilopoulos, D.; Waldemar, G. A novel panel of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for the differential diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease versus normal aging and frontotemporal dementia. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2007, 24, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spellman, D.S.; Wildsmith, K.R.; Honigberg, L.A.; Tuefferd, M.; Baker, D.; Raghavan, N.; Nairn, A.C.; Croteau, P.; Schirm, M.; Allard, R.; et al. Development and evaluation of a multiplexed mass spectrometry based assay for measuring candidate peptide biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) CSF. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2015, 9, 715–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijte, D.; McDonnell, L.A.; Balog, C.I.; Bossers, K.; Deelder, A.M.; Swaab, D.F.; Verhaagen, J.; Mayboroda, O.A. A novel peptidomics approach to detect markers of Alzheimer’s disease in cerebrospinal fluid. Methods 2012, 56, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockenstein, E.; Nuber, S.; Overk, C.R.; Ubhi, K.; Mante, M.; Patrick, C.; Adame, A.; Trejo-Morales, M.; Gerez, J.; Picotti, P.; et al. Accumulation of oligomer-prone alpha-synuclein exacerbates synaptic and neuronal degeneration in vivo. Brain 2014, 137, 1496–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bereczki, E.; Francis, P.T.; Howlett, D.; Pereira, J.B.; Hoglund, K.; Bogstedt, A.; Cedazo-Minguez, A.; Baek, J.H.; Hortobagyi, T.; Attems, J.; et al. Synaptic proteins predict cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease and Lewy body dementia. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2016, 12, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, A.; Chai, Y.L.; Tan, J.M.; Lee, J.H.; Francis, P.T.; Chen, C.P.; Sze, S.K.; Lai, M.K.P. An iTRAQ-based proteomic analysis reveals dysregulation of neocortical synaptopodin in Lewy body dementias. Mol. Brain 2017, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duits, F.H.; Brinkmalm, G.; Teunissen, C.E.; Brinkmalm, A.; Scheltens, P.; Van der Flier, W.M.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K. Synaptic proteins in CSF as potential novel biomarkers for prognosis in prodromal Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2018, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llano, D.A.; Devanarayan, P.; Devanarayan, V.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging, I. VGF in Cerebrospinal Fluid Combined With Conventional Biomarkers Enhances Prediction of Conversion From MCI to AD. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeKosky, S.T.; Scheff, S.W. Synapse loss in frontal cortex biopsies in Alzheimer’s disease: Correlation with cognitive severity. Ann. Neurol. 1990, 27, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.L.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J. Presynaptic alpha-synuclein aggregates, not Lewy bodies, cause neurodegeneration in dementia with Lewy bodies. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukaetova-Ladinska, E.B.; Garcia-Siera, F.; Hurt, J.; Gertz, H.J.; Xuereb, J.H.; Hills, R.; Brayne, C.; Huppert, F.A.; Paykel, E.S.; McGee, M.; et al. Staging of cytoskeletal and beta-amyloid changes in human isocortex reveals biphasic synaptic protein response during progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Flier, W.M.; Pijnenburg, Y.A.; Prins, N.; Lemstra, A.W.; Bouwman, F.H.; Teunissen, C.E.; van Berckel, B.N.; Stam, C.J.; Barkhof, F.; Visser, P.J.; et al. Optimizing patient care and research: The Amsterdam Dementia Cohort. