Synthesis, Microtubule-Binding Affinity, and Antiproliferative Activity of New Epothilone Analogs and of an EGFR-Targeted Epothilone-Peptide Conjugate
Abstract
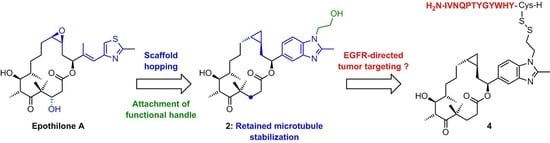
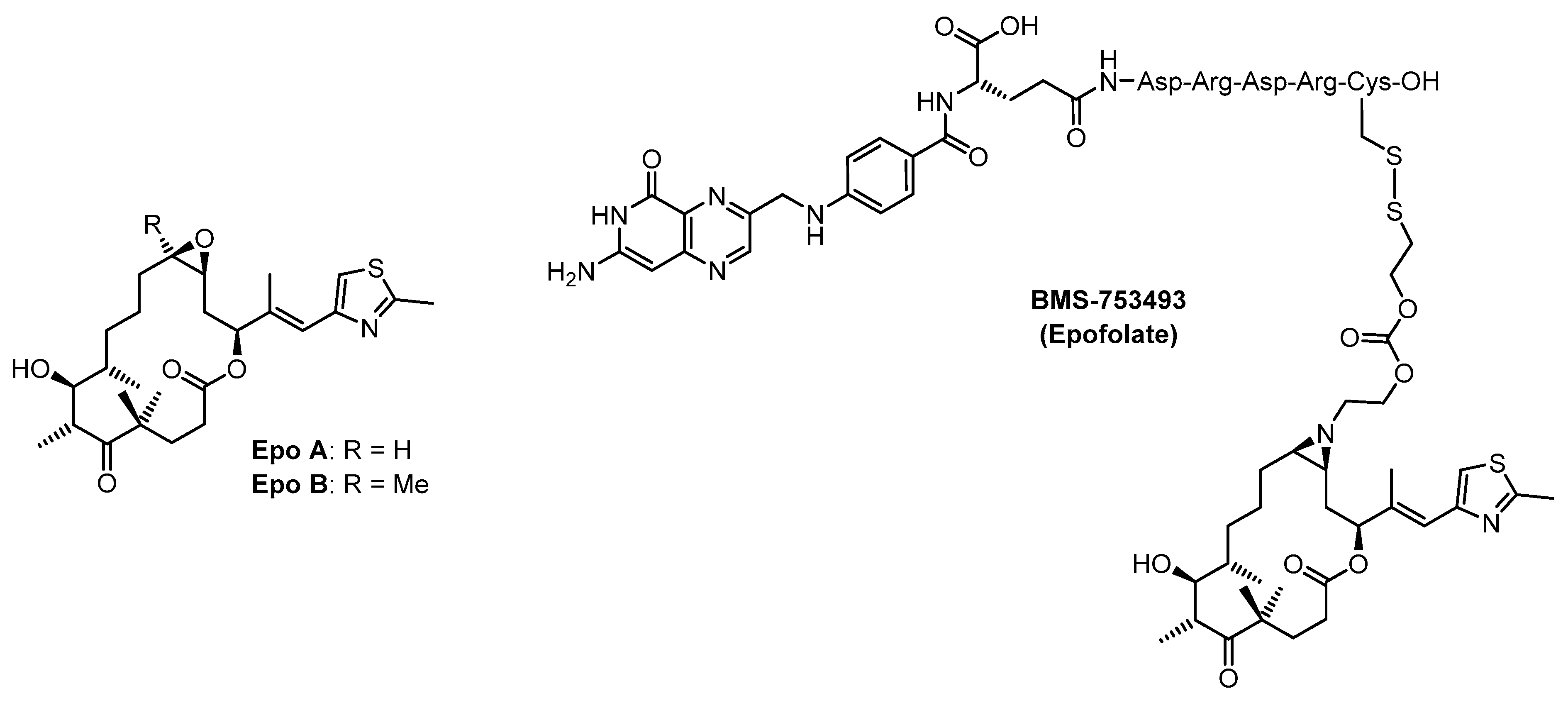
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
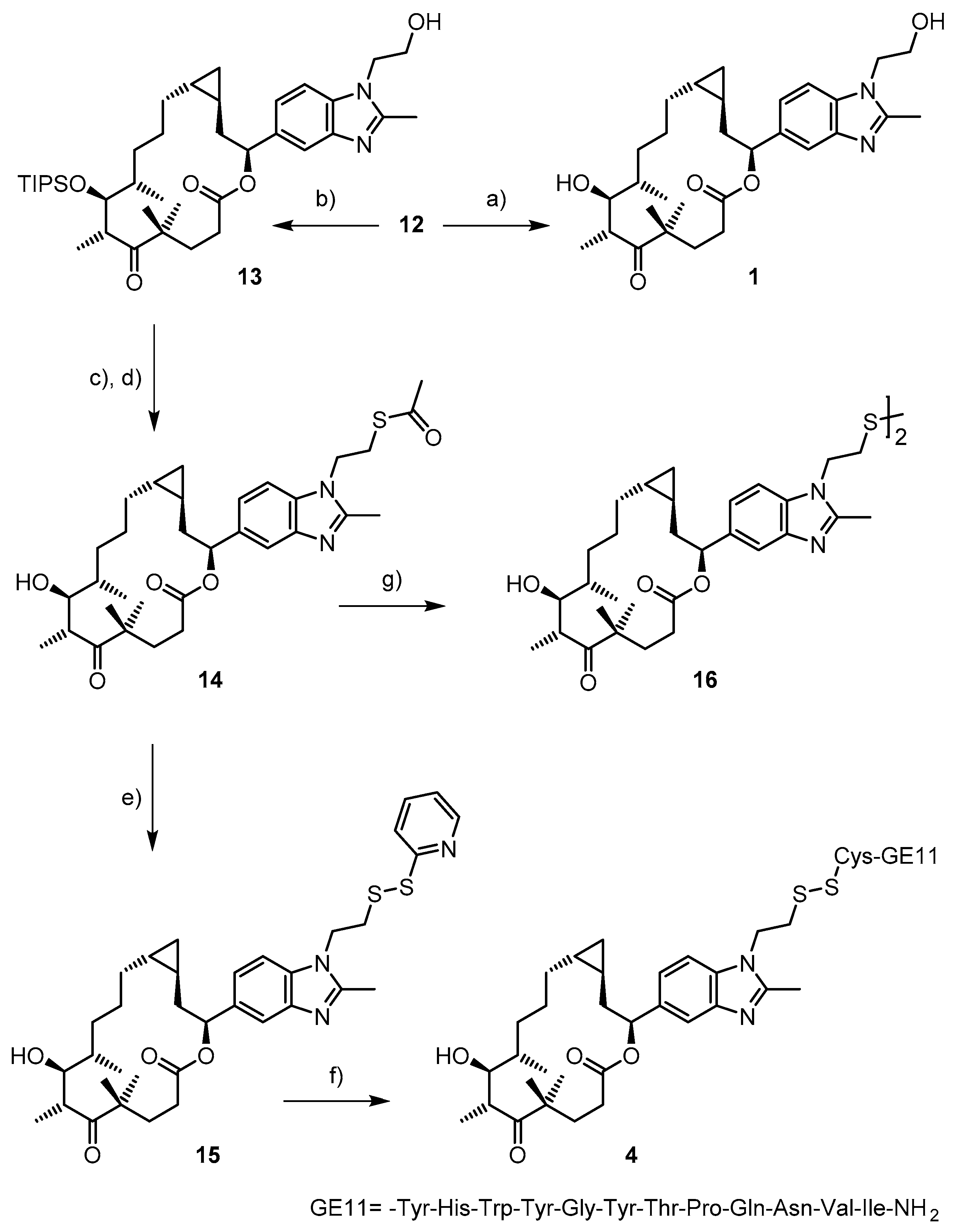
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Assessment
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. Glutathione Cleavage Assay
3.3. Determination of Microtubule Binding Constants
3.4. Antiproliferative Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References and Note
- Todd, A.; Groundwater, P.W.; Gill, J.H. Anticancer Therapeutics: From Drug Discovery to Clinical Applications; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 211–232. [Google Scholar]
- LaPointe, N.E.; Morfini, G.; Brady, S.T.; Feinstein, S.C.; Wilson, L.; Jordan, M.A. Effects of eribulin, vincristine, paclitaxel and ixabepilone on fast axonal transport and kinesin-1 driven microtubule gliding: Implications for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. NeuroToxicology 2013, 37, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chari, R.V.; Miller, M.L.; Widdison, W.C. Antibody-drug conjugates: An emerging concept in cancer therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 3796–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasiri, H.; Valedkarimi, Z.; Aghebati-Maleki, L.; Majidi, J. Antibody-drug conjugates: Promising and efficient tools for targeted cancer therapy. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 6441–6457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, N.; Qin, Y.; Liu, H.; Cheng, Z. Tumor-Targeting Peptides: Ligands for Molecular Imaging and Therapy. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasarao, M.; Galliford, C.V.; Low, P.S. Principles in the design of ligand-targeted cancer therapeutics and imaging agents. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casi, G.; Neri, D. Antibody-Drug Conjugates and Small Molecule-Drug Conjugates: Opportunities and Challenges for the Development of Selective Anticancer Cytotoxic Agents. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 8751–8761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, C.; Guan, X.; Ma, H.; Cong, H.; Zhang, W.; Miao, Z. Small molecule-drug conjugates: A novel strategy for cancer-targeted treatment. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 163, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frigerio, M.; Kyle, A.F. The Chemical Design and Synthesis of Linkers Used in Antibody Drug Conjugates. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 3393–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menchon, G.; Prota, A.E.; Lucena-Agell, D.; Bucher, P.; Jansen, R.; Irschik, H.; Müller, R.; Paterson, I.; Díaz, J.F.; Altmann, K.-H.; et al. A fluorescence anisotropy assay to discover and characterize ligands targeting the maytansine site of tubulin. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerth, K.; Bedorf, N.; Höfle, G.; Irschik, H.; Reichenbach, H. Epothilons A and B: Antifungal and Cytotoxic Compounds from Sorangium cellulosum (Myxobacteria). Production, Physico-chemical and Biological Properties. J. Antibiot. 1996, 49, 560–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollag, D.M.; McQueney, P.A.; Zhu, J.; Hensens, O.; Koupal, L.; Liesch, J.; Goetz, M.; Lazarides, E.; Woods, C.M. Epothilones, a new class of microtubule-stabilizing agents with a Taxol-like mechanism of action. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 2325–2333. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kowalski, R.J.; Giannakakou, P.; Hamel, E. Activities of the microtubule-stabilizing agents epothilones A and B with purified tubulin and in cells resistant to paclitaxel (Taxol). J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 2534–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altmann, K.-H.; Wartmann, M.; O’Reilly, T. Epothilones and related structures—A new class of microtubule inhibitors with potent in vivo antitumor activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1470, M79–M91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, T.; Wartmann, M.; Brueggen, J.; Allegrini, P.R.; Flörsheimer, A.; Maira, M.; McSheehy, P.M.J. Pharmacokinetic profile of the microtubule stabilizer patupilone in tumor-bearing rodents and comparison of anti-cancer activity with other MTS in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2008, 62, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, T.; McSheehy, P.M.J.; Wenger, F.; Hattenberger, M.; Muller, M.; Vaxelaire, J.; Altmann, K.-H.; Wartmann, M. EPO906 (epothilone B) is active in vivo against experimental prostate tumors. Prostate 2005, 65, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altmann, K.