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 41, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teunissen, C.E.; Tumani, H.; Engelborghs, S.; Mollenhauer, B. Biobanking of CSF: International standardization to optimize biomarker development. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 47, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tijms, B.M.; Willemse, E.A.J.; Zwan, M.D.; Mulder, S.D.; Visser, P.J.; van Berckel, B.N.M.; van der Flier, W.M.; Scheltens, P.; Teunissen, C.E. Unbiased Approach to Counteract Upward Drift in Cerebrospinal Fluid Amyloid-beta 1-42 Analysis Results. Clin. Chem. 2018, 64, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulder, C.; Verwey, N.A.; van der Flier, W.M.; Bouwman, F.H.; Kok, A.; van Elk, E.J.; Scheltens, P.; Blankenstein, M.A. Amyloid-beta(1-42), total tau, and phosphorylated tau as cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for the diagnosis of Alzheimer disease. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duits, F.H.; Teunissen, C.E.; Bouwman, F.H.; Visser, P.J.; Mattsson, N.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Hansson, O.; Minthon, L.; Andreasen, N.; et al. The cerebrospinal fluid “Alzheimer profile”: Easily said, but what does it mean? Alzheimer’s Dement. 2014, 10, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiasserini, D.; Biscetti, L.; Eusebi, P.; Salvadori, N.; Frattini, G.; Simoni, S.; De Roeck, N.; Tambasco, N.; Stoops, E.; Vanderstichele, H.; et al. Differential role of CSF fatty acid binding protein 3, alpha-synuclein, and Alzheimer’s disease core biomarkers in Lewy body disorders and Alzheimer’s dementia. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2017, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, K.; Takahashi, N.; Satoh, M.; Yamasaki, M.; Minamino, N. A peptidomics strategy for discovering endogenous bioactive peptides. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 5047–5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noli, B.; Brancia, C.; D’Amato, F.; Ferri, G.L.; Cocco, C. VGF changes during the estrous cycle: A novel endocrine role for TLQP peptides? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amato, F.; Cocco, C.; Noli, B.; Cabras, T.; Messana, I.; Ferri, G.L. VGF peptides upon osmotic stimuli: Changes in neuroendocrine regulatory peptides 1 and 2 in the hypothalamic-pituitary-axis and plasma. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2012, 44, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noli, B.; Sanna, F.; Brancia, C.; D’Amato, F.; Manconi, B.; Vincenzoni, F.; Messana, I.; Melis, M.R.; Argiolas, A.; Ferri, G.L.; et al. Profiles of VGF Peptides in the Rat Brain and Their Modulations after Phencyclidine Treatment. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2017, 11, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeckl, P.; Metzger, F.; Nagl, M.; von Arnim, C.A.; Halbgebauer, S.; Steinacker, P.; Ludolph, A.C.; Otto, M. Alpha-, Beta-, and Gamma-synuclein Quantification in Cerebrospinal Fluid by Multiple Reaction Monitoring Reveals Increased Concentrations in Alzheimer’s and Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease but No Alteration in Synucleinopathies. Mol. Cell Proteomics 2016, 15, 3126–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| DLB (n = 44) | AD (n = 20) | Controls (n = 22) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | |||
| Female (n, %) | 5 (11%) | 2 (10%) | 4 (18%) |
| Age | 67 (6) a | 65 (6) | 63 (5) |
| Education, years | 10 [9–13] | 10 [9.5–13] | 13 [10–13] |
| MMSE | 23 [21–26] b,c | 18 [16–22] b | 29 [27–30] |