-H.; Pfeiffer, B.; Arseniyadis, S.; Pratt, B.A.; Nicolaou, K.C. The chemistry and biology of epothilones—The wheel keeps turning. ChemMedChem 2007, 2, 397–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Epothilones: An Outstanding Family of Anti-Tumor Agents (Progress Chem. Org. Nat. Prod. 90); Kinghorn, A.D.; Falk, H.; Kobayashi, J. (Eds.) Springer: Wienna, Austria; New York, NY, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-3-211-78207-1. [Google Scholar]
- Lechleider, R.J.; Kaminskas, E.; Jiang, X.; Aziz, R.; Bullock, J.; Kasliwal, R.; Harapanhalli, R.; Pope, S.; Sridhara, R.; Leighton, J.; et al. Ixabepilone in Combination with Capecitabine and as Monotherapy for Treatment of Advanced Breast Cancer Refractory to Previous Chemotherapies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 4378–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barten, D.M.; Fanara, P.; Andorfer, C.; Hoque, N.; Wong, P.Y.A.; Husted, K.H.; Cadelina, G.W.; DeCarr, L.B.; Yang, L.; Liu, V.; et al. Hyperdynamic microtubules, cognitive deficits, and pathology are improved in tau transgenic mice with low doses of the microtubule-stabilizing agent BMS-241027. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 7137–7145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Sun, T.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, X.J.; Cui, S.; Teng, Y.; Hu, X.-C.; Yang, J.; et al. Utidelone plus capecitabine versus capecitabine alone for heavily pretreated metastatic breast cancer refractory to anthracyclines and taxanes: A multicentre, open-label, superiority, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UTD1 (utidelone, depoxythilone) is being developed by Beijing Biostar Technologies (see ref. 21 and the English translation of the company webpage: https://translate.google.ch/translate?hl=de&sl=zh-CN&u=http://www.biostar-pharm.com/&prev=search). According to a SciFinder search, the company has filed two patent applications on epothilone-type compounds (Tang, L.; Qiu, R. De-epoxidized epothilone derivative preparation, preparation of same and use thereof in the treatment of tumour. CN 107041886, 6 February, 2016; WO 2017133706, 6 February, 2017.) While both of these applications are in Chinese, it is clear that the major claims are for Epo D or a closely related compound. We thus consider it likely that UTD1 is a close analog of Epo D, if not Epo D itself.