| APOEε4 carrier (n, %) | 23 (54%) | 12 (63%) | 7 (32%) |
| Cognitive function z-scores | |||
| Memory | −2.67 (1.67) b | −3.12 (1.91) b | −0.26 (0.75) |
| Attention | −2.89 (2.18) b,c | −4.39 (3.41) b | −0.27 (0.71) |
| Executive functions | −4.32 (2.79) b | −5.27 (3.21) b | −0.41 (0.88) |
| Language | −1.13 (0.69) a,c | −2.44 (2.71) b | −0.20 (0.56) |
| Visual spatial functions | −0.85 (0.94) d | −2.37 (1.68) b | −0.38 (0.96) |
| Global cognition score | −2.90 (1.69) b,d | −4.41 (2.32) b | −0.32 (0.62) |
| CSF AD biomarkers | |||
| Aβ1-42 (pg/mL) | 780 [658–977] b,d | 586 [492–642] b | 1040 [913–1150] |
| tau (pg/mL) | 292 [224–367] a,d | 596 [498–905] b | 194 [169–256] |
| p-tau (pg/mL) | 47 [35–59] a,d | 87 [66–122] b | 39 [30–46] |
| CSF α-synuclein (pg/mL) | 1805 [1540–2169] | NA | 1466 [1280–1911] |
| CSF VGF | |||
| VGF373-417 ELISA (pmol/mL) | 2.5 [2.1–3.4] b,c | 3.3 [2.5–3.9] | 3.6 [3.0–4.9] |
| VGF SRM [L.H.ratio] § | 0.14 [0.12–0.18] b,c | 0.17 [0.14–0.22] | 0.17 [0.16–0.24] |
| Cognitive Domains | Estimated Baseline Performance | Estimated Change Over time | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β (SE) | p | β (SE) | p | |
| VGF373-417 ELISA | ||||
| MMSE | 1.26 (0.56) | 0.03 * | −0.32 (0.14) | 0.02 * |
| Memory | 0.00 (0.24) | 0.99 | 0.04 (0.06) | 0.52 |
| Attention | 0.87 (0.42) | 0.03 * | −0.29 (0.12) | 0.01 * |
| Executive functions | 1.27 (0.43) | 0.004 ** | −0.31 (0.10) | 0.002 ** |
| Language | 0.21 (0.09) | 0.03 * | −0.04 (0.02) | 0.10 |
| Visuospatial functions | 0.46 (0.29) | 0.12 | −0.01 (0.09) | 0.91 |
| Global cognition | 0.69 (0.25) | 0.008 ** | −0.16 (0.06) | 0.008 ** |
| VGF SRM | ||||
| MMSE | 1.11 (0.56) | 0.04 * | −0.38 (0.13) | 0.006 ** |
| Memory | 0.04 (0.23) | 0.85 | 0.00 (0.06) | 0.97 |
| Attention | 0.92 (0.41) | 0.02 * | −0.26 (0.12) | 0.03 * |
| Executive functions | 1.32 (0.42) | 0.003 ** | −0.35 (0.10) | <0.001 *** |
| Language | 0.19 (0.09) | 0.05 | −0.03 (0.02) | 0.25 |
| Visuospatial functions | 0.53 (0.29) | 0.07 | −0.09 (0.09) | 0.31 |
| Global cognition | 0.72 (0.25) | 0.006 ** | −0.18 (0.05) | 0.002 ** |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
van Steenoven, I.; Noli, B.; Cocco, C.; Ferri, G.-L.; Oeckl, P.; Otto, M.; Koel-Simmelink, M.J.A.; Bridel, C.; van der Flier, W.M.; Lemstra, A.W.; et al. VGF Peptides in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4674. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194674
van Steenoven I, Noli B, Cocco C, Ferri G-L, Oeckl P, Otto M, Koel-Simmelink MJA, Bridel C, van der Flier WM, Lemstra AW, et al. VGF Peptides in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Dementia with Lewy Bodies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(19):4674. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194674
Chicago/Turabian Stylevan Steenoven, Inger, Barbara Noli, Cristina Cocco, Gian-Luca Ferri, Patrick Oeckl, Markus Otto, Marleen J. A. Koel-Simmelink, Claire Bridel, Wiesje M. van der Flier, Afina W. Lemstra, and et al. 2019. "VGF Peptides in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Dementia with Lewy Bodies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 19: 4674. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194674
APA Stylevan Steenoven, I., Noli, B., Cocco, C., Ferri, G.-L., Oeckl, P., Otto, M., Koel-Simmelink, M. J. A., Bridel, C., van der Flier, W. M., Lemstra, A. W., & Teunissen, C. E. (2019). VGF Peptides in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Dementia with Lewy Bodies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(19), 4674. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194674