- Vlahov, I.R.; Vite, G.D.; Kleindl, P.J.; Wang, Y.; Santhapuram, H.K.R.; You, F.; Howard, S.J.; Kim, S.-H.; Lee, F.F.Y.; Leamon, C.P. Regioselective synthesis of folate receptor-targeted agents derived from epothilone analogs and folic acid. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 4578–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzniewski, C.N.; Gertsch, J.; Wartmann, M.; Altmann, K.-H. Total Synthesis of Hypermodified Epothilone Analogs with Potent in vitro Antitumor Activity. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 1183–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaugaz, F.Z.; Redondo-Horcajo, M.; Barasoain, I.; Díaz, J.F.; Cobos-Correa, A.; Kaufmann, M.; Altmann, K.-H. The Impact of Cyclopropane Configuration on the Biological Activity of Cyclopropyl-Epothilones. ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 2227–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, R.; Wu, X.; Sun, Y.; Yao, M.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Gu, J. Identification and characterization of a novel peptide ligand of epidermal growth factor receptor for targeted delivery of therapeutics. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1978–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullrich, A.; Coussens, L.; Hayflick, J.S.; Dull, T.J.; Gray, A.; Tam, A.W.; Lee, J.; Yarden, Y.; Libermann, T.A.; Schlessinger, J.; et al. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. Nature 1984, 309, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsudomi, T.; Yatabe, Y. Epidermal growth factor receptor in relation to tumor development: EGFR gene and cancer. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Liu, D.; Peng, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, Z.; Gu, J.-R.; Xu, Y. Peptide ligand-mediated liposome distribution and targeting to EGFR expressing tumor in vivo. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 363, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, C.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Min, H.; Han, X.; Lang, J.; Qin, H.; Shi, Q.; et al. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Targeting Peptide Nanoparticles Simultaneously Deliver Gemcitabine and Olaparib to Treat Pancreatic Cancer with Breast Cancer 2 (BRCA2) Mutation. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 10785–10796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, H.; Srinivasan, S.; Das, D.; Stayton, P.S.; Convertine, A.J. Fully synthetic macromolecular prodrug chemotherapeutics with EGFR targeting and controlled camptothecin release kinetics. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 5224–5233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-J.; Chan, C.-H.; Lin, K.-L.; Chen, J.-H.; Tseng, C.-H.; Wang, P.-Y.; Chien, C.-Y.; Yu, H.-M.; Lin, W.-J. 68Ga-labelled NOTA-RGD-GE11 peptide for dual integrin and EGFR-targeted tumour imaging. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2019. published online. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charette, A.B.; Juteau, H.; Lebel, H.; Molinaro, C. Enantioselective Cyclopropanation of Allylic Alcohols with Dioxaborolane Ligands: Scope and Synthetic Applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 11943–11952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzniewski, C.N.; Glauser, S.; et al. Synthesis, Profiling and Bioactive Conformation of trans-Cyclopropyl Epothilones. Manuscript submitted.
- Cusack, N.J.; Reese, C.B.; Risius, A.C.; Roozpeikar, B. 2,4,6-Tri-isopropylbenzenesulphonyl hydrazide: A convenient source of di-imide. Tetrahedron 1976, 32, 2157–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haukaas, M.; O’Doherty, G.A. Enantioselective synthesis of 2-deoxy-and 2,3-dideoxyhexoses. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 1771–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inanaga, J.; Hirata, K.; Saeki, H.; Katsuki, T.; Yamaguchi, M. A Rapid Esterification by Means of Mixed Anhydride and Its Application to Large-ring Lactonization. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1979, 52, 1989–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheidt, K.A.; Chen, H.; Follows, B.C.; Chemler, S.R.; Coffey, D.S.; Roush, W.R. Tris(dimethylamino)sulfonium Difluorotrimethylsilicate, a Mild Reagent for the Removal of Silicon Protecting Groups. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 6436–6437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Yin, L.; Yang, Y.; Guan, Y.; Wang, W.; Xu, H.; Tao, N. Quantification of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Expression Level and Binding Kinetics on Cell Surfaces by Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9960–9965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shigeta, K.; Hayashida, T.; Hoshino, Y.; Okabayashi, K.; Endo, T.; Ishii, Y.; Hasegawa, H.; Kitagawa, Y. Expression of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Detected by Cetuximab Indicates Its Efficacy to Inhibit In Vitro and In Vivo Proliferation of Colorectal Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Belenda, C.; Leroux, J.-C.; Gauthier, M.A. Interplay of Chemical Microenvironment and Redox Environment on Thiol–Disulfide Exchange Kinetics. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 10064–10070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buey, R.M.; Díaz, J.F.; Andreu, J.M.; O’Brate, A.; Giannakakou, P.; Nicolaou, K.C.; Sasmal, P.K.; Ritzen, A.; Namoto, K. Interaction of Epothilone Analogs with the Paclitaxel Binding Site: Relationship between Binding Affinity, Microtubule Stabilization, and Cytotoxicity. Chem. Biol. 2004, 11, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Díaz, J.F.; Strobe, R.; Engelborghs, Y.; Souto, A.A.; Andreu, J.M. Molecular Recognition of Taxol by Microtubules: Kinetics and thermodynamics of binding of fluorescent taxol derivatives to an exposed site. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 26265–26276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feyen, F.; Cachoux, F.; Gertsch, J.; Wartmann, M.; Altmann, K.-H. Epothilones as Lead Structures for the Synthesis-Based Discovery of New Chemotypes for Microtubule Stabilization. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jantsch, A.; Nieto, L.; Gertsch, J.; Rodríguez-Salarichs, J.; Matesanz, R.; Jiménez-Barbero, J.; Díaz, J.F.; Canales, Á.; Altmann, K.-H. Synthesis, Biological Profiling and Determination of the Tubulin-Bound Conformation of 12-Aza-Epothilones (Azathilones). Molecules 2016, 21, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, C.D.; Wen, X.; Gazzard, L.; Nelson, C.; Scheller, R.H.; Scales, S.J. Oxidizing potential of endosomes and lysosomes limits intracellular cleavage of disulfide-based antibody-drug conjugates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 17987–17992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abourbeh, G.; Shir, A.; Mishani, E.; Ogris, M.; Rödl, W.; Wagner, E.; Levitzki, A. PolyIC GE11 polyplex inhibits EGFR-overexpressing tumors. IUBMB Life 2012, 64, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuo, W.-T.; Lin, W.-C.; Chang, K.-C.; Huang, J.-Y.; Yen, K.-C.; Young, I.-C.; Sun, Y.-J.; Young, I.-C.; Lin, F.-H. Quantitative Analysis of Ligand-EGFR Interactions: A Platform for Screening Targeting Molecules. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Striese, F.; Sihver, W.; Gao, F.; Bergmann, R.; Walther, M.; Pietzsch, J.; Steinbach, J.; Pietzsch, H.-J. Exploring pitfalls of 64Cu-labeled EGFR-targeting peptide GE11 as a potential PET tracer. Amino Acids 2018, 50, 1415–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, J.F.; Andreu, J.M. Assembly of purified GDP-tubulin into microtubules induced by taxol and taxotere: Reversibility, ligand stoichiometry, and competition. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 2747–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


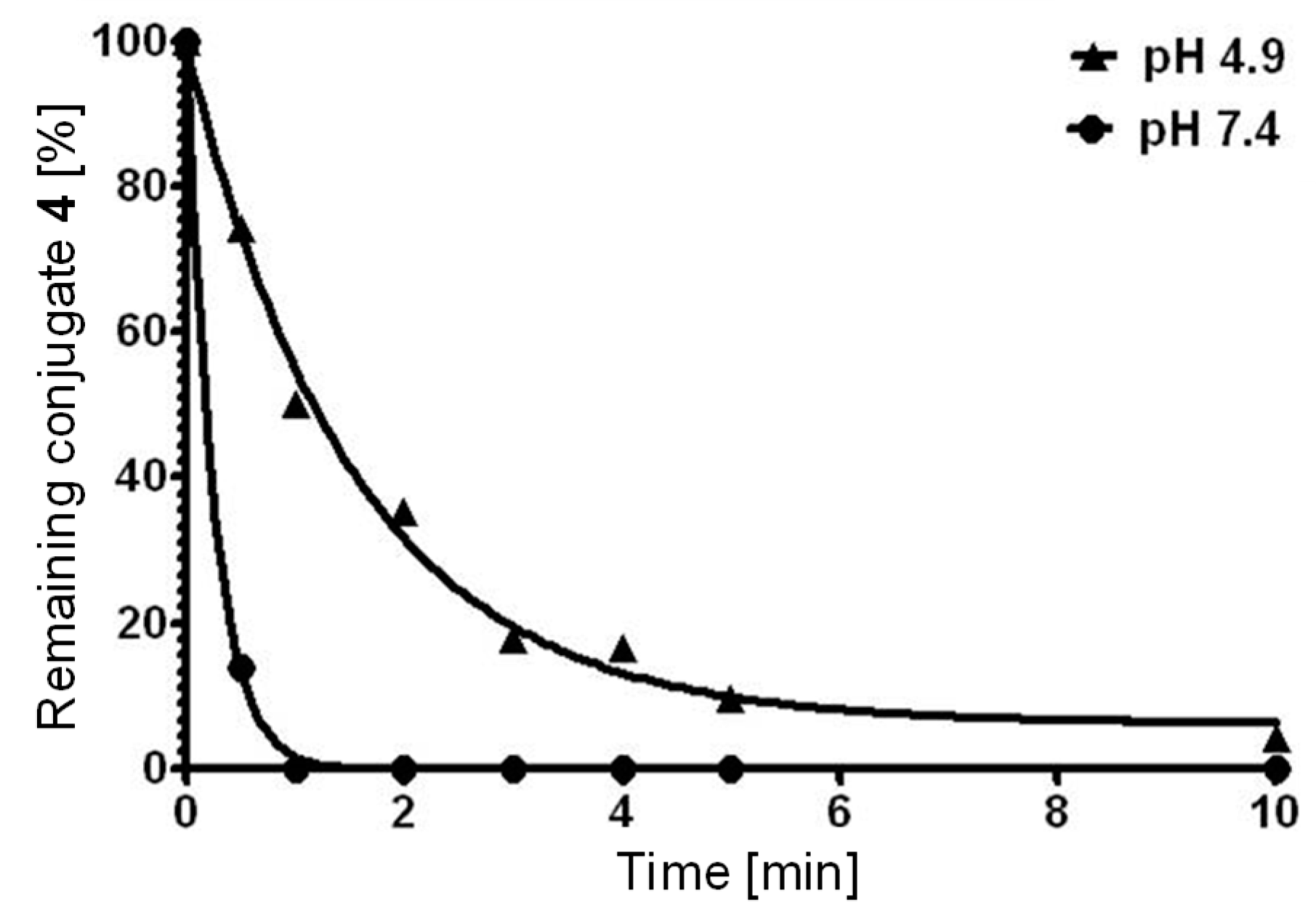

| Compound | Kb [106 M−1] |
|---|---|
| 1 | 78.5 ± 17.2 |
| 14 | 5.4 ± 0.8 |
| 16 | 9.8 ± 0.3 |
| 4 | 9.3 ± 0.5 |
| CysCE11 | 0.05 ± 0.02 |
| Epo A | 31.7 ± 3.1 |
| Docetaxel | 26.7 ± 3.3 |
| Compound | A431 | SW480 | HEK293 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.32 ± 0.60 | 17.56 ± 3.50 | 0.87 ± 0.13 |
| 16 | 8.37 ± 0.81 | 8.91 ± 1.26 | 2.08 ± 0.53 |
| 4 | 74.74 ± 6.65 | 180.8 ± 25.9 | 31.09 ± 6.21 |
| Epo A | 2.94 ± 0.30 | 14.52 ± 1.09 | 2.71 ± 0.62 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gaugaz, F.Z.; Chicca, A.; Redondo-Horcajo, M.; Barasoain, I.; Díaz, J.F.; Altmann, K.-H. Synthesis, Microtubule-Binding Affinity, and Antiproliferative Activity of New Epothilone Analogs and of an EGFR-Targeted Epothilone-Peptide Conjugate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051113
Gaugaz FZ, Chicca A, Redondo-Horcajo M, Barasoain I, Díaz JF, Altmann K-H. Synthesis, Microtubule-Binding Affinity, and Antiproliferative Activity of New Epothilone Analogs and of an EGFR-Targeted Epothilone-Peptide Conjugate. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(5):1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051113
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaugaz, Fabienne Zdenka, Andrea Chicca, Mariano Redondo-Horcajo, Isabel Barasoain, J. Fernando Díaz, and Karl-Heinz Altmann. 2019. "Synthesis, Microtubule-Binding Affinity, and Antiproliferative Activity of New Epothilone Analogs and of an EGFR-Targeted Epothilone-Peptide Conjugate" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 5: 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051113
APA StyleGaugaz, F. Z., Chicca, A., Redondo-Horcajo, M., Barasoain, I., Díaz, J. F., & Altmann, K.-H. (2019). Synthesis, Microtubule-Binding Affinity, and Antiproliferative Activity of New Epothilone Analogs and of an EGFR-Targeted Epothilone-Peptide Conjugate. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(5), 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051113